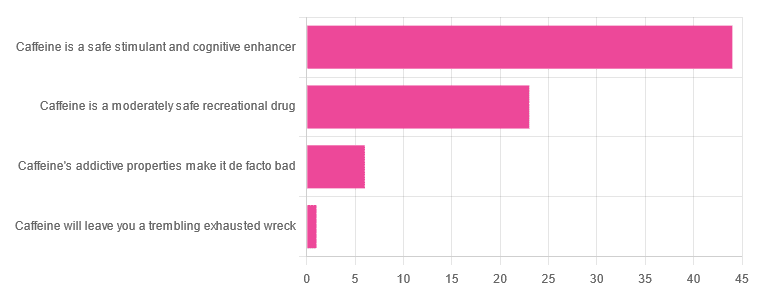The Metabolism Reset Diet – by Alan Christianson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The liver is an incredible organ that does a very important job, but what’s not generally talked about is how we can help it… Beyond the obvious “try to not poison it too much with alcohol, tobacco, etc”. But what can we do that’s actually positive for it?
That’s what Alan Christianson offers in this book.
Now, usually when someone speaks of a “four week cleanse” as this book advertises on its front cover, it’s a lot of bunk. The liver cleanses itself, and the liver and kidneys between them (along with some other organs and processes) detoxify your body for you. No amount of celery juice will do that. However, this book does better than that:
What it’s about, is not really about trying to do a “detox” at all, so much as supporting your liver function by:
- Giving your liver what it needs to regenerate (mostly: protein)
- Not over-taxing your liver while it does so
The liver is a self-regenerating organ (the mythological story of Prometheus aside, here in real life it can regenerate up to 80% of itself, given the opportunity), so whatever the current state of your liver, it’s probably not too late to fix it.
Maybe you’ve been drinking a little too much, or maybe you’ve been taking some meds that have hobbled it a bit (some medications strain the liver rather), or maybe your diet hasn’t been great. Christianson invites you to draw a line under that, and move forwards:
The book gives an overview of the science involved, and explains about the liver’s role in metabolism (hence the promised weight loss benefits) and our dietary habits’ impact on liver function. This is about what we eat, and also about when we eat it, and how and when our body metabolizes that.
Christianson also provides meal ideas and recipes. If we’re honest (and we always are), the science/principles part of the book are worth a lot more than the meal-plan part of the book, though.
In short: a great book for understanding how the liver works and how we can help it do its job effectively.
Click here to check out “The Metabolism Reset Diet” on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Two Sides Of Caffeine
We asked you for your health-related opinions on caffeine itself, not necessarily the coffee, tea, energy drinks, etc that might contain it.
We have, by the way previously written about the health effects of coffee and tea specifically:
As for our question about caffeine itself, though, we got the above-depicted, below-described, set of results:
- About 59% said “caffeine is a safe stimulant and cognitive enhancer”
- About 31% said “caffeine is a moderately safe recreational drug”
- About 8% said “caffeine’s addictive properties make it de facto bad”
- One (1) person said “caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck”
But what does the science say?
Caffeine is addictive: True or False?
True, though one will find occasional academics quibbling the definition. Most of the studies into the mechanisms of caffeine addiction have been conducted on rats, but human studies exist too and caffeine is generally considered addictive for humans, for example:
See also:
Notwithstanding its addictive status, caffeine is otherwise safe: True or False?
True-ish, for most people. Some people with heart conditions or a hypersensitivity to caffeine may find it is not safe for them at all, and for the rest of us, the dose makes the poison. For example:
❝Can too much caffeine kill you? Although quite rare, caffeine can be fatal in cases of overdose; such circumstances are generally not applicable to healthy individuals who typically consume caffeine via beverages such as tea or coffee.❞
this paper, by the way, also includes a good example of academics quibbling the definition of addiction!
Caffeine is a cognitive enhancer: True or False?
True, but only in the case of occasional use. If you are using it all the time, your physiology will normalize it and you will require caffeine in order to function at your normal level. To attain higher than that, once addicted to caffeine, would now require something else.
Read more: Caffeine: benefits and drawbacks for technical performance
Caffeine will leave you a trembling exhausted wreck: True or False?
True or False depending on usage:
- The famously moderate 3–5 cups per day will not, for most people, cause any such problems.
- Using/abusing it to make up for lost sleep (or some other source of fatigue, such as physical exhaustion from exertion), however, is much more likely to run into problems.
In the latter case, caffeine really is the “payday loan” of energy! It’ll give you an adrenal boost now (in return, you must suffer the adrenal dumping later, along with lost energy expended in the adrenaline surge), and also, the tiredness that you thought was gone, was just caffeine’s adenosine-blocking activities temporarily preventing you from being able to perceive the tiredness. So you’ll have to pay that back later, with interest, because of the extra time/exertion too.
Want to make caffeine a little more gentle on your system?
Taking l-theanine alongside caffeine can ameliorate some of caffeine’s less wonderful effects—and as a bonus, l-theanine has some nifty benefits of its own, too:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Strategic Wellness
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Strategic Wellness: planning ahead for a better life!
This is Dr. Michael Roizen. With hundreds of peer-reviewed publications and 14 US patents, his work has been focused on the importance of lifestyle factors in healthy living. He’s the Chief Wellness Officer at the world-famous Cleveland Clinic, and is known for his “RealAge” test and related personalized healthcare services.
If you’re curious about that, you can take the RealAge test here.
(they will require you inputting your email address if you do, though)
What’s his thing?
Dr. Roizen is all about optimizing health through lifestyle factors—most notably, diet and exercise. Of those, he is particularly keen on optimizing nutritional habits.
Is this just the Mediterranean Diet again?
Nope! Although: he does also advocate for that. But there’s more, he makes the case for what he calls “circadian eating”, optimally timing what we eat and when.
Is that just Intermittent Fasting again?
Nope! Although: he does also advocate for that. But there’s more:
Dr. Roizen takes a more scientific approach. Which isn’t to say that intermittent fasting is unscientific—on the contrary, there’s mountains of evidence for it being a healthful practice for most people. But while people tend to organize their intermittent fasting purely according to convenience, he notes some additional factors to take into account, including:
- We are evolved to eat when the sun is up
- We are evolved to be active before eating (think: hunting and gathering)
- Our insulin resistance increases as the day goes on
Now, if you’ve a quick mind about you, you’ll have noticed that this means:
- We should keep our eating to a particular time window (classic intermittent fasting), and/but that time window should be while the sun is up
- We should not roll out of bed and immediately breakfast; we need to be active for a bit first (moderate exercise is fine—this writer does her daily grocery-shopping trip on foot before breakfast, for instance… getting out there and hunting and gathering those groceries!)
- We should not, however, eat too much later in the day (so, dinner should be the smallest meal of the day)
The latter item is the one that’s perhaps biggest change for most people. His tips for making this as easy as possible include:
- Over-cater for dinner, but eat only one portion of it, and save the rest for an early-afternoon lunch
- First, however, enjoy a nutrient-dense protein-centric breakfast with at least some fibrous vegetation, for example:
- Salmon and asparagus
- Scrambled tofu and kale
- Yogurt and blueberries
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Yes, we still need chickenpox vaccines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For people who grew up before a vaccine was available, chickenpox is largely remembered as an unpleasant experience that almost every child suffered through. The highly contagious disease tore through communities, leaving behind more than a few lasting scars.
For many children, chickenpox was much more than a week or two of itchy discomfort. It was a serious and sometimes life-threatening infection.
Prior to the chickenpox vaccine’s introduction in 1995, 90 percent of children got chickenpox. Those children grew into adults with an increased risk of developing shingles, a disease caused by the same virus—varicella-zoster—as chickenpox, which lies dormant in the body for decades.
The vaccine changed all that, nearly wiping out chickenpox in the U.S. in under three decades. The vaccine has been so successful that some people falsely believe the disease no longer exists and that vaccination is unnecessary. This couldn’t be further from the truth.
Vaccination spares children and adults from the misery of chickenpox and the serious short- and long-term risks associated with the disease. The CDC estimates that 93 percent of children in the U.S. are fully vaccinated against chickenpox. However, outbreaks can still occur among unvaccinated and under-vaccinated populations.
Here are some of the many reasons why we still need chickenpox vaccines.
Chickenpox is more serious than you may remember
For most children, chickenpox lasts around a week. Symptoms vary in severity but typically include a rash of small, itchy blisters that scab over, fever, fatigue, and headache.
However, in one out of every 4,000 chickenpox cases, the virus infects the brain, causing swelling. If the varicella-zoster virus makes it to the part of the brain that controls balance and muscle movements, it can cause a temporary loss of muscle control in the limbs that can last for months. Chickenpox can also cause other serious complications, including skin, lung, and blood infections.
Prior to the U.S.’ approval of the vaccine in 1995, children accounted for most of the country’s chickenpox cases, with over 10,000 U.S. children hospitalized with chickenpox each year.
The chickenpox vaccine is very effective and safe
Chickenpox is an extremely contagious disease. People without immunity have a 90 percent chance of contracting the virus if exposed.
Fortunately, the chickenpox vaccine provides lifetime protection and is around 90 percent effective against infection and nearly 100 percent effective against severe illness. It also reduces the risk of developing shingles later in life.
In addition to being incredibly effective, the chickenpox vaccine is very safe, and serious side effects are extremely rare. Some people may experience mild side effects after vaccination, such as pain at the injection site and a low fever.
Although infection provides immunity against future chickenpox infections, letting children catch chickenpox to build up immunity is never worth the risk, especially when a safe vaccine is available. The purpose of vaccination is to gain immunity without serious risk.
The chickenpox vaccine is one of the greatest vaccine success stories in history
It’s difficult to overstate the impact of the chickenpox vaccine. Within five years of the U.S. beginning universal vaccination against chickenpox, the disease had declined by over 80 percent in some regions.
Nearly 30 years after the introduction of the chickenpox vaccine, the disease is almost completely wiped out. Cases and hospitalizations have plummeted by 97 percent, and chickenpox deaths among people under 20 are essentially nonexistent.
Thanks to the vaccine, in less than a generation, a disease that once swept through schools and affected nearly every child has been nearly eliminated. And, unlike vaccines introduced in the early 20th century, no one can argue that improved hygiene, sanitation, and health helped reduce chickenpox cases beginning in the 1990s.
Having chickenpox as a child puts you at risk of shingles later
Although most people recover from chickenpox within a week or two, the virus that causes the disease, varicella-zoster, remains dormant in the body. This latent virus can reactivate years after the original infection as shingles, a tingling or burning rash that can cause severe pain and nerve damage.
One in 10 people who have chickenpox will develop shingles later in life. The risk increases as people get older as well as for those with weakened immune systems.
Getting chickenpox as an adult can be deadly
Although chickenpox is generally considered a childhood disease, it can affect unvaccinated people of any age. In fact, adult chickenpox is far deadlier than pediatric cases.
Serious complications like pneumonia and brain swelling are more common in adults than in children with chickenpox. One in 400 adults who get chickenpox develops pneumonia, and one to two out of 1,000 develop brain swelling.
Vaccines have virtually eliminated chickenpox, but outbreaks still happen
Although the chickenpox vaccine has dramatically reduced the impact of a once widespread disease, declining immunity could lead to future outbreaks. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analysis found that chickenpox vaccination rates dropped in half of U.S. states in the 2022-2023 school year compared to the previous year. And more than a dozen states have immunization rates below 90 percent.
In 2024, New York City and Florida had chickenpox outbreaks that primarily affected unvaccinated and under-vaccinated children. With declining public confidence in routine vaccines and rising school vaccine exemption rates, these types of outbreaks will likely become more common.
The CDC recommends that children receive two chickenpox vaccine doses before age 6. Older children and adults who are unvaccinated and have never had chickenpox should also receive two doses of the vaccine.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
L-Theanine: What’s The Tea?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
L-Theanine: What’s The Tea?
We’ve touched previously on l-theanine, when this newsletter was new, and we had only a few hundred subscribers and the carefully organized format wasn’t yet what it is today.
So now it’s time to give this potent dietary compound / nutritional supplement the “Monday Research Review” treatment…
What is it?
L-theanine is an amino acid found in tea. The human body can’t produce it, and/but it’s not essential for humans. It does have a lot of benefits, though. See for example:
L-Theanine as a Functional Food Additive: Its Role in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion
How does it work?
L-theanine works by moderating and modulating the brain’s neurotransmitters.
This sounds fancy, but basically it means: it doesn’t actually add anything in the manner of a drug, but it changes how we use what we have naturally.
What does it do? Read on…
It increases mental focus
It has been believed that l-theanine requires the presence of caffeine to achieve this (i.e., it’s a combination-only effect). For example:
But as it turns out, when a group of researchers actually checked… This isn’t true, as Foxe et al. write:
❝We asked whether either compound alone, or both in combination, would affect performance of the task in terms of reduced error rates over time, and whether changes in alpha-band activity would show a relationship to such changes in performance. When treated with placebo, participants showed a rise in error rates, a pattern that is commonly observed with increasing time-on-task, whereas after caffeine and theanine ingestion, error rates were significantly reduced. The combined treatment did not confer any additional benefits over either compound alone, suggesting that the individual compounds may confer maximal benefits at the dosages employed❞
It promotes a calmly wakeful feeling of serenity
Those are not words typically found in biopharmaceutical literature, but they’re useful here to convey:
- L-theanine promotes relaxation without causing drowsiness
- L-theanine promotes mental alertness without being a stimulant
Here is where l-theanine really stands out from caffeine. If both substances promote mental focus, but one of them does it by making us “wired” and the other does it while simultaneously promoting calm, it makes the choice between them clearer!
Read more: L-theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state
It relieves stress and anxiety
Building on from the above, but there’s more: l-theanine relieves stress and anxiety in people experiencing stressful situations, without any known harmful side effects… This is something that sets it apart from a lot of anxiolytic (antianxiety) drugs!
Here’s what a big systematic review of clinical trials had to say:
Theanine consumption, stress and anxiety in human clinical trials: A systematic review
L-theanine has other benefits too
We’ve talked about some of the most popular benefits of l-theanine, and we can’t make this newsletter too long, but research also suggests that it…
- Supports healthy weight management
- Reduces inflammation
- Supports immune health
- Helps fight cancer
- May extend lifespan ← this one’s a C. elegans study, but despite being a tiny worm, they actually function very similarly to humans on a cellular level; it’s why they’re used so much for anti-aging research
If you’re interested in this topic, we recommend also reading our previous article on l-theanine—pardon that we hadn’t really nailed down our style yet—but there’s a bunch of useful information about how l-theanine makes caffeine “better” in terms of benefits. We also talk dosage, and reference some other studies we didn’t have room to include today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Neuropsychologist Explains What She’s Got Out Of 6 Years Taking L-Theanine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inka Land, MSc neuropsychology, PgDip(c) Nutrition and Disease, talks about her use of l-theanine and the biochemistry behind it:
So, what’s the tea?
While she’s tested over 60 supplements, she regularly uses only a few. L-theanine made the cut, and has been a staple for over six years due to its noticeable effects on her brain, nervous system in general, and gut. Some notes from the video:
- L-theanine was discovered during university studies as a way to enhance focus and reduce stress. Initially, 50mg doses combined with coffee showed no effect, but increasing to 150mg, paired with 100mg of caffeine, produced significant nootropic benefits.
- L-theanine enhances sustained focus, enabling prolonged attention on repetitive tasks while avoiding distractions. It’s particularly effective for maintaining concentration during monotonous activities.
- L-theanine alleviates gut inflammation by boosting antioxidant activity and supporting glutamine metabolism. Combined with l-glutamine, it is more effective for reducing gut inflammation, and she mentions anecdotally that it seemed to help her personally recover quickly from food poisoning.
- Known for its calming effects, L-theanine reduces anxiety and regulates the nervous system. It is beneficial before stressful or crowded events and has anecdotal support for alleviating social anxiety specifically, though that’s not been formally tested in RCTs (yet). That said, since it has been tested against anxiety in the lab (usually combined with stress tests), it would be strange if it didn’t help alleviate social anxiety too, since what’s required for the nervous system is the same.
- Studies suggest 100–200mg twice daily, but she personally takes 250mg in the morning with coffee or 200–250mg PRN.
Want to try some? Here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
For more on all of this, enjoy (and kindly disregard that she clearly is holding a jar of curcumin in the thumbnail):
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
L-Theanine Against Stress, Anxiety, Inflammation, & More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Origin of Everyday Moods – by Dr. Robert Thayer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First of all, what does this title mean by “everyday moods”? By this the author is referring to the kinds of moods we have just as a matter of the general wear-and-tear of everyday life—not the kind that come from major mood disorders and/or serious trauma.
The latter kinds of mood take less explaining, in any case. Dr. Thayer, therefore, spends his time on the less obvious ones—which in turn are the ones that affect most of the most, every day.
Critical to Dr. Thayer’s approach is the mapping of moods by four main quadrants:
- High energy, high tension
- High energy, low tension
- Low energy, high tension
- Low energy, low tension
…though this can be further divided into 25 sectors, if we rate each variable on a scale of 0–4. But for the first treatment, it suffices to look at whether energy and tension are high or low, respectively, and which we’d like to have more or less of.
Then (here be science) how to go about achieving that in the most efficient, evidence-based ways. So, it’s not just a theoretical book; it has great practical value too.
The style of the book is accessible, and walks a fine line between pop-science and hard science, which makes it a great book for laypersons and academics alike.
Bottom line: if you’d like the cheat codes to improve your moods and lessen the impact of bad ones, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out The Origin of Everyday Moods, and manage yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: