The Cluttered Mind – by Deborah McKenna
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coming from an eclectic psychotherapy background, Deborah McKenna outlines a wide array of techniques to “do what it says on the tin”, that is:
Organizing the junk drawer of your mind.
McKenna argues that it’s natural for something so gargantuan as our mind to get cluttered… but that it’s perfectly possible, with a good system, to tidy up considerably.
The benefit of this is much like the benefit of tidying a room:
Imagine a kitchen in which half the things have not been put away; there are dishes in the sink, something is growing behind the trash can… and you have a vague suspicion that if you open a certain cupboard, its contents are going to come falling out on your head. How are you going to cook a meal here?
Imagine a mind when many thoughts have been left untended; there are things you needed to process, and there’s a steady resentment of something growing in some dark part of your mind… and there’s some part of your memory that you’re afraid to even look at it, because of all it’ll cause to come surging back at you. How are you going to strategize your life here?
Fortunately, McKenna is here to guide you through doing for your mind what Marie Kondo would do for your home. And, even better, McKenna does it with a simple and clear writing style, assorted diagrams, and a step-by-step approach to getting everything in order.
Give Your Mind A Spring-Cleaning With This Book From Amazon Today
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Brazil Nuts vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Brazil nuts to cashews, we picked the cashews.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, Brazil nuts have more fat and fiber, while cashews have more carbs and protein. So, it really comes down to what you want to prioritize. We’d generally consider fiber the tie-breaker, making this category a subjective marginal win for Brazil nuts—and especially marginal since they are both low glycemic index foods in any case.
When it comes to vitamins, Brazil nuts have more of vitamins C, E, and choline, while cashews have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and K, so while both are great, this category is a clear by-the-numbers win for cashews.
The category of minerals is an interesting one. Brazil nuts have more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and selenium, while cashews have more copper, iron, manganese, and zinc. That would be a 4:4 tie, but let’s take a closer look at those selenium levels:
- A cup of cashews contains 109% of the RDA of selenium. Your hair will be luscious and shiny.
- A cup of Brazil nuts contains 10,456% of the RDA of selenium. This is way past the point of selenium toxicity, and your (luscious, shiny) hair will fall out.
For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
We consider that a point against Brazil nuts.
Adding up the section makes for a win for cashews. Of course, enjoy Brazil nuts too if you will, but in careful moderation please!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Three Critical Kitchen Prescriptions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Three Critical Kitchen Prescriptions
This is Dr. Saliha Mahmood-Ahmed. She’s a medical doctor—specifically, a gastroenterologist. She’s also a chef, and winner of the BBC’s MasterChef competition. So, from her gastroenterology day-job and her culinary calling, she has some expert insights to share on eating well!
❝Food and medicine are inextricably linked to one another, and it is an honour to be a doctor who specialises in digestive health and can both cook, and teach others to cook❞
~ Dr. Saliha Mahmood-Ahmed, after winning MasterChef and being asked if she’d quit medicine to be a full-time chef
Dr. Mahmood-Ahmed’s 3 “Kitchen Prescriptions”
They are:
- Cook, cook, cook
- Feed your gut bugs
- Do not diet
Let’s take a look at each of those…
Cook, cook, cook
We’re the only species on Earth that cooks food. An easy knee-jerk response might be to think maybe we shouldn’t, then, but… We’ve been doing it for at least 30,000 years, which is about 1,500 generations, while a mere 100 generations is generally sufficient for small evolutionary changes. So, we’ve evolved this way now.
More importantly in this context: we, ourselves, should cook our own food, at least per household.
Not ready meals; we haven’t evolved for those (yet! Give it another few hundred generations maybe)
Feed your gut bugs
The friendly ones. Enjoy prebiotics, probiotics, and plenty of fiber—and then be mindful of what else you do or don’t eat. Feeding the friendly bacteria while starving the unfriendly ones may seem like a tricky task, but it actually can be quite easily understood and implemented. We did a main feature about this a few weeks ago:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
Do not diet
Dr. Mahmood-Ahmed is a strong critic of calorie-counting as a weight-loss strategy:
Rather than focusing on the number of calories consumed, try focusing on introducing enough variety of food into your daily diet, and on fostering good microbial diversity within your gut.
It’s a conceptual shift from restrictive weight loss, to prescriptive adding of things to one’s diet, with fostering diversity of microbiota as a top priority.
This, too, she recommends be undertaken gently, though—making small, piecemeal, but sustainable improvements. Nobody can reasonably incorporate, say, 30 new fruits and vegetables into one’s diet in a week; it’s unrealistic, and more importantly, it’s unsustainable.
Instead, consider just adding one new fruit or vegetable per shopping trip!
Share This Post
-
Lettuce vs Arugula – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing lettuce to arugula, we picked the arugula.
Why?
These two salad leaves that often fulfil quite similar culinary roles (base of a green salad) are actually of different families, and it shows…
In terms of macros, arugula is lower in carbs, and much higher in protein and fiber—to the point that the protein content in arugula is almost equal to the carb content, which for leaves, is not that common a thing to see.
When it comes to vitamins, things are more even: lettuce has more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B6, and K, while arugula has more of vitamins B5, B9, C, E, and choline. All in all, we can comfortably call it a tie on the vitamin front.
In the category of minerals, things are once again more decided: arugula has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. In contrast, lettuce boasts only more selenium. An easy win for arugula.
Both of these plants have plenty of health-giving phytochemicals, including flavonoids and carotenoids along with other less talked-about things, and while the profiles are quite different for each of them, they stack up about the same in terms of overall benefits in this category.
Taking the various categories into account, this of course adds up to an easy win for arugula, but do enjoy both, especially as lettuce brings benefits that arugula doesn’t in the two categories where they tied!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- How To Avoid Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Spinach vs Kale – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
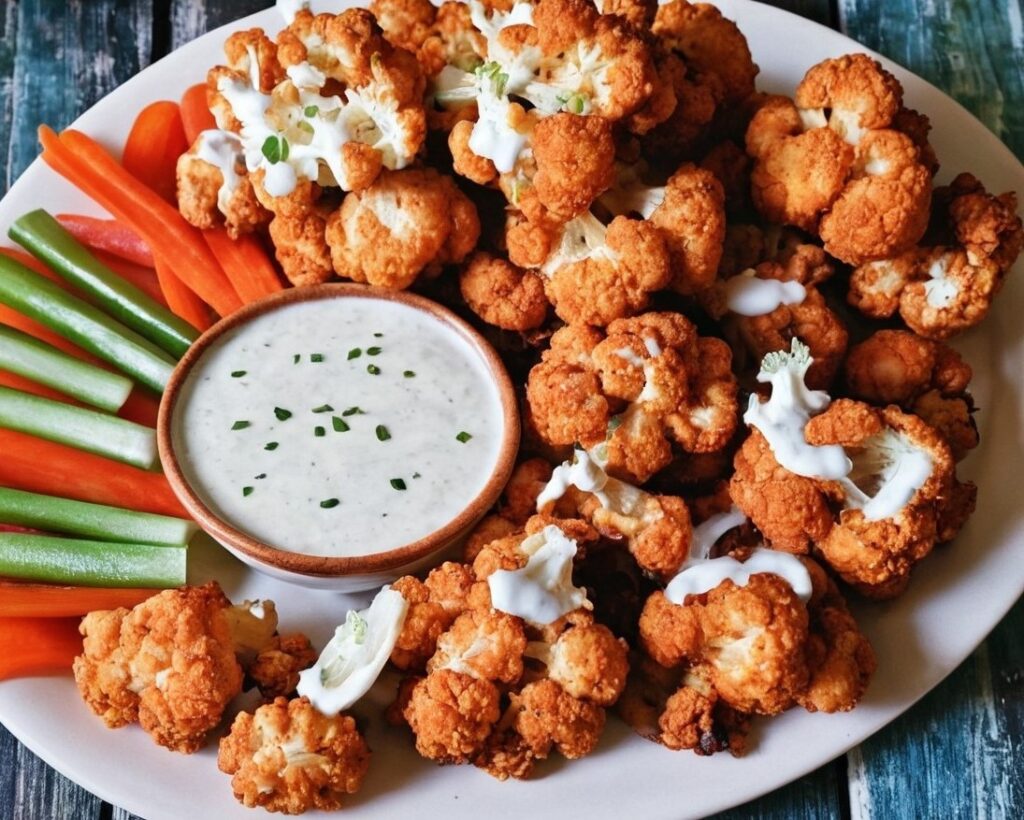
Buffed-Up Buffalo Cauliflower
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a tasty snack that also more protein than you’d think, because of the garbanzo bean flour. It also has plenty of health-giving spices, as well as blood-sugar-balancing vinegar, no added sugar, and very little salt.
You will need
- 1 medium head of cauliflower, cut into florets
- ½ cup garbanzo bean flour
- ½ cup water
- ⅓ cup hot sauce (we recommend a low-sugar kind; Nando’s hot sauce is good for this if available where you are, as it has no added sugar and its main ingredient by volume is vinegar, which is good for balancing blood sugars)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for the pan
- 2 tsp garlic powder
- 2 tsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, freshly ground
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low sodium salt
For the ranch sauce:
- ½ cup raw sunflower seeds
- ⅓ cup water
- ⅓ cup milk (plant milk being healthiest if you choose one that’s unsweetened)
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tsp onion powder
- 1 tsp dried thyme
- 1 tsp dried oregano
- 1 tsp dried dill
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉/200℃.
2) Blend the ranch sauce ingredients until smooth, and set aside.
3) Mix the buffalo cauliflower ingredients except for the cauliflower, in a big bowl.
4) Add the cauliflower to the big bowl, mixing well to coat evenly.
5) Bake the buffalo cauliflower florets on a baking tray lined with baking paper, for about 25 minutes, turning gently if it seems they are at risk of cooking unevenly.
6) Serve hot, with the sunflower ranch on the side!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing avocado oil to olive oil, we picked the olive oil.
Why?
Avocados and olives are both very healthy foods. However, when they are made into oils, there’s an important distinguishing factor:
Olive oil usually retains a lot of the micronutrients from the olives (including vitamins E and K), whereas no measurable micronutrients usually remain in avocado oil.
So while both olive oil and avocado oil have a similar (excellent; very heart-healthy!) lipids profile, the olive oil has some bonuses that the avocado oil doesn’t.
We haven’t written about the nutritional profiles of either avocados or olives yet, but here’s what we had to say on the different kinds of olive oil available:
And here’s an example of a good one on Amazon, for your convenience 😎
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The End of Food Allergy – by Dr. Kari Nadeau & Sloan Barnett
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We don’t usually mention author credentials beyond their occupation/title. However, in this case it bears acknowledging at least the first line of the author bio:
❝Kari Nadeau, MD, PhD, is the director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford University and is one of the world’s leading experts on food allergy❞
We mention this, because there’s a lot of quack medicine out there [in general, but especially] when it comes to things such as food allergies. So let’s be clear up front that Dr. Nadeau is actually a world-class professional at the top of her field.
This book is, by the way, about true allergies—not intolerances or sensitivities. It does touch on those latter two, but it’s not the main meat of the book.
In particular, most of the research cited is around peanut allergies, though the usual other common allergens are all discussed too.
The authors’ writing style is that of a science educator (Dr. Nadeau’s co-author, Sloan Barnett, is lawyer and health journalist). We get a clear explanation of the science from real-world to clinic and back again, and are left with a strong understanding, not just a conclusion.
The titular “End of Food Allergy” is a bold implicit claim; does the book deliver? Yes, actually.
The book lays out guidelines for safely avoiding food allergies developing in infants, and yes, really, how to reverse them in adults. But…
Big caveat:
The solution for reversing severe food allergies (e.g. “someone nearby touched a peanut three hours ago and now I’m in anaphylactic shock”), drug-assisted oral immunotherapy, takes 6–24 months of weekly several-hour-long clinic visits, relies on having a nearby clinic offering the service, and absolutely 100% cannot be done at home (on pain of probable death).
Bottom line: it’s by no means a magic bullet, but yes, it does deliver.
Click here to check out The End of Food Allergy to learn more!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: