The Brain’s Way of Healing – by Dr. Norman Doidge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book isn’t: any sort of wishy-washy “think yourself better” fluff, and nor is it a “tapping into your Universal Divine Essence” thing.
In contrast, Dr. Norman Doidge sticks with science, and the only “vibrational frequencies” involved are the sort that come from an MRI machine or similar.
The author makes bold claims of the potential for leveraging neuroplasticity to heal many chronic diseases. All of them are neurological in whole or in part, ranging from chronic pain to Parkinson’s.
How well are these claims backed up, you ask?
The book makes heavy use of case studies. In science, case studies rarely prove anything, so much as indicate a potential proof of principle. Clinical trials are what’s needed to become more certain, and for Dr. Doidge’s claims, these are so far sadly lacking, or as yet inconclusive.
Where the book’s strengths lie is in describing exactly what is done, and how, to effect each recovery. Specific exercises to do, and explanations of the mechanism of action. To that end, it makes them very repeatable for any would-be “citizen scientist” who wishes to try (in the cases that they don’t require special equipment).
Bottom line: this book would be more reassuring if its putative techniques had enjoyed more clinical studies… But in the meantime, it’s a fair collection of promising therapeutic approaches for a number of neurological disorders.
Click here to check out The Brain’s Way of Healing, and learn more!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Fiber Effect – by Nichole Dandrea-Russert
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a registered dietician-nutritionist (RDN), brings to this work her decades of professional experience specializing in heart disease, diabetes, sports nutrition, and women’s health—and it shows.
The main premise is, of course “eat more fiber”, but she also talks us through what happens if we don’t, and how very many people (including 95% of Americans) suffer the consequences of a fiber-deficient diet, usually without even knowing that that’s the reason.
This book details the many different kinds of fiber (which is one of the reasons for consuming a wide variety of plants, not just one or two star-performers), what they do, what we need to prioritize for what, and more.
The recipes, of which there are 40 (enough to furnish us with a 14-day meal plan, which she does) are plant-based and varied.
The style is energetic and friendly, with plenty of (well-referenced) scientific information, but little-to-no jargon.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your fiber intake, then this book can help you supercharge that!
Click here to check out The Fiber Effect, and feel the difference!
Share This Post
-
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Bitter Is Better
A good general rule of thumb for “does this food contain a lot of healthy polyphenols?” is:
“is this (edible) plant bitter/astringent/pungent”?
If it is, it’s probably rich in polyphenols:
Deciphering the role of bitter and astringent polyphenols in promoting well-being
…which is why it’s no surprise that black coffee and bitter chocolate score highly, as do hot peppers and even garlic.
See also: Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Even fruits, generally considered something sweet to eat, often contain more polyphenols when they are bitter—many berries are great examples of this!
Read more: Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
You can read more about the science of this here:
Sensory Nutrition and Bitterness and Astringency of Polyphenols
Important for multiple reasons (including heart and brain health)
Polyphenols have many benefits, and they’re most well known for their heart-healthy properties, but their antioxidant effect (and other mechanisms) also means these foods are generally neuroprotectants too:
The science of this is not all as obvious as you might think!
It is reasonable to expect “ok, this has antioxidant effect, so it will reduce oxidative damage to brain cells too”, and while that is true (and yes, polyphenols do cross the blood-brain barrier), they also help in other ways, including through the gut:
What if I don’t like bitter/astringent/pungent foods?
If you do not have a medical condition that proscribes them (do check with your doctor if unsure), the best advice is to simply eat them anyway, and your tastes will adapt.
It will also help if you avoid sweet foods (though this too is also a good general rule of thumb!), as this will move the balance of where your brain’s “set range” is for “good taste”.
Bonus tip: dark chocolate (80%+ cocoa if possible, 95% if you can get it) and chilli peppers go great with each other. Here’s an example of a chilli chocolate product on Amazon; it’s 70% cocoa (which is not bad, but could be better). You might be able to get a higher percentage locally, especially if you ask your local chocolatière, or make it yourself!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Unlock Your Flexibility With These 4 New Stretches
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People often stick to the same few stretches, which may limit flexibility progress, especially as the most common stretches often miss deeper, harder-to-reach areas.
So, here are some new (well, probably new to most people, at least) stretches that can get things moving in different directions:
Diversity Continues To Be Good!
The stretches are:
90/90 Hip stretch with a twist:
- Sit with your knees forming 90° angles; add an arm bar and twist your chest upward.
- Hold for 5 deep breaths and repeat.
- This one targets top glute muscles and quadratus lumborum in the lower back.
Shoulder mobility stretch using a wall:
- Kneel in front of a wall with your forearms placed shoulder-width apart, hands turned outward.
- Lift your hips, push your chest toward your legs, and use the wall and your body weight for deeper leverage.
- This one targets multiple shoulder and rotator cuff muscles through external rotation.
Quad stretch using body weight:
- Sit with your feet hip-width apart, lift your hips, step one foot back, and tuck in your tailbone.
- Focus on pointing your knee down and forward for a deep quad stretch.
- This one targets all four quad muscles, hip flexors, plantar fascia, and opens chest/shoulders.
Chicken wing stretch for upper back:
- Sit with bent knees, place the back of one hand on your waist (chicken wing position).
- Tuck the “wing” into the inner thigh, press your knee inward while resisting with the arm.
- This one broadens the shoulder blade and stretches rear shoulder/upper back muscles; it’s particularly effective for reaching difficult upper back areas not typically stretched.
For more on each of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Yoga Teacher: “If I wanted to get flexible in 2025, here’s what I’d do”
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
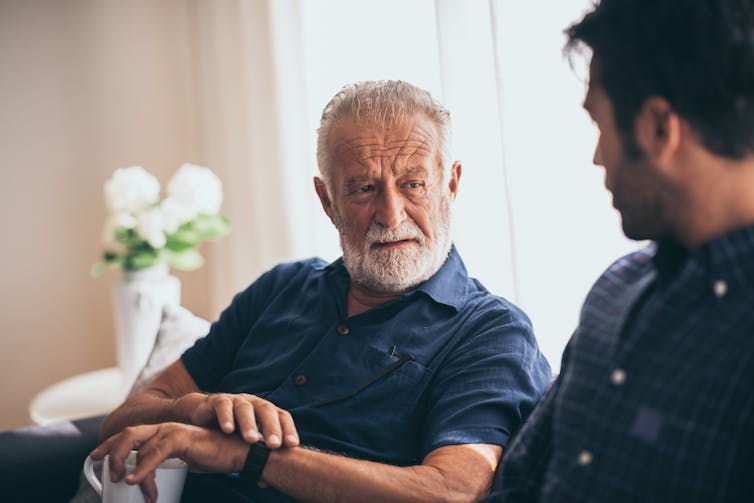
Your friend has been diagnosed with cancer. Here are 6 things you can do to support them
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Across the world, one in five people are diagnosed with cancer during their lifetime. By age 85, almost one in two Australians will be diagnosed with cancer.
When it happens to someone you care about, it can be hard to know what to say or how to help them. But providing the right support to a friend can make all the difference as they face the emotional and physical challenges of a new diagnosis and treatment.
Here are six ways to offer meaningful support to a friend who has been diagnosed with cancer.
1. Recognise and respond to emotions
When facing a cancer diagnosis and treatment, it’s normal to experience a range of emotions including fear, anger, grief and sadness. Your friend’s moods may fluctuate. It is also common for feelings to change over time, for example your friend’s anxiety may decrease, but they may feel more depressed.
Spending time together can mean a lot to someone who is feeling isolated during cancer treatment. Chokniti-Studio/Shutterstock Some friends may want to share details while others will prefer privacy. Always ask permission to raise sensitive topics (such as changes in physical appearance or their thoughts regarding fears and anxiety) and don’t make assumptions. It’s OK to tell them you feel awkward, as this acknowledges the challenging situation they are facing.
When they feel comfortable to talk, follow their lead. Your support and willingness to listen without judgement can provide great comfort. You don’t have to have the answers. Simply acknowledging what has been said, providing your full attention and being present for them will be a great help.
2. Understand their diagnosis and treatment
Understanding your friend’s diagnosis and what they’ll go through when being treated may be helpful.
Being informed can reduce your own worry. It may also help you to listen better and reduce the amount of explaining your friend has to do, especially when they’re tired or overwhelmed.
Explore reputable sources such as the Cancer Council website for accurate information, so you can have meaningful conversations. But keep in mind your friend has a trusted medical team to offer personalised and accurate advice.
3. Check in regularly
Cancer treatment can be isolating, so regular check-ins, texts, calls or visits can help your friend feel less alone.
Having a normal conversation and sharing a joke can be very welcome. But everyone copes with cancer differently. Be patient and flexible in your support – some days will be harder for them than others.
Remembering key dates – such as the next round of chemotherapy – can help your friend feel supported. Celebrating milestones, including the end of treatment or anniversary dates, may boost morale and remind your friend of positive moments in their cancer journey.
Always ask if it’s a good time to visit, as your friend’s immune system may be compromised by their cancer or treatments such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy. If you’re feeling unwell, it’s best to postpone visits – but they may still appreciate a call or text.
4. Offer practical support
Sometimes the best way to show your care is through practical support. There may be different ways to offer help, and what your friend needs might change at the beginning, during and after treatment.
For example, you could offer to pick up prescriptions, drive them to appointments so they have transport and company to debrief, or wait with them at appointments.
Meals will always be welcome. However it’s important to remember cancer and its treatments may affect taste, smell and appetite, as well as your friend’s ability to eat enough or absorb nutrients. You may want to check first if there are particular foods they like. Good nutrition can help boost their strength while dealing with the side effects of treatment.
There may also be family responsibilities you can help with, for example, babysitting kids, grocery shopping or taking care of pets.
There may be practical ways you can help, such as dropping off meals. David Trinks/Unsplash 5. Explore supports together
Studies have shown mindfulness practices can be an effective way for people to manage anxiety associated with a cancer diagnosis and its treatment.
If this is something your friend is interested in, it may be enjoyable to explore classes (either online or in-person) together.
You may also be able to help your friend connect with organisations that provide emotional and practical help, such as the Cancer Council’s support line, which offers free, confidential information and support for anyone affected by cancer, including family, friends and carers.
Peer support groups can also reduce your friend’s feelings of isolation and foster shared understanding and empathy with people who’ve gone through a similar experience. GPs can help with referrals to support programs.
6. Stick with them
Be committed. Many people feel isolated after their treatment. This may be because regular appointments have reduced or stopped – which can feel like losing a safety net – or because their relationships with others have changed.
Your friend may also experience emotions such as worry, lack of confidence and uncertainty as they adjust to a new way of living after their treatment has ended. This will be an important time to support your friend.
But don’t forget: looking after yourself is important too. Making sure you eat well, sleep, exercise and have emotional support will help steady you through what may be a challenging time for you, as well as the friend you love.
Our research team is developing new programs and resources to support carers of people who live with cancer. While it can be a challenging experience, it can also be immensely rewarding, and your small acts of kindness can make a big difference.
Stephanie Cowdery, Research Fellow, Carer Hub: A Centre of Excellence in Cancer Carer Research, Translation and Impact, Deakin University; Anna Ugalde, Associate Professor & Victorian Cancer Agency Fellow, Deakin University; Trish Livingston, Distinguished Professor & Director of Special Projects, Faculty of Health, Deakin University, and Victoria White, Professor of Pyscho-Oncology, School of Psychology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Metformin Slows Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Metformin And How It Slows Down Aging
That’s a bold claim for a title, but the scientific consensus is clear, and this Research Review Monday we’re going to take a look at exactly that!
Metformin is a common diabetes-management drug, used to lower blood sugar levels in people who either don’t have enough insulin or the insulin isn’t being recognized well enough by the body.
However, it also slows aging, which is a quality it’s also been studied for for more than a decade. We’ll look at some of the more recent research, though. Let’s kick off with an initial broad statement, from the paper “The Use of Metformin to Increase the Human Healthspan”, as part of the “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology” series:
In recent years, more attention has been paid to the possibility of using metformin as an anti-aging drug. It was shown to significantly increase the lifespan in some model organisms and delay the onset of age-associated declines. Growing amounts of evidence from clinical trials suggest that metformin can effectively reduce the risk of many age-related diseases and conditions, including cardiometabolic disorders, neurodegeneration, chronic inflammation and frailty.
How does it work?
That’s still being studied, but the scientific consensus is that it works by inducing hormesis—the process by which minor stress signals cells to start repairing themselves. How does it induce that hormesis? Again, still being studied, but it appears to do it by activating a specific enzyme; namely, the AMP-activated protein kinase:
Read: Metformin-enhances resilience via hormesis
It also has been found to slow aging by means of an anti-inflammatory effect, as a bonus!
Any bad news?
Well, firstly, in most places it’s only prescribed for diabetes management, not for healthy life extension. A lot of anti-aging enthusiasts have turned to the grey market online to get it, and we can’t recommend that.
Secondly, it does have some limitations:
- Its bioavailability isn’t great in tablet form (the form in which it is most commonly given)
- It has quite a short elimination half-life (around 6 hours), which makes it great to fix transient hyperglycemia in diabetics—job done and it’s out—but presents a logistical challenge when it comes to something so pernicious as aging.
- Some people are non-responders (a non-responder, in medicine, is someone for whom a drug simply doesn’t work, for no obvious reason)
Want to know more? Check out:
Metformin in aging and aging-related diseases: clinical applications and relevant mechanism
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is It Dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Spot The Signs (Because None Of Us Are Immune)
Dementia affects increasingly many people, and unlike a lot of diseases, it disproportionately affects people in wealthy industrialized nations.
There are two main reasons for this:
- Longevity (in poorer countries, more people die of other things sooner; can’t get age-related cognitive decline if you don’t age)
- Lifestyle (in the age of convenience, it has never been easier to live an unhealthy lifestyle)
The former is obviously no bad thing for those of us lucky enough to be in wealthier countries (though even in such places, good healthcare access is of course sadly not a given for all).
The latter, however, is less systemic and more epidemic. But it does cut both ways:
- An unhealthy lifestyle is much easier here, yes
- A healthier lifestyle is much easier here, too!
This then comes down to two factors in turn:
- Information: knowing about dementia, what things lead to it, what to look out for, what to do
- Motivation: priorities, and how much attention we choose to give this matter
So, let’s get some information, and then give it our attention!
More than just memory
It’s easy to focus on memory loss, but the four key disabilities directly caused by dementia (each person may not get all four), can be remembered by the mnemonic: “AAAA!”
No, somebody didn’t just murder your writer. It’s:
- Amnesia: memory loss, in one or more of its many forms
- e.g. short term memory loss, and/or inability to make new memories
- Aphasia: loss of ability to express oneself, and/or understand what is expressed
- e.g. “More people have been to Berlin than I have”
- Or even less communication-friendly, Broca’s (Expressive) Aphasia and Wernicke’s (Receptive) Aphasia
- Apraxia: loss of ability to do things, through no obvious physical disability
- e.g. staring at the bathroom mirror wondering how to brush one’s teeth
- Agnosia: loss of ability to recognize things
- e.g. prosopagnosia, also called face-blindness.
If any of those seem worryingly familiar, be aware that while yes, it could be a red flag, what’s most important is patterns of these things.
Another difference between having a momentary brainlapse and having dementia might be, for example, the difference between forgetting your keys, and forgetting what keys do or how to use one.
That said, some are neurological deficits that may show up quite unrelated to dementia, including most of those given as examples above. So if you have just one, then that’s probably worthy of note, but probably not dementia.
Writer’s anecdote: I have had prosopagnosia all my life. To give an example of what that is like and how it’s rather more than just “bad with faces”…
Recently I saw my neighbor, and I could tell something was wrong with her face, but I couldn’t put my finger on what it was. Then some moments later, I realized I had mistaken her hat for her face. It was a large beanie with a panda design on it, and that was facelike enough for me to find myself looking at the wrong face.
Subjective memory matters as much as objective
Objective memory tests are great indicators of potential cognitive decline (or improvement!), but even a subjective idea of having memory problems, that one’s memory is “not as good as it used to be”, can be an important indicator too:
Subjective memory may be marker for cognitive decline
And more recently:
If your memory feels like it’s not what it once was, it could point to a future dementia risk
If you’d like an objective test of memory and other cognitive impairments, here’s the industry’s gold standard test (it’s free):
SAGE: A Test to Detect Signs of Alzheimer’s and Dementia
(The Self-Administered Gerocognitive Exam (SAGE) is designed to detect early signs of cognitive, memory or thinking impairments)
There are things that can look like dementia that aren’t
A person with dementia may be unable to recognize their partner, but hey, this writer knows that feeling very well too. So what sets things apart?
More than we have room for today, but here’s a good overview:
What are the early signs of dementia, and how does it differ from normal aging?
Want to read more?
You might like our previous article more specifically about reducing Alzheimer’s risk:
Reducing Alzheimer’s Risk Early!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: