The Brain Fog Fix – by Dr. Mike Dow
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The three weeks mentioned in the subtitle is in fact a week-by-week plan:
- Adjusting diet (inclusions and exclusions) and cognitive strategies
- Focusing on sleep, exercise, and memory-boosting “brain games”
- Bringing in the social aspect, and connection to something larger than oneself
In this reviewer’s opinion, a week is too short a time to completely overhaul one’s diet; most changes need to be gradual, so doing several at once in a week is quite extreme. But, even if it takes a month for each stage instead of a week, the method is reasonable.
The nutritional advice is good, and consistent with current best science on the topic. There’s a lot about keeping even blood sugars and improving insulin sensitivity, as well as doing what is best for the heart and blood in general (e.g. fiber, managing triglycerides, doing the right kinds of exercise, etc).
As a psychotherapist, he also talks a fair bit about neurotransmitters, and making sure one’s gut and brain are fed appropriately to keep the correct balance (remembering for example that serotonin is made in the gut, and dopamine is made in the brain). Unlike many of his colleagues, he’s not a fan of medicating beyond absolute necessity.
The style is a little salesy for this reviewer’s personal taste—but then again, perhaps he made the reasonable assumption that a person reading a book entitled “the brain fog fix” needs their attention grabbing and re-grabbing every paragraph or so. As such, maybe it’s not a bad call.
Bottom line: if you have brain fog and would like to not have brain fog, this book offers a scientifically sound, evidence-based, holistic approach that can certainly improve things.
Click here to check out The Brain Fog Fix, and fix your brain fog!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fennel vs Artichoke – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing fennel to artichoke, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Both are great! But artichoke wins on nutritional density.
In terms of macros, artichoke has more protein and more fiber, for only slightly more carbs.
Vitamins are another win for artichoke, boasting more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, and choline. Meanwhile, fennel has more of vitamins A, E, and K, which is also very respectable but does allow artichoke a 6:3 lead.
In the category of minerals, artichoke has a lot more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus, while fennel has a little more calcium, potassium, and selenium.
One other relevant factor is that fennel is a moderate appetite suppressant, which may be good or bad depending on your food-related goals.
All in all though, we say the artichoke wins by virtue of its greater abundance of nutrients!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? ← appropriately enough, with fennel hearts and artichoke hearts!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Built from Broken – by Scott Hogan, CPT, COES
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So many exercise programs come with the caveat “consult your doctor before engaging in any new activity”, and the safe-but-simple “do not try to train through an injury”.
Which is all very well and good for someone in fabulous health who sprained an ankle while running and can just wait a bit, but what about those of us carrying…
- long-term injuries
- recurring injuries
- or just plain unfixable physical disabilities?
That’s where physiotherapist Scott Hogan comes in. The subtitle line goes:
❝A Science-Based Guide to Healing Painful Joints, Preventing Injuries, and Rebuilding Your Body❞
…but he does also recognize that there are some things that won’t bounce back.
On the other hand… There are a lot of things that get written off by doctors as “here’s some ibuprofen” that, with consistent mindful training, could actually be fixed.
Hogan delivers again and again in this latter category! You’ll see on Amazon that the book has thousands of 4- and 5-star ratings and many glowing reviews, and it’s for a reason or three:
- The book first lays a foundational knowledge of the most common injuries likely to impede us from training
- It goes on to give step-by-step corrective exercises to guide your body through healing itself. Your body is trying to heal itself anyway; you might as well help it accomplish that!
- It finishes up with a comprehensive (and essential) guide to train for the strength and mobility that will help you avoid future problems.
In short: a potentially life-changing book if you have some (likely back- or joint-related) problem that needs overcoming!
And if you don’t? An excellent pre-emptive guide all the same. This is definitely one of those “an ounce of prevention is better than a pound of cure” things.
Share This Post
-
Never Too Old?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Age Limits On Exercise?
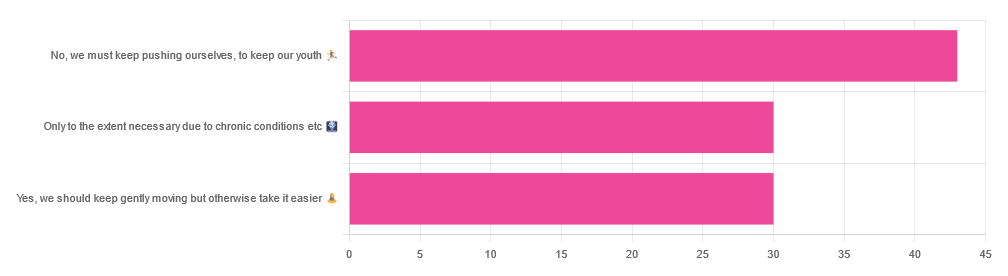
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on whether we should exercise less as we get older, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 42% said “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“
- About 29% said “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc”
- About 29% said “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier”
One subscriber who voted for “No, we must keep pushing ourselves, to keep our youth“ wrote to add:
❝I’m 71 and I push myself. I’m not as fast or strong as I used to be but, I feel great when I push myself instead of going through the motions. I listen to my body!❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted for “Only to the extent necessary due to chronic conditions etc” wrote to add:
❝It’s never too late to get stronger. Important to keep your strength and balance. I am a Silver Sneakers instructor and I see first hand how helpful regular exercise is for seniors.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
One subscriber who voted to say “Yes, we should keep gently moving but otherwise take it easier” wrote to add:
❝Keep moving but be considerate and respectful of your aging body. It’s a time to find balance in life and not put yourself into a positon to damage youself by competing with decades younger folks (unless you want to) – it will take much longer to bounce back.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
These will be important, because we’ll come back to them at the end.
So what does the science say?
Endurance exercise is for young people only: True or False?
False! With proper training, age is no barrier to serious endurance exercise.
Here’s a study that looked at marathon-runners of various ages, and found that…
- the majority of middle-aged and elderly athletes have training histories of less than seven years of running
- there are virtually no relevant running time differences (p<0.01) per age in marathon finishers from 20 to 55 years
- after 55 years, running times did increase on average, but not consistently (i.e. there were still older runners with comparable times to the younger age bracket)
The researchers took this as evidence of aging being indeed a biological process that can be sped up or slowed down by various lifestyle factors.
See also:
Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
this covers the many aspects of biological aging (it’s not one number, but many!) and how our various different biological ages are often not in sync with each other, and how we can optimize each of them that can be optimized
Resistance training is for young people only: True or False?
False! In fact, it’s not only possible for older people, but is also associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality.
Specifically, those who reported strength-training at least once per week enjoyed longer lives than those who did not.
You may be thinking “is this just the horse-riding thing again, where correlation is not causation and it’s just that healthier people (for other reasons) were able to do strength-training more, rather than the other way around?“
…which is a good think to think of, so well-spotted if you were thinking that!
But in this case no; the benefits remained when other things were controlled for:
❝Adjusted for demographic variables, health behaviors and health conditions, a statistically significant effect on mortality remained.
Although the effects on cardiac and cancer mortality were no longer statistically significant, the data still pointed to a benefit.
Importantly, after the physical activity level was controlled for, people who reported strength exercises appeared to see a greater mortality benefit than those who reported physical activity alone.❞
See the study: Is strength training associated with mortality benefits? A 15 year cohort study of US older adults
And a pop-sci article about it: Strength training helps older adults live longer
Closing thoughts
As it happens… All three of the subscribers we quoted all had excellent points!
Because in this case it’s less a matter of “should”, and more a selection of options:
- We (most of us, at least) can gain/regain/maintain the kind of strength and fitness associated with much younger people, and we need not be afraid of exercising accordingly (assuming having worked up to such, not just going straight from couch to marathon, say).
- We must nevertheless be mindful of chronic conditions or even passing illnesses/injuries, but that goes for people of any age
- We also can’t argue against a “safety first” cautious approach to exercise. After all, sure, maybe we can run marathons at any age, but that doesn’t mean we have to. And sure, maybe we can train to lift heavy weights, but if we’re content to be able to carry the groceries or perhaps take our partner’s weight in the dance hall (or the bedroom!), then (if we’re also at least maintaining our bones and muscles at a healthy level) that’s good enough already.
Which prompts the question, what do you want to be able to do, now and years from now? What’s important to you?
For inspiration, check out: Train For The Event Of Your Life!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Junk Food Turns Public Villain as Power Shifts in Washington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The new Trump administration could be coming for your snacks.
For years, the federal government has steered clear of regulating junk food, fast food, and ultra-processed food.
Now attitudes are changing. Some members of President-elect Donald Trump’s inner circle are gearing up to battle “Big Food,” or the companies that make most of the food and beverages consumed in the United States. Nominees for top health agencies are taking aim at ultra-processed foods that account for an estimated 70% of the nation’s food supply. Based on recent statements, a variety of potential politically charged policy options to regulate ultra-processed food may land on the Trump team menu, including warning labels, changes to agribusiness subsidies, and limits on which products consumers can buy with government food aid.
The push to reform the American diet is being driven largely by conservatives who have taken up the cause that has long been a darling of the left. Trump supporters such as Robert F. Kennedy Jr., whose controversial nomination to lead the Department of Health and Human Services still faces Senate confirmation, are embracing a concept that champions natural foods and alternative medicine. It’s a movement they’ve dubbed “MAHA,” or Make America Healthy Again. Their interest has created momentum because their goals have fairly broad bipartisan support even amid a bitterly divided Congress in which lawmakers from both sides of the aisle focused on the issue last year.
It’s likely to be a pitched battle because the food industry wields immense political influence and has successfully thwarted previous efforts to regulate its products or marketing. The category of “food processing and sales companies,” which includes Tyson Foods and Nestle SA, tallied $26.7 million in spending on lobbying in 2024, according to OpenSecrets. That’s up from almost $10 million in 1998.
“They have been absolutely instrumental and highly, highly successful at delaying any regulatory effectiveness in America,” said Laura Schmidt, a health policy professor at the University of California-San Francisco. “It really does feel like there needs to be a moment of reckoning here where people start asking the question, ‘Why do we have to live like this?’”
“Ultra-processed food” is a widely used term that means different things to different people and is used to describe items ranging from sodas to many frozen meals. These products often contain added fats, starches, and sugars, among other things. Researchers say consumption of ultra-processed foods is linked — in varying levels of intensity — to chronic conditions like diabetes, cancer, mental health problems, and early death.
Nutrition and health leaders are optimistic that a reckoning is already underway. Kennedy has pledged to remove processed foods from school lunches, restrict certain food additives such as dyes in cereal, and shift federal agricultural subsidies away from commodity crops widely used in ultra-processed foods.
The intensifying focus in Washington has triggered a new level of interest on the legal front as lawyers explore cases to take on major foodmakers for selling products they say result in chronic disease.
Bryce Martinez, now 18, filed a lawsuit in December against almost a dozen foodmakers such as Kraft Heinz, The Coca-Cola Co., and Nestle USA. He developed diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by age 16, and is seeking to hold them accountable for his illnesses. According to the suit, filed in the Philadelphia Court of Common Pleas, the companies knew or should have known ultra-processed foods were harmful and addictive.
The lawsuit noted that Martinez grew up eating heavily advertised, brand-name foods that are staples of the American diet — sugary soft drinks, Cheerios and Lucky Charms, Skittles and Snickers, frozen and packaged dinners, just to name a few.
Nestle, Coca-Cola, and Kraft Heinz didn’t return emails seeking comment for this article. The Consumer Brands Association, a trade association for makers of consumer packaged goods, disputed the allegations.
“Attempting to classify foods as unhealthy simply because they are processed, or demonizing food by ignoring its full nutrient content, misleads consumers and exacerbates health disparities,” said Sarah Gallo, senior vice president of product policy, in a statement.
Other law firms are on the hunt for children or adults who believe they were harmed by consuming ultra-processed foods, increasing the likelihood of lawsuits.
One Indiana personal injury firm says on its website that “we are actively investigating ultra processed food (UPF) cases.” Trial attorneys in Texas also are looking into possible legal action against the federal regulators they say have failed to police ultra-processed foods.
“If you or your child have suffered health problems that your doctor has linked directly to the consumption of ultra-processed foods, we want to hear your story,” they say on their website.
Meanwhile, the FDA on Jan. 14 announced it is proposing to require a front-of-package label to appear on most packaged foods to make information about a food’s saturated fat, sodium, and added sugar content easily visible to consumers.
And on Capitol Hill, Sens. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), Ron Johnson (R-Wis.), and Cory Booker (D-N.J.) are sounding the alarm over ultra-processed food. Sanders introduced legislation in 2024 that could lead to a federal ban on junk food advertising to children, a national education campaign, and labels on ultra-processed foods that say the products aren’t recommended for children. Booker cosigned the legislation along with Sens. Peter Welch (D-Vt.) and John Hickenlooper (D-Colo.).
The Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions held a December hearing examining links between ultra-processed food and chronic disease during which FDA Commissioner Robert Califf called for more funding for research.
Food companies have tapped into “the same neural circuits that are involved in opioid addiction,” Califf said at the hearing.
Sanders, who presided over the hearing, said there’s “growing evidence” that “these foods are deliberately designed to be addictive,” and he asserted that ultra-processed foods have driven epidemics of diabetes and obesity, and hundreds of billions of dollars in medical expenses.
Research on food and addiction “has accumulated to the point where it’s reached a critical mass,” said Kelly Brownell, an emeritus professor at Stanford who is one of the editors of a scholarly handbook on the subject.
Attacks from three sides — lawyers, Congress, and the incoming Trump administration, all seemingly interested in taking up the fight — could lead to enough pressure to challenge Big Food and possibly spur better health outcomes in the U.S., which has the lowest life expectancy among high-income countries.
“Maybe getting rid of highly processed foods in some things could actually flip the switch pretty quickly in changing the percentage of the American public that are obese,” said Robert Redfield, a virologist who led the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention during the previous Trump administration, in remarks at a December event hosted by the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank.
Claims that Big Food knowingly manufactured and sold addictive and harmful products resemble the claims leveled against Big Tobacco before the landmark $206 billion settlement was reached in 1998.
“These companies allegedly use the tobacco industry’s playbook to target children, especially Black and Hispanic children, with integrated marketing tie-ins with cartoons, toys, and games, along with social media advertising,” Rene Rocha, one of the lawyers at Morgan & Morgan representing Martinez, told KFF Health News.
The 148-page Martinez lawsuit against foodmakers draws from documents made public in litigation against tobacco companies that owned some of the biggest brands in the food industry.
Similar allegations were made against opioid manufacturers, distributors, and retailers before they agreed to pay tens of billions of dollars in a 2021 settlement with states.
The FDA ultimately put restrictions on the labeling and marketing of tobacco, and the opioid epidemic led to legislation that increased access to lifesaving medications to treat addiction.
But the Trump administration’s zeal in taking on Big Food may face unique challenges.
The ability of the FDA to impose regulation is hampered in part by funding. While the agency’s drug division collects industry user fees, its division of food relies on a more limited budget determined by Congress.
Change can take time because the agency moves at what some critics call a glacial pace. Last year, the FDA revoked a regulation allowing brominated vegetable oil in food products. The agency determined in 1970 that the additive was not generally recognized as safe.
Efforts to curtail the marketing of ultra-processed food could spur lawsuits alleging that any restrictions violate commercial speech protected by the First Amendment. And Kennedy — if he is confirmed as HHS secretary — may struggle to get support from a Republican-led Congress that champions less federal regulation and a president-elect who during his previous term served fast food in the White House.
“The question is, will RFK be able to make a difference?” said David L. Katz, a doctor who founded True Health Initiative, a nonprofit group that combats public health misinformation. “No prior administration has done much in this space, and RFK is linked to a particularly anti-regulatory administration.”
Meanwhile, the U.S. population is recognized as among the most obese in the world and has the highest rate of people with multiple chronic conditions among high-income countries.
“There is a big grassroots effort out there because of how sick we are,” said Jerold Mande, who served as deputy undersecretary for food safety at the Department of Agriculture from 2009 to 2011. “A big part of it is people shouldn’t be this sick this young in their lives. You’re lucky if you get to 18 without a chronic disease. It’s remarkable.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
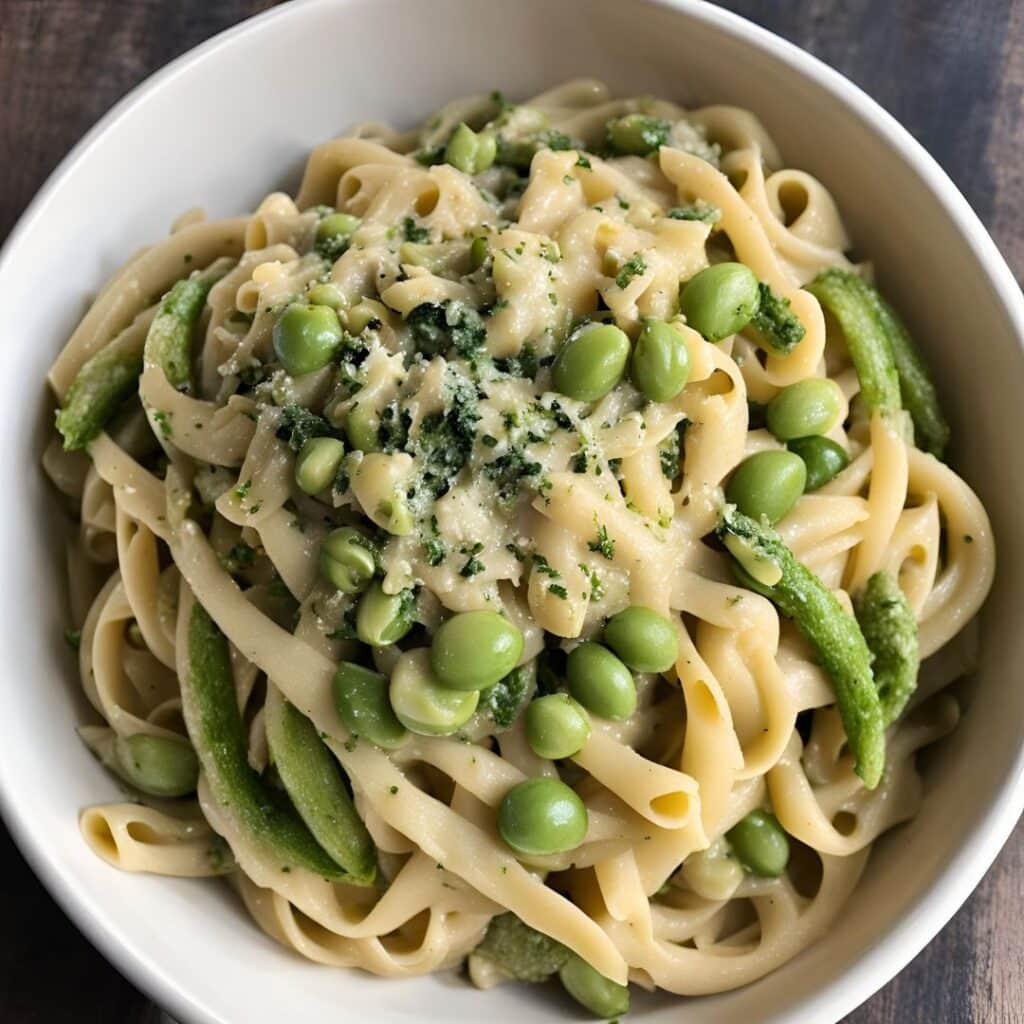
Creamy Zucchini, Edamame, & Asparagus Linguine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein, fiber, and polyphenols are the dish of the day here:
You will need
- 1½ cups milk (your choice what kind; we recommend soy for its neutral taste, though hazelnut’s nutty flavor would also work in this recipe)
- 6 oz wholegrain linguine (or your pasta of choice)
- 2 zucchini, thinly sliced
- 5 oz edamame beans (frozen is fine)
- 5 oz asparagus tips, cut into 2″ lengths
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 small handful arugula
- 1 small handful parsley, chopped
- A few mint leaves, chopped
- Juice of ½ lemon
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a sauté pan or similar, over a low to medium heat. Add the zucchini and cook for 5 minutes until they start to soften.
2) Add the garlic and continue cooking for 1 minute, stirring gently.
3) Add the milk, bring to the boil, and add the past, chia seeds (the resistant starch from the pasta will help thicken the sauce, as will the chia seeds), and MSG or salt.
4) Reduce the heat, cover, and simmer for 8 minutes.
5) Add the edamame beans and asparagus, and cook for a further 2 minutes, or until the pasta is cooked but still firm to the bite. The sauce should be quite thick now.
6) Stir in the remaining ingredients and serve, adding a garnish if you wish.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
3 signs your diet is causing too much muscle loss – and what to do about it
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When trying to lose weight, it’s natural to want to see quick results. So when the number on the scales drops rapidly, it seems like we’re on the right track.
But as with many things related to weight loss, there’s a flip side: rapid weight loss can result in a significant loss of muscle mass, as well as fat.
So how you can tell if you’re losing too much muscle and what can you do to prevent it?
EvMedvedeva/Shutterstock Why does muscle mass matter?
Muscle is an important factor in determining our metabolic rate: how much energy we burn at rest. This is determined by how much muscle and fat we have. Muscle is more metabolically active than fat, meaning it burns more calories.
When we diet to lose weight, we create a calorie deficit, where our bodies don’t get enough energy from the food we eat to meet our energy needs. Our bodies start breaking down our fat and muscle tissue for fuel.
A decrease in calorie-burning muscle mass slows our metabolism. This quickly slows the rate at which we lose weight and impacts our ability to maintain our weight long term.
How to tell you’re losing too much muscle
Unfortunately, measuring changes in muscle mass is not easy.
The most accurate tool is an enhanced form of X-ray called a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. The scan is primarily used in medicine and research to capture data on weight, body fat, muscle mass and bone density.
But while DEXA is becoming more readily available at weight-loss clinics and gyms, it’s not cheap.
There are also many “smart” scales available for at home use that promise to provide an accurate reading of muscle mass percentage.
Some scales promise to tell us our muscle mass. Lee Charlie/Shutterstock However, the accuracy of these scales is questionable. Researchers found the scales tested massively over- or under-estimated fat and muscle mass.
Fortunately, there are three free but scientifically backed signs you may be losing too much muscle mass when you’re dieting.
1. You’re losing much more weight than expected each week
Losing a lot of weight rapidly is one of the early signs that your diet is too extreme and you’re losing too much muscle.
Rapid weight loss (of more than 1 kilogram per week) results in greater muscle mass loss than slow weight loss.
Slow weight loss better preserves muscle mass and often has the added benefit of greater fat mass loss.
One study compared people in the obese weight category who followed either a very low-calorie diet (500 calories per day) for five weeks or a low-calorie diet (1,250 calories per day) for 12 weeks. While both groups lost similar amounts of weight, participants following the very low-calorie diet (500 calories per day) for five weeks lost significantly more muscle mass.
2. You’re feeling tired and things feel more difficult
It sounds obvious, but feeling tired, sluggish and finding it hard to complete physical activities, such as working out or doing jobs around the house, is another strong signal you’re losing muscle.
Research shows a decrease in muscle mass may negatively impact your body’s physical performance.
3. You’re feeling moody
Mood swings and feeling anxious, stressed or depressed may also be signs you’re losing muscle mass.
Research on muscle loss due to ageing suggests low levels of muscle mass can negatively impact mental health and mood. This seems to stem from the relationship between low muscle mass and proteins called neurotrophins, which help regulate mood and feelings of wellbeing.
So how you can do to maintain muscle during weight loss?
Fortunately, there are also three actions you can take to maintain muscle mass when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet to lose weight.
1. Incorporate strength training into your exercise plan
While a broad exercise program is important to support overall weight loss, strength-building exercises are a surefire way to help prevent the loss of muscle mass. A meta-analysis of studies of older people with obesity found resistance training was able to prevent almost 100% of muscle loss from calorie restriction.
Relying on diet alone to lose weight will reduce muscle along with body fat, slowing your metabolism. So it’s essential to make sure you’ve incorporated sufficient and appropriate exercise into your weight-loss plan to hold onto your muscle mass stores.
Strength-building exercises help you retain muscle. BearFotos/Shutterstock But you don’t need to hit the gym. Exercises using body weight – such as push-ups, pull-ups, planks and air squats – are just as effective as lifting weights and using strength-building equipment.
Encouragingly, moderate-volume resistance training (three sets of ten repetitions for eight exercises) can be as effective as high-volume training (five sets of ten repetitions for eight exercises) for maintaining muscle when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet.
2. Eat more protein
Foods high in protein play an essential role in building and maintaining muscle mass, but research also shows these foods help prevent muscle loss when you’re following a calorie-restricted diet.
But this doesn’t mean just eating foods with protein. Meals need to be balanced and include a source of protein, wholegrain carb and healthy fat to meet our dietary needs. For example, eggs on wholegrain toast with avocado.
3. Slow your weight loss plan down
When we change our diet to lose weight, we take our body out of its comfort zone and trigger its survival response. It then counteracts weight loss, triggering several physiological responses to defend our body weight and “survive” starvation.
Our body’s survival mechanisms want us to regain lost weight to ensure we survive the next period of famine (dieting). Research shows that more than half of the weight lost by participants is regained within two years, and more than 80% of lost weight is regained within five years.
However, a slow and steady, stepped approach to weight loss, prevents our bodies from activating defence mechanisms to defend our weight when we try to lose weight.
Ultimately, losing weight long-term comes down to making gradual changes to your lifestyle to ensure you form habits that last a lifetime.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Charles Perkins Centre Research Program Leader, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: