The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One Lump Mechanism Of Addiction Or Two?
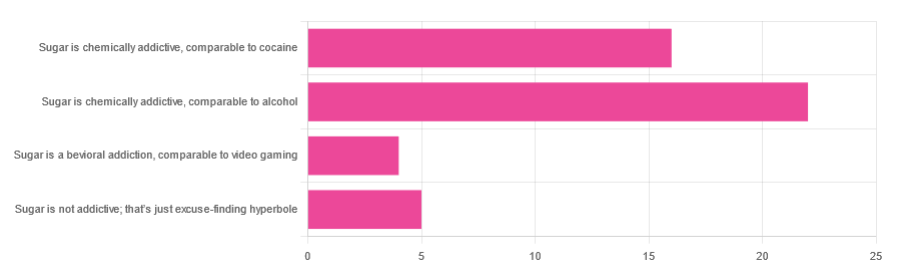
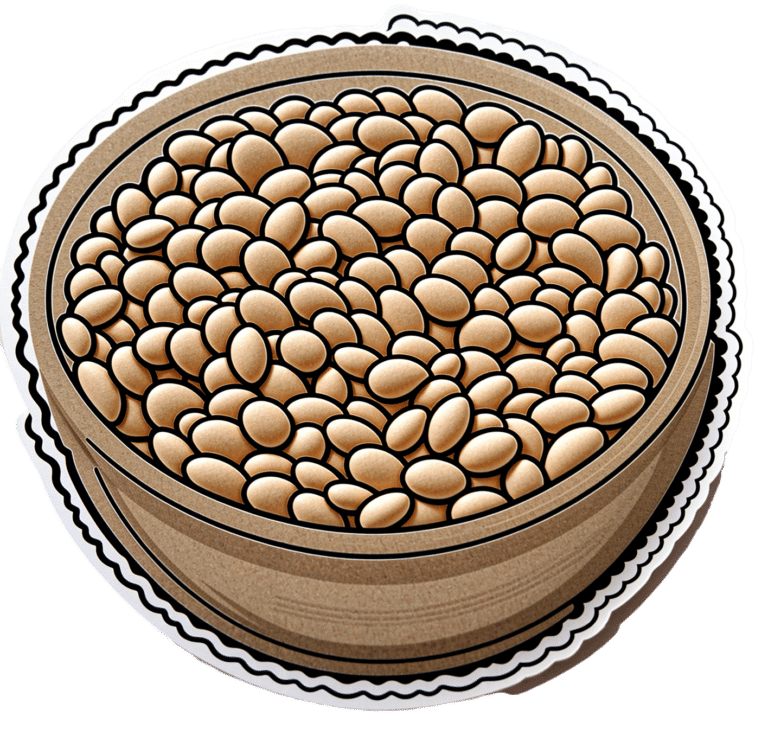
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you to what extent, if any, you believe sugar is addictive; we got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “Sugar is chemically addictive, comparable to alcohol”
- About 34% said “Sugar is chemically addictive, comparable to cocaine”
- About 11% said “Sugar is not addictive; that’s just excuse-finding hyperbole”
- About 9% said “Sugar is a behavioral addiction, comparable to video gaming”
So what does the science say?
Sugar is not addictive; that’s just excuse-finding hyperbole: True or False?
False, by broad scientific consensus. As ever, the devil’s in the details definitions, but while there is still discussion about how best to categorize the addiction, the scientific consensus as a whole is generally: sugar is addictive.
That doesn’t mean scientists* are a hive mind, and so there will be some who disagree, but most papers these days are looking into the “hows” and “whys” and “whats” of sugar addiction, not the “whether”.
*who are also, let us remember, a diverse group including chemists, neurobiologists, psychologists, social psychologists, and others, often collaborating in multidisciplinary teams, each with their own focus of research.
Here’s what the Center of Alcohol and Substance Use Studies has to say, for example:
Sugar Addiction: More Serious Than You Think
Sugar is a chemical addiction, comparable to alcohol: True or False?
True, broadly, with caveats—for this one, the crux lies in “comparable to”, because the neurology of the addiction is similar, even if many aspects of it chemically are not.
In both cases, sugar triggers the release of dopamine while also (albeit for different chemical reasons) having a “downer” effect (sugar triggers the release of opioids as well as dopamine).
Notably, the sociology and psychology of alcohol and sugar addictions are also similar (both addictions are common throughout different socioeconomic strata as a coping mechanism seeking an escape from emotional pain).
See for example in the Journal of Psychoactive Drugs:
On the other hand, withdrawal symptoms from heavy long-term alcohol abuse can kill, while withdrawal symptoms from sugar are very much milder. So there’s also room to argue that they’re not comparable on those grounds.
Sugar is a chemical addiction, comparable to cocaine: True or False?
False, broadly. There are overlaps! For example, sugar drives impulsivity to seek more of the substance, and leads to changes in neurobiological brain function which alter emotional states and subsequent behaviours:
The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors
However!
Cocaine triggers a release of dopamine (as does sugar), but cocaine also acts directly on our brain’s ability to remove dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine:
The Neurobiology of Cocaine Addiction
…meaning that in terms of comparability, they (to use a metaphor now, not meaning this literally) both give you a warm feeling, but sugar does it by turning up the heating a bit whereas cocaine does it by locking the doors and burning down the house. That’s quite a difference!
Sugar is a behavioral addiction, comparable to video gaming: True or False?
True, with the caveat that this a “yes and” situation.
There are behavioral aspects of sugar addiction that can reasonably be compared to those of video gaming, e.g. compulsion loops, always the promise of more (without limiting factors such as overdosing), anxiety when the addictive element is not accessible for some reason, reduction of dopaminergic sensitivity leading to a craving for more, etc. Note that the last is mentioning a chemical but the mechanism itself is still behavioral, not chemical per se.
So, yes, it’s a behavioral addiction [and also arguably chemical in the manners we’ve described earlier in this article].
For science for this, we refer you back to:
The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors
Want more?
You might want to check out:
Beating Food Addictions: When It’s More Than “Just” Cravings
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Reclaiming Body Trust – by Hilary Kinavey & Dana Sturtevant
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Authored by a therapist and a dietician, this book draws from both of their extensive professional clinical experiences, to explore how we can (often early in our lives) be led into disordered thinking when it comes to food and our bodies, and how we can “take back that which has been stolen from us”.
More prosaically: the presented goal here is for us to each figure out where we are with our own body, and how we might build our relationship with same going forwards, in the way that will work the best for us.
The style is relaxed and conversational, while taking care to cover topics that are often tricky with no less seriousness. Chapter headings such as “Your coping is rooted in wisdom”, “What does grief have to do with it?” and “Allowing for pleasure and satisfaction” give an idea of the flavors at hand here.
Bottom line: if you think your relationship with food and your body could be better, not only are you probably right, but also, this book can help.
Share This Post
-
An apple cider vinegar drink a day? New study shows it might help weight loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Made from fermented apples and naturally high in acetic acid, apple cider vinegar has been popular in recent years for its purported health benefits – from antibacterial properties to antioxidant effects and potential for helping manage blood sugars.
Its origins as a health tonic stretch much further back. Hippocrates used it to treat wounds, fever and skin sores.
An experimental study, released today, looks into whether apple cider vinegar could be effective for weight loss, reduce blood glucose levels and reduce blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides).
The results suggest it could reduce all three – but it might not be as simple as downing an apple cider vinegar drink a day.
What did they do?
A group of scientists in Lebanon did a double-blinded, randomised, clinical trial in a group of overweight and obese young people aged from 12–25 years.
Researchers randomly placed 30 participants in one of four groups. The participants were instructed to consume either 5, 10 or 15ml of apple cider vinegar diluted into 250ml of water each morning before they ate anything for 12 weeks. A control group consumed an inactive drink (a placebo) made (from lactic acid added to water) to look and taste the same.
Typically this sort of study provides high quality evidence as it can show cause and effect – that is the intervention (apple cider vinegar in this case) leads to a certain outcome. The study was also double-blinded, which means neither the participants or the scientists involved with collecting the data knew who was in which group.
So, what did they find?
After a period of three months apple cider vinegar consumption was linked with significant falls in body weight and body mass index (BMI). On average, those who drank apple cider vinegar during that period lost 6–8kg in weight and reduced their BMI by 2.7–3 points, depending on the dose. They also showed significant decreases in the waist and hip circumference.
The authors also report significant decreases in levels of blood glucose, triglycerides, and cholesterol in the apple cider groups. This finding echoes previous studies. The placebo group, who were given water with lactic acid, had much smaller decreases in weight and BMI. There were also no significant decreases in blood glucose and blood lipids.
From animal studies, it is thought the acetic acid in apple cider vinegar may affect the expression of genes involved in burning fats for energy. The new study did not explore whether this mechanism was involved in any weight loss.
Is this good news?
While the study appears promising, there are also reasons for caution.
Firstly, study participants were aged from 12 to 25, so we can’t say whether the results could apply to everyone.
The statistical methods used in the study don’t allow us to confidently say the same amount of weight loss would occur again if the study was done again.
And while the researchers kept records of the participants’ diet and exercise during the study, these were not published in the paper. This makes it difficult to determine if diet or exercise may have had an impact. We don’t know whether participants changed the amount they ate or the types of food they ate, or whether they changed their exercise levels.
The study used a placebo which they tried to make identical in appearance and taste to the active treatment. But people may still be able to determine differences. Researchers may ask participants at the end of a study to guess which group they were in to test the integrity of the placebo. Unfortunately this was not done in this study, so we can’t be certain if the participants knew or not.
Finally, the authors do not report whether anyone dropped out of the study. This could be important and influence results if people who did not lose weight quit due to lack of motivation.
Is that you mother? The enzymes in apple cider vinegar might be health-giving.
ShutterstockAny other concerns?
Apple cider vinegar is acidic and there are concerns it may erode tooth enamel. This can be a problem with any acidic beverages, including fizzy drinks, lemon water and orange juice.
To minimise the risk of acid erosion some dentists recommend the following after drinking acidic drinks:
- rinsing out your mouth with tap water afterwards
- chewing sugar-free gum afterwards to stimulate saliva production
- avoiding brushing your teeth immediately after drinking because it might damage the teeth’s softened top layer
- drink with a straw to minimise contact with the teeth.
Rinsing with water could prevent acid damaging your teeth.
ShutterstockDown the hatch?
This study provides us with some evidence of a link between apple cider vinegar and weight loss. But before health professionals can recommend this as a weight loss strategy we need bigger and better conducted studies across a wider age range.
Such research would need to be done alongside a controlled background diet and exercise across all the participants. This would provide more robust evidence that apple cider vinegar could be a useful aid for weight loss.
Still, if you don’t mind the taste of apple cider vinegar then you could try drinking some for weight loss, alongside a healthy balanced and varied dietary intake. This study does not suggest people can eat whatever they like and drink apple cider vinegar as a way to control weight.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Cluttered Mind – by Deborah McKenna
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coming from an eclectic psychotherapy background, Deborah McKenna outlines a wide array of techniques to “do what it says on the tin”, that is:
Organizing the junk drawer of your mind.
McKenna argues that it’s natural for something so gargantuan as our mind to get cluttered… but that it’s perfectly possible, with a good system, to tidy up considerably.
The benefit of this is much like the benefit of tidying a room:
Imagine a kitchen in which half the things have not been put away; there are dishes in the sink, something is growing behind the trash can… and you have a vague suspicion that if you open a certain cupboard, its contents are going to come falling out on your head. How are you going to cook a meal here?
Imagine a mind when many thoughts have been left untended; there are things you needed to process, and there’s a steady resentment of something growing in some dark part of your mind… and there’s some part of your memory that you’re afraid to even look at it, because of all it’ll cause to come surging back at you. How are you going to strategize your life here?
Fortunately, McKenna is here to guide you through doing for your mind what Marie Kondo would do for your home. And, even better, McKenna does it with a simple and clear writing style, assorted diagrams, and a step-by-step approach to getting everything in order.
Give Your Mind A Spring-Cleaning With This Book From Amazon Today
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why do I need to get up during the night to wee? Is this normal?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It can be normal to wake up once or even twice during the night to wee, especially as we get older.
One in three adults over 30 makes at least two trips to the bathroom every night.
Waking up from sleep to urinate on a regular basis is called nocturia. It’s one of the most commonly reported bothersome urinary symptoms (others include urgency and poor stream).
So what causes nocturia, and how can it affect wellbeing?
A range of causes
Nocturia can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, such as heart or kidney problems, poorly controlled diabetes, bladder infections, an overactive bladder, or gastrointestinal issues. Other causes include pregnancy, medications and consumption of alcohol or caffeine before bed.
While nocturia causes disrupted sleep, the reverse is true as well. Having broken sleep, or insomnia, can also cause nocturia.
When we sleep, an antidiuretic hormone is released that slows down the rate at which our kidneys produce urine. If we lie awake at night, less of this hormone is released, meaning we continue to produce normal rates of urine. This can accelerate the rate at which we fill our bladder and need to get up during the night.
Stress, anxiety and watching television late into the night are common causes of insomnia.
Sometimes we need to get up late at night to pee.
Christian MoroEffects of nocturia on daily functioning
The recommended amount of sleep for adults is between seven and nine hours per night. The more times you have to get up in the night to go to the bathroom, the more this impacts sleep quantity and quality.
Decreased sleep can result in increased tiredness during the day, poor concentration, forgetfulness, changes in mood and impaired work performance.
If you’re missing out on quality sleep due to nighttime trips to the bathroom, this can affect your quality of life.
In more severe cases, nocturia has been compared to having a similar impact on quality of life as diabetes, high blood pressure, chest pain, and some forms of arthritis. Also, frequent disruptions to quality and quantity of sleep can have longer-term health impacts.
Nocturia not only upsets sleep, but also increases the risk of falls from moving around in the dark to go to the bathroom.
Further, it can affect sleep partners or others in the household who may be disturbed when you get out of bed.
Can you have a ‘small bladder’?
It’s a common misconception that your trips to the bathroom are correlated with the size of your bladder. It’s also unlikely your bladder is smaller relative to your other organs.
If you find you are having to wee more than your friends, this could be due to body size. A smaller person drinking the same amount of fluids as someone larger will simply need to go the bathroom more often.
If you find you are going to the bathroom quite a lot during the day and evening (more than eight times in 24 hours), this could be a symptom of an overactive bladder. This often presents as frequent and sudden urges to urinate.
If you are concerned about any lower urinary tract symptoms, it’s worth having a chat with your family GP.
There are some medications that can assist in the management of nocturia, and your doctor will also be able to help identify any underlying causes of needing to go to the toilet during the night.
A happy and healthy bladder
Here are some tips to maintain a happy and healthy bladder, and reduce the risk you’ll be up at night:
- make your sleep environment comfortable, with a suitable mattress and sheets to suit the temperature
- get to bed early, and limit screens, or activites before bed
- limit foods and drinks that irritate the bladder, such as coffee or alcohol, especially before bedtime
- sit in a relaxed position when urinating, and allow time for the bladder to completely empty
- practice pelvic floor muscle exercises
- drink an adequate amount of fluids during the day, and avoid becoming dehydrated
- maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat nutritious foods and do not do anything harmful to the body such as smoking or using illicit drugs
- review your medications, as the time you take some pharmaceuticals may affect urine production or sleep
- if you have swollen legs, raise them a few hours before bedtime to let the fluid drain.
Christian Moro, Associate Professor of Science & Medicine, Bond University and Charlotte Phelps, Senior Teaching Fellow, Medical Program, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Most Anti Aging Exercise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve referenced this (excellent) video before, but never actually put it under the spotlight in one of these features, so here we go!
Deep squats
It’s about deep squats, also called Slav squats, Asian squats, sitting squats, resting squats, or various other names. However, fear not; you don’t need to be Slavic or Asian to do it; you just need to practice.
As for why this is called “anti-aging”, by the way, it’s because being able to get up off the ground is one of the main tests of age-related mobility decline, and if you can deep-squat comfortably, then you can do that easily. And so long as you continue being able to deep-squat comfortably, you’ll continue to be able to get up off the ground easily too, because you have the strength in the right muscles, as well as the suppleness, comfort with range of motion, and balance (those stabilizing muscles are used constantly in a deep squat, whereas Western lifestyle sitting leaves those muscles very neglected and thus atrophied).
Epidemiological note: chairs, couches, and assorted modern conveniences reduce the need for squatting in daily life, leading to stiffness in joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Many adults in developed countries struggle with deep squats due to lack of use, not aging. Which is a problem, because a lack of full range of motion in joints causes wear and tear, leading to chronic pain and degenerative joint diseases. People in countries where squatting is a common resting position have lower incidences of osteoarthritis, for example—contrary to what some might expect, squatting does not harm joints but rather protects them from arthritis and knee pain. Strengthening leg muscles through squatting can alleviate knee pain, whereas knee pain is often worsened by inactivity.
Notwithstanding the thumbnail, which is showing an interim position, one’s feet should be flat on the ground, by the way, and one’s butt should be nearby, just a few inches off the ground (in other words, the position that we see her in for most of this video).
Troubleshooting: if you’re accustomed to sitting in chairs a lot, then this may be uncomfortable at first. Zuzka advises us to go gently, and/but gradually increase our range of motion and (equally importantly) duration in the resting position.
You can use a wall or doorway to partially support you, at first, if you struggle with mobility or balance. Just try to gradually use it less, until you’re comfortable deep-squatting with no support.
Since this is not an intrinsically very exciting exercise, once you build up the duration for which you’re comfortable deep-squatting, it can be good to get in the habit of “sitting” this way (i.e. deep squatting, still butt-off-the-floor, but doing the job of sitting) while doing other things such as working (if you have an appropriate work set-up for that*), reading, or watching TV.
*this is probably easiest with a laptop placed on an object/surface of appropriate height, such as a coffee table or such. As a bonus, having your hands in front of you while working will also bring your center of gravity forwards a bit, making the position easier and more comfortable to maintain. This writer (hi, it’s me) prefers her standing desk for work in general, with a nice ergonomic keyboard and all that, but if using a laptop from time to time, then squatting is a very good option.
In terms of working up duration, if you can only manage seconds to start with, that’s fine. Just do a few more seconds each time, until it’s 30, 60, 120, and so on until it’s 5 minutes, 10, 15, and so on.
You can even start that habit-forming while you’re still in the “seconds at a time” stage! You can deep-squat just for some seconds while you:
- pick up something from the floor
- check on something in the oven
- get something out of the bottom of the fridge
…etc!
For more on all this, plus many visual demonstrations including interim exercises to get you there if it’s difficult for you at first, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Mobility For Now & For Later: Train For The Marathon That Is Your Life!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Two Awesome Hours – by Dr. Josh Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The brain is an amazing and powerful organ, with theoretically unlimited potential in some respects. So why doesn’t it feel that way a lot of the time?
The truth is that not only are we often tired, dehydrated, or facing other obvious physiological challenges to peak brain health, but also… We’re simply not making the best use of it!
What Dr. Davis does is outline for us how we can create the conditions for “two awesome hours” of effective mental performance by:
- Recognizing when to most effectively flip the switch on our automatic thinking
- Scheduling tasks based on their “processing demand” and recovery time
- Learning how to direct attention, rather than avoid distractions
- Feeding and moving our bodies in ways that prep us for success
- Identifying what matters in our environment to be at the top of our mental game
Why only two hours? Why not four, or eight, or more?
Well, our brains need recovery time too, so we can’t be “always on” and operating and peak efficiency. But, what we can do is optimize a couple of hours for absolute peak efficiency, and then enjoy the rest of time with lower cognitive-load activities.
Bottom line: if the idea of what you could accomplish if you could just be guaranteed two schedulable hours (your preference when!) of peak cognitive performance per day, then this is a great book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: