Successful Aging – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know about age-related cognitive decline. What if there’s a flipside, though?
Neuroscientist Dr. Daniel Levitin explores the changes that the brain undergoes with age, and notes that it’s not all downhill.
From cumulative improvements in the hippocampi to a dialling-down of the (often overfunctioning) amygdalae, there are benefits too.
The book examines the things that shape our brains from childhood into our eighties and beyond. Many milestones may be behind us, but neuroplasticity means there’s always time for rewiring. Yes, it also covers the “how”.
We learn also about the neurogenesis promoted by such simple acts as taking a different route and/or going somewhere new, and what other things improve the brain’s healthspan.
The writing style is very accessible “pop-science”, and is focused on being of practical use to the reader.
Bottom line: if you want to get the most out of your aging wizening brain, this book is a great how-to manual.
Click here to check out Successful Aging and level up your later years!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
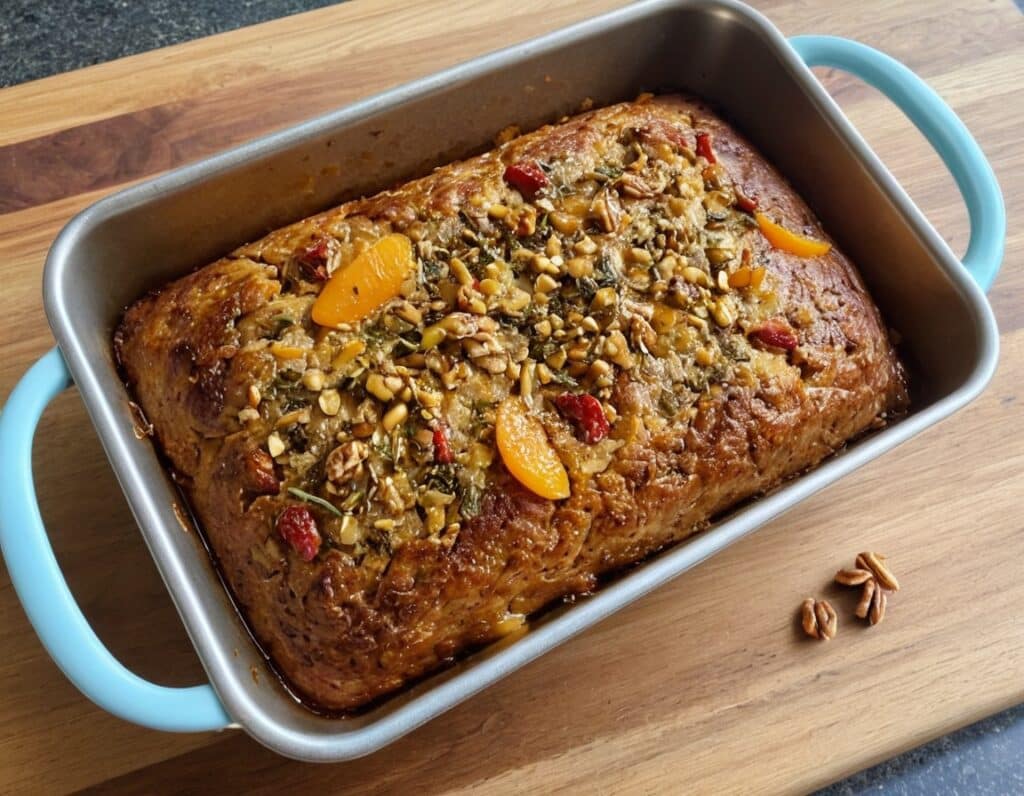
Walnut, Apricot, & Sage Nut Roast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s important to have at least one good nut roast recipe in your repertoire. It’s something that’s very good for making a good dish out of odds and ends that are in your house, and done well, it’s not only filling and nutritious, but a tasty treat too. Done badly, everyone knows the results can be unfortunate… Making this the perfect way to show off your skills!
You will need
- 1 cup walnuts
- ½ cup almonds
- ¼ cup whole mixed seeds (chia, pumpkin, & poppy are great)
- ¼ cup ground flax (also called flax meal)
- 1 medium onion, finely chopped
- 1 large carrot, grated
- 4 oz dried apricots, chopped
- 3 oz mushrooms, chopped
- 1 oz dried goji berries
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp fresh sage, chopped
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp dried rosemary
- 2 tsp dried thyme
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp yeast extract (even if you don’t like it; trust us; it will work) dissolved in ¼ cup hot water
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃, and line a 2 lb loaf tin with baking paper.
2) Heat some oil in a skillet over a moderate heat, and fry the onion for a few minutes until translucent. Add the garlic, carrot, and mushrooms, cooking for another 5 minutes, stirring well. Set aside to cool a little once done.
3) Process the nuts in a food processor, pulsing until they are well-chopped but not so much that they turn into flour.
4) Combine the nuts, vegetables, and all the other ingredients in a big bowl, and mix thoroughly. If it doesn’t have enough structural integrity to be thick and sticky and somewhat standing up by itself if you shape it, add more ground flax. If it is too dry, add a little water but be sparing.
5) Spoon the mixture into the loaf tin, press down well (or else it will break upon removal), cover with foil and bake for 30 minutes. Remove the foil, and bake for a further 15 minutes, until firm and golden. When done, allow it to rest in the tin for a further 15 minutes, before turning it out.
6) Serve, as part of a roast dinner (roast potatoes, vegetables, gravy, etc).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Chia Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Ergothioneine: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Lettuce vs Arugula – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing lettuce to arugula, we picked the arugula.
Why?
These two salad leaves that often fulfil quite similar culinary roles (base of a green salad) are actually of different families, and it shows…
In terms of macros, arugula is lower in carbs, and much higher in protein and fiber—to the point that the protein content in arugula is almost equal to the carb content, which for leaves, is not that common a thing to see.
When it comes to vitamins, things are more even: lettuce has more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B6, and K, while arugula has more of vitamins B5, B9, C, E, and choline. All in all, we can comfortably call it a tie on the vitamin front.
In the category of minerals, things are once again more decided: arugula has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. In contrast, lettuce boasts only more selenium. An easy win for arugula.
Both of these plants have plenty of health-giving phytochemicals, including flavonoids and carotenoids along with other less talked-about things, and while the profiles are quite different for each of them, they stack up about the same in terms of overall benefits in this category.
Taking the various categories into account, this of course adds up to an easy win for arugula, but do enjoy both, especially as lettuce brings benefits that arugula doesn’t in the two categories where they tied!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- How To Avoid Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Spinach vs Kale – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Beetroot vs Red Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to red cabbage, we picked the red cabbage.
Why?
Both are great, and both have their strengths!
In terms of macros, beetroot has very slightly more protein, carbs, and fiber, but the margins of difference are very small in each case. However, in terms of glycemic index, red cabbage has the considerably lower glycemic index, of 32 (low) as opposed to beetroot’s GI of 64 (medium). On the strength of this GI difference, we call this category a win for red cabbage.
In the category of vitamins, beetroot has more of vitamin B9, while red cabbage has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, C, E, K, and choline. By strength of numbers and also by having very large margins of difference on most of those, red cabbage is the clear winner here.
When it comes to minerals, beetroot has more copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while red cabbage has more calcium (and about ⅓ of the sodium). By the numbers, this is a win for beetroot, though it’s worth noting that the margins of difference were small, i.e. red cabbage was right behind beetroot on each of those.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall red cabbage win, but as we say, beetroot is great too, especially when it comes to minerals!
As ever, enjoy either or both; diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
No, beetroot isn’t vegetable Viagra. But here’s what it can do!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Live Life in Crescendo – by Stephen Covey and Cynthia Covey-Haller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Stephen Covey is of course best known for his “7 Habits of Highly Effective People“, while the dozen books he wrote afterwards, not including this one, did not get the same acclaim.
Not including this one, because this one was published posthumously and, notwithstanding the order of the names on the cover, in all likelihood his daughter wrote most of.
And yet! The very spirit of this book is in defiance of 7 Habits being his “early career” magnum opus. We say “early career”, because he was 57 already when that was published, but it was one of his earlier books.
In this work the authors lay out the case for how “your most important work is always ahead of you“, and that it is perfectly possible to “live life in crescendo“, and keep on giving whatever it is that we want to give to the world.
We also learn, mostly through storytelling, of how people are infinitely more important than things, and that it is there that we should put our investments. And that while adversity may not make us stronger, it just means we may need to change our approach, to continue to be productive in whatever way is meaningful to us.
Bottom line: if ever you wonder how your future could live up to your past (in a good way), this is the book to get you thinking.
Click here to check out Live Life in Crescendo, and figure out what your next great work will be!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
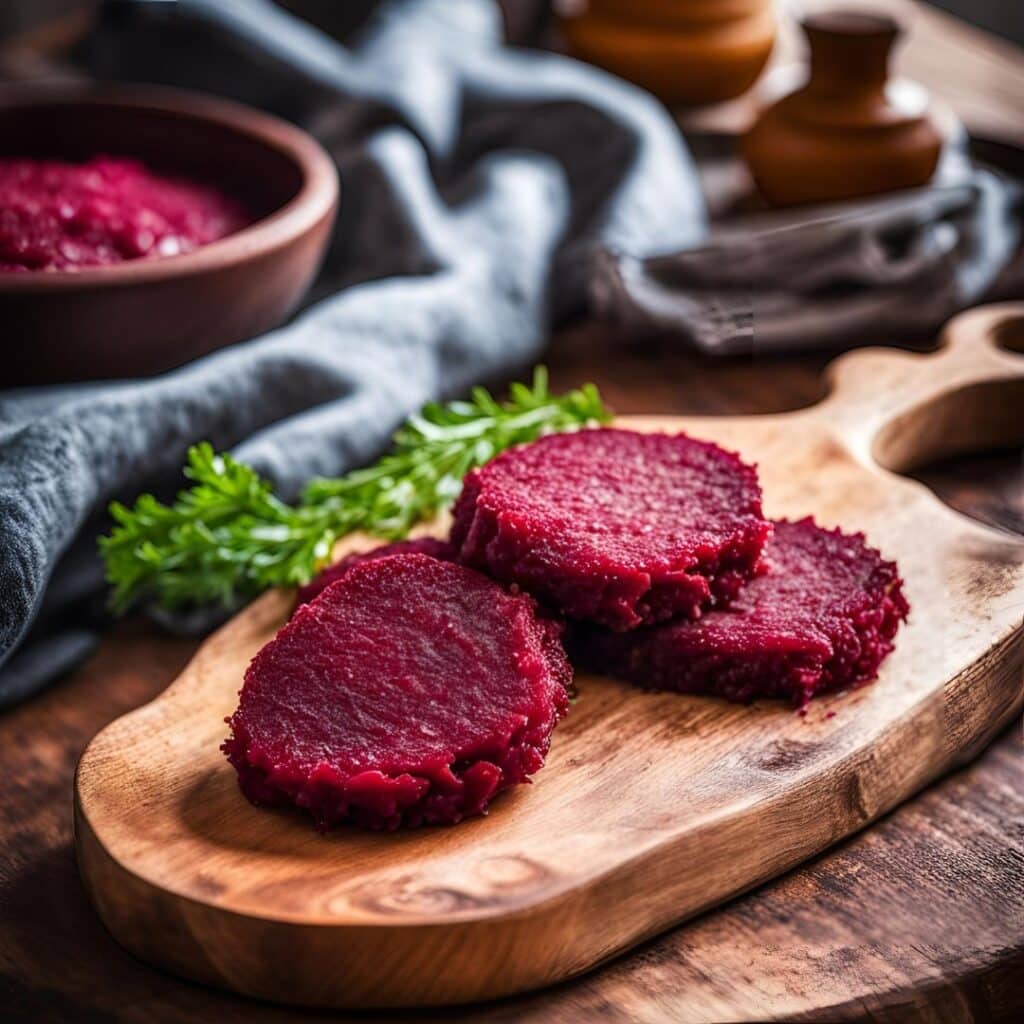
Blood-Sugar Balancing Beetroot Cutlets
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These beetroot cutlets are meaty and proteinous and fibrous and even have a healthy collection of fats, making these much better for your heart and blood than an animal-based equivalent.
You will need
- 1 can kidney beans, drained and rinsed (or 1 cup same, cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- ½ cup chopped roasted or steamed beetroot, blotted dry
- ½ cup chopped walnuts (if allergic, substitute with ¼ cup pumpkin seeds)
- ½ cup cooked (ideally: mixed) grains of your choice (if you need gluten-free, there are plenty of gluten-free grains and pseudocereals)
- ¼ cup finely chopped onion
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced or crushed
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tbsp ground flaxseeds
- 2 tbsp ground chia seeds
- 2 tsp tomato purée
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp white miso paste
- ½ tsp smoked paprika
- ½ tsp cayenne pepper
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the beetroot, beans, walnuts, grains, and onion in a food processor, and process until a coarse even mixture.
2) Add the remaining ingredients and process to mix thoroughly.
3) Transfer the mixture to a clean work surface and divide into six balls. If the structural integrity is not good (i.e. too soft), add a little more of any or all of these ingredients: chopped walnuts, ground flax, ground chia, nutritional yeast.
4) Press the balls firmly into cutlets, and refrigerate for at least 1 hour, but longer is even better if you have the time. Alternatively, if you’d like to freeze them for later use, then this is the point at which to do that.
5) Preheat the oven to 375℉ / 190℃.
6) Roast the cutlets on a baking tray lined with baking paper, for about 30 minutes, turning over carefully with a spatula halfway through. They should be firm when done; if they’re not, give them a little longer.
7) Serve hot, for example on a bed of greens and with a drizzle of aged balsamic vinegar.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Beetroot’s Many Benefits
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Curious Kids: what are the main factors in forming someone’s personality?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“What are the main factors in forming someone’s personality?” – Emma, age 10, from Shanghai
Hello Emma, and thank you for this very interesting question!
Let’s start by exploring what we mean by personality. Have you noticed no two people are completely alike? We all see, experience, and understand the world in different ways.
For example, some people love spending time with friends and being the centre of attention, whereas other people are more shy and enjoy having time to themselves.
Your unique personality is shaped by your genes as well as various influences in your environment. And your personality plays an important role in how you interact with the world.
The big five
Did you know there are scientists who spend time researching personality? Their research is concerned with describing the ways people differ from each other, and understanding how these differences could be important for other parts of life such as our health and how well we do in school or at work.
There are many different perspectives on personality. A widely accepted viewpoint based on a lot of research is called the five factor model or the “big five”. According to this theory, a great deal of a person’s personality can be summarised in terms of where they sit on five dimensions, called traits:
- the introversion-extraversion trait refers to how much someone is outgoing and social (extroverted) or prefers being with smaller groups of friends or focusing on their own thoughts (introverted)
- agreeableness captures how much someone tends to be cooperative and helps others
- openness to experience refers to how much a person is creative and enjoys experiencing new things
- neuroticism describes a person’s tendency to experience negative feelings, like worrying about things that could go wrong
- conscientiousness encompasses how much a person is organised, responsible, and dedicated to things that are important to them, like schoolwork or training for a sports team.
A person can have high, low, or moderate levels of each of these traits. And understanding whether someone has higher or lower levels of the big five can tell us a lot about how we might expect them to behave in different situations.
So what shapes our personalities?
A number of factors shape our personalities, including our genes and social environment.
Our bodies are made up of many very small structures called cells. Within these cells are genes. We inherit genes from our parents, and they carry the information needed to make our bodies and personalities. So, your personality may be a bit like your parents’ personalities. For example, if you’re an outgoing sort of person who loves to meet new people, perhaps one or both of your parents are very social too.
Our personalities are influenced by the genes we get from our parents.
KieferPix/ShutterstockPersonalities are also affected by our environment, such as our experiences and our relationships with family and friends. For example, some research has shown our relationships with our parents can influence our personality. If we have loving and warm relationships, we may be more agreeable and open. But if our relationships are hurtful or stressful, this may increase our neuroticism.
Another study showed that, over time, young children who were more physically active were less introverted (less shy) and less likely to get very upset when things don’t go their way, compared to children who were less physically active. Although we don’t know why this is for sure, one possible explanation is that playing sport leads to reduced shyness because it introduces children to different people.
While we’re learning more about personality development all the time, research in this area presents quite a few challenges. Many different biological, cultural and environmental influences shape our development, and these factors can interact with each other in complex ways.
Is our personality fixed once we become adults?
Although we develop most of our personality when we are young, and people’s personalities tend to become more stable as they get older, it is possible for aspects of a person’s personality to change, even when they are fully grown.
A good example of this can be seen among people who seek treatment for conditions like anxiety or depression. People who respond well to working with a psychologist can show decreases in neuroticism, indicating they become less likely to worry a lot or feel strong negative feelings when something stressful happens.
Hello, Curious Kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to mailto:[email protected]
Tim Windsor, Professor, Director, Generations Research Initiative, College of Education, Psychology and Social Work, Flinders University and Natalie Goulter, Lecturer, College of Education, Psychology and Social Work, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: