Serotonin vs Dopamine (Know The Differences)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of the various neurotransmitters that people confuse with each other, serotonin and dopamine are the two highest on the list (with oxytocin coming third as people often attribute its effects to serotonin). But, for all they are both “happiness molecules”, serotonin and dopamine are quite different, and are even opposites in some ways:
More than just happiness
Let’s break it down:
Similarities:
- Both are neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and monoamines.
- Both impact cognition, mood, energy, behavior, memory, and learning.
- Both influence social behavior, though in different ways.
Differences (settle in; there are many):
- Chemical structure:
- Dopamine: catecholamine (derived from phenylalanine and tyrosine)
- Serotonin: indoleamine (derived from tryptophan)
- Derivatives:
- Dopamine → noradrenaline and adrenaline (stress and alertness)
- Serotonin → melatonin (sleep and circadian rhythm)
- Effects on mental state:
- Dopamine: drives action, motivation, and impulsivity.
- Serotonin: promotes calmness, behavioral inhibition, and cooperation.
- Role in memory and learning:
- Dopamine: key in attention and working memory
- Serotonin: crucial for hippocampus activation and long-term memory
Symptoms of imbalance:
- Low dopamine:
- Loss of motivation, focus, emotion, and activity
- Linked to Parkinson’s disease and ADHD
- Low serotonin:
- Sadness, irritability, poor sleep, and digestive issues
- Linked to PTSD, anxiety, and OCD
- High dopamine:
- Excessive drive, impulsivity, addictions, psychosis
- High serotonin:
- Nervousness, nausea, and in extreme cases, serotonin syndrome (which can be fatal)
Brain networks:
- Dopamine: four pathways controlling movement, attention, executive function, and hormones.
- Serotonin: widely distributed across the cortex, partially overlapping with dopamine systems.
Speed of production:
- Dopamine: can spike and deplete quickly; fatigues faster with overuse.
- Serotonin: more stable, releasing steadily over longer periods.
Illustrative examples:
- Coffee boosts dopamine but loses its effect with repeated use.
- Sunlight helps maintain serotonin levels over time.
If you remember nothing else, remember this:
- Dopamine: action, motivation, and alertness.
- Serotonin: contentment, happiness, and calmness.
For more on all of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Honey vs Maple Syrup – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing honey to maple syrup, we picked the honey.
Why?
It was very close, as both have small advantages:
• Honey has some medicinal properties (and depending on type, may contain an antihistamine)
• Maple syrup is a good source of manganese, as well as low-but-present amounts of other mineralsHowever, you wouldn’t want to eat enough maple syrup to rely on it as a source of those minerals, and honey has the lower GI (average 46 vs 54; for comparison, refined sugar is 65), which works well as a tie-breaker.
(If GI’s very important to you, though, the easy winner here would be agave syrup if we let it compete, with its GI of 15)
Read more:
• Can Honey Relieve Allergies?
• From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose C’sShare This Post
-
Stretching for 50+ – by Dr. Karl Knopf
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Knopf explores in this book the two-way relationship between aging and stretching (i.e., each can have a large impact on the other). Thinking about stretching in those terms is an important reframe for going into any stretching program. We’d say “after the age of 50”, but honestly, at any age. But this book is written with over-50s in mind, as the title goes.
There’s an extensive encyclopedic section on stretches per body part, which is exactly as you might expect from any book of this kind. There is also a flexibility self-assessment, so that progress can be measured easily, and so that the reader knows where might need more improvement.
Perhaps this book’s greatest strength is the section on specialized programs based on things ranging from working to improve symptoms of any chronic conditions you may have (or at least working around them, if outright improvement is not possible by stretching), to your recreational activities of importance to you—so, what kinds of flexibilities will be important to you, and also, what kinds of injury you are most likely to need to avoid.
Bottom line: if you’re 50 and would like to do more stretching and less aging, then this book can help with that.
Click here to check out Stretching for 50+, and extend your healthspan!
Share This Post
-
Stop Walking on Eggshells – by Randi Kreger & Paul Mason
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As you may gather from the title, the angle here is not “Borderline Personality Disorder is fine and dandy”, but nor is it something anyone chooses to have, and as such, importantly, this book’s advice is also not “and so you should immediately disown, divorce, defenestrate your partner”, either.
Rather, it has a balanced and compassionate approach that examines both the pitfalls and the possibilities, and provides the tools to make your relationship feel (and hopefully, actually be) safe for all concerned.
And yes, ending a relationship is always an option too, even if it can sometimes feel like it’s not, on account of how the relationships of people with BPD often have a lot of “near miss” situations, nearly ending but not quite, or (in the case of a partner who’s amenable to such), off-and-on relationships—either of which can make it seem like it’ll never truly be over.
First, though, the authors do look at a variety of ways of avoiding that outcome; making changes within oneself, setting boundaries and honing related skills, asserting your needs with confidence and clarity, and dealing with the lies, rumor-mongering, and accusations that often come with BPD. For that matter, the authors do also note that not all conflict is abuse (something that many forget), but on the flipside, how to tell when it actually is, too.
The style is very pop-science, light in tone albeit sometimes heavy in content.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one has BPD, or even just has a lot of the same symptoms as such, this book can be very helpful.
Click here to check out Stop Walking On Eggshells, and stop walking on eggshells!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
10 Great Exercises to Improve Your Eyesight
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If your eyesight has been declining a bit, all is not lost. Just like many other muscles in the body, the muscles of the eye—including those responsible for changing the focal length of your vision—can atrophy without exercise. So, without further ado, here are the exercises recommended:
The eyes (still) have it
- Blink for a minute: blink rapidly for 30–60 seconds to regulate blood circulation, lubricate your eyes, and prevent dryness.
- Rotate your head while staring ahead: turn your head in a circular motion while keeping your gaze straight ahead. This improves blood circulation to your eyes.
- Look to your right and left: slowly move your gaze from right to left while breathing. This one relaxes and stretches the eye muscles.
- Close your eyes and relax: close your eyes for at least 30 seconds to relax and strengthen your photoreceptor cells.
- Move your gaze in different directions: shift your gaze right-left, up-down, in circular motions, and trace a figure 8 with your eyes. This improves visual perception for both near- and far-sightedness.
- Close and open your eyes: tighten your eyes shut for 3–5 seconds, then open them. Repeat seven times to improve blood circulation and relax your eye muscles. ← 10almonds note: the duration makes this different from #4, so do try both!
- Push against your temples with your fingers: gently press your temples with your fingers for two seconds, then release. Repeat 4–5 times to improve fluid circulation in your eyes.
- Draw geometric figures with your gaze: use your eyes to trace shapes such as triangles, squares, and circles to enhance your eye coordination and muscle strength.
- Move your eyeballs up and down: close your eyes and slowly move your eyeballs up and down five times to stretch and relax the muscles ← 10almonds note: this seems to be the same as part of #5 and has a considerable overlap with #8, but we’re listing it anyway, or else everyone will wonder where #9 went!
- Strengthen near and far focusing: focus on your thumb 10 inches away for 10–15 seconds, then switch focus to an object 10–20 feet away. Repeat five times to improve focus adjustment ability.
By practicing these exercises daily, we are told that you can improve eye health and vision within a week.
For more on all these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are Brain Chips Safe?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ready For Cyborgization?
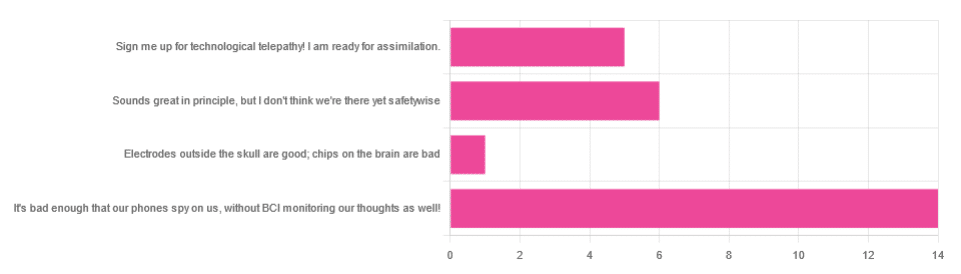
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your views on Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs), such as the Utah Array and Neuralink’s chips on/in brains that allow direct communication between brains and computers, so that (for example) a paralysed person can use a device to communicate, or manipulate a prosthetic limb or two.
We didn’t get as many votes as usual; it’s possible that yesterday’s newsletter ended up in a lot of spam filters due to repeated use of a word in “extra ______ olive oil” in its main feature!
However, of the answers we did get…
- About 54% said “It’s bad enough that our phones spy on us, without BCI monitoring our thoughts as well!”
- About 23% said “Sounds great in principle, but I don’t think we’re there yet safetywise”
- About 19% said “Sign me up for technological telepathy! I am ready for assimilation”
- One (1) person said “Electrode outside the skull are good; chips on the brain are bad”
But what does the science say?
We’re not there yet safetywise: True or False?
True, in our opinion, when it comes to the latest implants, anyway. While it’s very difficult to prove a negative (it could be that everything goes perfectly in human trials), “extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence”, and so far this seems to be lacking.
The stage before human trials is usually animal trials, starting with small creatures and working up to non-human primates if appropriate, before finally humans.
- Good news: the latest hot-topic BCI device (Neuralink) was tested on animals!
- Bad news: to say it did not go well would be an understatement
The Gruesome Story of How Neuralink’s Monkeys Actually Died
The above is a Wired article, and we tend to go for more objective sources, however we chose this one because it links to very many objective sources, including an open letter from the Physicians’ Committee for Responsible Medicine, which basically confirms everything in the Wired article. There are lots of links to primary (medical and legal) sources, too.
Electrodes outside the skull are good; chips on/in the brain are bad: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done. The Utah Array (an older BCI implant, now 20 years old, though it’s been updated many times since) has had a good safety record, after being used by a few dozen people with paralysis to control devices:
How the Utah Array is advancing BCI science
The Utah Array works on the same general principle as Neuralink, but the mechanics of its implementation are very different:
- The Utah Array involves a tiny bundle of microelectrodes (held together by a rigid structure that looks a bit like a nanoscale hairbrush) put in place by a brain surgeon, and that’s that.
- The Neuralink has a dynamic web of electrodes, implanted by a little robot that acts like a tiny sewing machine to implant many polymer threads, each containing its own a bunch of electrodes.
In theory, the latter is much more advanced. In practice, so far, the former has a much better safety record.
I am right to be a little worried about giving companies access to my brain: True or False?
True or False, depending on the nature of your concern.
For privacy: current BCI devices have quite simple switches operated consciously by the user. So while technically any such device that then runs its data through Bluetooth or WiFi could be hacked, this risk is no greater than using a wireless mouse and/or keyboard, because it has access to about the same amount of information.
For safety: yes, probably there is cause to be worried. Likely the first waves of commercial users of any given BCI device will be severely disabled people who are more likely to waive their rights in the hope of a life-changing assistance device, and likely some of those will suffer if things go wrong.
Which on the one hand, is their gamble to make. And on the other hand, makes rushing to human trials, for companies that do that, a little more predatory.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Non-Alcohol Mouthwash vs Alcohol Mouthwash – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing non-alcohol mouthwash to alcohol mouthwash, we picked the alcohol.
Why?
Note: this is a contingent choice and is applicable to most, but not all, people.
In short, there has been some concern about alcohol mouthwashes increasing cancer risk, but research has shown this is only the case if you already have an increased risk of oral cancer (for example if you smoke, and/or have had an oral cancer before).
For those for whom this is not the case (for example, if you don’t smoke, and/or have no such cancer history), then best science currently shows that alcohol mouthwash does not cause any increased risk.
What about non-alcohol mouthwashes? Well, they have a different problem; they usually use chlorine-based chemicals like chlorhexidine or cetylpyridinium chloride, which are (exactly as the label promises) exceptionally good at killing oral bacteria.
(They’d kill us too, at higher doses, hence: swill and spit)
Unfortunately, much like the rest of our body, our mouth is supposed to have bacteria there and bad things happen when it doesn’t. In the case of our oral microbiome, cleaning it with such powerful antibacterial agents can kill our “good” bacteria along with the bad, which lowers the pH of our saliva (that’s bad; it means it is more acidic), and thus indirectly erodes tooth enamel.
You can read more about the science of all of the above (with references), here:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
Summary:
For most people, alcohol mouthwashes are a good way to avoid the damage that can be done by chlorhexidine in non-alcohol mouthwashes.
Here are some examples, but there will be plenty in your local supermarket:
Non-Alcohol, by Colgate | Alcohol, by Listerine
If you have had oral cancer, or if you smoke, then you may want to seek a third alternative (and also, please, stop smoking if you can).
Or, really, most people could probably skip mouthwashes, if you’ve good oral care already by other means. See also:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
(yes, it’s the same link as before, but we’re now drawing your attention to the fact it has information about toothpastes too)
If you do want other options though, might want to check out:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← miswak sticks are especially effective
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: