Red Light, Go!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Casting Yourself In A Healthier Light
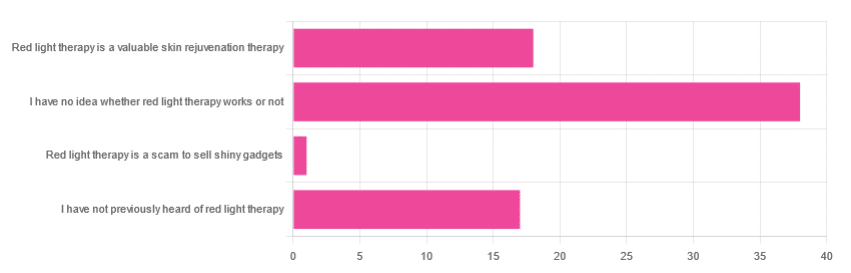
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of red light therapy (henceforth: RLT), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 51% said “I have no idea whether light therapy works or not”
- About 24% said “Red light therapy is a valuable skin rejuvenation therapy”
- About 23% said “I have not previously heard of red light therapy”
- One (1) person said: “Red light therapy is a scam to sell shiny gadgets”
A number of subscribers wrote with personal anecdotes of using red light therapy to beneficial effect, for example:
❝My husband used red light therapy after surgery on his hand. It did seem to speed healing of the incision and there is very minimal scarring. I would like to know if the red light really helped or if he was just lucky❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
And one wrote to report having observed mixed results amongst friends, per:
❝Some people it works, others I’ve seen it breaks them out❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
So, what does the science say?
RLT rejuvenates skin, insofar as it reduces wrinkles and fine lines: True or False?
True! This one’s pretty clear-cut, so we’ll just give one example study of many, which found:
❝The treated subjects experienced significantly improved skin complexion and skin feeling, profilometrically assessed skin roughness, and ultrasonographically measured collagen density.
The blinded clinical evaluation of photographs confirmed significant improvement in the intervention groups compared with the control❞
~ Dr. Alexander Wunsch & Dr. Karsten Matuschka
RLT helps speed up healing of wounds: True or False?
True! There is less science for this than the above claim, but the studies that have been done are quite compelling, for example this NASA technology study found that…
❝LED produced improvement of greater than 40% in musculoskeletal training injuries in Navy SEAL team members, and decreased wound healing time in crew members aboard a U.S. Naval submarine.❞
Read more: Effect of NASA light-emitting diode irradiation on wound healing
RLT’s benefits are only skin-deep: True or False?
False, probably, but we’d love to see more science for this, to be sure.
However, it does look like wavelengths in the near-infrared spectrum reduce the abnormal tau protein and neurofibrillary tangles associated with Alzheimer’s disease, resulting in increased blood flow to the brain, and a decrease in neuroinflammation:
Therapeutic Potential of Photobiomodulation In Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Would you like to try RLT for yourself?
There are some contraindications, for example:
- if you have photosensitivity (for obvious reasons)
- if you have Lupus (mostly because of the above)
- if you have hyperthyroidism (because if you use RLT to your neck as well as face, it may help stimulate thyroid function, which in your case is not what you want)
As ever, please check with your own doctor if you’re not completely sure; we can’t cover all bases here, and cannot speak for your individual circumstances.
For most people though, it’s very safe, and if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product on Amazon, and by all means do read reviews and shop around for the ideal device for you
Take care! 😎
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pumpkin Protein Crackers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ten of these (give or take what size you make them) will give you the 20g protein that most people’s body’s can use at a time. Five of these plus some of one of the dips we list at the bottom will also do it:
You will need
- 1 cup chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- 2 tbsp pumpkin seeds
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tsp baking powder
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 350℉ / 180℃.
2) Combine the dry ingredients in a mixing bowl, and mix thoroughly.
3) Add the oil, and mix thoroughly.
4) Add water, 1 tbsp at a time, mixing thoroughly until the mixture comes together and you have a dough ball. You’ll probably need 3–4 tbsp in total, but do add them one at a time.
5) Roll out the dough as thinly and evenly as you can between two sheets of baking paper. Remove the top layer of the paper, and slice the dough into squares or triangles. You could use a cookie-cutter to make other shapes if you like, but then you’ll need to repeat the rolling to use up the offcuts. So we recommend squares or triangles at least for your first go.
6) Bake them in the oven for 12–15 minutes or until golden and crispy. Enjoy immediately or keep in an airtight container.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some things to go with what we have going on today:
- Muhammara ← this is a very nutritionally-dense dip (not to mention tasty; seriously, check out these flavors)
- Hero Homemade Hummus ← a classic
- Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese ← also a very respectable option
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Reading At Night: Good Or Bad For Sleep? And Other Questions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would be interested in your views about “reading yourself to sleep”. I find that current affairs magazines and even modern novels do exactly the opposite. But Dickens – ones like David Copperfield and Great Expectations – I find wonderfully effective. It’s like entering a parallel universe where none of your own concerns matter. Any thoughts on the science that may explain this?!❞
Anecdotally: this writer is (like most writers) a prolific reader, and finds reading some fiction last thing at night is a good way to create a buffer between the affairs of the day and the dreams of night—but I could never fall asleep that way, unless I were truly sleep-deprived. The only danger is if I “one more chapter” my way deep into the night! For what it’s worth, bedtime reading for me means a Kindle self-backlit with low, soft lighting.
Scientifically: this hasn’t been a hugely researched area, but there are studies to work from. But there are two questions at hand (at least) here:
- one is about reading, and
- the other is about reading from electronic devices with or without blue light filters.
Here’s a study that didn’t ask the medium of the book, and concluded that reading a book in bed before going to sleep improved sleep quality, compared to not reading a book in bed:
Here’s a study that concluded that reading on an iPad (with no blue light filter) that found no difference in any metrics except EEG (so, there was no difference on time spent in different sleep states or sleep onset latency), but advised against it anyway because of the EEG readings (which showed slow wave activity being delayed by approximately 30 minutes, which is consistent with melatonin production mechanics):
Here’s another study that didn’t take EEG readings, and/but otherwise confirmed no differences being found:
We’re aware this goes against general “sleep hygiene” advice in two different ways:
- General advice is to avoid electronic devices before bedtime
- General advice is to not do activities besides sleep (and sex) in bed
…but, we’re committed to reporting the science as we find it!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Healing Trauma – by Dr. Peter Levine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Levine’s better-selling book about trauma, Waking The Tiger, laid the foundations for this one, but the reason we’re skipping straight into Healing Trauma, is that while the former book is more about the ideas that led him to what he currently believes is the best approach to healing trauma, this book is the one that explains how to actually do it.
The core thesis is that trauma is a natural, transient response, and is not inherently pathological, but that it can become so if not allowed to do its thing.
This book outlines exercises, trademarked as “somatic experiencing”, which allow the body to go through the physiological processes it needs to, to facilitate healing. If you buy the physical book, there is also an audio CD, which this reviewer has not listened to and cannot comment on, but the exercises are clearly described in the book in any case.
The physical aspects of the exercises are similar to the principles of progressive relaxation, while the mental aspects of the exercises are about re-experiencing trauma in a safer fashion, in small doses.
Any kind of dealing with trauma is not going to be comfortable, so this book is not an enjoyable read.
As for how useful the exercises are, your mileage may vary. Like many books about trauma, the expectation is that once upon a time you were in a situation that was unsafe, and now you are safe. If that describes your trauma, you will get the most out of this. However, if your trauma is unrelated to your personal safety, or if it is about your personal safety but the threat still remains extant, then a lot of this may not help and may even make things worse.
In terms of discussing sexual trauma specifically, it was probably not a good choice to favorably quote Woody Allen, and little things like that may be quite jarring for a lot of readers.
Bottom line: if your trauma is PTSD of the kind “you faced an existential threat and now it is gone”, then chances are that this book can help you a lot. If your trauma is different, then your mileage may vary widely on this one.
Click here to check out Healing Trauma, if it seems right for you!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Codependent No More – by Melody Beattie
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a book review, not a book summary, but first let’s quickly cover a common misconception, because the word “codependent” gets misused a lot in popular parlance:
- What codependence isn’t: “we depend on each other and must do everything together”
- What codependence is:“person 1 has a dependency on a substance (or perhaps a behavior, such as gambling); person 2 is trying to look after person 1, and so has developed a secondary relationship with the substance/behavior. Person 2 is now said to be codependent, because it becomes all-consuming for them too, even if they’re not using the substance/behavior directly”
Funny how often it happens that the reality is more complex than the perception, isn’t it?
Melody Beattie unravels all this for us. We get a compassionate and insightful look at how we can look after ourselves, while looking after another. Perhaps most importantly: how and where to draw a line of what we can and cannot do/change for them.
Because when we love someone, of course we want to fight their battles with them, if not for them. But if we want to be their rock of strength, we can’t get lost in it too, and of course that hurts.
Beatty takes us through these ideas and more, for example:
- How to examine our own feelings even when it’s scary
- How to practice self-love and regain self-worth, while still caring for them
- How to stop being reactionary, step back, and act with purpose
If the book has any weak point, it’s that it repeatedly recommends 12-step programs, when in reality that’s just one option. But for those who wish to take another approach, this book does not require involvement in a 12-step program, so it’s not a barrier to usefulness.
Click here to check out Codependent No More and take care of yourself, too
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Best Workouts for Women Over 40 To Give Your Metabolism A Makeover
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
After 40, the usual course of events goes: your lean muscle mass decreases, which slows your metabolism and makes it easier to gain fat. At the same time, bone density decreases, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and frailty. This leads to lower mobility, flexibility, and overall frustration.
But it doesn’t have to be that way! Fitness coach Jessica Cooke explains how:
It all depends on this
Strength training helps counteract these effects by increasing lean muscle mass, which boosts metabolism and fat burning. It also improves bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Plus, it builds strength, fitness, and a toned physique.
The best part? It doesn’t require long workouts—short, effective sessions work best.
While walking is very beneficial for general health, it doesn’t provide the resistance needed to build muscle. Without resistance, your body composition won’t change, and so your metabolism will remain the same. Strength training is essential for burning fat at rest and improving overall fitness.
You don’t have to do high-impact exercises or jumping to see results. Low-impact strength training is effective and gentle on the joints. Lifting weights or using your body weight in a controlled manner will help build muscle and improve strength.
Many women only do cardio and neglect strength training, leading to minimal progress. Another common mistake is overcomplicating workouts—simple, consistent strength training is all you need.
Aim to strength train three times per week for 20 minutes. Focus on compound movements that work multiple muscle groups, such as:
- squats
- lunges
- deadlifts
- press-ups
- shoulder presses
- upright rows
- planks
- glute bridges
- sit-ups
- Russian twists
Start with light (e.g. 2-3 kg) weights and maintain proper form.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Don’t Let Menopause Run You Down: 4 Critical Things Female Runners Should Know
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
When Your Brain’s “Get-Up-And-Go” Has Got Up And Gone…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes, there are days when the body feels heavy, the brain feels sluggish, and even the smallest tasks feel Herculean.
When these days stack up, this is usually a sign of depression, and needs attention. Unfortunately, when one is in such a state, taking action about it is almost impossible.
Almost, but not quite, as we wrote about previously:
The Mental Health First-Aid You’ll Hopefully Never Need ← this is about as close to true mental health bootstrapping as actually works
Today though, we’re going to assume it’s just an off-day or such. So, what to do about it?
Try turning it off and on again
Sometimes, a reboot is all that’s needed, and if napping is an option, it’s worth considering. However, if you don’t do it right, you can end up groggy and worse off than before, so do check out:
How To Be An Expert Nap-Artist (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
If your exhaustion is nevertheless accompanied by stresses that are keeping you from resting, then there’s another “turn it off and on again” process for that:
Fuel in the tank
Our brain is an energy-intensive organ, and cannot run on empty for long. Thus, lacking energy can sometimes simply be a matter of needing to supply some energy. Simple, no? Except, a lot of energy-giving foods can cause a paradoxical slump in energy, so here’s how to avoid that:
Eating For Energy (In Ways That Actually Work)
There are occasions when exhausted, when preparing food seems like too much work. If you’re not in a position to have someone else do it for you, how can you get “most for least” in terms of nutrition for effort?
Many of the above-linked items can help (a bowl of nuts and/or dried fruit is probably not going to break the energy-bank, for instance), but beyond that, there are other considerations too:
How To Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue (While Chronically Fatigued) ← as the title tells, this is about chronic fatigue, but the advice therein definitely goes for acute fatigue also.
The lights aren’t on
Sometimes it may be that your body is actually fine, but your brain is working in a clunky fashion at best. Assuming there is no more drastic underlying cause for this, a lack of motivation is often as simple as a lack of appropriate dopamine response. When that’s the case…
Lacking Motivation? Science Has The Answer
If, instead, the issue is more serotonin-based than dopamine based, then green places with blue skies are ideal. Depending on geography and season, those things may be in short supply, but the brain is easily tricked with artificial plants and artificial sunlight. Is it as good as a walk in the park on a pleasant summer morning? Probably not, but it’s many times better than nothing, so get those juices flowing:
Neurotransmitter Cheatsheet ← four for the price of one, here!
Schedule time for rest, or your body/brain will schedule it for you
There’s a saying in the field of engineering that “if you don’t schedule time for maintenance, your equipment will schedule it for you”, and the same is true of our body/brain. If you’re struggling to get good quantity, here’s how to at least get good quality:
How To Rest More Efficiently (Yes, Really)
And, importantly,
7 Kinds Of Rest When Sleep Is Not Enough
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: