Radishes vs Carrots – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing radishes to carrots, we picked the carrots.
Why?
In terms of macros, carrots have more fiber and carbs; the two root vegetables both have comparable (low) glycemic indices, so we’re saying that the one with more fiber wins, and that’s carrots.
In the category of vitamins, radishes have more of vitamins B9 and C, while carrots have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, E, K, and choline. An easy win for carrots.
When it comes to minerals, radishes have more selenium, while carrots have more calcium, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. Another clear win for carrots.
In terms of polyphenols, radishes do have some, but carrots have more, and thus win this category too.
All in all, enjoy either or both, but carrots deliver the most nutrients by far!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Women and Minorities Bear the Brunt of Medical Misdiagnosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Charity Watkins sensed something was deeply wrong when she experienced exhaustion after her daughter was born.
At times, Watkins, then 30, had to stop on the stairway to catch her breath. Her obstetrician said postpartum depression likely caused the weakness and fatigue. When Watkins, who is Black, complained of a cough, her doctor blamed the flu.
About eight weeks after delivery, Watkins thought she was having a heart attack, and her husband took her to the emergency room. After a 5½-hour wait in a North Carolina hospital, she returned home to nurse her baby without seeing a doctor.
When a physician finally examined Watkins three days later, he immediately noticed her legs and stomach were swollen, a sign that her body was retaining fluid. After a chest X-ray, the doctor diagnosed her with heart failure, a serious condition in which the heart becomes too weak to adequately pump oxygen-rich blood to organs throughout the body. Watkins spent two weeks in intensive care.
She said a cardiologist later told her, “We almost lost you.”
Watkins is among 12 million adults misdiagnosed every year in the U.S.
In a study published Jan. 8 in JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers found that nearly 1 in 4 hospital patients who died or were transferred to intensive care had experienced a diagnostic error. Nearly 18% of misdiagnosed patients were harmed or died.
In all, an estimated 795,000 patients a year die or are permanently disabled because of misdiagnosis, according to a study published in July in the BMJ Quality & Safety periodical.
Some patients are at higher risk than others.
Women and racial and ethnic minorities are 20% to 30% more likely than white men to experience a misdiagnosis, said David Newman-Toker, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and the lead author of the BMJ study. “That’s significant and inexcusable,” he said.
Researchers call misdiagnosis an urgent public health problem. The study found that rates of misdiagnosis range from 1.5% of heart attacks to 17.5% of strokes and 22.5% of lung cancers.
Weakening of the heart muscle — which led to Watkins’ heart failure — is the most common cause of maternal death one week to one year after delivery, and is more common among Black women.
Heart failure “should have been No. 1 on the list of possible causes” for Watkins’ symptoms, said Ronald Wyatt, chief science and chief medical officer at the Society to Improve Diagnosis in Medicine, a nonprofit research and advocacy group.
Maternal mortality for Black mothers has increased dramatically in recent years. The United States has the highest maternal mortality rate among developed countries. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, non-Hispanic Black mothers are 2.6 times as likely to die as non-Hispanic white moms. More than half of these deaths take place within a year after delivery.
Research shows that Black women with childbirth-related heart failure are typically diagnosed later than white women, said Jennifer Lewey, co-director of the pregnancy and heart disease program at Penn Medicine. That can allow patients to further deteriorate, making Black women less likely to fully recover and more likely to suffer from weakened hearts for the rest of their lives.
Watkins said the diagnosis changed her life. Doctors advised her “not to have another baby, or I might need a heart transplant,” she said. Being deprived of the chance to have another child, she said, “was devastating.”
Racial and gender disparities are widespread.
Women and minority patients suffering from heart attacks are more likely than others to be discharged without diagnosis or treatment.
Black people with depression are more likely than others to be misdiagnosed with schizophrenia.
Minorities are less likely than whites to be diagnosed early with dementia, depriving them of the opportunities to receive treatments that work best in the early stages of the disease.
Misdiagnosis isn’t new. Doctors have used autopsy studies to estimate the percentage of patients who died with undiagnosed diseases for more than a century. Although those studies show some improvement over time, life-threatening mistakes remain all too common, despite an array of sophisticated diagnostic tools, said Hardeep Singh, a professor at Baylor College of Medicine who studies ways to improve diagnosis.
“The vast majority of diagnoses can be made by getting to know the patient’s story really well, asking follow-up questions, examining the patient, and ordering basic tests,” said Singh, who is also a researcher at Houston’s Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center. When talking to people who’ve been misdiagnosed, “one of the things we hear over and over is, ‘The doctor didn’t listen to me.’”
Racial disparities in misdiagnosis are sometimes explained by noting that minority patients are less likely to be insured than white patients and often lack access to high-quality hospitals. But the picture is more complicated, said Monika Goyal, an emergency physician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington, D.C., who has documented racial bias in children’s health care.
In a 2020 study, Goyal and her colleagues found that Black kids with appendicitis were less likely than their white peers to be correctly diagnosed, even when both groups of patients visited the same hospital.
Although few doctors deliberately discriminate against women or minorities, Goyal said, many are biased without realizing it.
“Racial bias is baked into our culture,” Goyal said. “It’s important for all of us to start recognizing that.”
Demanding schedules, which prevent doctors from spending as much time with patients as they’d like, can contribute to diagnostic errors, said Karen Lutfey Spencer, a professor of health and behavioral sciences at the University of Colorado-Denver. “Doctors are more likely to make biased decisions when they are busy and overworked,” Spencer said. “There are some really smart, well-intentioned providers who are getting chewed up in a system that’s very unforgiving.”
Doctors make better treatment decisions when they’re more confident of a diagnosis, Spencer said.
In an experiment, researchers asked doctors to view videos of actors pretending to be patients with heart disease or depression, make a diagnosis, and recommend follow-up actions. Doctors felt far more certain diagnosing white men than Black patients or younger women.
“If they were less certain, they were less likely to take action, such as ordering tests,” Spencer said. “If they were less certain, they might just wait to prescribe treatment.”
It’s easy to see why doctors are more confident when diagnosing white men, Spencer said. For more than a century, medical textbooks have illustrated diseases with stereotypical images of white men. Only 4.5% of images in general medical textbooks feature patients with dark skin.
That may help explain why patients with darker complexions are less likely to receive a timely diagnosis with conditions that affect the skin, from cancer to Lyme disease, which causes a red or pink rash in the earliest stage of infection. Black patients with Lyme disease are more likely to be diagnosed with more advanced disease, which can cause arthritis and damage the heart. Black people with melanoma are about three times as likely as whites to die within five years.
The covid-19 pandemic helped raise awareness that pulse oximeters — the fingertip devices used to measure a patient’s pulse and oxygen levels — are less accurate for people with dark skin. The devices work by shining light through the skin; their failures have delayed critical care for many Black patients.
Seven years after her misdiagnosis, Watkins is an assistant professor of social work at North Carolina Central University in Durham, where she studies the psychosocial effects experienced by Black mothers who survive severe childbirth complications.
“Sharing my story is part of my healing,” said Watkins, who speaks to medical groups to help doctors improve their care. “It has helped me reclaim power in my life, just to be able to help others.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
What Happens Every Day When You Quit Sugar For 30 Days
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that sugar isn’t exactly a health food, but it can be hard to quit. How long can cravings be expected to last, and when can we expect to see benefits? Today’s video covers the timeline in a realistic yet inspiring fashion:
What to expect on…
Day 1: expect cravings and withdrawal symptoms including headaches, fatigue, mood swings, and irritability—as well as tiredness, without the crutch of sugar.
Days 2 & 3: more of the same, plus likely objections from the gut, since your Candida albicans content will not be enjoying being starved of its main food source.
Days 4–7: reduction of the above symptoms, better energy levels, improved sleep, and likely the gut will be adapting or have adapted.
Days 8–14: beginning of weight loss, clearer skin, improved complexion; taste buds adapt too, making foods taste sweeter. Continued improvement in energy and focus, as well.
Days 15–21: more of the same improvements, plus the immune system will start getting stronger around now. But watch out, because there may still be some cravings from time to time.
Days 22–30: all of the above positive things, few or no cravings now, and enhanced metabolic health as a whole.
For more specificity on each of these stages, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Chaga Mushrooms’ Immune & Anticancer Potential
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Do Chaga Mushrooms Do?
Chaga mushrooms, which also go by other delightful names including “sterile conk trunk rot” and “black mass”, are a type of fungus that grow on birch trees in cold climates such as Alaska, Northern Canada, Northern Europe, and Siberia.
They’ve enjoyed a long use as a folk remedy in Northern Europe and Siberia, mostly to boost immunity, mostly in the form of a herbal tea.
Let’s see what the science says…
Does it boost the immune system?
It definitely does if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any studies on humans yet. But for example:
- Immunomodulatory Activity of the Water Extract from Medicinal Mushroom Inonotus obliquus
- Inonotus obliquus extracts suppress antigen-specific IgE production through the modulation of Th1/Th2 cytokines in ovalbumin-sensitized mice
(cytokines are special proteins that regulate the immune system, and Chaga tells them to tell the body to produce more white blood cells)
Wait, does that mean it increases inflammation?
Definitely not if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any studies on humans yet. But for example:
- Anti-inflammatory effects of orally administered Inonotus obliquus in ulcerative colitis
- Orally administered aqueous extract of Inonotus obliquus ameliorates acute inflammation
Anti-inflammatory things often fight cancer. Does chaga?
Definitely if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any studies in human cancer patients yet. But for example:
While in vivo human studies are conspicuous by their absence, there have been in vitro human studies, i.e., studies performed on cancerous human cell samples in petri dishes. They are promising:
- Anticancer activities of extracts and compounds from the mushroom Inonotus obliquus
- Extract of Innotus obliquus induces G1 cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer cells
- Anticancer activity of Inonotus obliquus extract in human cancer cells
I heard it fights diabetes; does it?
You’ll never see this coming, but: definitely if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any human studies yet. But for example:
- Anti-diabetic effects of Inonotus obliquus in type 2 diabetic mice
- Anti-diabetic effects of Inonotus obliquus in type 2 diabetic mice and potential mechanism
Is it safe?
Honestly, there simply have been no human safety studies to know for sure, or even to establish an appropriate dosage.
Its only-partly-understood effects on blood sugar levels and the immune system may make it more complicated for people with diabetes and/or autoimmune disorders, and such people should definitely seek medical advice before taking chaga.
Additionally, chaga contains a protein that can prevent blood clotting. That might be great by default if you are at risk of blood clots, but not so great if you are already on blood-thinning medication, or otherwise have a bleeding disorder, or are going to have surgery soon.
As with anything, we’re not doctors, let alone your doctors, so please consult yours before trying chaga.
Where can we get it?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here’s an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
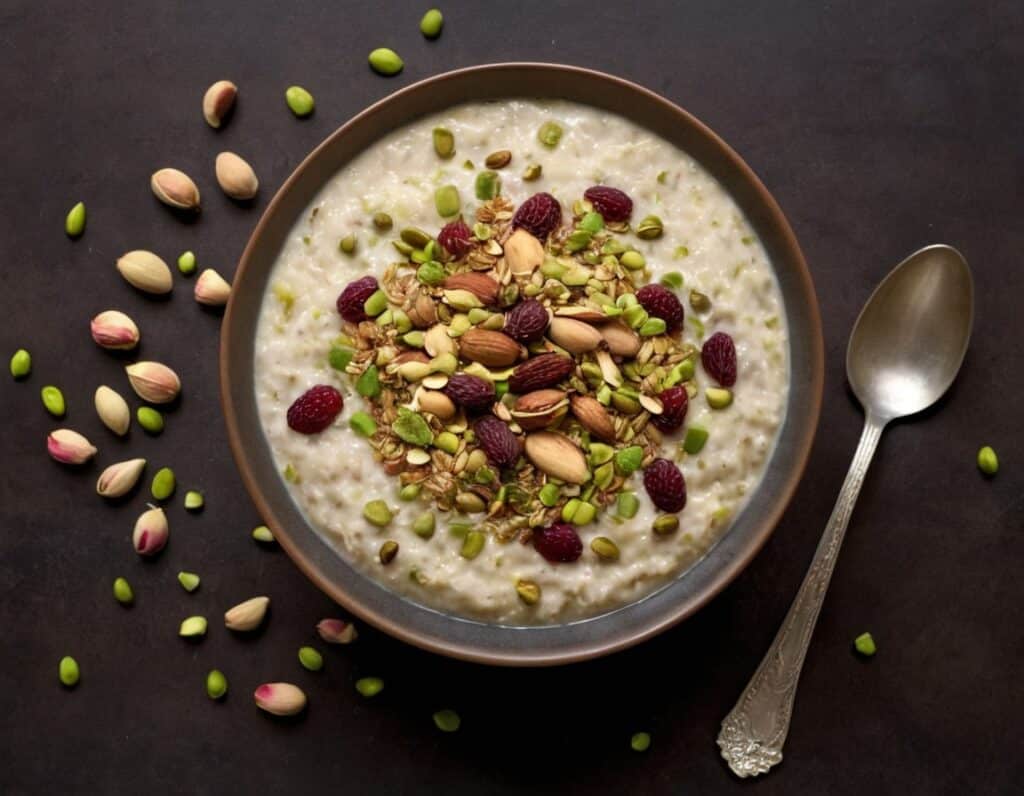
Anti-Cholesterol Cardamom & Pistachio Porridge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This tasty breakfast’s beta-glucan content binds to cholesterol and carries it out of the body; there are lots of other nutritional benefits too!
You will need
- 1 cup coconut milk
- ⅓ cup oats
- 4 tbsp crushed pistachios
- 6 cardamom pods, crushed
- 1 tsp rose water or 4 drops edible rose essential oil
- Optional sweetener: drizzle of honey or maple syrup
- Optional garnishes: rose petals, chopped nuts, dried fruit
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat the coconut milk, adding the oats and crushed cardamom pods. Simmer for 5–10 minutes depending on how cooked you want the oats to be.
2) Stir in the crushed pistachio nuts, as well as the rose water.
3) Serve in a bowl, adding any optional toppings:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s beta-glucan, which is fund abundantly in oats
- Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← coconut can!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Using the”Task Zero” approach
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Jonathan Frakes Asks You Things” Voice:
- Do you ever find yourself in a room and wonder what you’re doing there?
- Or set about a to-do list, but get quickly distracted by side-quests?
- Finally get through to a person in a call center, they ask how they can help, and your mind goes blank?
- Go to the supermarket and come out with six things, none of which were the one you came for?
This is a “working memory” thing and you’re not alone. There’s a trick that can help keep you on track more often than not:
Don’t try to overburden your working memory. It is very limited (this goes for everyone to a greater or lesser degree). Instead, hold only two tasks at once:
- Task zero (what you are doing right now)
- Task one (your next task)
When you’ve completed task zero, task one becomes the new task zero, and you can populate a new task one from your to-do list.
This way, you will always know what you’re doing right now, and what you’re doing next, and your focus will be so intent on task zero, that you will not get sidetracked by task seventeen!
Happy focusing
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Signs Of Low Estrogen In Women: What Your Skin, Hair, & Nails Are Trying To Tell You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Skin, hair, and nails are often thought of purely as a beauty thing, but in fact they can be indicative of a lot of other aspects of health. Dr. Andrea Suarez takes us through some of them in this video about the systemic (i.e., whole-body, not just related to sex things) effects of estrogen, and/or a deficiency thereof.
Beyond the cosmetic
Low estrogen levels are usual in women during and after untreated menopause, resulting in various changes in the skin, hair, and nails, that reflect deeper issues, down to bone health, heart health, brain health, and more. Since we can’t see our bones or hearts or brains without scans (or a serious accident/incident), we’re going to focus on the outward signs of estrogen deficiency.
Estrogen helps maintain healthy collagen production, skin elasticity, wound healing, and moisture retention, making it essential for youthful and resilient skin. Declining estrogen levels with menopause lead to a thinner epidermis, decreased collagen production, and more pronounced wrinkles. Skin elasticity also diminishes, which slows the skin’s ability to recover from stretching or deformation. Wound healing also becomes slower, increasing the risk of infections and extended recovery periods after injuries or surgeries—bearing in mind that collagen is needed in everything from our skin to our internal connective tissue (fascia) and joints and bones. So all those things are going to struggle to recover from injury (and surgery is also an injury) without it.
Other visible changes associated with declining estrogen include significant dryness as a result of reduced hyaluronic acid and glycosaminoglycan production, which are essential for moisture retention. The skin becomes more prone to irritation and increased water loss. Additionally, estrogen deficiency results in less resistance to oxidative stress, making the skin more susceptible to damage from environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollution, as well as any from-the-inside pollution that some may have depending on diet and lifestyle.
Acne and enlarged pores are associated with increased testosterone, but testosterone and estrogen are antagonistic in most ways, and in this case a decrease in estrogen will do the same, due increased unopposed androgen signaling affecting the oil glands. The loss of supportive collagen also causes the skin around pores to lose structure, making them appear larger. The reduction in skin hydration further exacerbates the visibility of pores and can contribute to the development of blackheads due to abnormal cell turnover.
Blood vessel issues tend to arise as estrogen levels drop, leading to a reduction in angiogenesis, i.e. the formation and integrity of blood vessels. This results in more fragile and leaky blood vessels, making the skin more prone to bruising, especially on areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the backs of the hands. This weakened vasculature also further contributes to the slower wound healing that we talked about, due to less efficient delivery of growth factors.
Hair and nail changes often accompany estrogen deficiency. Women may notice hair thinning, increased breakage, and a greater likelihood of androgenic alopecia. The texture of the hair can change, becoming more brittle. Similarly, nails can develop ridges, split more easily, and become more fragile due to reduced collagen and keratin production, which also affects the skin around the nails.
As for what to do about it? Management options for estrogen-deficient skin include:
- Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which can improve skin elasticity, boost collagen production, and reduce dryness and fragility, as well as addressing the many more serious internal things that are caused by the same deficiency as these outward signs.
- Low-dose topical estrogen cream, which can help alleviate skin dryness and increase skin strength, won’t give the systemic benefits (incl. to bones, heart, brain, etc) that only systemic HRT can yield.
- Plant-based phytoestrogens, which are not well-evidenced, but may be better than nothing if nothing is your only other option. However, if you are taking anything other form of estrogen, don’t use phytoestrogens as well, or they will compete for estrogen receptors, and do the job not nearly so well while impeding the bioidentical estrogen from doing its much better job.
And for all at any age, sunscreen continues to be one of the best things to put on one’s skin for general skin health, and this is even more true if running low on estrogen.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
These Signs Often Mean These Nutrient Deficiencies (Do You Have Any?)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: