The Path to a Better Tuberculosis Vaccine Runs Through Montana
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A team of Montana researchers is playing a key role in the development of a more effective vaccine against tuberculosis, an infectious disease that has killed more people than any other.
The BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guérin) vaccine, created in 1921, remains the sole TB vaccine. While it is 40% to 80% effective in young children, its efficacy is very low in adolescents and adults, leading to a worldwide push to create a more powerful vaccine.
One effort is underway at the University of Montana Center for Translational Medicine. The center specializes in improving and creating vaccines by adding what are called novel adjuvants. An adjuvant is a substance included in the vaccine, such as fat molecules or aluminum salts, that enhances the immune response, and novel adjuvants are those that have not yet been used in humans. Scientists are finding that adjuvants make for stronger, more precise, and more durable immunity than antigens, which create antibodies, would alone.
Eliciting specific responses from the immune system and deepening and broadening the response with adjuvants is known as precision vaccination. “It’s not one-size-fits-all,” said Ofer Levy, a professor of pediatrics at Harvard University and the head of the Precision Vaccines Program at Boston Children’s Hospital. “A vaccine might work differently in a newborn versus an older adult and a middle-aged person.”
The ultimate precision vaccine, said Levy, would be lifelong protection from a disease with one jab. “A single-shot protection against influenza or a single-shot protection against covid, that would be the holy grail,” Levy said.
Jay Evans, the director of the University of Montana center and the chief scientific and strategy officer and a co-founder of Inimmune, a privately held biotechnology company in Missoula, said his team has been working on a TB vaccine for 15 years. The private-public partnership is developing vaccines and trying to improve existing vaccines, and he said it’s still five years off before the TB vaccine might be distributed widely.
It has not gone unnoticed at the center that this state-of-the-art vaccine research and production is located in a state that passed one of the nation’s most extreme anti-vaccination laws during the pandemic in 2021. The law prohibits businesses and governments from discriminating against people who aren’t vaccinated against covid-19 or other diseases, effectively banning both public and private employers from requiring workers to get vaccinated against covid or any other disease. A federal judge later ruled that the law cannot be enforced in health care settings, such as hospitals and doctors’ offices.
In mid-March, the Bill & Melinda Gates Medical Research Institute announced it had begun the third and final phase of clinical trials for the new vaccine in seven countries. The trials should take about five years to complete. Research and production are being done in several places, including at a manufacturing facility in Hamilton owned by GSK, a giant pharmaceutical company.
Known as the forgotten pandemic, TB kills up to 1.6 million people a year, mostly in impoverished areas in Asia and Africa, despite its being both preventable and treatable. The U.S. has seen an increase in tuberculosis over the past decade, especially with the influx of migrants, and the number of cases rose by 16% from 2022 to 2023. Tuberculosis is the leading cause of death among people living with HIV, whose risk of contracting a TB infection is 20 times as great as people without HIV.
“TB is a complex pathogen that has been with human beings for ages,” said Alemnew Dagnew, who heads the program for the new vaccine for the Gates Medical Research Institute. “Because it has been with human beings for many years, it has evolved and has a mechanism to escape the immune system. And the immunology of TB is not fully understood.”
The University of Montana Center for Translational Medicine and Inimmune together have 80 employees who specialize in researching a range of adjuvants to understand the specifics of immune responses to different substances. “You have to tailor it like tools in a toolbox towards the pathogen you are vaccinating against,” Evans said. “We have a whole library of adjuvant molecules and formulations.”
Vaccines are made more precise largely by using adjuvants. There are three basic types of natural adjuvants: aluminum salts; squalene, which is made from shark liver; and some kinds of saponins, which are fat molecules. It’s not fully understood how they stimulate the immune system. The center in Missoula has also created and patented a synthetic adjuvant, UM-1098, that drives a specific type of immune response and will be added to new vaccines.
One of the most promising molecules being used to juice up the immune system response to vaccines is a saponin molecule from the bark of the quillay tree, gathered in Chile from trees at least 10 years old. Such molecules were used by Novavax in its covid vaccine and by GSK in its widely used shingles vaccine, Shingrix. These molecules are also a key component in the new tuberculosis vaccine, known as the M72 vaccine.
But there is room for improvement.
“The vaccine shows 50% efficacy, which doesn’t sound like much, but basically there is no effective vaccine currently, so 50% is better than what’s out there,” Evans said. “We’re looking to take what we learned from that vaccine development with additional adjuvants to try and make it even better and move 50% to 80% or more.”
By contrast, measles vaccines are 95% effective.
According to Medscape, around 15 vaccine candidates are being developed to replace the BCG vaccine, and three of them are in phase 3 clinical trials.
One approach Evans’ center is researching to improve the new vaccine’s efficacy is taking a piece of the bacterium that causes TB, synthesizing it, and combining it with the adjuvant QS-21, made from the quillay tree. “It stimulates the immune system in a way that is specific to TB and it drives an immune response that is even closer to what we get from natural infections,” Evans said.
The University of Montana center is researching the treatment of several problems not commonly thought of as treatable with vaccines. They are entering the first phase of clinical trials for a vaccine for allergies, for instance, and first-phase trials for a cancer vaccine. And later this year, clinical trials will begin for vaccines to block the effects of opioids like heroin and fentanyl. The University of Montana received the largest grant in its history, $33 million, for anti-opioid vaccine research. It works by creating an antibody that binds with the drug in the bloodstream, which keeps it from entering the brain and creating the high.
For now, though, the eyes of health care experts around the world are on the trials for the new TB vaccines, which, if they are successful, could help save countless lives in the world’s poorest places.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Insider’s Guide To Making Hospital As Comfortable As Possible
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Nobody Likes Surgery, But Here’s How To Make It Much Less Bad
This is Dr. Chris Bonney. He’s an anesthesiologist. If you have a surgery, he wants you to go in feeling calm, and make a quick recovery afterwards, with minimal suffering in between.
Being a patient in a hospital is a bit like being a passenger in an airplane:
- Almost nobody enjoys the thing itself, but we very much want to get to the other side of the experience.
- We have limited freedoms and comforts, and small things can make a big difference between misery and tolerability.
- There are professionals present to look after us, but they are busy and have a lot of other people to tend to too.
So why is it that there are so many resources available full of “tips for travelers” and so few “tips for hospital patients”?
Especially given the relative risks of each, and likelihood, or even near-certainty of coming to at least some harm… One would think “tips for patients” would be more in demand!
Tips for surgery patients, from an insider expert
First, he advises us: empower yourself.
Empowering yourself in this context means:
- Relax—doctors really want you to feel better, quickly. They’re on your side.
- Research—knowledge is power, so research the procedure (and its risks!). Dr. Bonney, himself an anesthesiologist, particularly recommends you learn what specific anesthetic will be used (there are many, and they’re all a bit different!), and what effects (and/or after-effects) that may have.
- Reframe—you’re not just a patient; you’re a customer/client. Many people suffer from MDeity syndrome, and view doctors as authority figures, rather than what they are: service providers.
- Request—if something would make you feel better, ask for it. If it’s information, they will be not only obliged, but also enthusiastic, to give it. If it’s something else, they’ll oblige if they can, and the worst case scenario is something won’t be possible, but you won’t know if you don’t ask.
Next up, help them to help you
There are various ways you can be a useful member of your own care team:
- Go into surgery as healthy as you can. If there’s ever a time to get a little fitter, eat a little healthier, prioritize good quality sleep more, the time approaching your surgery is the time to do this.
- This will help to minimize complications and maximize recovery.
- Take with you any meds you’re taking, or at least have an up-to-date list of what you’re taking. Dr. Bonney has very many times had patients tell him such things as “Well, let me see. I have two little pink ones and a little white one…” and when asked what they’re for they tell him “I have no idea, you’d need to ask my doctor”.
- Help them to help you; have your meds with you, or at least a comprehensive list (including: medication name, dosage, frequency, any special instructions)
- Don’t stop taking your meds unless told to do so. Many people have heard that one should stop taking meds before a surgery, and sometimes that’s true, but often it isn’t. Keep taking them, unless told otherwise.
- If unsure, ask your surgical team in advance (not your own doctor, who will not be as familiar with what will or won’t interfere with a surgery).
Do any preparatory organization well in advance
Consider the following:
- What do you need to take with you? Medications, clothes, toiletries, phone charger, entertainment, headphones, paperwork, cash for the vending machine?
- Will the surgeons need to shave anywhere, and if so, might you prefer doing some other form of depilation (e.g. waxing etc) yourself in advance?
- Is your list of medications ready?
- Who will take you to the hospital and who will bring you back?
- Who will stay with you for the first 24 hours after you’re sent home?
- Is someone available to look after your kids/pets/plants etc?
Be aware of how you do (and don’t) need to fast before surgery
The American Society of Anesthesiologists gives the following fasting guidelines:
- Non-food liquids: fast for at least 2 hours before surgery
- Food liquids or light snacks: fast for at least 6 hours before surgery
- Fried foods, fatty foods, meat: fast for at least 8 hours before surgery
(see the above link for more details)
Dr. Bonney notes that many times he’s had patients who’ve had the worst thirst, or caffeine headache, because of abstaining unnecessarily for the day of the surgery.
Unless told otherwise by your surgical team, you can have black coffee/tea up until two hours before your surgery, and you can and should have water up until two hours before surgery.
Hydration is good for you and you will feel the difference!
Want to know more?
Dr. Bonney has his own website and blog, where he offers lots of advice, including for specific conditions and specific surgeries, with advice for before/during/after your hospital stay.
He also has a book with many more tips like those we shared today:
Calm For Surgery: Supertips For A Smooth Recovery
Take good care of yourself!
Share This Post
-
Half Of Americans Over 50 Have Hemorrhoids, But They Can Be Prevented!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Hello. I was hoping you could give some useful tips about how to avoid a painful ailment that has affected Ernest Hemingway, Karl Marx, David Livingstone, Napoleon, Marilyn Monroe, King Alfred, and Martin Luther, and, I confess, me from time to time … namely, hemorrhoids. Help!❞
Firstly: that list could be a lot longer! We don’t have global stats, but in the US for example, half of adults over 50 have hemorrhoids.
So, you’re certainly not alone. People just don’t talk about it.
But, there are preventative things you can do:
Fiber, fiber, fiber. See also:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Hydrate, hydrate, hydrate.
This one’s simple enough. If you are dehydrated, constipation is more likely, and with it, hemorrhoids.
Watch your meds…
Some medications can cause constipation—painkillers containing codeine are a common culprit, for example.
When you go, go!
Not only can prolonged straining promote hemorrhoids, but also (if you’ll pardon the phrasing—there’s only so delicately we can say this) simply sitting with things partway “open” down there is not good for its health; things can quickly become irritated, and that can lead to hemorrhoids.
So: when you go, go. Leave your phone in another room!
Wash—but carefully.
Beyond your normal showering/bathing routine, a bidet is a great option for keeping things happy down there, if you have that option available to you.
However, if you have hemorrhoids, don’t use soap, as this can cause irritation and make it worse.
Warm water is fine, as is a salt bath, and pat dry and/or use gentle wet-wipes rather than rougher paper.
You can follow up with a hemorrhoid cream of your choice (or hydrocortisone, unless that’s contraindicated by another condition you have)
Know when to seek help
Hemorrhoids will usually go away by themselves if not exacerbated. But if it’s getting unduly difficult, and/or you’re bleeding down there, it’s time to see a doctor.
Note on bleeding: even if you’re 100% sure you have hemorrhoids, there are still other reasons you could be bleeding, and so it needs checking out.
Hemorrhoid treatment, if needed, will vary depending on severity. Beyond creams and lotions, there are other options that are less fun but sometimes necessary, including injections, electrotherapy, banding, or surgery.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not there?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Homeopathy: Evidence So Tiny That It’s Not There?
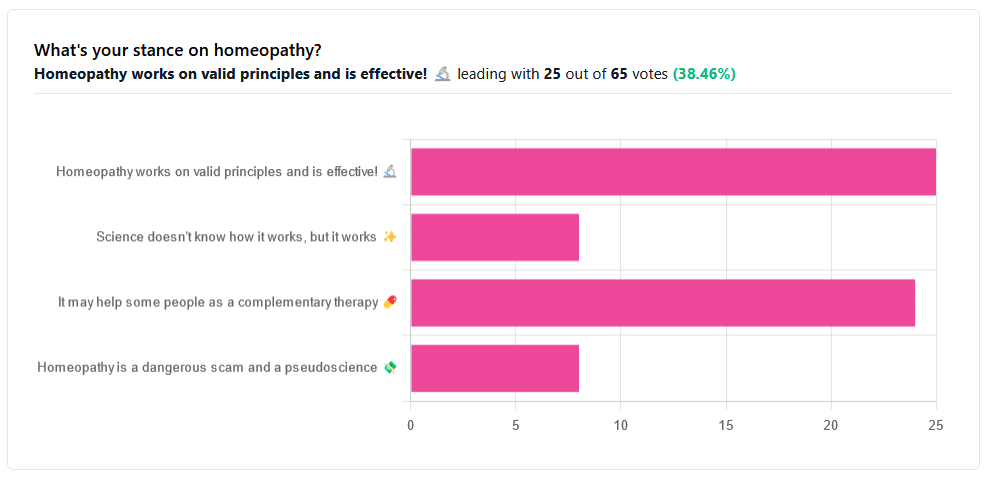
Yesterday, we asked you your opinions on homeopathy. The sample size of responses was a little lower than we usually get, but of those who did reply, there was a clear trend:
- A lot of enthusiasm for “Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective”
- Near equal support for “It may help some people as a complementary therapy”
- Very few people voted for “Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works”; this is probably because people who considered voting for this, voted for the more flexible “It may help some people as a complementary therapy” instead.
- Very few people considered it a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience.
So, what does the science say?
Well, let us start our investigation by checking out the position of the UK’s National Health Service, an organization with a strong focus on providing the least expensive treatments that are effective.
Since homeopathy is very inexpensive to arrange, they will surely want to put it atop their list of treatments, right?
❝Homeopathy is a “treatment” based on the use of highly diluted substances, which practitioners claim can cause the body to heal itself.
There’s been extensive investigation of the effectiveness of homeopathy. There’s no good-quality evidence that homeopathy is effective as a treatment for any health condition.❞
The NHS actually has a lot more to say about that, and you can read their full statement here.
But that’s just one institution. Here’s what Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council had to say:
❝There was no reliable evidence from research in humans that homeopathy was effective for treating the range of health conditions considered: no good-quality, well-designed studies with enough participants for a meaningful result reported either that homeopathy caused greater health improvements than placebo, or caused health improvements equal to those of another treatment❞
You can read their full statement here.
The American FDA, meanwhile, have a stronger statement:
❝Homeopathic drug products are made from a wide range of substances, including ingredients derived from plants, healthy or diseased animal or human sources, minerals and chemicals, including known poisons. These products have the potential to cause significant and even permanent harm if they are poorly manufactured, since that could lead to contaminated products or products that have potentially toxic ingredients at higher levels than are labeled and/or safe, or if they are marketed as substitute treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases and conditions, or to vulnerable populations.❞
You can read their full statement here.
Homeopathy is a dangerous scam and a pseudoscience: True or False?
False and True, respectively, mostly.
That may be a confusing answer, so let’s elaborate:
- Is it dangerous? Mostly not; it’s mostly just water. However, two possibilities for harm exist:
- Careless preparation could result in a harmful ingredient still being present in the water—and because of the “like cures like” principle, many of the ingredients used in homeopathy are harmful, ranging from heavy metals to plant-based neurotoxins. However, the process of “ultra-dilution” usually removes these so thoroughly that they are absent or otherwise scientifically undetectable.
- Placebo treatment has its place, but could result in “real” treatment going undelivered. This can cause harm if the “real” treatment was critically needed, especially if it was needed on a short timescale.
- Is it a scam? Probably mostly not; to be a scam requires malintent. Most practitioners probably believe in what they are practising.
- Is it a pseudoscience? With the exception that placebo effect has been highly studied and is a very valid complementary therapy… Yes, aside from that it is a pseudoscience. There is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “like cures like” principle, and there is no scientific evidence to support homeopathy’s “water memory” idea. On the contrary, they go against the commonly understood physics of our world.
It may help some people as a complementary therapy: True or False?
True! Not only is placebo effect very well-studied, but best of all, it can still work as a placebo even if you know that you’re taking a placebo… Provided you also believe that!
Science doesn’t know how it works, but it works: True or False?
False, simply. At best, it performs as a placebo.
Placebo is most effective when it’s a remedy against subjective symptoms, like pain.
However, psychosomatic effect (the effect that our brain has on the rest of our body, to which it is very well-connected) can mean that placebo can also help against objective symptoms, like inflammation.
After all, our body, directed primarily by the brain, can “decide” what immunological defenses to deploy or hold back, for example. This is why placebo can help with conditions as diverse as arthritis (an inflammatory condition) or diabetes (an autoimmune condition, and/or a metabolic condition, depending on type).
Here’s how homeopathy measures up, for those conditions:
(the short answer is “no better than placebo”)
Homeopathy works on valid principles and is effective: True or False?
False, except insofar as placebo is a valid principle and can be effective.
The stated principles of homeopathy—”like cures like” and “water memory”—have no scientific basis.
We’d love to show the science for this, but we cannot prove a negative.
However, the ideas were conceived in 1796, and are tantamount to alchemy. A good scientific attitude means being open-minded to new ideas and testing them. In homeopathy’s case, this has been done, extensively, and more than 200 years of testing later, homeopathy has consistently performed equal to placebo.
In summary…
- If you’re enjoying homeopathic treatment and that’s working for you, great, keep at it.
- If you’re open-minded to enjoying a placebo treatment that may benefit you, be careful, but don’t let us stop you.
- If your condition is serious, please do not delay seeking evidence-based medical treatment.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Physical Sunscreen or Chemical Sunscreen – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing physical sunscreens to chemical sunscreens, we picked the physical sunscreens.
Why?
It’s easy to vote against chemical sunscreens, because it has “chemical” in the name, which tends to be offputting PR-wise no matter how healthy something is.
But in this case, there’s actual science here too!
Physical sunscreens physically block the UV rays.
- On the simplest of levels, mud is a physical sunscreen, as you can see widely used by elephants, hippos, pigs, and other animals.
- On a more sophisticated level, modern physical sunscreens often use tiny zinc particles (or similar) to block the UV rays in a way that isn’t so obvious to the naked eye—so we can still see our skin, and it looks just like we applied an oil or other moisturizer.
Chemical sunscreens interact with the UV rays in a way that absorbs them.
- Specifically, they usually convert it into relatively harmless thermal energy (heat)
- However, this can cause problems if there’s too much heat!
- Additionally, chemical sunscreens can get “used up” in a way that physical sunscreens can’t* becoming effectively deactivated once the chemical reaction has run its course and there is no more reagent left unreacted.
- Worse, some of the reagents, when broken down by the UV rays, can potentially cause harm when absorbed by the skin.
*That said, physical sunscreens will still need “topping up” because we are a living organism and our body can’t resist redistributing and using stuff—plus, depending on the climate and our activities, we can lose some externally too.
Further reading
We wrote about sunscreens (of various kinds) here:
And you can also read specifically about today’s topic in more detail, here:
What’s The Difference Between Physical And Chemical Sunscreens?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Coffee-Cortisol Connection, And Two Ways To Tweak It For Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health opinions on coffee vary from “it’s an invigorating, healthful drink” to “it will leave you a shaking frazzled wreck”. So, what’s the truth and can we enjoy it healthily? Dr. Alan Mandell weighs in:
Enjoy it, but watch out!
Dr. Mandell is speaking only for caffeinated coffee in this video, and to this end, he’s conflating the health effects of coffee and caffeine. A statistically reasonable imprecision, since most people drink coffee with its natural caffeine in, but we’ll make some adjustment to his comments below, to disambiguate which statements are true for coffee generally, and which are true for caffeine:
- Drinking
coffeecaffeine first thing in the morning may not be ideal due to dehydration from overnight water loss. Coffeecaffeine is a diuretic, which means an increase in urination, thus further dehydrating the body.- Coffee contains great antioxidants, which are of course beneficial for the health in general.
- Cortisol, the body’s stress hormone, is generally at its peak in the morning. This is, in and of itself, good and correct—it’s how we wake up.
Coffeecaffeine consumption raises cortisol levels even more, leading to increased alertness and physical readiness, but it is possible to have too much of a good thing, and in this case, problems can arise because…- Elevated cortisol from early
coffeecaffeine drinking can build tolerance, leading to the need for morecoffeecaffeine over time. - It’s better, therefore, to defer drinking
coffeecaffeine until later in the morning when cortisol levels naturally drop. - All of this means that drinking
coffeecaffeine first thing can disrupt the neuroendocrine system, leading to fatigue, depression, and general woe. - Hydrate first thing in the morning before consuming
coffeecaffeine to keep the body balanced and healthy.
What you can see from this is that coffee and caffeine are not, in fact, interchangeable words, but the basic message is clear and correct: while a little spike of cortisol in the morning is good, natural, and even necessary, a big spike is none of those things, and caffeine can cause a big spike, and since for most people caffeine is easy to build tolerance to, there will indeed consistently be a need for more, worsening the problem.
In terms of hydration, it’s good to have water (or better yet, herbal tea) on one’s nightstand to drink when one wakes up.
If coffee is an important morning ritual for you, consider finding a good decaffeinated version for at least your first cup (this writer is partial to Lavazza’s “Dek Intenso”—which is not the same as their main decaf line, by the way, so do hold out for the “Dek Intenso” if you want to try my recommendation).
Decaffeinated coffee is hydrating and will not cause a cortisol spike (unless for some reason you find coffee as a concept very stressful in which case, yes, the stressor will cause a stress response).
Anyway, for more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Drinking
-
How to be kind to yourself (without going to a day spa)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“I have to be hard on myself,” Sarah told me in a recent telehealth psychology session. “I would never reach my potential if I was kind and let myself off the hook.”
I could empathise with this fear of self-compassion from clients such as Sarah (not her real name). From a young age, we are taught to be kind to others, but self-kindness is never mentioned.
Instead, we are taught success hinges on self-sacrifice. And we need a healthy inner critic to bully us forward into becoming increasingly better versions of ourselves.
But research shows there doesn’t have to be a trade-off between self-compassion and success.
Self-compassion can help you reach your potential, while supporting you to face the inevitable stumbles and setbacks along the way.
What is self-compassion?
Self-compassion has three key ingredients.
1. Self-kindness
This involves treating yourself with the same kindness you would extend towards a good friend – via your thoughts, feelings and actions – especially during life’s difficult moments.
For instance, if you find yourself fixating on a minor mistake you made at work, self-kindness might involve taking a ten-minute walk to shift focus, and reminding yourself it is OK to make mistakes sometimes, before moving on with your day.
2. Mindfulness
In this context, mindfulness involves being aware of your own experience of stress or suffering, rather than repressing or avoiding your feelings, or over-identifying with them.
Basically, you must see your stress with a clear (mindful) perspective before you can respond with kindness. If we avoid or are consumed by our suffering, we lose perspective.
3. Common humanity
Common humanity involves recognising our own experience of suffering as something that unites us as being human.
For instance, a sleep-deprived parent waking up (for the fourth time) to feed their newborn might choose to think about all the other parents around the world doing exactly the same thing – as opposed to feeling isolated and alone.
It’s not about day spas, or booking a manicure
When Sarah voiced her fear that self-compassion would prevent her success, I explained self-compassion is distinct from self-indulgence.
“So is self-compassion just about booking in more mani/pedis?” Sarah asked.
Not really, I explained. A one-off trip to a day spa is unlikely to transform your mental health.
Instead, self-compassion is a flexible psychological resilience factor that shapes our thoughts, feelings and actions.
It’s associated with a suite of benefits to our wellbeing, relationships and health.
A one-off trip to a day spa is unlikely to transform your mental health.
baranq/ShutterstockWhat does the science say?
Over the past 20 years, we’ve learned self-compassionate people enjoy a wide range of benefits. They tend to be happier and have fewer psychological symptoms of distress.
Those high on self-compassion persevere following a failure. They say they are more motivated to overcome a personal weakness than those low on self-compassion, who are more likely to give up.
So rather than feeling trapped by your inadequacies, self-compassion encourages a growth mindset, helping you reach your potential.
However, self-compassion is not a panacea. It will not change your life circumstances or somehow make life “easy”. It is based on the premise that life is hard, and provides practical tools to cope.
It’s a factor in healthy ageing
I research menopause and healthy ageing and am especially interested in the value of self-compassion through menopause and in the second half of life.
Because self-compassion becomes important during life’s challenges, it can help people navigate physical symptoms (for instance, menopausal hot flushes), life transitions such as divorce, and promote healthy ageing.
I’ve also teamed up with researchers at Autism Spectrum Australia to explore self-compassion in autistic adults.
We found autistic adults report significantly lower levels of self-compassion than neurotypical adults. So we developed an online self-compassion training program for this at-risk population.
Three tips for self-compassion
You can learn self-compassion with these three exercises.
1. What would you say to a friend?
Think back to the last time you made a mistake. What did you say to yourself?
If you notice you’re treating yourself more like an enemy than a friend, don’t beat yourself up about it. Instead, try to think about what you might tell a friend, and direct that same friendly language towards yourself.
2. Harness the power of touch
Soothing human touch activates the parasympathetic “relaxation” branch of our nervous system and counteracts the fight or flight response.
Specifically, self-soothing touch (for instance, by placing both hands on your heart, stroking your forearm or giving yourself a hug) reduces cortisol responses to psychosocial stress.
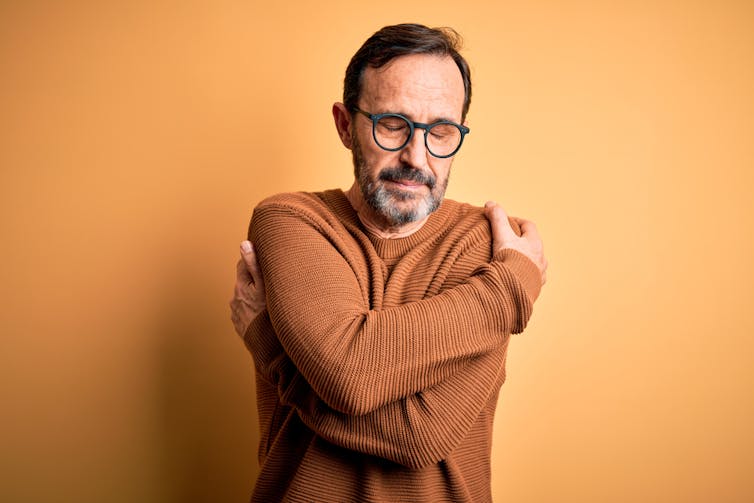
Yes, hugging yourself can help.
http://krakenimages.com/Shutterstock3. What do I need right now?
Sometimes, it can be hard to figure out exactly what self-compassion looks like in a given moment. The question “what do I need right now” helps clarify your true needs.
For example, when I was 37 weeks pregnant, I woke up bolt awake one morning at 3am.
Rather than beating myself up about it, or fretting about not getting enough sleep, I gently placed my hands on my heart and took a few deep breaths. By asking myself “what do I need right now?” it became clear that listening to a gentle podcast/meditation fitted the bill (even though I wanted to addictively scroll my phone).
Lydia Brown, Senior Lecturer in Psychology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: