Modern Friendship – by Anna Goldfarb
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s a topic we’ve covered before at 10almonds: Human Connection In An All-Too-Busy World.
Here, however, Goldfarb has an entire book to cover what we had one article to cover, so of course it’s a lot more in-depth.
Importantly, if also covers: what if you seem to be doing everything right, and it’s still not working out? What if you’re already reaching out, suggesting things, doing your part?
Piece by piece, she uncovers what the very many problems are, ranging from availability issues and priorities, to health concerns and financial difficulties, to challenges as diverse as trust issues and exhaustion, and much more.
After all the hard truths about modern friendship, she gets onto equally cheery topics such as why friendships fail, but fear not, solutions are forthcoming too—and indeed, that’s what most of the book is about.
Covering such topics as desire, diligence, and delight, we learn how to not only practise wholehearted friendship, but also, how to matter to others, too. She finishes up with a “14-day friendship cleanse”, which sounds a lot more alarming than it actually is.
The style is interesting, being personal and, well, friendly throughout—but still with scholarly citations as we go along, and actual social science rather than mere conjecture.
Bottom line: if you find that your friendships are facing challenges, this book can help you to get to the bottom of any problems and move forwards (likely doing so together).
Click here to check out Modern Friendship, and learn how to truly nurture and grow your connections!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ovarian cancer is hard to detect. Focusing on these 4 symptoms can help with diagnosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ovarian cancers are often found when they are already advanced and hard to treat.
Researchers have long believed this was because women first experienced symptoms when ovarian cancer was already well-established. Symptoms can also be hard to identify as they’re vague and similar to other conditions.
But a new study shows promising signs ovarian cancer can be detected in its early stages. The study targeted women with four specific symptoms – bloating, abdominal pain, needing to pee frequently, and feeling full quickly – and put them on a fast track to see a specialist.
As a result, even the most aggressive forms of ovarian cancer could be detected in their early stages.
So what did the study find? And what could it mean for detecting – and treating – ovarian cancer more quickly?
Ground Picture/Shutterstock Why is ovarian cancer hard to detect early?
Ovarian cancer cannot be detected via cervical cancer screening (which used to be called a pap smear) and pelvic exams aren’t useful as a screening test.
Current Australian guidelines recommend women get tested for ovarian cancer if they have symptoms for more than a month. But many of the symptoms – such as tiredness, constipation and changes in menstruation – are vague and overlap with other common illnesses.
This makes early detection a challenge. But it is crucial – a woman’s chances of surviving ovarian cancer are associated with how advanced the cancer is when she is diagnosed.
If the cancer is still confined to the original site with no spread, the five-year survival rate is 92%. But over half of women diagnosed with ovarian cancer first present when the cancer has already metastatised, meaning it has spread to other parts of the body.
If the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, the survival rate is reduced to 72%. If the cancer has already metastasised and spread to distant sites at the time of diagnosis, the rate is only 31%.
There are mixed findings on whether detecting ovarian cancer earlier leads to better survival rates. For example, a trial in the UK that screened more than 200,000 women failed to reduce deaths.
That study screened the general public, rather than relying on self-reported symptoms. The new study suggests asking women to look for specific symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis, meaning treatment can start more quickly.
What did the new study look at?
Between June 2015 and July 2022, the researchers recruited 2,596 women aged between 16 and 90 from 24 hospitals across the UK.
They were asked to monitor for these four symptoms:
- persistent abdominal distension (women often refer to this as bloating)
- feeling full shortly after starting to eat and/or loss of appetite
- pelvic or abdominal pain (which can feel like indigestion)
- needing to urinate urgently or more often.
Women who reported at least one of four symptoms persistently or frequently were put on a fast-track pathway. That means they were sent to see a gynaecologist within two weeks. The fast track pathway has been used in the UK since 2011, but is not specifically part of Australia’s guidelines.
Some 1,741 participants were put on this fast track. First, they did a blood test that measured the cancer antigen 125 (CA125). If a woman’s CA125 level was abnormal, she was sent to do a internal vaginal ultrasound.
What did they find?
The study indicates this process is better at detecting ovarian cancer than general screening of people who don’t have symptoms. Some 12% of women on the fast-track pathway were diagnosed with some kind of ovarian cancer.
A total of 6.8% of fast-tracked patients were diagnosed with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. It is the most aggressive form of cancer and responsible for 90% of ovarian cancer deaths.
Out of those women with the most aggressive form, one in four were diagnosed when the cancer was still in its early stages. That is important because it allowed treatment of the most lethal cancer before it had spread significantly through the body.
There were some promising signs in treating those with this aggressive form. The majority (95%) had surgery and three quarters (77%) had chemotherapy. Complete cytoreduction – meaning all of the cancer appears to have been removed – was achieved in six women out of ten (61%).
It’s a promising sign that there may be ways to “catch” and target ovarian cancer before it is well-established in the body.
What does this mean for detection?
The study’s findings suggest this method of early testing and referral for the symptoms leads to earlier detection of ovarian cancer. This may also improve outcomes, although the study did not track survival rates.
It also points to the importance of public awareness about symptoms.
Clinicians should be able to recognise all of the ways ovarian cancer can present, including vague symptoms like general fatigue.
But empowering members of the general public to recognise a narrower set of four symptoms can help trigger testing, detection and treatment of ovarian cancer earlier than we thought.
This could also save GPs advising every woman who has general tiredness or constipation to undergo an ovarian cancer test, making testing and treatment more targeted and efficient.
Many women remain unaware of the symptoms of ovarian cancer. This study shows recognising them may help early detection and treatment.
Jenny Doust, Clinical Professorial Research Fellow, Australian Women and Girls’ Health Research Centre, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How can I stop using food to cope with negative emotions?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever noticed changes in your eating habits when you are sad, bored or anxious?
Many people report eating either more, or less, as a way of helping them to cope when they experience difficult emotions.
Although this is a very normal response, it can take the pleasure out of eating, and can become distressing and bring about other feelings of shame and self-criticism.
Adding to the complexity of it all, we live in a world where diet culture is unavoidable, and our relationship to eating, food and body image can become complicated and confusing.
Drazen Zigic/Shutterstock Emotional eating is common
“Emotional eating” refers to the eating behaviours (typically eating more) that occur in response to difficult emotions.
Research shows around 20% of people regularly engage in emotional eating, with a higher prevalence among adolescents and women. In a study of more than 1,500 adolescents, 34% engaged in emotional eating while sad and 40% did so while anxious.
Foods consumed are often fast-foods and other energy-dense, nutrient-poor convenience foods.
Stress, strong emotions and depression
For some people, emotional eating was simply a habit formed earlier in life that has persisted over time.
But other factors might also contribute to the likelihood of emotional eating. The physiological effects of stress and strong emotions, for example, can influence hormones such as cortisol, insulin and glucose, which can also increase appetite.
Increased impulsivity (behaving before thinking things through), vulnerability to depression, a tendency to ruminate and difficulties regulating emotions also increase the likelihood of emotional eating.
Depression increases the likelihood of emotional eating. TommyStockProject/Shutterstock So what do you do?
First, know that fluctuations in eating are normal. However, if you find that the way you eat in response to difficult emotions is not working for you, there are a few things you can do.
Starting with small things that are achievable but can have a huge impact, such as prioritising getting enough sleep and eating regularly.
Then, you can start to think about how you handle your emotions and hunger cues.
Expand your emotional awareness
Often we label emotions as good or bad, and this can result in fear, avoidance, and unhelpful coping strategies such as emotional eating.
But it’s also important to differentiate the exact emotion. This might be feeling isolated, powerless or victimised, rather than something as broad as sad.
By noticing what the emotion is, we can bring curiosity to what it means, how we feel in our minds and bodies, and how we think and behave in response.
Tap into your feelings of hunger and fullness
Developing an intuitive way of eating is another helpful strategy to promote healthy eating behaviours.
Intuitive eating means recognising, understanding and responding to internal signals of hunger and fullness. This might mean tuning in to and acknowledging physical hunger cues, responding by eating food that is nourishing and enjoyable, and identifying sensations of fullness.
Intuitive eating encourages flexibility and thinking about the pleasure we get from food and eating. This style of eating also allows us to enjoy eating out with friends, and sample local delicacies when travelling.
It can also reduce the psychological distress from feeling out of control with your eating habits and the associated negative body image.
Try to be flexible in thinking about the pleasure of food and eating with friends. La Famiglia/Shutterstock When is it time to seek help?
For some people, the thoughts and behaviours relating to food, eating and body image can negatively impact their life.
Having the support of friends and family, accessing online resources and, in some instances, seeing a trained professional, can be very helpful.
There are many therapeutic interventions that work to improve aspects associated with emotional eating. These will depend on your situation, needs, stage of life and other factors, such as whether you are neurodivergent.
The best approach is to engage with someone who can bring compassion and understanding to your personal situation, and work with you collaboratively. This work might include:
- unpacking some of the patterns that could be underlying these emotions, thoughts and behaviours
- helping you to discover your emotions
- supporting you to process other experiences, such as trauma exposure
- developing a more flexible and intuitive way of eating.
One of the dangers that can occur in response to emotional eating is the temptation to diet, which can lead to disordered eating, and eating disorder behaviours. Indicators of a potential eating disorder can include:
- recent rapid weight loss
- preoccupation with weight and shape (which is usually in contrast to other people’s perceptions)
- eating large amounts of food within a short space of time (two hours or less) and feeling a sense of loss of control
- eating in secret
- compensating for food eaten (with vomiting, exercise or laxatives).
Evidence-based approaches can support people experiencing eating disorders. To find a health professional who is informed and specialises in this area, search the Butterfly Foundation’s expert database.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14, or the Butterfly Foundation on 1800 ED HOPE (1800 33 4673).
Inge Gnatt, PhD Candidate, Lecturer in Psychology, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
From eye exams to blood tests and surgery: how doctors use light to diagnose disease
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
You’re not feeling well. You’ve had a pounding headache all week, dizzy spells and have vomited up your past few meals.
You visit your GP to get some answers and sit while they shine a light in your eyes, order a blood test and request some medical imaging.
Everything your GP just did relies on light. These are just some of the optical technologies that have had an enormous impact in how we diagnose disease.
megaflopp/Shutterstock 1. On-the-spot tests
Point-of-care diagnostics allow doctors to test patients on the spot and get answers in minutes, rather than sending samples to a lab for analysis.
The “flashlight” your GP uses to view the inside of your eye (known as an ophthalmoscope) is a great example. This allows doctors to detect abnormal blood flow in the eye, deformations of the cornea (the outermost clear layer of the eye), or swollen optical discs (a round section at the back of the eye where the nerve link to the brain begins). Swollen discs are a sign of elevated pressure inside your head (or in the worst case, a brain tumour) that could be causing your headaches.
The invention of lasers and LEDs has enabled many other miniaturised technologies to be provided at the bedside or clinic rather than in the lab.
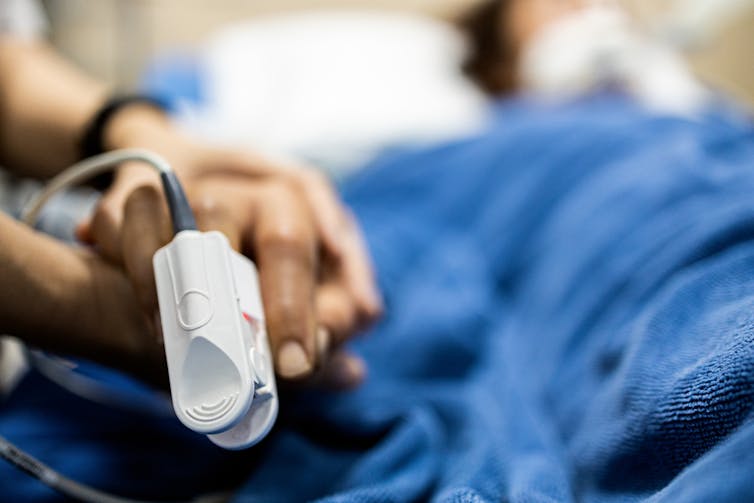
Pulse oximetry is a famous example, where a clip attached to your finger reports how well your blood is oxygenated. It does this by measuring the different responses of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood to different colours of light.
Pulse oximetry is used at hospitals (and sometimes at home) to monitor your respiratory and heart health. In hospitals, it is also a valuable tool for detecting heart defects in babies.
See that clip on the patient’s finger? That’s a pulse oximeter, which relies on light to monitor respiratory and heart health. CGN089/Shutterstock 2. Looking at molecules
Now, back to that blood test. Analysing a small amount of your blood can diagnose many different diseases.
A machine called an automated “full blood count analyser” tests for general markers of your health. This machine directs focused beams of light through blood samples held in small glass tubes. It counts the number of blood cells, determines their specific type, and reports the level of haemoglobin (the protein in red blood cells that distributes oxygen around your body). In minutes, this machine can provide a snapshot of your overall health.
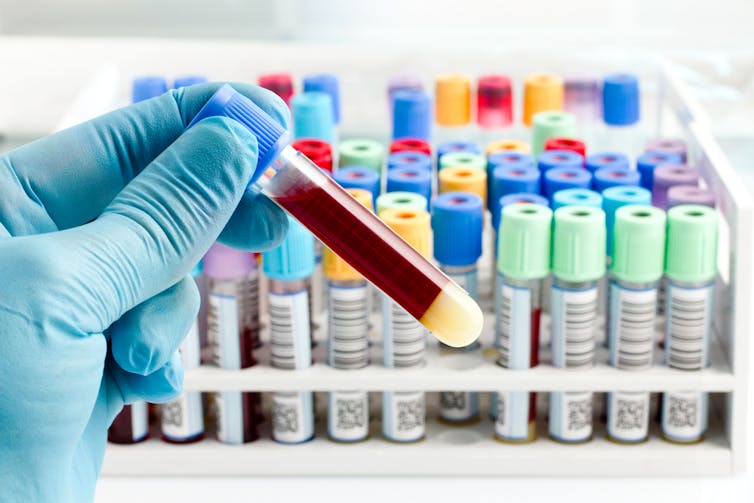
For more specific disease markers, blood serum is separated from the heavier cells by spinning in a rotating instrument called a centrifuge. The serum is then exposed to special chemical stains and enzyme assays that change colour depending on whether specific molecules, which may be the sign of a disease, are present.
These colour changes can’t be detected with the naked eye. However, a light beam from an instrument called a spectrometer can detect tiny amounts of these substances in the blood and determine if the biomarkers for diseases are present, and at what levels.
Light shines through the blood sample and tells us whether biomarkers for disease are present. angellodeco/Shutterstock 3. Medical imaging
Let’s re-visit those medical images your GP ordered. The development of fibre-optic technology, made famous for transforming high-speed digital communications (such as the NBN), allows light to get inside the body. The result? High-resolution optical imaging.
A common example is an endoscope, where fibres with a tiny camera on the end are inserted into the body’s natural openings (such as your mouth or anus) to examine your gut or respiratory tracts.
Surgeons can insert the same technology through tiny cuts to view the inside of the body on a video screen during laparoscopic surgery (also known as keyhole surgery) to diagnose and treat disease.
Doctors can insert this flexible fibre-optic tube with a camera on the end into your body. Eduard Valentinov/Shutterstock How about the future?
Progress in nanotechnology and a better understanding of the interactions of light with our tissues are leading to new light-based tools to help diagnose disease. These include:
- nanomaterials (materials on an extremely small scale, many thousands of times smaller than the width of a human hair). These are being used in next-generation sensors and new diagnostic tests
- wearable optical biosensors the size of your fingernail can be included in devices such as watches, contact lenses or finger wraps. These devices allow non-invasive measurements of sweat, tears and saliva, in real time
- AI tools to analyse how blood serum scatters infrared light. This has allowed researchers to build a comprehensive database of scatter patterns to detect any cancer
- a type of non-invasive imaging called optical coherence tomography for more detailed imaging of the eye, heart and skin
- fibre optic technology to deliver a tiny microscope into the body on the tip of a needle.
So the next time you’re at the GP and they perform (or order) some tests, chances are that at least one of those tests depend on light to help diagnose disease.
Matthew Griffith, Associate Professor and ARC Future Fellow and Director, UniSA Microscopy and Microanalysis Facilities, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cows’ Milk, Bird Flu, & You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to dairy products, generally speaking, fermented ones (such as most cheeses and yogurts) are considered healthy in moderation, and unfermented ones have their pros and cons that can be argued and quibbled “until the cows come home”. We gave a broad overview, here:
Furthermore, you may recall that there’s some controversy/dissent about when human babies can have cows’ milk:
When can my baby drink cow’s milk? It’s sooner than you think
So, what about bird flu now?
Earlier this year, the information from the dairy industry was that it was nothing to be worried about for the time being:
Bird Flu Is Bad for Poultry and Dairy Cows. It’s Not a Dire Threat for Most of Us — Yet.
More recently, the latest science has found:
❝We found a first-order decay rate constant of −2.05 day–1 equivalent to a T99 of 2.3 days. Viral RNA remained detectable for at least 57 days with no degradation. Pasteurization (63 °C for 30 min) reduced infectious virus to undetectable levels and reduced viral RNA concentrations, but reduction was less than 1 log10.
The prolonged persistence of viral RNA in both raw and pasteurized milk has implications for food safety assessments and environmental surveillance❞
You can find the study here:
Infectivity and Persistence of Influenza A Virus in Raw Milk
In short: raw milk keeps the infectious virus; pasteurization appears to render it uninfectious, though viral RNA remains present.
This is relevant, because of the bird flu virus being found in milk:
World Health Organization | H5N1 strain of bird flu found in milk
To this end, a moratorium has been placed on the sale of raw milk, first by the California Dept of Public Health (following an outbreak in California):
California halts sales of raw milk due to bird flu virus contamination
And then, functionally, by the USDA, though rather than an outright ban, it’s requiring testing for the virus:
USDA orders testing of milk supply for presence of bird flu virus
So, is pasteurized milk safe?
The official answer to this, per the FDA, is… Honestly, a lot of hand-wringing and shrugging. What we do know is:
- the bird flu virus has been found in pasteurized milk too
- the test for this is very sensitive, and has the extra strength/weakness that viral fragments will flag it as a positive
- it is assumed that the virus was inactivated by the pasteurization process
- it could, however, have been the entire virus, the test simply does not tell us which
In the FDA’s own words:
❝The pasteurization process has served public health well for more than 100 years. Even if the virus is detected in raw milk, pasteurization is generally expected to eliminate pathogens to a level that does not pose a risk to consumer health❞
So, there we have it: the FDA does not have a reassurance exactly, but it does have a general expectation.
Source: US Officials: Bird flu viral fragments found in pasteurized milk
Want to know more?
You might like this mythbusting edition we did a little while back:
Pasteurization: What It Does And Doesn’t Do ← this is about its effect on risks and nutrients
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bone on Bone – by Dr. Meredith Warner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What this is not: a book about one specific condition, injury, or surgery.
What this is: a guide to dealing with the common factors of many musculoskeletal conditions, inflammatory diseases, and their consequences.
Dr. Warner takes the opportunity to address the whole patient—presumably: the reader, though it could equally be a reader’s loved one, or even a reader’s patient, insofar as this book will probably be read by doctors also.
She takes an “inside-out and outside-in” approach; that is to say, addressing the problem from as many vectors as reasonably possible—including supplements, diet, dietary habits (things like intermittent fasting etc), exercise, and even sleep. And yes, she knows how difficult those latter items can be, and addresses them not merely with a “but it’s important” but also with practical advice.
As an orthopedic surgeon, she’s not a fan of surgery, and counsels the reader to avoid that if reasonably possible. She also talks about how many people in the US are encouraged to have MRI scans for financial reasons (as in, they can be profitable for the doctor/institution), and then any abnormality is used as justification for surgery, to backwards-justify the use of the MRI, even if the abnormality is not actually the cause of the pain.
Noteworthily, humans in general are a typically a pile of abnormalities in a trenchcoat. Our propensity to mutation has made us one of the most adaptable species on the planet, yet many would have us pretend that the insides of people look like they do in textbooks, or else are wrong. The reality is not so, and Dr. Warner rightly shows this for what it is.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one are suffering from, or at risk of, musculoskeletal and/or inflammatory conditions, this is a top-tier book for having a much easier time of it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Brain As A Work-In-Progress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
And The Brain Goes Marching On!
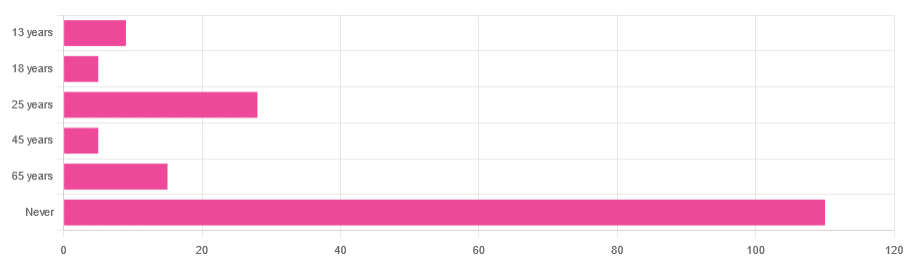
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you “when does the human brain stop developing?” and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 64% of people said “Never”
- About 16% of people said “25 years”
- About 9% of people said “65 years”
- About 5% of people said “13 years”
- About 3% of people said “18 years”
- About 3% of people said “45 years”
Some thoughts, before we get into the science:
An alternative wording for the original question was “when does the human brain finish developing”; the meaning is the same but the feeling is slightly different:
- “When does the human brain stop developing?” focuses attention on the idea of cessation, and will skew responses to later ages
- When does the human brain finish developing?” focuses on attention on a kind of “is it done yet?” and will skew responses to earlier ages
Ultimately, since we had to chose one word or another, we picked the shortest one, but it would have been interesting if we could have done an A/B test, and asked half one way, and half the other way!
Why we picked those ages
We picked those ages as poll options for reasons people might be drawn to them:
- 13 years: in English-speaking cultures, an important milestone of entering adolescence (note that the concept of a “teenager” is not precisely universal as most languages do not have “-teen” numbers in the same way; the concept of “adolescent” may thus be tied to other milestones)
- 18 years: age of legal majority in N. America and many other places
- 25 years: age popularly believed to be when the brain is finished developing, due to a study that we’ll talk about shortly (we guess that’s why there’s a spike in our results for this, too!)
- 45 years: age where many midlife hormonal changes occur, and many professionals are considered to have peaked in competence and start looking towards retirement
- 65 years: age considered “senior” in much of N. America and many other places, as well as the cut-off and/or starting point for a lot of medical research
Notice, therefore, how a lot of things are coming from places they really shouldn’t. For example, because there are many studies saying “n% of people over 65 get Alzheimer’s” or “n% of people over 65 get age-related cognitive decline”, etc, 65 becomes the age where we start expecting this—because of an arbitrary human choice of where to draw the cut-off for the study enrollment!
Similarly, we may look at common ages of legal majority, or retirement pensions, and assume “well it must be for a good reason”, and dear reader, those reasons are more often economically motivated than they are biologically reasoned.
So, what does the science say?
Our brains are never finished developing: True or False?
True! If we define “finished developing” as “we cease doing neurogenesis and neuroplasticity is no longer in effect”.
Glossary:
- Neurogenesis: the process of creating new brain cells
- Neuroplasticity: the process of the brain adapting to changes by essentially rebuilding itself to suit our perceived current needs
We say “perceived” because sometimes neuroplasticity can do very unhelpful things to us (e.g: psychological trauma, or even just bad habits), but on a biological level, it is always doing its best to serve our overall success as an organism.
For a long time it was thought that we don’t do neurogenesis at all as adults, but this was found to be untrue:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
Summary of conclusions of the above: we’re all growing new brain cells at every age, even if we be in our 80s and with Alzheimer’s disease, but there are things we can do to enhance our neurogenic potential along the way.
Neuroplasticity will always be somewhat enhanced by neurogenesis (after all, new neurons get given jobs to do), and we reviewed a great book about the marvels of neuroplasticity including in older age:
Our brains are still developing up to the age of 25: True or False?
True! And then it keeps on developing after that, too. Now this is abundantly obvious considering what we just talked about, but see what a difference the phrasing makes? Now it makes it sound like it stops at 25, which this statement doesn’t claim at all—it only speaks for the time up to that age.
A lot of the popular press about “the brain isn’t fully mature until the age of 25” stems from a 2006 study that found:
❝For instance, frontal gray matter volume peaks at about age 11.0 years in girls and 12.1 years in boys, whereas temporal gray matter volume peaks at about age at 16.7 years in girls and 16.2 years in boys. The dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex, important for controlling impulses, is among the latest brain regions to mature without reaching adult dimensions until the early 20s.❞
Source: Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Adolescent Brain
There are several things to note here:
- The above statement is talking about the physical size of the brain growing
- Nowhere does he say “and stops developing at 25”
However… The study only looked at brains up to the age of 25. After that, they stopped looking, because the study was about “the adolescent brain” so there has to be a cut-off somewhere, and that was the cut-off they chose.
This is the equivalent of saying “it didn’t stop raining until four o’clock” when the reality is that four o’clock is simply when you gave up on checking.
The study didn’t misrepresent this, by the way, but the popular press did!
Another 2012 study looked at various metrics of brain development, and found:
- Synapse overproduction into the teens
- Cortex pruning into the late 20s
- Prefrontal pruning into middle age at least (they stopped looking)
- Myelination beyond middle age (they stopped looking)
Source: Experience and the developing prefrontal cortex ← check out figure 1, and make sure you’re looking at the human data not the rat data
So how’s the most recent research looking?
Here’s a 2022 study that looked at 123,984 brain scans spanning the age range from mid-gestation to 100 postnatal years, and as you can see from its own figure 1… Most (if not all) brain-things keep growing for life, even though most slow down at some point, they don’t stop:
Brain charts for the human lifespan ← check out figure 1; don’t get too excited about the ventricular volume column as that is basically “brain that isn’t being a brain”. Do get excited about the rest, though!
Want to know how not to get caught out by science being misrepresented by the popular press? Check out:
How Science News Outlets Can Lie To You (Yes, Even If They Cite Studies!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: