Meditation for Fidgety Skeptics – by Dan Harris
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you already meditate regularly, this book isn’t aimed at you (though you may learn a thing or two anyway—this reviewer, who has practiced meditation for the past 30 years, learned a thing!).
However, if you’re—as the title suggests—someone who hasn’t so far been inclined towards meditation, you could get the most out of this one. We’ll say more on this (obviously), but first, there’s one other group that may benefit from this book:
If you have already practiced meditation, and/or already understand and want its benefits, but never really made it stick as a habit.
Now, onto what you’ll get:
- A fair scientific overview of meditation as an increasingly evidence-based way to reduce stress and increase both happiness and productivity
- A good grounding in what meditation is and isn’t
- A how-to guide for building up a consistent meditation habit that won’t get kiboshed when you have a particularly hectic day—or a cold.
- An assortment of very common (and some less common) meditative practices to try
- Some great auxiliary tools to build cognitive restructuring into your meditation
We don’t usually cite other people’s reviews, but we love that one Amazon reviewer wrote:
❝I am 3 weeks into daily meditation practice, and I already notice that I am no longer constantly wishing for undercarriage rocket launchers while driving. I will always think your driving sucks, but I no longer wish you a violent death because of it. Yes, I live in Boston❞
Bottom line: if you’re not already meditating daily, this is definitely a book for you. And if you are, you may learn a thing or two anyway!
Click here to get your copy of Meditation For Fidgety Skeptics from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Acid Reflux Diet Cookbook – by Dr. Harmony Reynolds
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Notwithstanding the title, this is far more than just a recipe book. Of course, it is common for health-focused recipe books to begin with a preamble about the science that’s going to be applied, but in this case, the science makes up a larger portion of the book than usual, along with practical tips about how to best implement certain things, at home and when out and about.
Dr. Reynolds also gives a lot of information about such things as medications that could be having an effect one way or the other, and even other lifestyle factors such as exercise and so forth, and yes, even stress management. Because for many people, what starts as acid reflux can soon become ulcers, and that’s not good.
The recipes themselves are diverse and fairly simple; they’re written solely with acid reflux in mind and not other health considerations, but they are mostly heathy in the generalized sense too.
The style is straight to the point with zero padding sensationalism, or chit-chat. It can make for a slightly dry read, but let’s face it, nobody is buying this book for its entertainment value.
Bottom line: if you have been troubled by acid reflux, this book will help you to eat your way safely out of it.
Click here to check out the Acid Reflux Diet Cookbook, and enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Why ’10almonds’? Newsletter Name Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: Why is your newsletter called 10almonds? Maybe I missed it in the intro email, but my curiosity wants to know the significance. Thanks!”
It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was online… So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a tongue-in-cheek reference to that story… but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Share This Post
-
Rethinking Exercise: The Workout Paradox
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The notion of running a caloric deficit (i.e., expending more calories than we consume) to reduce bodyfat is appealing in its simplicity, but… we’d say “it doesn’t actually work outside of a lab”, but honestly, it doesn’t actually work outside of a calculator.
Why?
For a start, exercise calorie costs are quite small numbers compared to metabolic base rate. Our brain alone uses a huge portion of our daily calories, and the rest of our body literally never stops doing stuff. Even if we’re lounging in bed and ostensibly not moving, on a cellular level we stay incredibly busy, and all that costs (and the currency is: calories).
Since that cost is reflected in the body’s budget per kg of bodyweight, a larger body (regardless of its composition) will require more calories than a smaller one. We say “regardless of its composition” because this is true regardless—but for what it’s worth, muscle is more “costly” to maintain than fat, which is one of several reasons why the average man requires more daily calories than the average woman, since on average men will tend to have more muscle.
And if you do exercise because you want to run out the budget so the body has to “spend” from fat stores?
Good luck, because while it may work in the very short term, the body will quickly adapt, like an accountant seeing your reckless spending and cutting back somewhere else. That’s why in all kinds of exercise except high-intensity interval training, a period of exercise will be followed by a metabolic slump, the body’s “austerity measures”, to balance the books.
You may be wondering: why is it different for HIIT? It’s because it changes things up frequently enough that the body doesn’t get a chance to adapt. To labor the financial metaphor, it involves lying to your accountant, so that the compensation is not made. Congratulations: you’re committing calorie fraud (but it’s good for the body, so hey).
That doesn’t mean other kinds of exercise are useless (or worse, necessarily counterproductive), though! Just, that we must acknowledge that other forms of exercise are great for various aspects of physical health (strengthening the body, mobilizing blood and lymph, preventing disease, enjoying mental health benefits, etc) that don’t really affect fat levels much (which are decided more in the kitchen than the gym—and even in the category of diet, it’s more about what and how and when you eat, rather than how much).
For more information on metabolic balance in the context of exercise, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Are You A Calorie-Burning Machine?
- Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism
- How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
- Lose Weight, But Healthily
- Build Muscle (Healthily!)
- How To Gain Weight (Healthily!)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What you need to know about xylazine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Xylazine is a non-opioid tranquilizer designed for veterinary use in animals. The sedative is not approved for use in people, yet it’s becoming more prevalent in the illicit drug supply.
Sometimes called “tranq,” it’s often mixed with other drugs, such as fentanyl, a potent opioid responsible for a growing number of overdose deaths. Last year, the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy declared fentanyl mixed with xylazine an “emerging threat.”
Read on to learn more about xylazine: what happens when people take it, what to do if an overdose is suspected, and how harm reduction tools can prevent overdose deaths.
How are people who use drugs exposed to xylazine?
Studies show people are exposed to xylazine—knowingly or unknowingly—when it’s mixed with other drugs like heroin, cocaine, meth, and, most frequently, fentanyl. When combined with opioids or other drugs, it increases the risk of a drug overdose.
What happens if someone takes xylazine?
Taking xylazine can cause drowsiness, amnesia, slow breathing, slow heart rate, dangerously low blood pressure, wounds that can become infected, and death, especially when taken in combination with other drugs.
Why does xylazine increase the risk of overdose?
Xylazine is a central nervous system depressant, which means that it slows down the body’s heart rate and breathing. It can also enhance the effects of other depressants, such as opioids, which may lead to suffocation.
What are the signs of a xylazine-related overdose?
Xylazine-related overdoses look like opioid overdoses. A person who has overdosed may exhibit a slow pulse, slow breathing, blurry vision, disorientation, drowsiness, confusion, blue skin, and loss of consciousness.
How many people die from xylazine-related overdoses in the U.S.?
Xylazine-related overdose deaths in the U.S. rose from 102 deaths in 2018 to 3,468 deaths in 2021. Most occurred in Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia. Fentanyl was the most frequently co-occurring drug involved in those deaths.
What should I do if an overdose is suspected?
If you suspect that a person has overdosed on any drug, call 911 and give them naloxone—sometimes sold under the brand name Narcan—a medication that can reverse an opioid overdose. You should also stay with the person who has overdosed until first responders arrive. Most states have Good Samaritan laws, which protect people who have overdosed and those assisting them from certain criminal penalties.
While naloxone cannot reverse the effects of xylazine alone, experts recommend administering naloxone if an overdose is suspected because it’s often mixed with opioids.
You can get naloxone for free from some nonprofit organizations and government-run programs. You can also purchase over-the-counter naloxone at pharmacies, grocery and convenience stores, and other retailers.
Learn how to use naloxone in this short training video from the American Medical Association, or sign up for a free online training.
How can people prevent xylazine-related overdoses?
Harm reduction programs are community programs that prevent drug overdoses, reduce the spread of infectious diseases, and connect people to medical care. These programs provide lifesaving tools like naloxone, as well as fentanyl and xylazine test strips, which can detect the presence of these drugs in a substance and prevent overdoses. Drug test strips can also be ordered online.
However, test strips are considered “drug paraphernalia” in some states and are not legal everywhere. Learn more about state laws around drug checking equipment from the Network for Public Health Law.
Learn more about harm reduction from the CDC.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
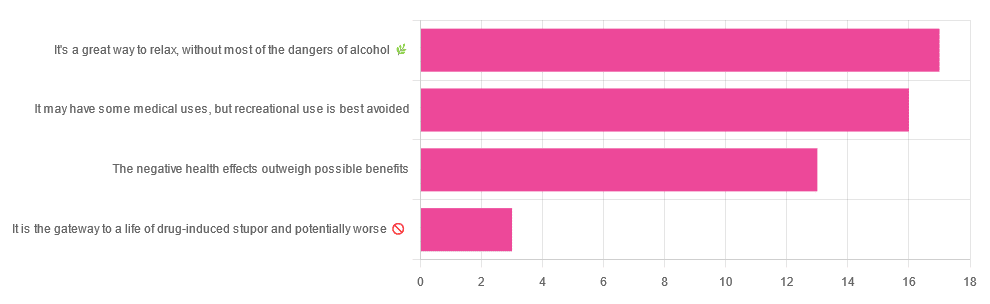
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
An unbroken night’s sleep is a myth. Here’s what good sleep looks like
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What do you imagine a good night’s sleep to be?
Often when people come into our sleep clinic seeking treatment, they share ideas about healthy sleep.
Many think when their head hits the pillow, they should fall into a deep and restorative sleep, and emerge after about eight hours feeling refreshed. They’re in good company – many Australians hold the same belief.
In reality, healthy sleep is cyclic across the night, as you move in and out of the different stages of sleep, often waking up several times. Some people remember one or more of these awakenings, others do not. Let’s consider what a healthy night’s sleep looks like.
Bricolage/Shutterstock Sleep cycles are a roller-coaster
As an adult, our sleep moves through different cycles and brief awakenings during the night. Sleep cycles last roughly 90 minutes each.
We typically start the night with lighter sleep, before moving into deeper sleep stages, and rising again into rapid eye movement (REM) sleep – the stage of sleep often linked to vivid dreaming.
If sleeping well, we get most of our deep sleep in the first half of the night, with REM sleep more common in the second half of the night.
Deepest sleep usually happens during the first half of the night. Verin/Shutterstock Adults usually move through five or six sleep cycles in a night, and it is entirely normal to wake up briefly at the end of each one. That means we might be waking up five times during the night. This can increase with older age and still be healthy. If you’re not remembering these awakenings that’s OK – they can be quite brief.
What does getting a ‘good’ sleep actually mean?
You’ll often hear that adults need between seven and nine hours of sleep per night. But good sleep is about more than the number of hours – it’s also about the quality.
For most people, sleeping well means being able to fall asleep soon after getting into bed (within around 30 minutes), sleeping without waking up for long periods, and waking feeling rested and ready for the day.
You shouldn’t be feeling excessively sleepy during the day, especially if you’re regularly getting at least seven hours of refreshing sleep a night (this is a rough rule of thumb).
But are you noticing you’re feeling physically tired, needing to nap regularly and still not feeling refreshed? It may be worthwhile touching base with your general practitioner, as there a range of possible reasons.
Common issues
Sleep disorders are common. Up to 25% of adults have insomnia, a sleep disorder where it may be hard to fall or stay asleep, or you may wake earlier in the morning than you’d like.
Rates of common sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnoea – where your breathing can partially or completely stop many times during the night – also increase with age, affecting 20% of early adults and 40% of people in middle age. There are effective treatments, so asking for help is important.
Beyond sleep disorders, our sleep can also be disrupted by chronic health conditions – such as pain – and by certain medications.
There can also be other reasons we’re not sleeping well. Some of us are woken by children, pets or traffic noise during the night. These “forced awakenings” mean we may find it harder to get up in the morning, take longer to leave bed and feel less satisfied with our sleep. For some people, night awakenings may have no clear cause.
A good way to tell if these awakenings are a problem for you is by thinking about how they affect you. When they cause feelings of frustration or worry, or are impacting how we feel and function during the day, it might be a sign to seek some help.
If waking up in the night is interfering with your normal day-to-day activities, it may indicate a problem. BearFotos/Shutterstock We also may struggle to get up in the morning. This could be for a range of reasons, including not sleeping long enough, going to bed or waking up at irregular times – or even your own internal clock, which can influence the time your body prefers to sleep.
If you’re regularly struggling to get up for work or family needs, it can be an indication you may need to seek help. Some of these factors can be explored with a sleep psychologist if they are causing concern.
Can my smart watch help?
It is important to remember sleep-tracking devices can vary in accuracy for looking at the different sleep stages. While they can give a rough estimate, they are not a perfect measure.
In-laboratory polysomnography, or PSG, is the best standard measure to examine your sleep stages. A PSG examines breathing, oxygen saturation, brain waves and heart rate during sleep.
Rather than closely examining nightly data (including sleep stages) from a sleep tracker, it may be more helpful to look at the patterns of your sleep (bed and wake times) over time.
Understanding your sleep patterns may help identify and adjust behaviours that negatively impact your sleep, such as your bedtime routine and sleeping environment.
And if you find viewing your sleep data is making you feel worried about your sleep, this may not be useful for you. Most importantly, if you are concerned it is important to discuss it with your GP who can refer you to the appropriate specialist sleep health provider.
Amy Reynolds, Associate Professor in Clinical Sleep Health, Flinders University; Claire Dunbar, Research Associate, Sleep Health, Flinders University; Gorica Micic, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Clinical Psychologist, Flinders University; Hannah Scott, Research Fellow in Sleep Health, Flinders University, and Nicole Lovato, Associate Professor, Adelaide Institute for Sleep Health, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: