Make Time – by Jake Knapp and John Zeratzky
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We live in an information-saturated world, and we have done for so long now that it’s easy to forget: we did not evolve for this!
It’s easy to say “unplug”, but the reality is:
We also have to actually function in this fast-paced info-dense world whether we want to or not, and we are expected to be able to handle it.
So… How?
Appropriately enough, authors Knapp and Zeratsky present the answer in a skimmer-friendly fashion, with summaries and bullet points and diagrams and emboldened text forease of speed-reading. Who uses such tricks?!
In short, less living life in “default mode scramble” and more about making an impact in the ways you actually want to, for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why is toddler milk so popular? Follow the money
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Toddler milk is popular and becoming more so. Just over a third of Australian toddlers drink it. Parents spend hundreds of millions of dollars on it globally. Around the world, toddler milk makes up nearly half of total formula milk sales, with a 200% growth since 2005. Growth is expected to continue.
We’re concerned about the growing popularity of toddler milk – about its nutritional content, cost, how it’s marketed, and about the impact on the health and feeding of young children. Some of us voiced our concerns on the ABC’s 7.30 program recently.
But what’s in toddler milk? How does it compare to cow’s milk? How did it become so popular?
What is toddler milk? Is it healthy?
Toddler milk is marketed as appropriate for children aged one to three years. This ultra-processed food contains:
- skim milk powder (cow, soy or goat)
- vegetable oil
- sugars (including added sugars)
- emulsifiers (to help bind the ingredients and improve the texture)
added vitamins and minerals.
Toddler milk is usually lower in calcium and protein, and higher in sugar and calories than regular cow’s milk. Depending on the brand, a serve of toddler milk can contain as much sugar as a soft drink.
Even though toddler milks have added vitamins and minerals, these are found in and better absorbed from regular foods and breastmilk. Toddlers do not need the level of nutrients found in these products if they are eating a varied diet.
Global health authorities, including the World Health Organization (WHO), and Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council, do not recommend toddler milk for healthy toddlers.
Some children with specific metabolic or dietary medical problems might need tailored alternatives to cow’s milk. However, these products generally are not toddler milks and would be a specific product prescribed by a health-care provider.
Toddler milk is also up to four to five times more expensive than regular cow’s milk. “Premium” toddler milk (the same product, with higher levels of vitamins and minerals) is more expensive.
With the cost-of-living crisis, this means families might choose to go without other essentials to afford toddler milk.
Toddler milk is more expensive than cow’s milk and contains more sugar.
Dragana Gordic/ShutterstockHow toddler milk was invented
Toddler milk was created so infant formula companies could get around rules preventing them from advertising their infant formula.
When manufacturers claim benefits of their toddler milk, many parents assume these claimed benefits apply to infant formula (known as cross-promotion). In other words, marketing toddler milks also boosts interest in their infant formula.
Manufacturers also create brand loyalty and recognition by making the labels of their toddler milk look similar to their infant formula. For parents who used infant formula, toddler milk is positioned as the next stage in feeding.
How toddler milk became so popular
Toddler milk is heavily marketed. Parents are told toddler milk is healthy and provides extra nutrition. Marketing tells parents it will benefit their child’s growth and development, their brain function and their immune system.
Toddler milk is also presented as a solution to fussy eating, which is common in toddlers.
However, regularly drinking toddler milk could increase the risk of fussiness as it reduces opportunities for toddlers to try new foods. It’s also sweet, needs no chewing, and essentially displaces energy and nutrients that whole foods provide.
Toddler milk is said to help fussy eating, but it may make things worse.
zlikovec/ShutterstockGrowing concern
The WHO, along with public health academics, has been raising concerns about the marketing of toddler milk for years.
In Australia, moves to curb how toddler milk is promoted have gone nowhere. Toddler milk is in a category of foods that are allowed to be fortified (to have vitamins and minerals added), with no marketing restrictions. The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission also has concerns about the rise of toddler milk marketing. Despite this, there is no change in how it’s regulated.
This is in contrast to voluntary marketing restrictions in Australia for infant formula.
What needs to happen?
There is enough evidence to show the marketing of commercial milk formula, including toddler milk, influences parents and undermines child health.
So governments need to act to protect parents from this marketing, and to put child health over profits.
Public health authorities and advocates, including us, are calling for the restriction of marketing (not selling) of all formula products for infants and toddlers from birth through to age three years.
Ideally, this would be mandatory, government-enforced marketing restrictions as opposed to industry self-regulation in place currently for infant formulas.
We musn’t blame parents
Toddlers are eating more processed foods (including toddler milk) than ever because time-poor parents are seeking a convenient option to ensure their child is getting adequate nutrition.
Formula manufacturers have used this information, and created a demand for an unnecessary product.
Parents want to do the best for their toddlers, but they need to know the marketing behind toddler milks is misleading.
Toddler milk is an unnecessary, unhealthy, expensive product. Toddlers just need whole foods and breastmilk, and/or cow’s milk or a non-dairy, milk alternative.
If parents are worried about their child’s eating, they should see a health-care professional.
Anthea Rhodes, a paediatrician from Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne and a lecturer at the University of Melbourne, co-authored this article.
Jennifer McCann, Lecturer Nutrition Sciences, Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University; Karleen Gribble, Adjunct Associate Professor, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Western Sydney University, and Naomi Hull, PhD candidate, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Focusing On Health In Our Sixties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What happens when you age in your sixties?❞
The good news is, a lot of that depends on you!
But, speaking on averages:
While it’s common for people to describe being over 50 as being “over the hill”, halfway to a hundred, and many greetings cards and such reflect this… Biologically speaking, our 60s are more relevant as being halfway to our likely optimal lifespan of 120. Humans love round numbers, but nature doesn’t care for such.
- In our 60s, we’re now usually the “wrong” side of the menopausal metabolic slump (usually starting at 45–55 and taking 5–10 years), or the corresponding “andropause” where testosterone levels drop (usually starting at 45 and a slow decline for 10–15 years).
- In our 60s, women will now be at a higher risk of osteoporosis, due to the above. The risk is not nearly so severe for men.
- In our 60s, if we’re ever going to get cancer, this is the most likely decade for us to find out.
- In our 60s, approximately half of us will suffer some form of hearing loss
- In our 60s, our body has all but stopped making new T-cells, which means our immune defenses drop (this is why many vaccines/boosters are offered to over-60s, but not to younger people)
While at first glance this does not seem a cheery outlook, knowledge is power.
- We can take HRT to avoid the health impact of the menopause/andropause
- We can take extra care to look after our bone health and avoid osteoporosis
- We can make sure we get the appropriate cancer screenings when we should
- We can take hearing tests, and if appropriate find the right hearing aids for us
- We can also learn to lip-read (this writer relies heavily on lip-reading!)
- We can take advantage of those extra vaccinations/boosters
- We can take extra care to boost immune health, too
Your body has no idea how many times you’ve flown around the sun and nor does it care. What actually makes a difference to it, is how it has been treated.
See also: Milestone Medical Tests You Should Take in Your 60s, 70s, and Beyond
Share This Post
-
52 Small Changes – by Brett Blumenthal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We see a lot of books that exhort us to get a six-pack in a month, change our life in 7 days, learn Japanese in 24 hours. The reality is, things take time!
Brett Blumenthal is more realistic while being just as motivational:
The idea is simple… Make one small change per week for 52 weeks, and at the end of the year, you’ll be healthier and happier.
At 10almonds, we’re big fans of small changes that add up (or rather: compound!) to make big differences, so this one’s absolutely our style!
Best of all, she offers us not just “do this” advice, but also “and here’s the information and resources you’ll need to make this change work the best it can for you”
The advices range in topic from nutrition to exercise to sleep to mental wellness to interpersonal stuff and more. The biggest focus is on personal health, though, with small changes to exercise and nutrition making up the lion’s share of the changes.
Bottom line: this is a book you’ll want to grab once a week. Consider setting a reminder on your phone to check in with it each Sunday, for example!
Take the first step and order “52 Small Changes” from Amazon today!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to pecans, we picked the pistachios.
Why?
Firstly, the macronutrients: pistachios have twice as much protein and fiber. Pecans have more fat, though in both of these nuts the fats are healthy.
The category of vitamins is an easy win for pistachios, with a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, and E. Especially the 8x vitamin A, 7x vitamin B6, 4x vitamin C, and 2x vitamin E, and as the percentages are good too, these aren’t small differences. Pecans, meanwhile, boast only a little more vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid, the one whose name means “it’s everywhere”, because that’s how easy it is to get it).
In terms of minerals, pistachios have more calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while pecans have more manganese and zinc. So, a fair win for pistachios on this one.
Adding up the three different kinds of win for pistachios means that *drumroll* pistachios win overall, and it’s not close.
As ever, do enjoy both though, because diversity is healthy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Anti-Cholesterol Cardamom & Pistachio Porridge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This tasty breakfast’s beta-glucan content binds to cholesterol and carries it out of the body; there are lots of other nutritional benefits too!
You will need
- 1 cup coconut milk
- ⅓ cup oats
- 4 tbsp crushed pistachios
- 6 cardamom pods, crushed
- 1 tsp rose water or 4 drops edible rose essential oil
- Optional sweetener: drizzle of honey or maple syrup
- Optional garnishes: rose petals, chopped nuts, dried fruit
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat the coconut milk, adding the oats and crushed cardamom pods. Simmer for 5–10 minutes depending on how cooked you want the oats to be.
2) Stir in the crushed pistachio nuts, as well as the rose water.
3) Serve in a bowl, adding any optional toppings:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s beta-glucan, which is fund abundantly in oats
- Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← coconut can!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I’ve recovered from a cold but I still have a hoarse voice. What should I do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cold, flu, COVID and RSV have been circulating across Australia this winter. Many of us have caught and recovered from one of these common upper respiratory tract infections.
But for some people their impact is ongoing. Even if your throat isn’t sore anymore, your voice may still be hoarse or croaky.
So what happens to the voice when we get a virus? And what happens after?
Here’s what you should know if your voice is still hoarse for days – or even weeks – after your other symptoms have resolved.
Why does my voice get croaky during a cold?
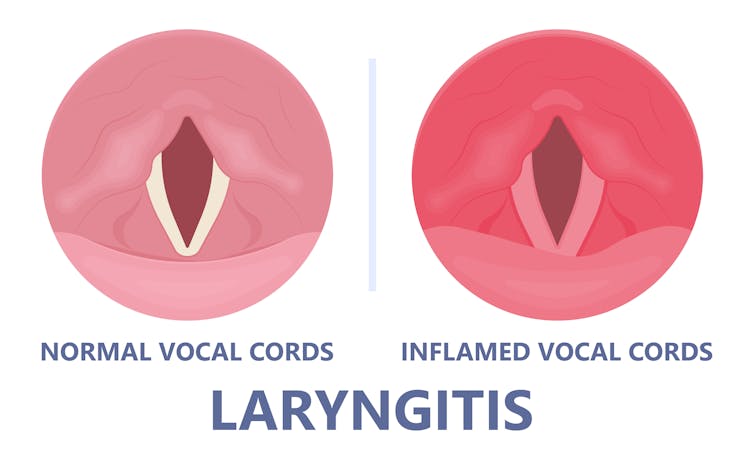
A healthy voice is normally clear and strong. It’s powered by the lungs, which push air past the vocal cords to make them vibrate. These vibrations are amplified in the throat and mouth, creating the voice we hear.
The vocal cords are two elastic muscles situated in your throat, around the level of your laryngeal prominence, or Adam’s apple. (Although everyone has one, it tends to be more pronounced in males.) The vocal cords are small and delicate – around the size of your fingernail. Any small change in their structure will affect how the voice sounds.
When the vocal cords become inflamed – known as laryngitis – your voice will sound different. Laryngitis is a common part of upper respiratory tract infections, but can also be caused through misuse.
Viruses such as the common cold can inflame the vocal cords. Pepermpron/Shutterstock Catching a virus triggers the body’s defence mechanisms. White blood cells are recruited to kill the virus and heal the tissues in the vocal cords. They become inflamed, but also stiffer. It’s harder for them to vibrate, so the voice comes out hoarse and croaky.
In some instances, you may find it hard to speak in a loud voice or have a reduced pitch range, meaning you can’t go as high or loud as normal. You may even “lose” your voice altogether.
Coughing can also make things worse. It is the body’s way of trying to clear the airways of irritation, including your own mucus dripping onto your throat (post-nasal drip). But coughing slams the vocal cords together with force.
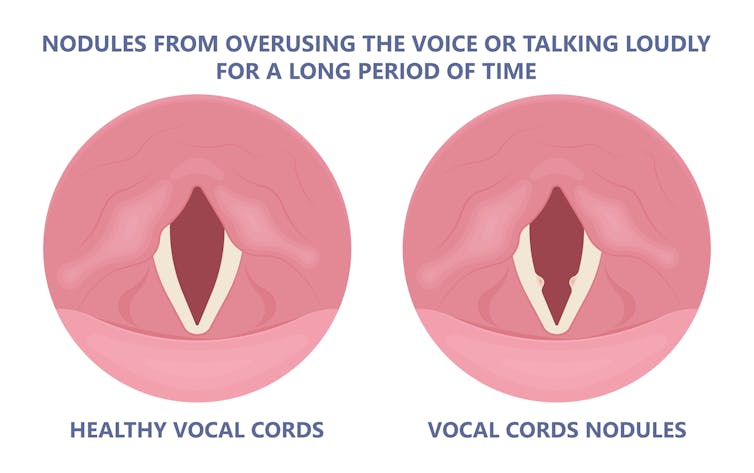
Chronic coughing can lead to persistent inflammation and even thicken the vocal cords. This thickening is the body trying to protect itself, similar to developing a callus when a pair of new shoes rubs.
Thickening on your vocal cords can lead to physical changes in the vocal cords – such as developing a growth or “nodule” – and further deterioration of your voice quality.
Coughing and exertion can cause inflamed vocal cords to thicken and develop nodules. Pepermpron/Shutterstock How can you care for your voice during infection?
People who use their voices a lot professionally – such as teachers, call centre workers and singers – are often desperate to resume their vocal activities. They are more at risk of forcing their voice before it’s ready.
The good news is most viral infections resolve themselves. Your voice is usually restored within five to ten days of recovering from a cold.
Occasionally, your pharmacist or doctor may prescribe cough suppressants to limit additional damage to the vocal cords (among other reasons) or mucolytics, which break down mucus. But the most effective treatments for viral upper respiratory tract infections are hydration and rest.
Drink plenty of water, avoid alcohol and exposure to cigarette smoke. Inhaling steam by making yourself a cup of hot water will also help clear blocked noses and hydrate your vocal cords.
Rest your voice by talking as little as possible. If you do need to talk, don’t whisper – this strains the muscles.
Instead, consider using “confidential voice”. This is a soft voice – not a whisper – that gently vibrates your vocal cords but puts less strain on your voice than normal speech. Think of the voice you use when communicating with someone close by.
During the first five to ten days of your infection, it is important not to push through. Exerting the voice by talking a lot or loudly will only exacerbate the situation. Once you’ve recovered from your cold, you can speak as you would normally.
What should you do if your voice is still hoarse after recovery?
If your voice hasn’t returned to normal after two to three weeks, you should seek medical attention from your doctor, who may refer you to an ear nose and throat specialist.
If you’ve developed a nodule, the specialist would likely refer you to a speech pathologist who will show you how to take care of your voice. Many nodules can be treated with voice therapy and don’t require surgery.
You may have also developed a habit of straining your vocal cords, if you forced yourself to speak or sing while they were inflamed. This can be a reason why some people continue to have a hoarse voice even when they’ve recovered from the cold.
In those cases, a speech pathologist may play a valuable role. They may teach you to exercises that make voicing more efficient. For example, lip trills (blowing raspberries) are a fun and easy way you can learn to relax the voice. This can help break the habit of straining your voice you may have developed during infection.
Yeptain Leung, Postdoctoral Research and Lecturer of Speech Pathology, School of Health Sciences, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: