Longevity Noodles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Noodles may put the “long” into “longevity”, but most of the longevity here comes from the ergothioneine in the mushrooms! The rest of the ingredients are great too though, including the noodles themselves—soba noodles are made from buckwheat, which is not a wheat, nor even a grass (it’s a flowering plant), and does not contain gluten*, but does count as one of your daily portions of grains!
*unless mixed with wheat flour—which it shouldn’t be, but check labels, because companies sometimes cut it with wheat flour, which is cheaper, to increase their profit margin
You will need
- 1 cup (about 9 oz; usually 1 packet) soba noodles
- 6 medium portobello mushrooms, sliced
- 3 kale leaves, de-stemmed and chopped
- 1 shallot, chopped, or ¼ cup chopped onion of any kind
- 1 carrot, diced small
- 1 cup peas
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tbsp rice vinegar
- 1 tsp grated fresh ginger
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tbsp low-sodium soy sauce
- Avocado oil, for frying (alternatively: extra virgin olive oil or cold-pressed coconut oil are both perfectly good substitutions)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the soba noodles per the packet instructions, rinse, and set aside
2) Heat a little oil in a skillet, add the shallot, and cook for about 2 minutes.
3) Add the carrot and peas and cook for 3 more minutes.
4) Add the mushrooms, kale, garlic, ginger, peppers, and vinegar, and cook for 1 more minute, stirring well.
5) Add the noodles, as well as the MSG or low-sodium soy sauce, and cook for yet 1 more minute.
6) Serve!

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Rice vs Buckwheat – Which is Healthier?
- The Magic Of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← 4/5 of these spices are in today’s dish!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nutrivore – by Dr. Sarah Ballantyne
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The core idea of this book is that foods can be assigned a numerical value according to their total nutritional value, and that this number can be used to guide a person’s diet such that we will eat, in aggregate, a diet that is more nutritious. So far, so simple.
What Dr. Ballantyne also does, besides explaining and illustrating this system (there are chapters explaining the calculation system, and appendices with values), is also going over what to consider important and what we can let slide, and what things we might need more of to address a wide assortment of potential health concerns. And yes, this is definitely a “positive diet” approach, i.e. it focuses on what to add in, not what to cut out.
The premise of the “positive diet” approach is simple, by the way: if we get a full set of good nutrients, we will be satisfied and not crave unhealthy food.
She also offers a lot of helpful “rules of thumb”, and provides a variety of cheat-sheets and suchlike to make things as easy as possible.
There’s also a recipes section! Though, it’s not huge and it’s probably not necessary, but it’s just one more “she’s thinking of everything” element.
Bottom line: if you’d like a single-volume “Bible of” nutrition-made-easy, this is a very usable tome.
Click here to check out Nutrivore, and start filling up your diet!
Share This Post
-
Eat to Your Heart’s Content – by Dr. Sat Bains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Making food heart-healthy and tasty is a challenge that vexes many, but it doesn’t have to be so difficult.
Dr. Sat Bains, a professional chef with multiple Michelin stars to his name, is an expert on “tasty”, and after surviving a heart attack himself, he’s become an expert on “heart-healthy” since then.
The book contains not only the recipes (of which there are 68, by the way), but also large sections of explanation of what makes various ingredients or methods heart-healthy or heart-unhealthy.
There’s science in there too, and these sections were written under the guidance of Dr. Neil Williams, a lecturer in physiology and nutrition.
You may be wondering as to why the author himself has a doctorate too; in fact he has three, none of which are relevant:
- Doctor of Arts
- Doctor of Laws
- Doctor of Hospitality (Honorary)
…but we prefix “Dr.” when people are that and he is that. The expertise we’re getting here though is really his culinary skill and extracurricular heart-healthy learning, plus Dr. Williams’ actual professional health guidance.
Bottom line: if you’d like heart-healthy recipes with restaurant-level glamour, this book is a fine choice.
Click here to check out Eat To Your Heart’s Content, and look after yours!
Share This Post
-
Move – by Caroline Williams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
- Get 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, says the American Heart Association
- There are over 10,000 minutes per week, says the pocket calculator
Is 150/10,000 really the goal here? Really?
For Caroline Williams, the answer is no.
In this book that’s practically a manifesto, she outlines the case that:
- Humans evolved to move
- Industrialization and capitalism scuppered that
- We now spend far too long each day without movement
Furthermore, for Williams this isn’t just an anthropological observation, it’s a problem to be solved, because:
- Our lack of movement is crippling us—literally
- Our stagnation affects not just our bodies, but also our minds
- (again literally—there’s a direct correlation with mental health)
- We urgently need to fix this
So, what now, do we need to move in to the gym and become full-time athletes to clock up enough hours of movement? No.
Williams convincingly argues the case (using data from supercentenarian “blue zones” around the world) that even non-exertive movement is sufficient. In other words, you don’t have to be running; walking is great. You don’t have to be lifting weights; doing the housework or gardening will suffice.
From that foundational axiom, she calls on us to find ways to build our life around movement… rather than production-efficiency and/or convenience. She gives plenty of tips for such too!
Bottom line: some books are “I couldn’t put it down!” books. This one’s more of a “I got the urge to get up and get moving!” book.
Get your get-up-and-go up and going with “Move”—order yours from Amazon today!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Our family is always glued to separate devices. How can we connect again?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Saturday afternoon and the kids are all connected to separate devices. So are the parents. Sounds familiar?
Many families want to set ground rules to help them reduce their screen time – and have time to connect with each other, without devices.
But it can be difficult to know where to start and how to make a plan that suits your family.
First, look at your own screen time
Before telling children to “hop off the tech”, it’s important parents understand how much they are using screens themselves.
Globally, the average person spends an average of six hours and 58 minutes on screens each day. This has increased by 13%, or 49 minutes, since 2013.
Parents who report high screen time use tend to see this filtering down to the children in their family too. Two-thirds of primary school-aged children in Australia have their own mobile screen-based device.
Australia’s screen time guidelines recommended children aged five to 17 years have no more than two hours of sedentary screen time (excluding homework) each day. For those aged two to five years, it’s no more than one hour a day. And the guidelines recommend no screen time at all for children under two.
Yet the majority of children, across age groups, exceed these maximums. A new Australian study released this week found the average three-year-old is exposed to two hours and 52 minutes of screen time a day.
Some screen time is OK, too much increases risks
Technology has profoundly impacted children’s lives, offering both opportunities and challenges.
On one hand, it provides access to educational resources, can develop creativity, facilitates communication with peers and family members, and allows students to seek out new information.
On the other hand, excessive screen use can result in too much time being sedentary, delays in developmental milestones, disrupted sleep and daytime drowsiness.
Disrupted sleep can leave children tired the next day.
Yulia Raneva/ShutterstockToo much screen time can affect social skills, as it replaces time spent in face-to-face social interactions. This is where children learn verbal and non-verbal communication, develop empathy, learn patience and how to take turns.
Many families also worry about how to maintain a positive relationship with their children when so much of their time is spent glued to screens.
What about when we’re all on devices?
When families are all using devices simultaneously, it results in less face-to-face interactions, reducing communication and resulting in a shift in family dynamics.
The increased use of wireless technology enables families to easily tune out from each other by putting in earphones, reducing the opportunity for conversation. Family members wearing earphones during shared activities or meals creates a physical barrier and encourages people to retreat into their own digital worlds.
Wearing earphones for long periods may also reduce connection to, and closeness with, family members. Research from video gaming, for instance, found excessing gaming increases feelings of isolation, loneliness and the displacement of real-world social interactions, alongside weakened relationships with peers and family members.
How can I set screen time limits?
Start by sitting down as a family and discussing what limits you all feel would be appropriate when using TVs, phones and gaming – and when is an appropriate time to use them.
Have set rules around family time – for example, no devices at the dinner table – so you can connect through face-to-face interactions.
One rule might be no devices at the dinner table.
Monkey Business Images/ShutterstockConsider locking your phone or devices away at certain periods throughout the week, such as after 9pm (or within an hour of bedtime for younger children) and seek out opportunities to balance your days with physical activities, such kicking a footy at the park or going on a family bush walk.
Parents can model healthy behaviour by regulating and setting limits on their own screen time. This might mean limiting your social media scrolling to 15 or 30 minutes a day and keeping your phone in the next room when you’re not using it.
When establishing appropriate boundaries and ensuring children’s safety, it is crucial for parents and guardians to engage in open communication about technology use. This includes teaching critical thinking skills to navigate online content safely and employing parental control tools and privacy settings.
Parents can foster a supportive and trusting relationship with children from an early age so children feel comfortable discussing their online experiences and sharing their fears or concerns.
For resources to help you develop your own family’s screen time plan, visit the Raising Children Network.
Elise Waghorn, Lecturer, School of Education, RMIT University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
“If the hardest thing you have to do in your day is eat a frog, eat that frog first!”, they say.
And, broadly speaking, it is indeed good to get anything stressful out of the way early, so that we can relax afterwards. But…
- Are we truly best at frog-eating when blurry-eyed and sleepy?
- Is there a spoonful of sugar that could make the medicine go down better?
- What do we need to turn eating the frog into an enjoyable activity?
Flow
“Flow” is a concept brought to public consciousness by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, and it refers to a state in which we feel good about what we’re doing, and just keep doing, at a peak performance level.
Writer’s note: as a writer, for example…
Sometimes I do not want to write, I pace to and fro near my computer, going on side-quests like getting a coffee or gazing out of the window into my garden. But once I get going, suddenly, something magical happens and before I know it, I have to trim my writing down because I’ve written too much. That magical window of effortless productivity was a state of flow.
Good morning!
What is a good morning, to you? Build that into your morning! Set parameters around it so you don’t get carried away timewise and find yourself in the afternoon (unless that would work for you!), but first thing in the morning is the time to light up each part of your brain with appropriate neurotransmitters.
Getting the brain juices flowing
Cortisol
When we wake up, we (unless we have some neurochemical imbalance, such as untreated depression) get a spike of cortisol. Cortisol is much-maligned and feared, and indeed it can be very much deleterious to the health in cases of chronic stress. But a little spike now and again is actually beneficial for us.
Quick Tip: if you want to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning cortisol spike, a cold shower is the way to go. Or even just a face-plunge into a bowl of ice-water (put ice in it, give it a couple of minutes to chill the water, then put your face in for a count of 30 seconds, or less if you can’t hold your breath that long).
Serotonin
Serotonin is generally thought of as “the happy chemical”, and it’s stimulated by blue/white light, and also by seeing greenery.
Quick tip: to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning serotonin boost, your best friend is sunlight. Even sun through a partly-clouded sky will tend to outperform artificial lighting, including artificial sunlight lighting. Try to get sun between 08:30 and 09:00, if you can. Best of all, do it in your garden or nearby park, as the greenery will be an extra boost!
Dopamine
Generally thought of as “the reward chemical”, but it’s also critical for a lot of kinds of brainwork, including language processing and problem-solving.
Quick Tip: to artificially stimulate* a dopamine surge to get you going, do something that you and/or your body finds rewarding. Examples include:
- Exercise, especially in a vigorous burst
- A good breakfast, a nice coffee, whatever feels right to you
- An app that has motivational bells and whistles, a streak for you to complete, etc
Note: another very enjoyable activity might come to mind that doesn’t even require you getting out of bed. Be aware, however, gentleman-readers specifically, that if you complete that activity, you’ll get a prolactin spike that will wipe out the dopamine you just worked up (because prolactin is antagonistic to dopamine). So that one’s probably better for a lazy morning when you can go back to sleep, than a day when you want to get up and go! Ladies, this is less of a worry for us as the physiology an orgasm driven by estrogen+progesterone rather than testosterone is different; there will not usually be a prolactin spike following the spike of dopamine; our orgasm-related dopamine spike is followed by a wave of oxytocin instead (“the cuddle chemical”), which is much more pleasant than prolactin.
*there’s no “(or enhance)” for this one; you won’t get dopamine from doing nothing, that’s just not how “the reward chemical” works
Flow-building in a stack
When you’ve just woken up and are in a blurry morning haze, that’s not the time to be figuring out “what should I be doing next?”, so instead:
- Work out the things you want to incorporate into your morning routine
- Put them in the order that will be easiest to perform—some things will go a lot better after others!
- Remember to also include things that are simply necessary—morning bathroom ablutions, for example
The goal here is to have a this-and-this-and-this-and-this list of items that you can go through without any deviations, and get in the habit of “after item 1 I automatically do item 2, after which I automatically do item 3, after which…”
Implement this, and your mornings will become practically automated, but in a joyous, life-enhancing way that sets you up in good order for whatever you want/need to do!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
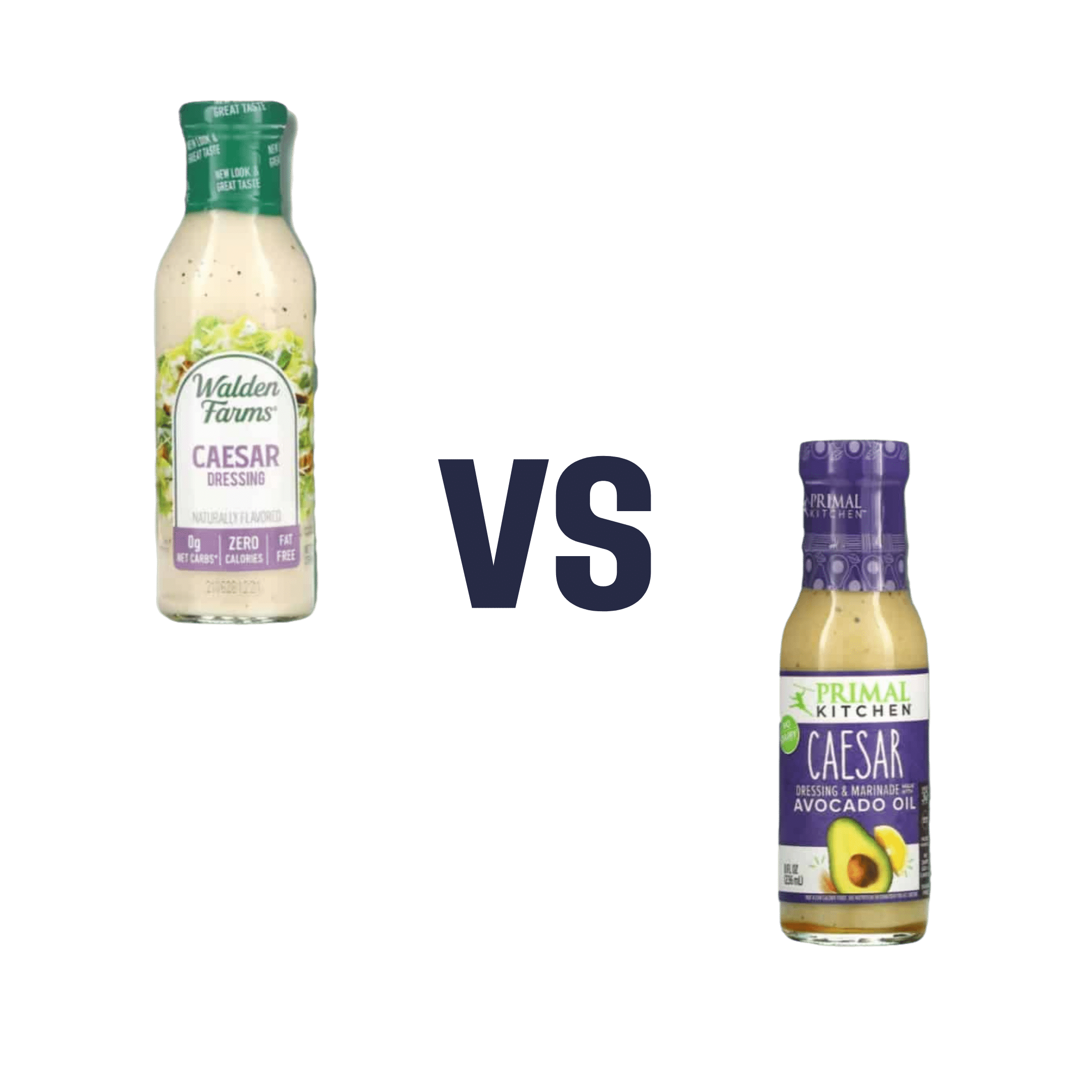
Walden Farms Caesar Dressing vs. Primal Kitchen Caesar Dressing – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Walden Farms Caesar Dressing to Primal Kitchen Caesar Dressing, we picked the Primal Kitchen.
Why?
As you can see from the front label, the Walden Farms product has 0 net carbs, 0 calories, and 0 fat. In fact, its ingredients list begins:
Water, white distilled vinegar, erythritol, corn fiber, salt, microcrystalline cellulose, xanthan gum, titanium dioxide (color)
…before it gets to something interesting (garlic purée), by which point the amount must be miniscule.
The Primal Kitchen product, meanwhile, has 140 calories per serving and 15g fat (of which, 1.5g is saturated). However! The ingredients list this time begins:
Avocado oil, water, organic coconut aminos (organic coconut sap, sea salt), organic apple cider vinegar, organic distilled vinegar, mushroom extract, organic gum acacia, organic guar gum
…before it too gets to garlic, which this time, by the way, is organic roasted garlic.
In case you’re wondering about the salt content in both, they add up to 190mg for the Walden Farms product, and 240mg for the Primal Kitchen product. We don’t think that the extra 50mg (out of a daily allowance of 2300–5000mg, depending on whom you ask) is worthy of note.
In short, the Walden Farms product is made of mostly additives of various kinds, whereas the Primal Kitchen product is made of mostly healthful ingredients.
So, the calories and fat are nothing to fear.
For this reason, we chose the product with more healthful ingredients—but we acknowledge that if you are specifically trying to keep your calories down, then the Walden Farms product may be a valid choice.
Read more:
• Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
• Caloric Restriction with Optimal NutritionDon’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: