Limitless Expanded Edition – by Jim Kwik
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a little flashier in presentation than we usually go for here, but the content is actually very good. Indeed, we’ve featured Jim Kwik before, with different, but also good content—in that case, physical exercises that strengthen the brain.
This time, Kwik (interspersed with motivational speeches that you may or may not benefit from, but they are there) offers a step-by-step course in improving various metrics of cognitive ability. His methods were produced by trial and error, and now have been refined and enjoyed by man. If it sounds like a sales gimmick, it is a bit, but the good news is that everything you need to benefit is in the book; it’s not about upselling to a course or “advanced” books or whatnot.
The style is enthusiastically conversational, and instructions when given (which is often) are direct and clear.
Bottom line: one of the most critical abilities a brain can have is the ability to improve itself, so whatever level your various cognitive abilities are at right now, if you apply this book, you will almost certainly improve in one or more areas, which will make it worth the price of the book.
Click here to check out Limitless, and find out what you can do!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cherries vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cherries to cranberries, we picked the cherries.
Why?
In terms of macros, cherries have a little more protein (but it’s not much) while cranberries have a little more fiber. Despite this, cherries have the lower glycemic index—about half that of cranberries.
In the category of vitamins, cherries have a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B9, and a little more choline, while cranberries have more of vitamins B5, B6, C, E, and K. A modest win for cherries here.
When it comes to minerals, things are more divided: cherries have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while cranberries have more manganese. An easy win for cherries here.
This all adds up to a total win for cherries, but both of these fruits are great and both have their own beneficial properties (see our main features below!)
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
- Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Artichoke vs Asparagus – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing artichoke to asparagus, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Both are great and it was close!
In terms of macros, artichoke has a little more protein and around 3x the carbs and fiber: the ratio there means that both vegetables have an identical glycemic index, so we’ll go with the “most food per food” reckoning of nutritional density, and call it for the artichoke.
When it comes to vitamins, artichoke has more of vitamins B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline, while asparagus has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, E, and K. Both very respectable nutritional sets, but artichoke gets a marginal 6:5 win on strength of numbers.
In the category of minerals, artichoke has more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while asparagus has more iron, selenium, and zinc. A clearer 6:3 win for artichoke this time.
Once again, both of these are great foods, so by all means enjoy either or both. But if you’re looking for the nutritionally densest option, it’s the artichoke!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How light tells you when to sleep, focus and poo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
Exposure to light is crucial for our physical and mental health, as this and future articles in the series will show.
But the timing of that light exposure is also crucial. This tells our body to wake up in the morning, when to poo and the time of day to best focus or be alert. When we’re exposed to light also controls our body temperature, blood pressure and even chemical reactions in our body.
But how does our body know when it’s time to do all this? And what’s light got to do with it?
nymphoenix/Shutterstock What is the body clock, actually?
One of the key roles of light is to re-set our body clock, also known as the circadian clock. This works like an internal oscillator, similar to an actual clock, ticking away as you read this article.
But rather than ticking you can hear, the body clock is a network of genes and proteins that regulate each other. This network sends signals to organs via hormones and the nervous system. These complex loops of interactions and communications have a rhythm of about 24 hours.
In fact, we don’t have one clock, we have trillions of body clocks throughout the body. The central clock is in the hypothalamus region of the brain, and each cell in every organ has its own. These clocks work in concert to help us adapt to the daily cycle of light and dark, aligning our body’s functions with the time of day.
However, our body clock is not precise and works to a rhythm of about 24 hours (24 hours 30 minutes on average). So every morning, the central clock needs to be reset, signalling the start of a new day. This is why light is so important.
The central clock is directly connected to light-sensing cells in our retinas (the back of the eye). This daily re-setting of the body clock with morning light is essential for ensuring our body works well, in sync with our environment.
In parallel, when we eat food also plays a role in re-setting the body clock, but this time the clock in organs other than the brain, such as the liver, kidneys or the gut.
So it’s easy to see how our daily routines are closely linked with our body clocks. And in turn, our body clocks shape how our body works at set times of the day.
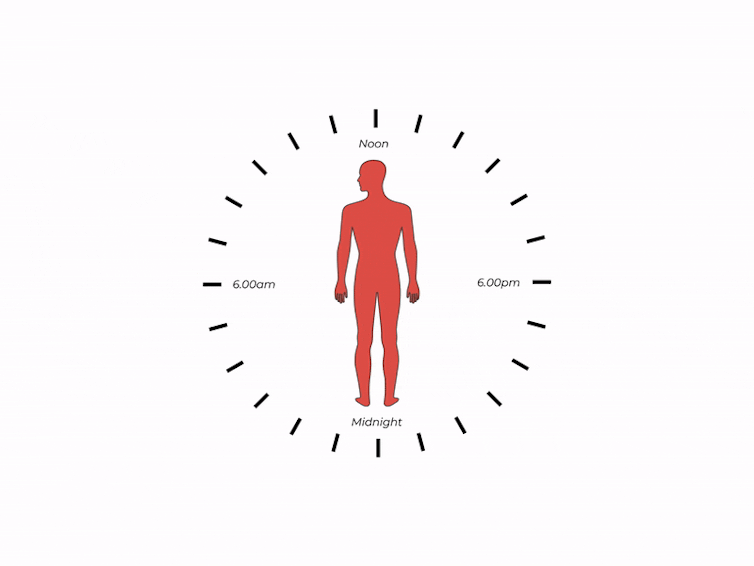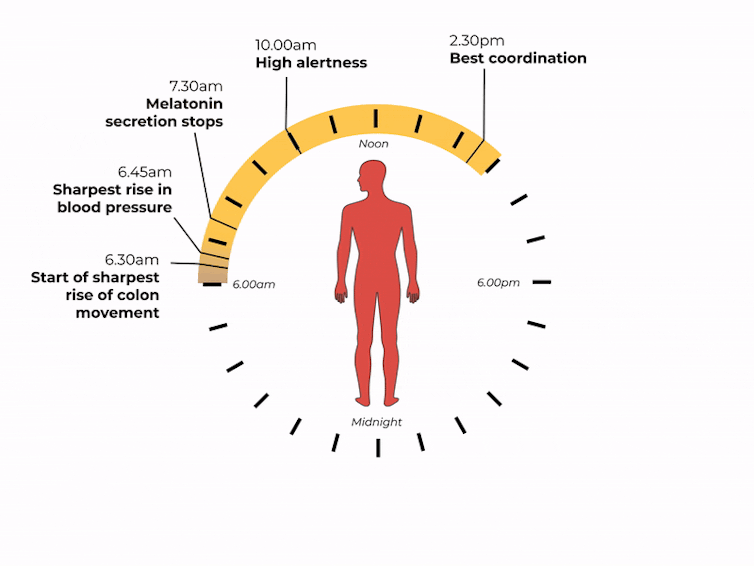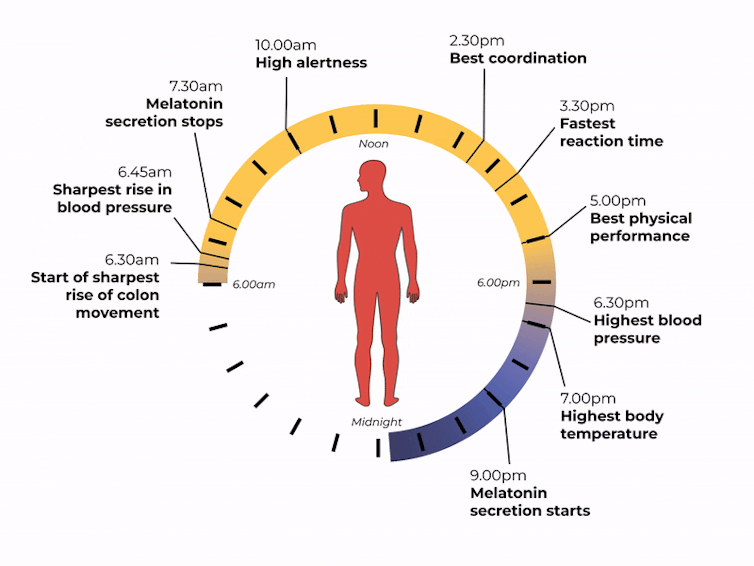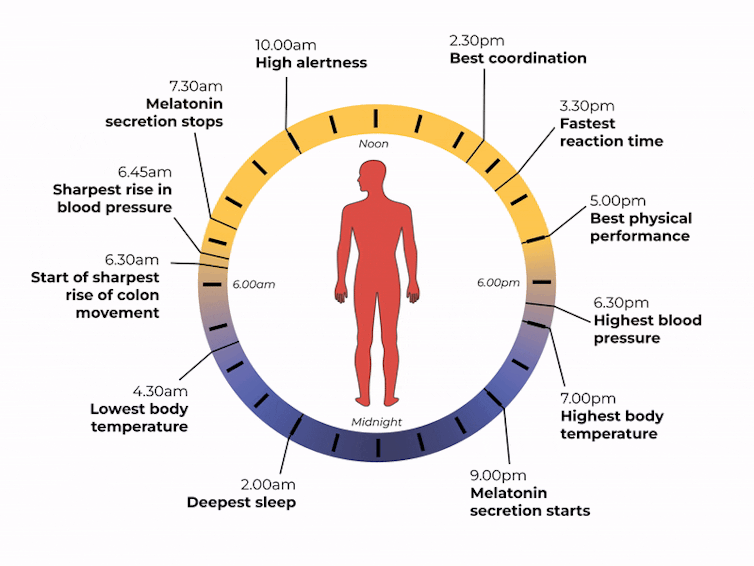
What time of day?
Matt Garrow/The Conversation. Adapted from Delos, CC BY Let’s take a closer look at sleep
The naturally occurring brain hormone melatonin is linked to our central clock and makes us feel sleepy at certain times of day. When it’s light, our body stops making melatonin (its production is inhibited) and we are alert. Closer to bedtime, the hormone is made, then secreted, making us feel drowsy.
Our sleep is also partly controlled by our genes, which are part of our central clock. These genes influence our chronotype – whether we are a “lark” (early riser), “night owl” (late sleeper) or a “dove” (somewhere in between).
But exposure to light at night when we are supposed to be sleeping can have harmful effects. Even dim light from light pollution can impair our heart rate and how we metabolise sugar (glucose), may lead to psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder, and increases the overall risk of premature death.
The main reason for these harmful effects is that light “at the wrong time” disturbs the body clock, and these effects are more pronounced for “night owls”.
This “misaligned” exposure to light is also connected to the detrimental health effects we often see in people who work night shifts, such as an increased risk of cancer, diabetes and heart disease.
How about the gut?
Digestion also follows a circadian rhythm. Muscles in the colon that help move waste are more active during the day and slow down at night.
The most significant increase in colon movement starts at 6.30am. This is one of the reasons why most people feel the urge to poo in the early morning rather than at night.
The gut’s day-night rhythm is a direct result of the action of the gut’s own clock and the central clock (which synchronises the gut with the rest of the body). It’s also influenced by when we eat.
At 6.30am, your gut really begins to get going for the day. Rendra Dria Septia Aji/Shutterstock How about focusing?
Our body clock also helps control our attention and alertness levels by changing how our brain functions at certain times of day. Attention and alertness levels improve in the afternoon and evening but dip during the night and early morning.
Those fluctuations impact performance and can lead to decreased productivity and an increased risk of errors and accidents during the less-alert hours.
So it’s important to perform certain tasks that require our attention at certain times of day. That includes driving. In fact, disruption of the circadian clock at the start of daylight savings – when our body hasn’t had a chance to adapt to the clocks changing – increases the risk of a car accident, particularly in the morning.
What else does our body clock control?
Our body clock influences many other aspects of our biology, including:
- physical performance by controlling the activity of our muscles
- blood pressure by controlling the system of hormones involved in regulating our blood volume and blood vessels
- body temperature by controlling our metabolism and our level of physical activity
- how our body handles drugs and toxins by controlling enzymes involved in how the liver and kidneys eliminate these substances from the body.
If you can, avoid driving long distances at night, as you’ll be less alert. trendobjects/Shutterstock Morning light is important
But what does this all mean for us? Exposure to light, especially in the morning, is crucial for synchronising our circadian clock and bodily functions.
As well as setting us up for a good night’s sleep, increased morning light exposure benefits our mental health and reduces the risk of obesity. So boosting our exposure to morning light – for example, by going for a walk, or having breakfast outside – can directly benefit our mental and metabolic health.
However, there are other aspects about which we have less control, including the genes that control our body clock.
Frederic Gachon, Associate Professor, Physiology of Circadian Rhythms, Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland and Benjamin Weger, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Heart Healthy Diet Plan – by Stephen William
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve covered heart-healthy cooking books before, but variety is good, and boredom is an enemy of health, so let’s shake it up with a fresh stack of recipes!
After a brief overview of the relevant science (which if you’re a regular 10almonds reader, probably won’t be new to you), the author takes the reader on a 28-day journey. Yes, we know the subtitle says 30 days, but unless they carefully hid the other two days somewhere we didn’t find, there are “only” 28 inside. Perhaps the publisher heard it was a month and took creative license. Or maybe there’s a different edition. Either way…
Rather than merely giving a diet plan (though yes, he also does that), he gives a wide range of “spotlight ingredients”, such that many of the recipes, while great in and of themselves, can also be jumping-off points for those of us who like to take recipes and immediately do our own things to them.
Each day gets a breakfast, lunch, dinner, and he also covers drinks, desserts, and such like.
Notwithstanding the cover art being a lot of plants, the recipes are not entirely plant-based; there are a selection of fish dishes (and other seafood, e.g. shrimp) and also some dairy products (e.g. Greek yoghurt). The recipes are certainly very “plant-forward” though and many are just plants. If you’re a strict vegan though, this probably isn’t the book for you.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cook heart-healthy but are often stuck wondering “aaah, what to cook again today?”, then this is the book to get you out of any culinary creative block!
Click here to check out the Heart Healthy Diet Plan, and widen your heart-healthy repertoire!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Heart Smarter for Women – by Dr. Jennifer Mieres
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Mieres takes us through understanding our own heart disease risks as individuals rather than as averages. As the title suggests, she does assume a female readership, so if you are a man and have no female loved ones, this might not be the book for you. But aside from that, she walks us through examining risk in the context of age, other health conditions, lifestyle factors, and so forth—including not turning a blind eye to factors that might intersect, such as for example if a physical condition reduces how much we can exercise, or if there’s some reason we can’t follow the usual gold standard of heart-healthy diet.
On which note, she does offer dietary advice, including information around recipes, meal-planning, and what things to always have in stock, as well as what things matter the most when it comes to what and how we eat.
It’s not all lifestyle medicine though; Dr. Mieres gives due attention to many of the medications available for heart health issues—and the pros and cons of these.
The style of the book is very simple and readable pop-science, without undue jargon, and with a generous glossary. As with many books of this genre, it does rely on (presumably apocryphal) anecdotes, though an interesting choice for this book is that it keeps a standing cast of four recurring characters, each to represent a set of circumstances and illustrate how certain things can go differently for different people, with different things then being needed and/or possible. Hopefully, any given reader will find themself represented at least moderately well somewhere in or between these four characters.
Bottom line: this is a very informative and accessible book, that demystifies a lot of common confusions around heart health.
Click here to check out Heart Smarter For Women, and take control of your health!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Corn Chips vs Potato Chips: Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing corn chips to potato chips, we picked the corn chips.
Why?
First, let it be said, this was definitely a case of “lesser evil voting” as there was no healthy choice here. But as for which is relatively least unhealthy…
Most of the macronutrient and micronutrient profile is quite similar. Both foods are high carb, moderately high fat, negligible protein, and contain some trace minerals and even some tiny amounts of vitamins. Both are unhealthily salty.
Exact numbers will of course vary from one brand’s product to another, but you can see some indicative aggregate scores here in the USDA’s “FoodData Central” database:
The biggest health-related difference that doesn’t have something to balance it out is that the glycemic index of corn chips averages around 63, whereas the glycemic index of potato chips averages around 70 (that is worse).
That’s enough to just about tip the scales in favor of corn chips.
The decision thus having been made in favor of corn chips (and the next information not having been part of that decision), we’ll mention one circumstantial extra benefit to corn chips:
Corn chips are usually eaten with some kind of dip (e.g. guacamole, sour cream, tomato salsa, etc) which can thus deliver actual nutrients. Potato chips meanwhile are generally eaten with no additional nutrients. So while we can’t claim the dip as being part of the nutritional make-up of the corn chips, we can say:
If you’re going to have a habit of eating one or the other, then corn chips are probably the least unhealthy of the two.
And yes, getting vegetables (e.g. in the dips) in ways that are not typically associated with “healthy eating” is still better than not getting vegetables at all!
Check out: Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: