Kidney Beans vs Fava Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kidney beans to fava beans, we picked the kidney beans.
Why?
It’s a simple and straightforward one today!
The macronutrient profiles are mostly comparable, but kidney beans do have a little more protein and a little more fiber.
In the category of vitamins, kidney beans have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, B9, C, E, & K, while fava beans boast only more of vitamins B2 and B3. They are both equally good sources of choline, but the general weight of vitamins is very much in kidney beans’ favor, with a 7:2 lead, most of which have generous margins.
When it comes to minerals, kidney beans have more iron, phosphorus, and potassium, while fava beans have more copper and selenium. They’re both equally good sources of other minerals they both contain. Still, a 3:2 victory for kidney beans on the mineral front.
Adding up the moderate victory on macros, the strong victory on vitamins, and the slight victory on minerals, all in all makes for a clear win for kidney beans.
Still, enjoy both! Diversity is healthy.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
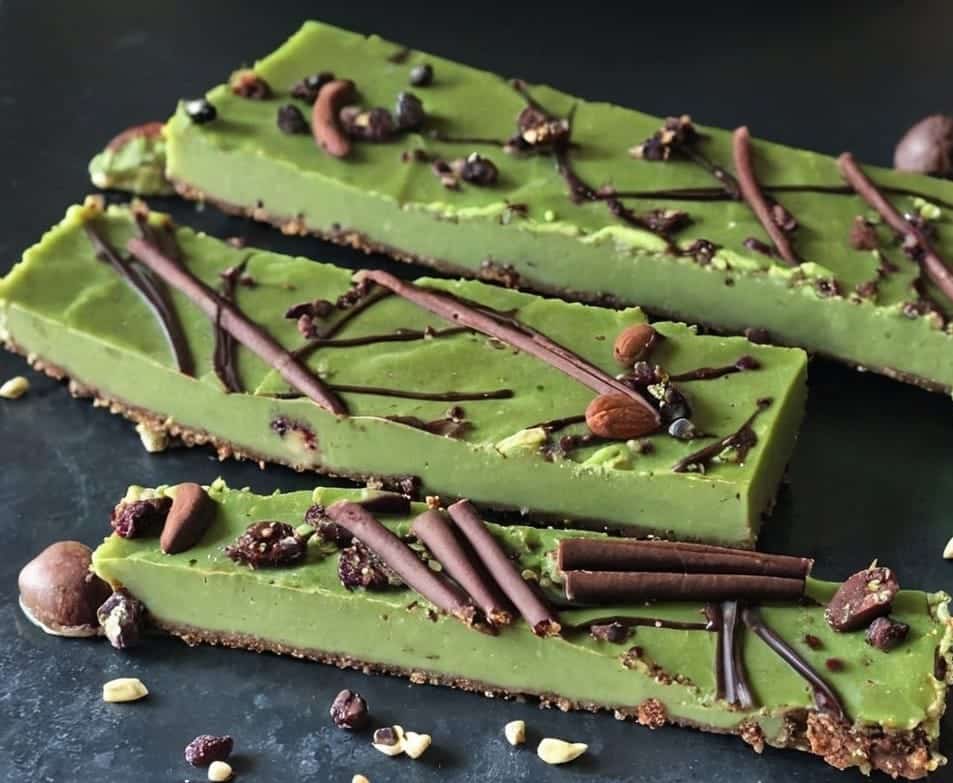
Antioxidant Matcha Snack Bars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The antioxidants in this come not just from the matcha, but also the cacao nibs and chocolate, as well as lots of nutrients from the hazelnuts and cashews. If you’re allergic to nuts, we’ll give you substitutions that will change the nutritional profile (and flavor), but still work perfectly well and be healthy too.
You will need
For the base:
- ⅔ cup roasted hazelnuts (if allergic, substitute dessicated coconut)
- ⅔ cup chopped dates
For the main part:
- 1 cup raw cashews (if allergic, substitute raw coconut, chopped)
- ½ cup almond milk (or your preferred milk of any kind)
- ½ cup cacao nibs
- 2 tbsp lime juice
- 1 tbsp matcha powder
- 1 tbsp maple syrup (omit if you don’t care for sweetness)
For the topping (optional):
- 2oz dark chocolate, melted (and if you like, tempered—but this isn’t necessary; it’ll just make it glossier if you do)
- Spare cacao nibs, chopped nuts, or anything else you might want on there
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the base ingredients in a food processor until it has a coarse sticky texture, but isn’t yet a paste or dough.
2) Line a cake pan with baking paper and spread the base mix on the base; press it down to compact it a little and ensure it is flat. If there’s room, put this in the freezer while you do the next bit. If not, the fridge will suffice.
3) Blend the main part ingredients apart from the cacao nibs, until smooth. Stir in the cacao nibs with a spoon.
4) Spread the main part evenly over the base, and allow everything you’ve built (in this recipe, not in life in general) to chill in the fridge for at least 4 hours.
5) Cut it into blocks of the size and shape you want to eat them, and (if adding the optional topping) separate the blocks slightly from each other, before drizzling with the chocolate topping. Put it back in the fridge to cool this too; an hour should be sufficient.
6) Serve!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
- Which Plant Milk?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Progesterone Menopausal HRT: When, Why, And How To Benefit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Progesterone doesn’t get talked about as much as other sex hormones, so what’s its deal? Dr. Heather Hirsch explains:
Menopausal progesterone
Dr. Hirsch considers progesterone essential for menopausal women who are taking estrogen and have an intact uterus, to keep conditions at bay such as endometriosis or even uterine cancer.
However, she advises it is not critical in those without a uterus, unless there was a previous case of one of the above conditions.
10almonds addition: on the other hand, progesterone can still be beneficial from a metabolic and body composition standpoint, so do speak with your endocrinologist about it.
As an extra bonus: while not soporific (it won’t make you sleepy), taking progesterone at night will improve the quality of your sleep once you do sleep, so that’s a worthwhile thing for many!
Dr. Hirsch also discusses the merits of continuous vs cyclic use; continuous maintains the above sleep benefits, for example, while cyclic use can help stabilize menstrual patterns in late perimenopause and early menopause.
For more on these things, plus discussion of different types of progesterone, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
- What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
- HRT: Bioidentical vs Animal – A Tale Of Two Approaches
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why is cancer called cancer? We need to go back to Greco-Roman times for the answer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One of the earliest descriptions of someone with cancer comes from the fourth century BC. Satyrus, tyrant of the city of Heracleia on the Black Sea, developed a cancer between his groin and scrotum. As the cancer spread, Satyrus had ever greater pains. He was unable to sleep and had convulsions.
Advanced cancers in that part of the body were regarded as inoperable, and there were no drugs strong enough to alleviate the agony. So doctors could do nothing. Eventually, the cancer took Satyrus’ life at the age of 65.
Cancer was already well known in this period. A text written in the late fifth or early fourth century BC, called Diseases of Women, described how breast cancer develops:
hard growths form […] out of them hidden cancers develop […] pains shoot up from the patients’ breasts to their throats, and around their shoulder blades […] such patients become thin through their whole body […] breathing decreases, the sense of smell is lost […]
Other medical works of this period describe different sorts of cancers. A woman from the Greek city of Abdera died from a cancer of the chest; a man with throat cancer survived after his doctor burned away the tumour.
Where does the word ‘cancer’ come from?
Why does the word ‘cancer’ have its roots in the ancient Greek and Latin words for crab? The physician Galen offers one explanation. Pierre Roche Vigneron/Wikimedia The word cancer comes from the same era. In the late fifth and early fourth century BC, doctors were using the word karkinos – the ancient Greek word for crab – to describe malignant tumours. Later, when Latin-speaking doctors described the same disease, they used the Latin word for crab: cancer. So, the name stuck.
Even in ancient times, people wondered why doctors named the disease after an animal. One explanation was the crab is an aggressive animal, just as cancer can be an aggressive disease; another explanation was the crab can grip one part of a person’s body with its claws and be difficult to remove, just as cancer can be difficult to remove once it has developed. Others thought it was because of the appearance of the tumour.
The physician Galen (129-216 AD) described breast cancer in his work A Method of Medicine to Glaucon, and compared the form of the tumour to the form of a crab:
We have often seen in the breasts a tumour exactly like a crab. Just as that animal has feet on either side of its body, so too in this disease the veins of the unnatural swelling are stretched out on either side, creating a form similar to a crab.
Not everyone agreed what caused cancer
The physician Erasistratus didn’t think black bile was to blame. Didier Descouens/Musée Ingres-Bourdelle/Wikimedia, CC BY-SA In the Greco-Roman period, there were different opinions about the cause of cancer.
According to a widespread ancient medical theory, the body has four humours: blood, yellow bile, phlegm and black bile. These four humours need to be kept in a state of balance, otherwise a person becomes sick. If a person suffered from an excess of black bile, it was thought this would eventually lead to cancer.
The physician Erasistratus, who lived from around 315 to 240 BC, disagreed. However, so far as we know, he did not offer an alternative explanation.
How was cancer treated?
Cancer was treated in a range of different ways. It was thought that cancers in their early stages could be cured using medications.
These included drugs derived from plants (such as cucumber, narcissus bulb, castor bean, bitter vetch, cabbage); animals (such as the ash of a crab); and metals (such as arsenic).
Galen claimed that by using this sort of medication, and repeatedly purging his patients with emetics or enemas, he was sometimes successful at making emerging cancers disappear. He said the same treatment sometimes prevented more advanced cancers from continuing to grow. However, he also said surgery is necessary if these medications do not work.
Surgery was usually avoided as patients tended to die from blood loss. The most successful operations were on cancers of the tip of the breast. Leonidas, a physician who lived in the second and third century AD, described his method, which involved cauterising (burning):
I usually operate in cases where the tumours do not extend into the chest […] When the patient has been placed on her back, I incise the healthy area of the breast above the tumour and then cauterize the incision until scabs form and the bleeding is stanched. Then I incise again, marking out the area as I cut deeply into the breast, and again I cauterize. I do this [incising and cauterizing] quite often […] This way the bleeding is not dangerous. After the excision is complete I again cauterize the entire area until it is dessicated.
Cancer was generally regarded as an incurable disease, and so it was feared. Some people with cancer, such as the poet Silius Italicus (26-102 AD), died by suicide to end the torment.
Patients would also pray to the gods for hope of a cure. An example of this is Innocentia, an aristocratic lady who lived in Carthage (in modern-day Tunisia) in the fifth century AD. She told her doctor divine intervention had cured her breast cancer, though her doctor did not believe her.
Innocentia from Carthage, in modern-day Tunisia, believed divine intervention cured her breast cancer. Valery Bareta/Shutterstock From the past into the future
We began with Satyrus, a tyrant in the fourth century BC. In the 2,400 years or so since then, much has changed in our knowledge of what causes cancer, how to prevent it and how to treat it. We also know there are more than 200 different types of cancer. Some people’s cancers are so successfully managed, they go on to live long lives.
But there is still no general “cure for cancer”, a disease that about one in five people develop in their lifetime. In 2022 alone, there were about 20 million new cancer cases and 9.7 million cancer deaths globally. We clearly have a long way to go.
Konstantine Panegyres, McKenzie Postdoctoral Fellow, Historical and Philosophical Studies, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Querying Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid (and thus, antioxidant) pigment found in many plants. Capers, radishes, and coriander/cilantro score highly, but the list is large:
USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods
Indeed,
❝Their regular consumption is associated with reduced risk of a number of chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease (CVD) and neurodegenerative disorders❞
~ Dr. Aleksandra Kozłpwsla & Dr. Dorota Szostak-Wegierek
Read more: Flavonoids—food sources and health benefits
For this reason, quercetin is often sold/consumed as a supplement on the strength of its health-giving properties.
But what does the science say?
Quercetin and inflammation
In short, it helps:
❝500 mg per day quercetin supplementation for 8 weeks resulted in significant improvements in clinical symptoms, disease activity, hs-TNFα, and Health Assessment Questionnaire scores in women with rheumatoid athritis❞
Quercetin and blood pressure
It works, if antihypertensive (i.e., blood pressure lowering) effect is what you want/need:
❝…significant effect of quercetin supplementation in the reduction of BP, possibly limited to, or greater with dosages of >500 mg/day.❞
~ Dr. Maria-Corina Serban et al.
Quercetin and diabetes
We’re less confident to claim this one, because (almost?) all of the research so far as been in non-human animals or in vitro. As one team of researchers put it:
❝Despite the wealth of in animal research results suggesting the anti-diabetic and its complications potential of quercetin, its efficacy in diabetic human subjects is yet to be explored❞
Quercetin and neuroprotection
Research has been done into the effect of quercetin on the risk of Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, and they found…
❝The data indicate that quercetin is the major neuroprotective component in coffee against Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease❞
Read more: Quercetin, not caffeine, is a major neuroprotective component in coffee
Summary
Quercetin is a wonderful flavonoid that can be enjoyed as part of one’s diet and by supplementation. In terms of its popular health claims:
- It has been found very effective for lowering inflammation
- It has a moderate blood pressure lowering effect
- It may have anti-diabetes potential, but the science is young
- It has been found to have a potent neuroprotective effect
Want to get some?
We don’t sell it, but for your convenience, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
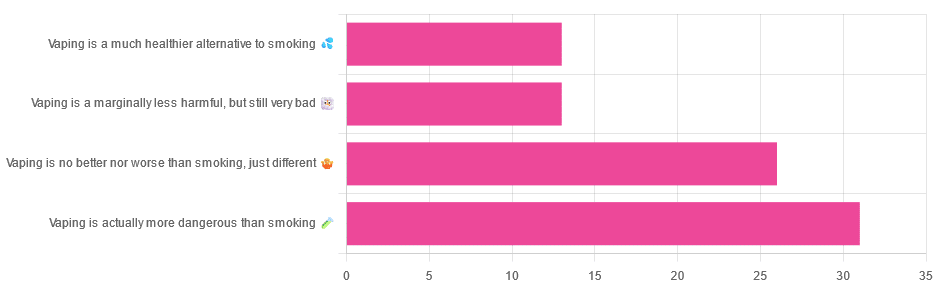
Yesterday, we asked you for your (health-related) opinions on vaping, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- A little over a third of respondents said it’s actually more dangerous than smoking
- A little under a third of respondents said it’s no better nor worse, just different
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s marginally less harmful, but still very bad
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s a much healthier alternative to smoking
So what does the science say?
Vaping is basically just steam inhalation, plus the active ingredient of your choice (e.g. nicotine, CBD, THC, etc): True or False?
False! There really are a lot of other chemicals in there.
And “chemicals” per se does not necessarily mean evil green glowing substances that a comicbook villain would market, but there are some unpleasantries in there too:
- Potential harmful health effects of inhaling nicotine-free shisha-pen vapor: a chemical risk assessment of the main components propylene glycol and glycerol
- Inflammatory and Oxidative Responses Induced by Exposure to Commonly Used e-Cigarette Flavoring Chemicals and Flavored e-Liquids without Nicotine
So, the substrate itself can cause irritation, and flavorings (with cinnamaldehyde, the cinnamon flavoring, being one of the worst) can really mess with our body’s inflammatory and oxidative responses.
Vaping can cause “popcorn lung”: True or False?
True and False! Popcorn lung is so-called after it came to attention when workers at a popcorn factory came down with it, due to exposure to diacetyl, a chemical used there.
That chemical was at that time also found in most vapes, but has since been banned in many places, including the US, Canada, the EU and the UK.
Vaping is just as bad as smoking: True or False?
False, per se. In fact, it’s recommended as a means of quitting smoking, by the UK’s famously thrifty NHS, that absolutely does not want people to be sick because that costs money:
Of course, the active ingredients (e.g. nicotine, in the assumed case above) will still be the same, mg for mg, as they are for smoking.
Vaping is causing a health crisis amongst “kids nowadays”: True or False?
True—it just happens to be less serious on a case-by-case basis to the risks of smoking.
However, it is worth noting that the perceived harmlessness of vapes is surely a contributing factor in their widespread use amongst young people—decades after actual smoking (thankfully) went out of fashion.
On the other hand, there’s a flipside to this:
Flavored vape restrictions lead to higher cigarette sales
So, it may indeed be the case of “the lesser of two evils”.
Want to know more?
For a more in-depth science-ful exploration than we have room for here…
BMJ | Impact of vaping on respiratory health
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Kiwi vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi to passion fruit, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
This fruit is so passionate about delivery nutrient-dense goodness, that at time of writing, nothing has beaten it yet!
In terms of macros, passion fruit has a little more protein, as well as 50% more carbs, and/but more than 3x the fiber. That last stat is particularly impressive, and also results in passion fruit having a much lower glycemic index, too. In short, a clear win for passion fruit in the macros category.
In the category of vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins B9, C, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and B6, making for a tie this time.
As for minerals, kiwi has more calcium, copper, manganese, and zinc, while passion fruit has more iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, resulting in a modest, marginal win for passion fruit in this category.
Adding up the categories gives a convincing win for passion fruit, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good! And kiwi has its merits too (for example, it’s particularly high in vitamin K, appropriately enough).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: