Is still water better for you than sparkling water?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Still or sparkling? It’s a question you’ll commonly hear in a café or restaurant and you probably have a preference. But is there any difference for your health?
If you love the fizz, here’s why you don’t have to pass on the sparkling water.

What makes my water sparkle?
This article specifically focuses on comparing still filtered water to carbonated filtered water (called “sparkling water” or “unflavoured seltzer”). Soda water, mineral water, tonic water and flavoured water are similar, but not the same product.
The bubbles in sparkling water are created by adding carbon dioxide to filtered water. It reacts to produce carbonic acid, which makes sparkling water more acidic (a pH of about 3.5) than still (closer to neutral, with a pH around 6.5-8.5).
Which drink is healthiest?
Water is the best way to hydrate our bodies. Research shows when it comes to hydration, still and sparkling water are equally effective.
Some people believe water is healthier when it comes from a sealed bottle. But in Australia, tap water is monitored very carefully. Unlike bottled water, it also has the added benefit of fluoride, which can help protect young children against tooth decay and cavities.
Sparkling or still water is always better than artificially sweetened flavoured drinks or juices.
Isn’t soda water bad for my teeth and bones?
There’s no evidence sparkling water damages your bones. While drinking a lot of soft drinks is linked to increased fractures, this is largely due to their association with higher rates of obesity.
Sparkling water is more acidic than still water, and acidity can soften the teeth’s enamel. Usually this is not something to be too worried about, unless it is mixed with sugar or citrus, which has much higher levels of acidity and can harm teeth.
However, if you grind your teeth often, the softening could enhance the damage it causes. If you’re undertaking a home whitening process, sparkling water might discolour your teeth.
In most other cases, it would take a lot of sparkling water to pass by the teeth, for a long period of time, to cause any noticeable damage.
How does drinking water affect digestion?
There is a misconception drinking water (of any kind) with a meal is bad for digestion.
While theoretically water could dilute stomach acid (which breaks down food), the practice of drinking it doesn’t appear to have any negative effect. Your digestive system simply adapts to the consistency of the meal.
Some people do find that carbonated beverages cause some stomach upset. This is due to the build-up of gases, which can cause bloating, cramping and discomfort. For people with an overactive bladder, the acidity might also aggravate the urinary system.
Interestingly, the fizzy “buzz” you feel in your mouth from sparkling water fades the more you drink it.
Is cold water harder to digest?
You’ve chosen still or sparkling water. What about its temperature?
There are surprisingly few studies about the effect of drinking cold water compared to room temperature. There is some evidence colder water (at two degrees Celsius) might inhibit gastric contractions and slow down digestion. Ice water may constrict blood vessels and cause cramping.
However other research suggests drinking cold water might temporarily boost metabolism, as the body needs to expend energy to warm it up to body temperature. This effect is minimal and unlikely to lead to significant weight loss.
Which water wins?
The bottom line is water is essential, hydrates us and has countless other health benefits. Water, with carbonated bubbles or without, will always be the healthiest drink to choose.
And if you’re concerned about any impact to teeth enamel, one trick is to follow sparkling water with a glass of still. This helps rinse the teeth and return your mouth’s acidity back to normal.
Christian Moro, Associate Professor of Science & Medicine, Bond University and Charlotte Phelps, Senior Teaching Fellow, Medical Program, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Covering obesity: 6 tips for dispelling myths and avoiding stigmatizing news coverage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When researchers looked at news coverage of obesity in the United States and the United Kingdom a few years ago, they found that images in news articles often portrayed people with larger bodies “in a stigmatizing manner” — they emphasized people’s abdomens, for example, or showed them eating junk food, wearing tight clothes or lounging in front of a TV.
When people with larger bodies were featured in photos and videos, nearly half were shown only from their necks down or with part of their heads missing, according to the analysis, published in November 2023. The researchers examined a total of 445 images posted to the websites of four U.S. news outlets and four U.K. news outlets between August 2018 and August 2019.
The findings underscore the need for dramatic changes in the way journalists report on obesity and people who weigh more than what medical authorities generally consider healthy, Rebecca Puhl, one of the paper’s authors, told The Journalist’s Resource in an email interview.
“Using images of ‘headless stomachs’ is dehumanizing and stigmatizing, as are images that depict people with larger bodies in stereotypical ways (e.g., eating junk food or being sedentary),” wrote Puhl, deputy director of the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Health at the University of Connecticut and a leading scholar on weight stigma.
She noted that news images influence how the public views and interacts with people with obesity, a complicated and often misunderstood condition that the American Medical Association considers a disease.
In the U.S., an estimated 42% of adults aged 20 years and older have obesity, a number researchers predict will rise to 50% over the next six years. While the disease isn’t as common in other parts of the planet, the World Obesity Federation projects that by 2035, more than half the global population will have obesity or overweight.
Several other studies Puhl has conducted demonstrate that biased new images can have damaging consequences for individuals affected by obesity.
“Our research has found that seeing the stigmatizing image worsens people’s attitudes and weight bias, leading them to attribute obesity to laziness, increasing their dislike of people with higher weight, and increasing desire for social distance from them,” Puhl explained.
Dozens of studies spotlight problems in news coverage of obesity in the U.S. and abroad. In addition to stigmatizing images, journalists use stigmatizing language, according to a 2022 research review in eClinicalMedicine, a journal published by The Lancet.
The research also suggests people with higher weights feel excluded and ridiculed by news outlets.
“Overt or covert discourses in news media, social media, and public health campaigns included depictions of people with overweight or obesity as being lazy, greedy, undisciplined, unhappy, unattractive, and stupid,” write the authors of the review, which examines 113 academic studies completed before Dec. 2, 2021.
To help journalists reflect on and improve their work, The Journalist’s Resource asked for advice from experts in obesity, weight stigma, health communication and sociolinguistics. They shared their thoughts and opinions, which we distilled into the six tips that appear below.
In addition to Puhl, we interviewed these six experts:
Jamy Ard, a professor of epidemiology and prevention at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and co-director of the Wake Forest Baptist Health Weight Management Center. He’s also president of The Obesity Society, a professional organization of researchers, health care providers and other obesity specialists.
Leslie Cofie, an assistant professor of health education and promotion at East Carolina University’s College of Health and Human Performance. He has studied obesity among immigrants and military veterans.
Leslie Heinberg, director of Enterprise Weight Management at the Cleveland Clinic, an academic medical center. She’s also vice chair for psychology in the Cleveland Clinic’s Center for Behavioral Health Department of Psychiatry and Psychology.
Monu Khanna, a physician in Missouri who is board certified in obesity medicine.
Jenn Lonzer, manager of the Cleveland Clinic Health Library and the co-author of several academic papers on health communication.
Cindi SturtzSreetharan, an anthropologist and professor at the Arizona State University School of Human Evolution and Social Change. She studies the language people of different cultures use to describe human bodies.
1. Familiarize yourself with recent research on what causes obesity and how obesity can affect a person’s health. Many long-held beliefs about the disease are wrong.
Journalists often report incorrect or misleading information about obesity, possibly because they’re unaware that research published in recent decades dispels many long-held beliefs about the disease, the experts say. Obesity isn’t simply the result of eating too many calories and doing too little exercise. A wide range of factors drive weight gain and prevent weight loss, many of which have nothing to do with willpower or personal choices.
Scholars have learned that stress, gut health, sleep duration and quality, genetics, medication, personal income, access to healthy foods and even climate can affect weight regulation. Prenatal and early life experiences also play a role. For example, childhood trauma such as child abuse can become “biologically embedded,” altering children’s brain structures and influencing their long-term physical and mental health, according to a 2020 research review published in the journal Physiology & Behavior.
“The causes of obesity are numerous and each individual with obesity will have a unique set of contributors to their excess weight gain,” Jamy Ard, president of The Obesity Society, wrote to The Journalist’s Resource.
The experts urge journalists to help dispel myths, correct misinformation and share new research findings. News outlets should examine their own work, which often “ignores the science and sets up situation blaming,” says Leslie Heinberg, director of Enterprise Weight Management at the Cleveland Clinic.
“So much of the media portrayal is simply ‘This is a person who eats too much and the cure is simply to eat less or cut out that food’ or something overly, overly simplistic,” Heinberg says.
Journalists need to build their knowledge of the problem before they can explain it to their audiences. Experts point out that educating policymakers, health care providers and the public about obesity is key to eliminating the stigma associated with having a larger body.
Weight stigma alone is so physically and emotionally damaging that 36 international experts issued a consensus statement in 2020 to raise awareness about it. The document, endorsed by dozens of medical and academic organizations, outlines 13 recommendations for eliminating weight bias and stigma.
Recommendation No. 5: “We call on the media to produce fair, accurate, and non-stigmatizing portrayals of obesity. A commitment from the media is needed to shift the narrative around obesity.”
2. Use person-first language — the standard among health and medical professionals for communicating about people with chronic diseases.
The experts we interviewed encourage journalists to ditch the adjectives “obese” and “overweight” because they are dehumanizing. Use person-first language, which avoids labeling people as their disease by putting the person before the disease.
Instead of saying “an obese teenager,” say “a teenager who has obesity” or “a teenager affected by obesity.” Instead of writing “overweight men,” write “men who have overweight.”
Jenn Lonzer, manager of the Cleveland Clinic Health Library, says using “overweight” as a noun might look and sound awkward at first. But it makes sense considering other diseases are treated as nouns, she notes. Journalists would not typically refer to someone in a news story as “a cancerous person,” for example. They would report that the individual has cancer.
It’s appropriate to refer to people with overweight or obesity using neutral weight terminology. Puhl wrote that she uses “people with higher body weight” or “people with high weight” and, sometimes, “people with larger bodies” in her own writing.
While the Associated Press stylebook offers no specific guidance on the use of terms such as “obese” or “overweight,” it advises against “general and often dehumanizing ‘the’ labels such as the poor, the mentally ill, the disabled, the college-educated.”
The Association of Health Care Journalists recommends person-first language when reporting on obesity. But it also advises journalists to ask sources how they would like to be characterized, provided their weight or body size is relevant to the news story.
Anthropologist Cindi SturtzSreetharan, who studies language and culture, says sources’ responses to that question should be part of the story. Some individuals might prefer to be called “fat,” “thick” or “plus-sized.”
“I would include that as a sentence in the article — to signal you’ve asked and that’s how they want to be referred to,” SturtzSreetharan says.
She encourages journalists to read how authors describe themselves in their own writing. Two books she recommends: Thick by Tressie McMillan Cottom and Heavy: An American Memoir by Kiese Laymon.
3. Carefully plan and choose the images that will accompany news stories about obesity.
Journalists need to educate themselves about stigma and screen for it when selecting images, Puhl noted. She shared these four questions that journalists should ask themselves when deciding how to show people with higher weights in photos and video.
- Does the image imply or reinforce negative stereotypes?
- Does it provide a respectful portrayal of the person?
- Who might be offended, and why?
- Can an alternative image convey the same message and eliminate possible bias?
“Even if your written piece is balanced, accurate, and respectful, a stigmatizing image can undermine your message and promote negative societal attitudes,” Puhl wrote via email.
Lonzer says newsrooms also need to do a better job incorporating images of people who have different careers, interests, education levels and lifestyles into their coverage of overweight and obesity.
“We are diverse,” says Lonzer, who has overweight. “We also have diversity in body shape and size. It’s good to have images that reflect what Americans look like.”
If you’re looking for images and b-roll videos that portray people with obesity in non-stigmatizing ways, check out the Rudd Center Media Gallery. It’s a collection of original images of people from various demographic groups that journalists can use for free in their coverage.
The Obesity Action Coalition, a nonprofit advocacy organization, also provides images. But journalists must sign up to use the OAC Bias-Free Image Gallery.
Other places to find free images: The World Obesity Image Bank, a project of the World Obesity Federation, and the Flickr account of Obesity Canada.
4. Make sure your story does not reinforce stereotypes or insinuate that overcoming obesity is simply a matter of cutting calories and doing more exercise.
“Think about the kinds of language used in the context of eating habits or physical activity, as some can reinforce shame or stereotypes,” Puhl wrote.
She suggested journalists avoid phrases such as “resisting temptations,” “cheating on a diet,” “making excuses,” “increasing self-discipline” and “lacking self-control” because they perpetuate the myth that individuals can control their weight and that the key to losing weight is eating less and moving more.
Lonzer offers this advice: As you work on stories about obesity or weight-related issues, ask yourself if you would use the same language and framing if you were reporting on someone you love.
Here are other questions for journalists to contemplate:
“Am I treating this as a complex medical condition or am I treating it as ‘Hey, lay off the French fries?’” Lonzer adds. “Am I treating someone with obesity differently than someone with another disease?”
It’s important to also keep in mind that having excess body fat does not, by itself, mean a person is unhealthy. And don’t assume everyone who has a higher weight is unhappy about it.
“Remember, not everyone with obesity is suffering,” physician Monu Khanna wrote to The Journalist’s Resource.
5. To help audiences understand how difficult it is to prevent and reduce obesity, explain that even the places people live can affect their waistlines.
When news outlets report on obesity, they often focus on weight-loss programs, surgical procedures and anti-obesity medications. But there are other important issues to cover. Experts stress the need to help the public understand how factors not ordinarily associated with weight gain or loss can influence body size.
For example, a paper published in 2018 in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine indicates adults who are regularly exposed to loud noise have a higher waist circumference than adults who are not. Research also finds that people who live in neighborhoods with sidewalks and parks are more active.
“One important suggestion I would offer to journalists is that they need to critically explore environmental factors (e.g., built environment, food deserts, neighborhood safety, etc.) that lead to disproportionately high rates of obesity among certain groups, such as low-income individuals and racial/ethnic minorities,” Leslie Cofie, an assistant professor at East Carolina University, wrote to The Journalist’s Resource.
Cofie added that moving to a new area can prompt weight changes.
“We know that immigrants generally have lower rates of obesity when they first migrate to the U.S.,” he wrote. “However, over time, their obesity rates resemble that of their U.S.-born counterparts. Hence, it is critical for journalists to learn about how the sociocultural experiences of immigrants change as they adapt to life in the U.S. For example, cultural perspectives about food, physical activities, gender roles, etc. may provide unique insights into how the pre- and post-migration experiences of immigrants ultimately contribute to the unfavorable trends in their excessive weight gain.”
Other community characteristics have been linked to larger body sizes for adults or children: air pollution, lower altitudes, higher temperatures, lower neighborhood socioeconomic status, perceived neighborhood safety, an absence of local parks and closer proximity to fast-food restaurants.
6. Forge relationships with organizations that study obesity and advocate on behalf of people living with the disease.
Several organizations are working to educate journalists about obesity and help them improve their coverage. Five of the most prominent ones collaborated on a 10-page guide book, “Guidelines for Media Portrayals of Individuals Affected by Obesity.”
- The Rudd Center for Food Policy and Health, based at the University of Connecticut, “promotes solutions to food insecurity, poor diet quality, and weight bias through research and policy,” according to its website. Research topics include food and beverage marketing, weight-related bullying and taxes on sugary drinks.
- The Obesity Society helps journalists arrange interviews with obesity specialists. It also offers journalists free access to its academic journal, Obesity, and free registration to ObesityWeek, an international conference of researchers and health care professionals held every fall. This year’s conference is Nov. 2-6 in San Antonio, Texas.
- The Obesity Medicine Association represents health care providers who specialize in obesity treatment and care. It also helps journalists connect with obesity experts and offers, on an individual basis, free access to its events, including conferences and Obesity Medicine Fundamentals courses.
- The Obesity Action Coalition offers free access to its magazine, Weight Matters, and guides on weight bias at work and in health care.
- The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery represents surgeons and other health care professionals who work in the field of metabolic and bariatric surgery. It provides the public with resources such as fact sheets and brief explanations of procedures such as the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass.
For further reading
Weight Stigma in Online News Images: A Visual Content Analysis of Stigma Communication in the Depictions of Individuals with Obesity in U.S. and U.K. News
Aditi Rao, Rebecca Puhl and Kirstie Farrar. Journal of Health Communication, November 2023.Influence and Effects of Weight Stigmatization in Media: A Systematic Review
James Kite; et al. eClinicalMedicine, June 2022.Has the Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity and Central Obesity Leveled Off in the United States? Trends, Patterns, Disparities, and Future Projections for the Obesity Epidemic
Youfa Wang; et al. International Journal of Epidemiology, June 2020.This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Is stress turning my hair grey?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When we start to go grey depends a lot on genetics.
Your first grey hairs usually appear anywhere between your twenties and fifties. For men, grey hairs normally start at the temples and sideburns. Women tend to start greying on the hairline, especially at the front.
The most rapid greying usually happens between ages 50 and 60. But does anything we do speed up the process? And is there anything we can do to slow it down?
You’ve probably heard that plucking, dyeing and stress can make your hair go grey – and that redheads don’t. Here’s what the science says.
Oksana Klymenko/Shutterstock What gives hair its colour?
Each strand of hair is produced by a hair follicle, a tunnel-like opening in your skin. Follicles contain two different kinds of stem cells:
- keratinocytes, which produce keratin, the protein that makes and regenerates hair strands
- melanocytes, which produce melanin, the pigment that colours your hair and skin.
There are two main types of melanin that determine hair colour. Eumelanin is a black-brown pigment and pheomelanin is a red-yellow pigment.
The amount of the different pigments determines hair colour. Black and brown hair has mostly eumelanin, red hair has the most pheomelanin, and blonde hair has just a small amount of both.
So what makes our hair turn grey?
As we age, it’s normal for cells to become less active. In the hair follicle, this means stem cells produce less melanin – turning our hair grey – and less keratin, causing hair thinning and loss.
As less melanin is produced, there is less pigment to give the hair its colour. Grey hair has very little melanin, while white hair has none left.
Unpigmented hair looks grey, white or silver because light reflects off the keratin, which is pale yellow.
Grey hair is thicker, coarser and stiffer than hair with pigment. This is because the shape of the hair follicle becomes irregular as the stem cells change with age.
Interestingly, grey hair also grows faster than pigmented hair, but it uses more energy in the process.
Can stress turn our hair grey?
Yes, stress can cause your hair to turn grey. This happens when oxidative stress damages hair follicles and stem cells and stops them producing melanin.
Oxidative stress is an imbalance of too many damaging free radical chemicals and not enough protective antioxidant chemicals in the body. It can be caused by psychological or emotional stress as well as autoimmune diseases.
Environmental factors such as exposure to UV and pollution, as well as smoking and some drugs, can also play a role.
Melanocytes are more susceptible to damage than keratinocytes because of the complex steps in melanin production. This explains why ageing and stress usually cause hair greying before hair loss.
Scientists have been able to link less pigmented sections of a hair strand to stressful events in a person’s life. In younger people, whose stems cells still produced melanin, colour returned to the hair after the stressful event passed.
4 popular ideas about grey hair – and what science says
1. Does plucking a grey hair make more grow back in its place?
No. When you pluck a hair, you might notice a small bulb at the end that was attached to your scalp. This is the root. It grows from the hair follicle.
Plucking a hair pulls the root out of the follicle. But the follicle itself is the opening in your skin and can’t be plucked out. Each hair follicle can only grow a single hair.
It’s possible frequent plucking could make your hair grey earlier, if the cells that produce melanin are damaged or exhausted from too much regrowth.
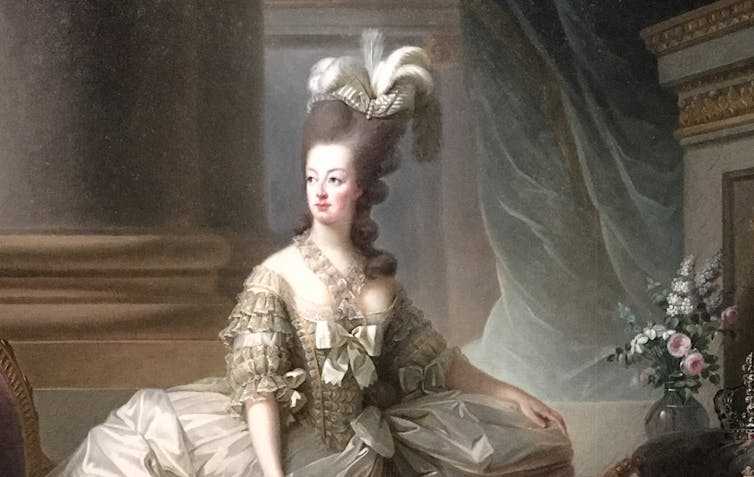
2. Can my hair can turn grey overnight?
Legend says Marie Antoinette’s hair went completely white the night before the French queen faced the guillotine – but this is a myth.
It is not possible for hair to turn grey overnight, as in the legend about Marie Antoinette. Yann Caradec/Wikimedia, CC BY-NC-SA Melanin in hair strands is chemically stable, meaning it can’t transform instantly.
Acute psychological stress does rapidly deplete melanocyte stem cells in mice. But the effect doesn’t show up immediately. Instead, grey hair becomes visible as the strand grows – at a rate of about 1 cm per month.
Not all hair is in the growing phase at any one time, meaning it can’t all go grey at the same time.
3. Will dyeing make my hair go grey faster?
This depends on the dye.
Temporary and semi-permanent dyes should not cause early greying because they just coat the hair strand without changing its structure. But permanent products cause a chemical reaction with the hair, using an oxidising agent such as hydrogen peroxide.
Accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and other hair dye chemicals in the hair follicle can damage melanocytes and keratinocytes, which can cause greying and hair loss.
4. Is it true redheads don’t go grey?
People with red hair also lose melanin as they age, but differently to those with black or brown hair.
This is because the red-yellow and black-brown pigments are chemically different.
Producing the brown-black pigment eumelanin is more complex and takes more energy, making it more susceptible to damage.
Producing the red-yellow pigment (pheomelanin) causes less oxidative stress, and is more simple. This means it is easier for stem cells to continue to produce pheomelanin, even as they reduce their activity with ageing.
With ageing, red hair tends to fade into strawberry blonde and silvery-white. Grey colour is due to less eumelanin activity, so is more common in those with black and brown hair.
Your genetics determine when you’ll start going grey. But you may be able to avoid premature greying by staying healthy, reducing stress and avoiding smoking, too much alcohol and UV exposure.
Eating a healthy diet may also help because vitamin B12, copper, iron, calcium and zinc all influence melanin production and hair pigmentation.
Theresa Larkin, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
CBD Oil’s Many Benefits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
CBD Oil: What Does The Science Say?
First, a quick legal (and practical) note:
CBD and THC are both derived from the hemp or cannabis plant, but only the latter has euphoriant psychoactive effects, i.e., will get you high. We’re writing here about CBD derived from hemp and not containing THC (thus, will not get you high).
Laws and regulations differ far too much from place to place for us to try to advise here, so please check your own local laws and regulations. And also, while you’re at it, with your doctor and/or pharmacist.
As ever, this newsletter is for purposes of education and enjoyment, and does not constitute any kind of legal (or medical) advice.
With that in mind, onwards to today’s research review…
CBD for Pain Relief
CBD has been popularly touted as a pain relief panacea, and there are a lot of pop-science articles out there “debunking” this, but…
The science seems to back it up. We couldn’t find studies refuting the claim (of CBD as a viable pain relief option). We did, however, find research showing it was good against:
Note that that latter (itself a research review, not a single study, hence covering a lot of bases) describes it matter-of-factly, with no caveats or weasel-words, as:
“CBD, a non-euphoriant, anti-inflammatory analgesic with CB1 receptor antagonist and endocannabinoid modulating effects”
As a quick note: all of the above is about the topical use of CBD oil, not any kind of ingestion
CBD for Anxiety/Depression
There’s a well-cited study with what honestly we think was a bit of a small sample size, but compelling results within that:
A study published in the Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry tested the anxiety levels of 57 men in a simulated public speaking test.
Compared to placebo…
- Those who received 300mg of CBD experienced significantly reduced anxiety during the test.
- Those who received either 150mg or 600mg of CBD experienced more anxiety during the test than the 300mg group
- This means there’s a sweet spot to the dosage
There was also a clinical study that found CBD to have anti-depressant effects.
The methodology was a lot more robust, but the subjects were mice. We can’t have everything in one study, apparently! There is probably a paucity of human volunteers to have their brain slices looked at after tests, though.
Anyway, what makes this study interesting is that it measured quite an assortment of biological markers in the brain, and found that the CBD had a similar physiological effect to the antidepressant imipramine.
CBD for Treating Opioid Addiction
There are a lot of studies for this, both animal and human, but we’d like to put the spotlight on a human study (with the participation of heroin users) that found:
❝Within one week, CBD significantly reduced cravings, anxiety, resting heart rate, and salivary cortisol levels. No serious adverse effects were found.❞
This is groundbreaking because the very thing about heroin is that it’s so addictive and the body rapidly needs more and more of it. You might think “duh”, but most people don’t realize this part:
Heroin is attractive because it offers (and delivers) an immediate guaranteed “downer”, instant relaxation… with none of the bad side effects of, for example, alcohol. No nausea, no hangover, nothing.
The problem is that the body gets tolerant to heroin very quickly, meaning your doses need to get bigger and more frequent to have the same effect.
Before you know it, what seemed like an affordable “self-medication for a stressful life” is very much out of control! Many doctors have personally found this out the hard way.
So, it’s ruinous:
- first to your financial health, as the costs rapidly spiral
- then to your physical health, as you either suffer from withdrawal or eventually overdose
Consequently, heroin is an incredibly easy drug to get hooked onto, and incredibly difficult to get back off.
So CBD offering relief is really a game-changer.
And more…
CBD has been well-studied and found to be effective for a lot of things, more than we could hope to cover in a single edition here.
Some further reading that may interest you includes:
- CBD against Diabetes in mice / in vitro / in humans
- CBD against neurological diseases (in general, in humans)
- CBD against arthritis in mice / in humans
- CBD specifically against the pain of rheumatoid arthritis / of osteoarthritis
Let us know if there’s any of these (or other) conditions you’d like us to look more into the CBD-related research for, because there’s a lot! You can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom
Read (and shop, if you want and it’s permitted where you are):
10 Best CBD Oils of 2023, According to the Forbes Health Advisory Board
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Get On It! – by Jane Aronovitch, Miriane Taylor, & Colleen Craig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Balance is important; without it, we die early. That’s quite a strong selling point for improving one’s balance, but why this book in particular?
This is—with one drawback—the best book of balance ball exercises we’ve seen. Notwithstanding the cover photo, many exercises do, by the way, involve standing on it with one or both feet, doing various kinds of squats, lunges, get-ups, and so forth. The ball (it’s not really a ball so much as an oblate hemisphere) can also be flipped and used the other way around, with a flat platform that will now wobble per your weight distribution, and train balance in different ways (dome-up trains large stabilizing muscles more; platform-up trains smaller stabilizing muscles more).
Indeed, that’s where the brand name Bosu, often stylized “BOSU”, comes from: both sides up!
So, what’s the drawback? Alas, the photos are black and white, which means in some cases they’re not as clear as they could be. Nothing that will prevent understanding the exercises, which are well-explained in any case, but it does mean that sometimes it’s necessary to look closely to see which leg is in front of the other for a given exercise, for example.
Still, with 80 different exercises it really does cover the whole body, and even gives workout program varieties for those who want that, including targeted to particular areas, e.g. lower body, core, upper body, or complete.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your balance (and have, or are willing to acquire, a balance ball like the Bosu), then this book will give you everything else you need in that regard.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healing Arthritis – by Dr. Susan Blum
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We previously reviewed another book by this author, her Immune System Recovery Plan, and today it’s more specific: healing arthritis
Of course, not all arthritis is rooted in immune dysfunction, but a) all of it is made worse by immune dysfunction and b) rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disease, affects 1% of the population.
This book tackles all kinds of arthritis, by focusing on addressing the underlying causes and treating those, and (whether it was the cause or not) reducing inflammation without medication, because that will always help.
The “3 steps” mentioned in the subtitle are three stages of a plan to improve the gut microbiome in such a way that it not only stops worsening your arthritis, but starts making it better.
The style here is on the hard end of pop-science, so if you want something more conversational/personable, then this won’t be so much for you, but if you just want the information and explanation, then this does it just fine, and it has frequent references to the science to back it up, with a reassuringly extensive bibliography.
Bottom line: if you have arthritis and want a book that will help you to get either symptom-free or as close to that as is possible from your current condition (bearing in mind that arthritis is generally degenerative), then this is a great book for that.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sticky Jackfruit Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All the taste and experience of pulled pork, without the increased risk of cancer and metabolic disease. On the contrary, jackfruit introduces lots of fiber, vitamins, carotenoids, and flavanones. We’ll have to do a main feature about jackfruit sometime; it’s an unusual fruit especially for its protein content, but for now, let’s get cooking!
You will need
- 1 can (14oz/400g) green jackfruit, drained (the flesh will not, in fact, be green—this is referring to the fruit being unripe and thus still firm in texture, which is what we want. The outside of the fruit, which will not be in the can, will have been green)
- 1/4 red cabbage, thinly sliced
- 1/2 carrot, grated
- 6 mangetout, thinly sliced
- 2 tbsp mayonnaise (your preference what kind, and yes, vegan is fine too)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp gochujang paste (if you can’t find gochujang paste locally, you can either order it online (here it is on Amazon) or substitute with harissa paste, which is not the same—it uses different spices—but will do the same job here re texture, umami taste, and level of spiciness)
- 1 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tbsp balsamic vinegar
- 1 tsp apple cider vinegar
- 1 tsp garlic paste
- 1 tsp tomato paste
- 1 tsp ginger paste
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 3½ fl oz water
- 2 burger buns (unless you make them yourself, burger buns will probably not be healthy; you can, however, also look for small round wholemeal breads—the name of which varies far too much by region for us to try to get a catch-all name here—and use them in place of burger buns)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the garlic paste, ginger paste, tomato paste, gochujang paste, soy sauce, balsamic vinegar, and chili flakes in a saucepan
2) Boil the 3½ fl oz water we mentioned; add it to the saucepan, mixing well, turn on the heat and let it simmer for 5 minutes or until it is thick and sticky (it will thicken more as it cools, too, so don’t worry if it doesn’t seem thick enough yet). Set it aside.
3) Dry the jackfruit (using strong kitchen paper should be fine), add the olive oil to a skillet and bring it to a high heat; add the jackfruit and fry on both sides for a few minutes, until it looks cooked (remember, while this may look like animal meat, it’s not, so there’s no danger of undercooking here).
4) When the jackfruit looks a nice golden-brown, add two thirds of the sauce from the saucepan, and break apart the jackfruit a bit (this can be done with a wooden/bamboo spatula, so as to not damage your pan), When it all looks how you’d expect pulled jackfruit (or pulled pork) to look, take it off the heat.
5) Combine the carrot, cabbage, and mangetout in a small bowl, adding the apple cider vinegar and mixing well; this will be the coleslaw element
6) Mix the remaining sauce with the mayonnaise
7) (optional) toast the burger buns
8) Assemble the burgers; we recommend the following order: bottom bun, pulled jackfruit, coleslaw, gochujang mayo, top bun
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake, The Fun Way!
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: