Take Care Of Your “Unwanted” Parts Too!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Meet The Family…
If you’ve heard talk of “healing your inner child” or similar ideas, then today’s featured type of therapy takes that to several extra levels, in a way that helps many people.
It’s called Internal Family Systems therapy, often “IFS” for short.
Here’s a quick overview:
Psychology Today | Internal Family Systems Therapy
Note: if you are delusional, paranoid, schizophrenic, or have some other related disorder*, then IFS would probably be a bad idea for you as it could worsen your symptoms, and/or play into them badly.
*but bipolar disorder, in its various forms, is not usually a problem for IFS. Do check with your own relevant healthcare provider(s), of course, to be sure.
What is IFS?
The main premise of IFS is that your “self” can be modelled as a system, and its constituent parts can be examined, questioned, given what they need, and integrated into a healthy whole.
For example…
- Exile is the name given to parts that could be, for example, the “inner child” referenced in a lot of pop-psychology, but it could also be some other ignored and pushed-down part of oneself, often from some kind of trauma. The defining characteristic of an exile is that it’s a part of ourself that we don’t consciously allow ourselves to see as a current part of ourself.
- Protector is the name given to a part of us that looks to keep us safe, and can do this in an adaptive (healthy) or maladaptive (unhealthy) way, for example:
- Firefighter is the name given to a part of us that will do whatever is necessary in the moment to deal with an exile that is otherwise coming to the surface—sometimes with drastic actions/reactions that may not be great for us.
- Manager is the name given to a part of us that has a more nurturing protective role, keeping us from harm in what’s often a more prophylactic manner.
To give a simple illustration…
A person was criticized a lot as a child, told she was useless, and treated as a disappointment. Consequently, as an adult she now has an exile “the useless child”, something she strives to leave well behind in her past, because it was a painful experience for her. However, sometimes when someone questions and/or advises her, she will get defensive as her firefighter “the hero” will vigorously speak up for her competence, like nobody did when she was a child. This vigor, however, manifests as rude abrasiveness and overcompensation. Finally, she has a manager, “the advocate”, who will do the same job, but in a more quietly confident fashion.
This person’s therapy will look at transferring the protector job from the firefighter to the manager, which will involve examining, questioning, and addressing all three parts.
The above example is fictional and created for simplicity and clarity; here’s a real-world case study if you’d like a more in-depth overview of how it can work:
How it all fits together in practice
IFS looks to make sure all the parts’ needs are met, even the “bad” ones, because they all have their functions.
Good IFS therapy, however, can make sure a part is heard, and then reassure that part in a way that effectively allows that part to “retire”, safe and secure in the knowledge that it has done what it needed to, and/or the job is being done by another part now.
That can involve, for example, thanking the firefighter for looking after our exile for all these years, but that our exile is safe and in good hands now, so it can put that fire-axe away.
See also: On Being Reactive vs Being Responsive
Questions you might ask yourself
While IFS therapy is best given by a skilled practitioner, we can take some of the ideas of it for self-therapy too. For example…
- What is a secret about yourself that you will take to the grave? And now, why did that part of you (now an exile) come to exist?
- What does that exile need, that it didn’t get? What parts of us try to give it that nowadays?
- What could we do, with all that information in mind, to assign the “protection” job to the part of us best-suited to healthy integration?
Want to know more?
We’ve only had the space of a small article to give a brief introduction to Family Systems therapy, so check out the “resources” tab at:
IFS Institute | What Is Internal Family Systems Therapy?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why are people on TikTok talking about going for a ‘fart walk’? A gastroenterologist weighs in
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Fart walks” have become a cultural phenomenon, after a woman named Mairlyn Smith posted online a now-viral video about how she and her husband go on walks about 60 minutes after dinner and release their gas.
Smith, known on TikTok as @mairlynthequeenoffibre and @mairlynsmith on Instagram, has since appeared on myriad TV and press interviews extolling the benefits of a fart walk. Countless TikTok and Instagram users and have now shared their own experiences of feeling better after taking up the #fartwalk habit.
So what’s the evidence behind the fart walk? And what’s the best way to do it?
CandyBox Images/Shutterstock Exercise can help get the gas out
We know exercise can help relieve bloating by getting gas moving and out of our bodies.
Researchers from Barcelona, Spain in 2006 asked eight patients complaining of bloating, seven of whom had irritable bowel syndrome, to avoid “gassy” foods such as beans for two days and to fast for eight hours before their study.
Each patient was asked to sit in an armchair, in order to avoid any effects of body position on the movement of gas. Gas was pumped directly into their small bowel via a thin plastic tube that went down their mouth, and the gas expelled from the body was collected into a bag via a tube placed in the rectum. This way, the researchers could determine how much gas was retained in the gut.
The patients were then asked to pedal on a modified exercise bike while remaining seated in their armchairs.
The researchers found that much less gas was retained in the patients’ gut when they exercised. They determined exercise probably helped the movement and release of intestinal gas.
Walking may have another bonus; it may trigger a nerve reflex that helps propel foods and gas contents through the gut.
Walking can also increase internal abdominal pressure as you use your abdominal muscles to stay upright and balance as you walk. This pressure on the colon helps to push intestinal gas out.
Proper fart walk technique
One study from Iran studied the effects of walking in 94 individuals with bloating.
They asked participants to carry out ten to 15 minutes of slow walking (about 1,000 steps) after eating lunch and dinner. They filled out gut symptom questionnaires before starting the program and again at the end of the four week program.
The researchers found walking after meals resulted in improvements to gut symptoms such as belching, farting, bloating and abdominal discomfort.
Now for the crucial part: in the Iranian study, there was a particular way in which participants were advised to walk. They were asked to clasp hands together behind their back and to flex their neck forward.
The clasped hands posture leads to more internal abdominal pressure and therefore more gentle squeezing out of gas from the colon. The flexed neck posture decreases the swallowing of air during walking.
This therefore is the proper fart walk technique, based on science.
Could walking with your hands behind your back yield better or more farts? candy candy/Shutterstock What about constipation?
A fart walk can help with constipation.
One study involved middle aged inactive patients with chronic constipation, who did a 12 week program of brisk walking at least 30 minutes a day – combined with 11 minutes of strength and flexibility exercises.
This program, the researchers found, improved constipation symptoms through reduced straining, less hard stools and more complete evacuation.
It also appears that the more you walk the better the benefits for gut symptoms.
In patients with irritable bowel syndrome, one study increasing the daily step count to 9,500 steps from 4,000 steps led to a 50% reduction in the severity of their symptoms.
And just 30 minutes of a fart walk has been shown to improve blood sugar levels after eating.
Walking after eating can help keep your blood sugar levels under control. IndianFaces/Shutterstock What if I can’t get outside the house?
If getting outside the house after dinner is impossible, could you try walking slowly on a treadmill or around the house for 1,000 steps?
If not, perhaps you could borrow an idea from the Barcelona research: sit back in an armchair and pedal using a modified exercise bike. Any type of exercise is better than none.
Whatever you do, don’t be a couch potato! Research has found more leisure screen time is linked to a greater risk of developing gut diseases.
We also know physical inactivity during leisure time and eating irregular meals are linked to a higher risk of abdominal pain, bloating and altered bowel motions.
Try the fart walk today
It may not be for everyone but this simple physical activity does have good evidence behind it. A fart walk can improve common symptoms such as bloating, abdominal discomfort and constipation.
It can even help lower blood sugar levels after eating.
Will you be trying a fart walk today?
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How Useful Are Our Dreams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s In A Dream?
We were recently asked:
❝I have a question or a suggestion for coverage in your “Psychology Sunday”. Dreams: their relevance, meanings ( if any) interpretations? I just wondered what the modern psychological opinions are about dreams in general.❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
There are two main schools of thought, and one main effort to reconcile those two. The third one hasn’t quite caught on so far as to be considered a “school of thought” yet though.
The Top-Down Model (Psychoanalysts)
Psychoanalysts broadly follow the theories of Freud, or at least evolved from there. Freud was demonstrably wrong about very many things. Most of his theories have been debunked and ditched—hence the charitable “or at least evolved from there” phrasing when it comes to modern psychoanalytic schools of thought. Perhaps another day, we’ll go into all the ways Freud went wrong. However, for today, one thing he wasn’t bad at…
According to Freud, our dreams reveal our subconscious desires and fears, sometimes directly and sometimes dressed in metaphor.
Examples of literal representations might be:
- sex dreams (revealing our subconscious desires; perhaps consciously we had not thought about that person that way, or had not considered that sex act desirable)
- getting killed and dying (revealing our subconscious fear of death, not something most people give a lot of conscious thought to most of the time)
Examples of metaphorical representations might be:
- dreams of childhood (revealing our subconscious desires to feel safe and nurtured, or perhaps something else depending on the nature of the dream; maybe a return to innocence, or a clean slate)
- dreams of being pursued (revealing our subconscious fear of bad consequences of our actions/inactions, for example, responsibilities to which we have not attended, debts are a good example for many people; or social contact where the ball was left in our court and we dropped it, that kind of thing)
One can read all kinds of guides to dream symbology, and learn such arcane lore as “if you dream of your teeth crumbling, you have financial worries”, but the truth is that “this thing means that other thing” symbolic equations are not only highly personal, but also incredibly culture-bound.
For example:
- To one person, bees could be a symbol of feeling plagued by uncountable small threats; to another, they could be a symbol of abundance, or of teamwork
- One culture’s “crow as an omen of death” is another culture’s “crow as a symbol of wisdom”
- For that matter, in some cultures, white means purity; in others, it means death.
Even such classically Freudian things as dreaming of one’s mother and/or father (in whatever context) will be strongly informed by one’s own waking-world relationship (or lack thereof) with same. Even in Freud’s own psychoanalysis, the “mother” for the sake of such analysis was the person who nurtured, and the “father” was the person who drew the nurturer’s attention away, so they could be switched gender roles, or even different people entirely than one’s parents.
The only real way to know what, if anything, your dreams are trying to tell you, is to ask yourself. You can do that…
- by reflection and personal interrogation (see for example: The Easiest Way To Take Up Journaling)
- or by externalising parts of your subconscious (as in Internal Family Systems therapy)
- or by talking directly to your subconscious where it is, by means of lucid dreaming.
The idea with lucid dreaming is that since any dream character is a facet of your subconscious generated by your own mind, by talking to that character you can ask questions directly of your subconscious (the popular 2010 movie “Inception” was actually quite accurate in this regard, by the way).
To read more about how to do this kind of self-therapy through lucid dreaming, you might want to check out this book we reviewed previously; it is the go-to book of lucid dreaming enthusiasts, and will honestly give you everything you need in one go:
Lucid Dreaming: A Concise Guide to Awakening in Your Dreams and in Your Life – by Dr. Stephen LaBerge
The Bottom-Up Model (Neuroscientists)
This will take a lot less writing, because it’s practically a null hypothesis (i.e., the simplest default assumption before considering any additional evidence that might support or refute it; usually some variant of “nothing unusual going on here”).
The Bottom-Up model holds that our brains run regular maintenance cycles during REM sleep (a biological equivalent of defragging a computer), and the brain interprets these pieces of information flying by and, because of the mind’s tendency to look for patterns, fills in the rest (much like how modern generative AI can “expand” a source image to create more of the same and fill in the blanks), resulting in the often narratively wacky, but ultimately random, vivid hallucinations that we call dreams.
The Hybrid Model (per Cartwright, 2012)
This is really just one woman’s vision, but it’s an incredibly compelling one, that takes the Bottom-Up model and asks “what if we did all that bio-stuff, and then our subconscious mind influenced the interpretation of the random patterns, to create dreams that are subjectively meaningful, and thus do indeed represent our subconscious?
It’s best explained in her own words, though, so it’s time for another book recommendation (we’ve reviewed this one before, too):
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Serotonin vs Dopamine (Know The Differences)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of the various neurotransmitters that people confuse with each other, serotonin and dopamine are the two highest on the list (with oxytocin coming third as people often attribute its effects to serotonin). But, for all they are both “happiness molecules”, serotonin and dopamine are quite different, and are even opposites in some ways:
More than just happiness
Let’s break it down:
Similarities:
- Both are neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and monoamines.
- Both impact cognition, mood, energy, behavior, memory, and learning.
- Both influence social behavior, though in different ways.
Differences (settle in; there are many):
- Chemical structure:
- Dopamine: catecholamine (derived from phenylalanine and tyrosine)
- Serotonin: indoleamine (derived from tryptophan)
- Derivatives:
- Dopamine → noradrenaline and adrenaline (stress and alertness)
- Serotonin → melatonin (sleep and circadian rhythm)
- Effects on mental state:
- Dopamine: drives action, motivation, and impulsivity.
- Serotonin: promotes calmness, behavioral inhibition, and cooperation.
- Role in memory and learning:
- Dopamine: key in attention and working memory
- Serotonin: crucial for hippocampus activation and long-term memory
Symptoms of imbalance:
- Low dopamine:
- Loss of motivation, focus, emotion, and activity
- Linked to Parkinson’s disease and ADHD
- Low serotonin:
- Sadness, irritability, poor sleep, and digestive issues
- Linked to PTSD, anxiety, and OCD
- High dopamine:
- Excessive drive, impulsivity, addictions, psychosis
- High serotonin:
- Nervousness, nausea, and in extreme cases, serotonin syndrome (which can be fatal)
Brain networks:
- Dopamine: four pathways controlling movement, attention, executive function, and hormones.
- Serotonin: widely distributed across the cortex, partially overlapping with dopamine systems.
Speed of production:
- Dopamine: can spike and deplete quickly; fatigues faster with overuse.
- Serotonin: more stable, releasing steadily over longer periods.
Illustrative examples:
- Coffee boosts dopamine but loses its effect with repeated use.
- Sunlight helps maintain serotonin levels over time.
If you remember nothing else, remember this:
- Dopamine: action, motivation, and alertness.
- Serotonin: contentment, happiness, and calmness.
For more on all of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
From eye exams to blood tests and surgery: how doctors use light to diagnose disease
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
You’re not feeling well. You’ve had a pounding headache all week, dizzy spells and have vomited up your past few meals.
You visit your GP to get some answers and sit while they shine a light in your eyes, order a blood test and request some medical imaging.
Everything your GP just did relies on light. These are just some of the optical technologies that have had an enormous impact in how we diagnose disease.
megaflopp/Shutterstock 1. On-the-spot tests
Point-of-care diagnostics allow doctors to test patients on the spot and get answers in minutes, rather than sending samples to a lab for analysis.
The “flashlight” your GP uses to view the inside of your eye (known as an ophthalmoscope) is a great example. This allows doctors to detect abnormal blood flow in the eye, deformations of the cornea (the outermost clear layer of the eye), or swollen optical discs (a round section at the back of the eye where the nerve link to the brain begins). Swollen discs are a sign of elevated pressure inside your head (or in the worst case, a brain tumour) that could be causing your headaches.
The invention of lasers and LEDs has enabled many other miniaturised technologies to be provided at the bedside or clinic rather than in the lab.
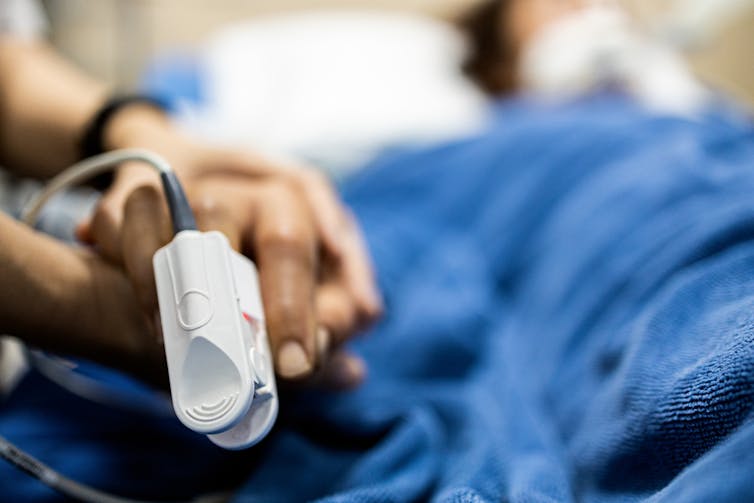
Pulse oximetry is a famous example, where a clip attached to your finger reports how well your blood is oxygenated. It does this by measuring the different responses of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood to different colours of light.
Pulse oximetry is used at hospitals (and sometimes at home) to monitor your respiratory and heart health. In hospitals, it is also a valuable tool for detecting heart defects in babies.
See that clip on the patient’s finger? That’s a pulse oximeter, which relies on light to monitor respiratory and heart health. CGN089/Shutterstock 2. Looking at molecules
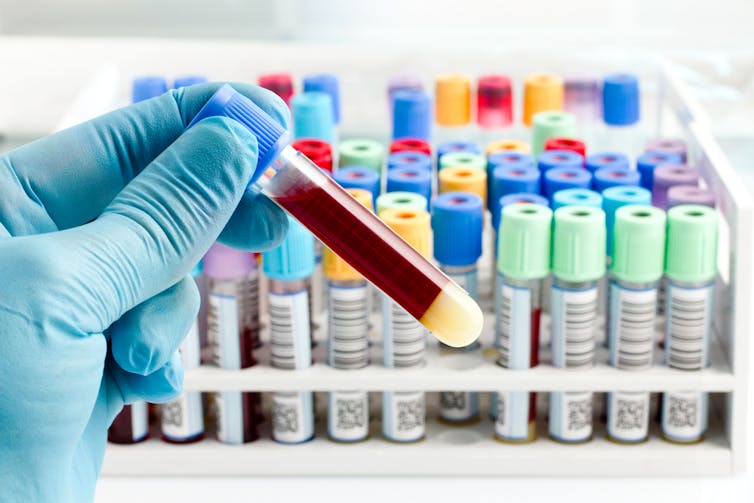
Now, back to that blood test. Analysing a small amount of your blood can diagnose many different diseases.
A machine called an automated “full blood count analyser” tests for general markers of your health. This machine directs focused beams of light through blood samples held in small glass tubes. It counts the number of blood cells, determines their specific type, and reports the level of haemoglobin (the protein in red blood cells that distributes oxygen around your body). In minutes, this machine can provide a snapshot of your overall health.
For more specific disease markers, blood serum is separated from the heavier cells by spinning in a rotating instrument called a centrifuge. The serum is then exposed to special chemical stains and enzyme assays that change colour depending on whether specific molecules, which may be the sign of a disease, are present.
These colour changes can’t be detected with the naked eye. However, a light beam from an instrument called a spectrometer can detect tiny amounts of these substances in the blood and determine if the biomarkers for diseases are present, and at what levels.
Light shines through the blood sample and tells us whether biomarkers for disease are present. angellodeco/Shutterstock 3. Medical imaging
Let’s re-visit those medical images your GP ordered. The development of fibre-optic technology, made famous for transforming high-speed digital communications (such as the NBN), allows light to get inside the body. The result? High-resolution optical imaging.
A common example is an endoscope, where fibres with a tiny camera on the end are inserted into the body’s natural openings (such as your mouth or anus) to examine your gut or respiratory tracts.
Surgeons can insert the same technology through tiny cuts to view the inside of the body on a video screen during laparoscopic surgery (also known as keyhole surgery) to diagnose and treat disease.
Doctors can insert this flexible fibre-optic tube with a camera on the end into your body. Eduard Valentinov/Shutterstock How about the future?
Progress in nanotechnology and a better understanding of the interactions of light with our tissues are leading to new light-based tools to help diagnose disease. These include:
- nanomaterials (materials on an extremely small scale, many thousands of times smaller than the width of a human hair). These are being used in next-generation sensors and new diagnostic tests
- wearable optical biosensors the size of your fingernail can be included in devices such as watches, contact lenses or finger wraps. These devices allow non-invasive measurements of sweat, tears and saliva, in real time
- AI tools to analyse how blood serum scatters infrared light. This has allowed researchers to build a comprehensive database of scatter patterns to detect any cancer
- a type of non-invasive imaging called optical coherence tomography for more detailed imaging of the eye, heart and skin
- fibre optic technology to deliver a tiny microscope into the body on the tip of a needle.
So the next time you’re at the GP and they perform (or order) some tests, chances are that at least one of those tests depend on light to help diagnose disease.
Matthew Griffith, Associate Professor and ARC Future Fellow and Director, UniSA Microscopy and Microanalysis Facilities, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is stress turning my hair grey?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When we start to go grey depends a lot on genetics.
Your first grey hairs usually appear anywhere between your twenties and fifties. For men, grey hairs normally start at the temples and sideburns. Women tend to start greying on the hairline, especially at the front.
The most rapid greying usually happens between ages 50 and 60. But does anything we do speed up the process? And is there anything we can do to slow it down?
You’ve probably heard that plucking, dyeing and stress can make your hair go grey – and that redheads don’t. Here’s what the science says.
Oksana Klymenko/Shutterstock What gives hair its colour?
Each strand of hair is produced by a hair follicle, a tunnel-like opening in your skin. Follicles contain two different kinds of stem cells:
- keratinocytes, which produce keratin, the protein that makes and regenerates hair strands
- melanocytes, which produce melanin, the pigment that colours your hair and skin.
There are two main types of melanin that determine hair colour. Eumelanin is a black-brown pigment and pheomelanin is a red-yellow pigment.
The amount of the different pigments determines hair colour. Black and brown hair has mostly eumelanin, red hair has the most pheomelanin, and blonde hair has just a small amount of both.
So what makes our hair turn grey?
As we age, it’s normal for cells to become less active. In the hair follicle, this means stem cells produce less melanin – turning our hair grey – and less keratin, causing hair thinning and loss.
As less melanin is produced, there is less pigment to give the hair its colour. Grey hair has very little melanin, while white hair has none left.
Unpigmented hair looks grey, white or silver because light reflects off the keratin, which is pale yellow.
Grey hair is thicker, coarser and stiffer than hair with pigment. This is because the shape of the hair follicle becomes irregular as the stem cells change with age.
Interestingly, grey hair also grows faster than pigmented hair, but it uses more energy in the process.
Can stress turn our hair grey?
Yes, stress can cause your hair to turn grey. This happens when oxidative stress damages hair follicles and stem cells and stops them producing melanin.
Oxidative stress is an imbalance of too many damaging free radical chemicals and not enough protective antioxidant chemicals in the body. It can be caused by psychological or emotional stress as well as autoimmune diseases.
Environmental factors such as exposure to UV and pollution, as well as smoking and some drugs, can also play a role.
Melanocytes are more susceptible to damage than keratinocytes because of the complex steps in melanin production. This explains why ageing and stress usually cause hair greying before hair loss.
Scientists have been able to link less pigmented sections of a hair strand to stressful events in a person’s life. In younger people, whose stems cells still produced melanin, colour returned to the hair after the stressful event passed.
4 popular ideas about grey hair – and what science says
1. Does plucking a grey hair make more grow back in its place?
No. When you pluck a hair, you might notice a small bulb at the end that was attached to your scalp. This is the root. It grows from the hair follicle.
Plucking a hair pulls the root out of the follicle. But the follicle itself is the opening in your skin and can’t be plucked out. Each hair follicle can only grow a single hair.
It’s possible frequent plucking could make your hair grey earlier, if the cells that produce melanin are damaged or exhausted from too much regrowth.
2. Can my hair can turn grey overnight?
Legend says Marie Antoinette’s hair went completely white the night before the French queen faced the guillotine – but this is a myth.
It is not possible for hair to turn grey overnight, as in the legend about Marie Antoinette. Yann Caradec/Wikimedia, CC BY-NC-SA Melanin in hair strands is chemically stable, meaning it can’t transform instantly.
Acute psychological stress does rapidly deplete melanocyte stem cells in mice. But the effect doesn’t show up immediately. Instead, grey hair becomes visible as the strand grows – at a rate of about 1 cm per month.
Not all hair is in the growing phase at any one time, meaning it can’t all go grey at the same time.
3. Will dyeing make my hair go grey faster?
This depends on the dye.
Temporary and semi-permanent dyes should not cause early greying because they just coat the hair strand without changing its structure. But permanent products cause a chemical reaction with the hair, using an oxidising agent such as hydrogen peroxide.
Accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and other hair dye chemicals in the hair follicle can damage melanocytes and keratinocytes, which can cause greying and hair loss.
4. Is it true redheads don’t go grey?
People with red hair also lose melanin as they age, but differently to those with black or brown hair.
This is because the red-yellow and black-brown pigments are chemically different.
Producing the brown-black pigment eumelanin is more complex and takes more energy, making it more susceptible to damage.
Producing the red-yellow pigment (pheomelanin) causes less oxidative stress, and is more simple. This means it is easier for stem cells to continue to produce pheomelanin, even as they reduce their activity with ageing.
With ageing, red hair tends to fade into strawberry blonde and silvery-white. Grey colour is due to less eumelanin activity, so is more common in those with black and brown hair.
Your genetics determine when you’ll start going grey. But you may be able to avoid premature greying by staying healthy, reducing stress and avoiding smoking, too much alcohol and UV exposure.
Eating a healthy diet may also help because vitamin B12, copper, iron, calcium and zinc all influence melanin production and hair pigmentation.
Theresa Larkin, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Oat Milk vs Almond Milk – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing oat milk to almond milk, we picked the almond milk.
Why?
This one’s quite straightforward, and no, it’s not just our bias for almonds
Rather, almonds contain a lot more vitamins and minerals, all of which usually make it into the milk.
Oat milk is still a fine choice though, and has a very high soluble fiber content, which is great for your heart.
Just make sure you get versions without added sugar or other unpleasantries! You can always make your own at home, too.
You can read a bit more about the pros and cons of various plant milks here:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: