Eat To Beat Hyperthyroidism!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would love to see more on eating vegan. I am allergic to soy in any form which seems to be in everything❞
There is a lot of it about, isn’t there? Happily, these days, a lot of meat and dairy alternatives are also made from other sources, for example pea protein is getting used a lot more nowadays in meat substitutes, and there are many kinds of alternatives to dairy (e.g. nut milks, oat milk, hemp milk, and—which is a branding nightmare but very healthy—pea milk).
You might like these previous main features of ours:
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Down Meat Consumption
- Plant-Based Milks—What’s Best?
Also, if doing a whole foods plant-based diet, lentils (especially brown lentils) can be used as a great substitute for minced beef/lamb in recipes that call for such.
Boil the lentils (a liter of water to a cup of lentils is great; use a rice cooker if you have one!) along with the seasonings you will use (herbs appropriate to your dish, and then: black pepper is always good; you shouldn’t need to add salt; a teaspoon of low-sodium yeast extract is great though, or to really get the best nutritional benefits, nooch).
When it is done, you shouldn’t have excess water now, so just use as is, or if you want a slightly fatty kick, fry briefly in a little extra virgin olive oil, before using it however you were planning to use it.
Enjoy!
❝What foods should I eat for hyperthyroidism? My doctor tells me what foods to avoid, but not what to eat❞
Great question! We’ll have to do a main feature on hyperthyroidism one of these days, as so far we’ve only done features on hypothyroidism:
As for hyperthyroidism…
Depending on your medications, your doctor might recommend a low iodine diet. If so, then you might want to check out:
American Thyroid Association | Low Iodine Diet Plan
…for recommendations.
But in a way, that’s still a manner of “what to avoid” (iodine) and then the foods to eat to avoid that.
You may be wondering: is there any food that actively helps against hyperthyroidism, as opposed to merely does not cause problems?
And the answer is: yes!
Cruciferous vegetables (e.g. cabbage, sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower, etc) contain goitrin, which in immoderate quantities can cause problems for people with hypothyroidism because it can reduce thyroid hormone synthesis. If you have hyperthyroidism, however, this can work in your favor.
Read more: The role of micronutrients in thyroid dysfunction
The above paper focuses on children, but it was the paper we found that explains it most clearly while showing good science. However, the same holds true for adults:
Notwithstanding that the title comes from the angle of examining hypothyroidism, the mechanism of action makes clear its beneficence in the case of hyperthyroidism.
Selenium is also a great nutrient in the case of autoimmune hyperthyroidism, because it is needed to metabolize thyroid hormone (if you don’t metabolize it, it’ll just build up):
Selenium and Thyroid Disease: From Pathophysiology to Treatment
The absolute top best dietary source of selenium is Brazil nuts, to the point that people without hyperthyroidism have to take care to not eat more than a few per day (because too much selenium could then cause problems):
NIH | Selenium Fact Sheet for Health Professionals
(this contains information on the recommended amount, the upper limit amount, how much is in Brazil nuts and other foods, and what happens if you get too much or too little)
Note: after Brazil nuts (which are about 5 times more rich in selenium than the next highest source), the other “good” sources of selenium—mostly various kinds of fish—are also “good” source of iodine, so you might want to skip those.
Want more ideas?
You might like this from LivHealth:
Hyperthyroidism Diet: 9 Foods To Ease Symptoms
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Zucchini vs Okra – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing zucchini to okra, we picked the okra.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, okra has nearly 2x the protein and more than 3x the fiber (for about 2x the carbs).
In terms of vitamins, things are also quite one-sided; zucchini has a little more vitamin B2, while okra has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline.
Nor does the mineral situation make any compelling counterargument; zucchini is higher only in sodium, while okra has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium*, selenium, and zinc.
*Actually it’s only a little more potassium. But the rest are with big margins of difference.
Both of these on-the-cusp-of-being-pungent vegetables have beneficial antioxidant polyphenols (especially various forms of quercetin), but okra has more.
In short: enjoy both, of course, but there’s a clear winner here and it’s okra.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter/Astringent/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How To Keep Your Mind From Wandering
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whether your mind keeps wandering more as you get older, or you’re a young student whose super-active brain is more suited to TikTok than your assigned reading, sustained singular focus can be a challenge for everyone—and yet (alas!) it remains a required skill for so much in life.
Today’s edition of 10Almonds presents a nifty trick to get yourself through those tasks! We’ll also be taking some time to reply to your questions and comments, in our weekly interactive Q&A.
First of all though, we’ve a promise to make good on, so…
How To Stay On The Ball (Or The Tomato?) The Easy Way
For most of us, we face three main problems when it comes to tackling our to-dos:
- Where to start?
- The task seems intimidating in its size
- We get distracted and/or run out of energy
If you’re really not sure where to start, we recommended a powerful tool in last Friday’s newsletter!
For the rest, we love the Pomodoro Technique:
- Set a timer for 25 minutes, and begin your task.
- Keep going until the timer is done! No other tasks, just focus.
- Take a 5-minute break.
- Repeat
This approach has three clear benefits:
- No matter the size of the task, you are only committing to 25 minutes—everything is much less overwhelming when there’s an end in sight!
- Being only 25 minutes means we are much more likely to stay on track; it’s easier to defer other activities if we know that there will be a 5-minute break for that soon.
- Even without other tasks to distract us, it can be difficult to sustain attention for long periods; making it only 25 minutes at a time allows us to approach it with a (relatively!) fresh mind.
Have you heard that a human brain can sustain attention for only about 40 minutes before focus starts to decline rapidly?
While that’s been a popular rationale for school classroom lesson durations (and perhaps coincidentally ties in with Zoom’s 40-minute limit for free meetings), the truth is that focus starts dropping immediately, to the point that one-minute attention tests are considered sufficient to measure the ability to focus.
So a 25-minute Pomodoro is a more than fair compromise!
Why’s it called the “Pomodoro” technique?
And why is the 25-minute timed work period called a Pomodoro?
It’s because back in the 80s, university student Francesco Cirillo was struggling to focus and made a deal with himself to focus just for a short burst at a time—and he used a (now “retro” style) kitchen timer in the shape of a tomato, or “pomodoro”, in Italian.
If you don’t have a penchant for kitsch kitchenware, you can use this free, simple Online Pomodoro Timer!
(no registration/login/download necessary; it’s all right there on the web page)
Share This Post
-
Self-Compassion – by Dr. Kristin Neff
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of people struggle with self-esteem, and depending on one’s surrounding culture, it can even seem socially obligatory to be constantly valuing oneself highly (or else, who else will if we do not?). But, as Dr. Neff points out, there’s an inherent problem with reinforcing for oneself even a positive message like “I am smart, strong, and capable!” because sometimes all of us have moments of being stupid, weak, and incapable (occasionally all three at once!), which places us in a position of having to choose between self-deceit and self-deprecation, neither of which are good.
Instead, Dr. Neff advocates for self-compassion, for treating oneself as one (hopefully) would a loved one—seeing their/our mistakes, weaknesses, failures, and loving them/ourself anyway.
She does not, however, argue that we should accept just anything from ourselves uncritically, but rather, we identify our mistakes, learn, grow, and progress. So not “I should have known better!”, nor even “How was I supposed to know?!”, but rather, “Now I have learned a thing”.
The style of the book is quite personal, as though having a heart-to-heart over a hot drink perhaps, but the format is organized and progresses naturally from one idea to the next, taking the reader to where we need to be.
Bottom line: if you have trouble with self-esteem (as most people do), then that’s a trap that there is a way out of, and it doesn’t require being perfect or lowering one’s standards, just being kinder to oneself along the way—and this book can help inculcate that.
Click here to check out Self-Compassion, and indeed be kind to yourself!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Celery vs Cucumber – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to cucumber, we picked the celery.
Why?
They are both great, of course! But celery came out on top:
Their macros are very comparable; they’re both 95% water with just enough other things to hold them together, and those other things are in approximately the same proportions in both celery and cucumber.
In the category of vitamins, however, celery has a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B9, E, and K, as well as slightly more vitamin C. Cucumber, meanwhile, only boasts slightly higher vitamin B1.
An easy win for celery on the vitamin front!
Minerals are closer, but celery still comes out on top with its notably higher calcium and potassium content. Cucumber has more iron and zinc, but the margin is smaller.
As a point in cucumber’s favor, it has been noted for its anti-inflammatory effect in ways that celery hasn’t, but we don’t think this is enough to say it wins over celery sweeping the vitamins category and coming out top for minerals too.
However! They are both great, so enjoy them both, of course.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety ← both celery and cucumber are great for this
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Who Screens The Sunscreens?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Screen The Sunscreens!
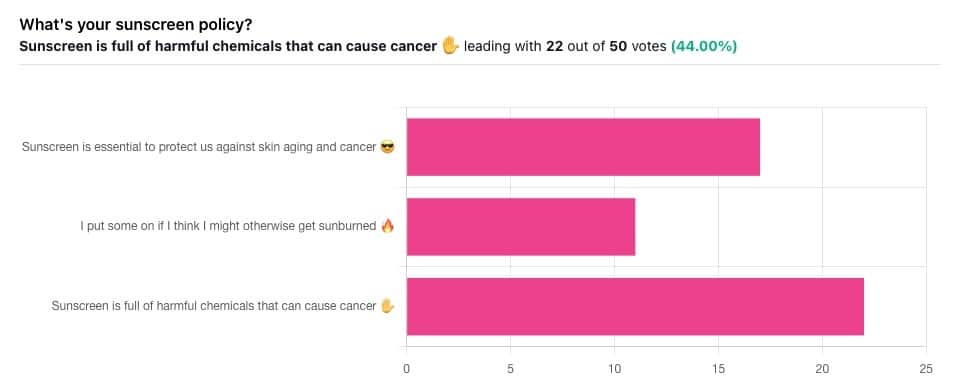
Yesterday, we asked you what your sunscreen policy was, and got a spread of answers. Apparently this one was quite polarizing!
One subscriber who voted for “Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer” wrote:
❝My mom died of complications from melanoma, so we are vigilant about sun and sunscreen. We are a family of campers and hikers and gardeners—outdoors in all seasons—and we never burn❞
Our condolences with regard to your mom! Life is so precious, and when something like that happens, it tends to stick with us. We’re glad you and your family are taking care of yourselves.
Of the subscribers who voted for “I put some on if I think I might otherwise get sunburned”, about half wrote to express uncertainties:
- uncertainty about how safe it is, and
- uncertainty about how helpful it is
…so we’re going to tackle those questions in a moment. But what of those who voted for “Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer”?
Of those, only one wrote a message, which was to say one has to be very careful of what is in the formula.
Let’s take a look, then…
Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer: True or False?
False—according to current best science. Research is ongoing!
There are four main chemicals (found in most sunscreens) that people tend to worry about:
- Abobenzone
- Oxybenzone
- Octocrylene
- Ecamsule
Now, these two sound like four brands of rocket fuel, but then, dihydrogen monoxide (DHMO), which is also found in most sunscreens, sounds like a deadly toxin too. That’s water, by the way.
But what of these four chemicals? Well, as we say, research is ongoing, but we found a study that measured all four, to see how much got into the blood, and what adverse effects, if any, this caused.
We’ll skip to their conclusion:
❝In this preliminary study involving healthy volunteers, application of 4 commercially available sunscreens under maximal use conditions resulted in plasma concentrations that exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens. The systemic absorption of sunscreen ingredients supports the need for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings. These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.❞
Now, “exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens” sounds alarming, so why did they close with the words “These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen”?
Let’s skip back up to a line from the results:
❝The most common adverse event was rash, which developed in 1 participant with each sunscreen.❞
This was most probably due to the oxybenzone, which can cause allergic skin reactions in some people.
Let us take a moment to remember the most common adverse event that occurs from not wearing sunscreen: sunburn!
You can read the full study here:
None of those ingredients have been found to be carcinogenic, even at the maximal blood plasma concentrations studied, from applications 4x/day to 75% of the body.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are absolutely very much known to cause cancer, and the effect is cumulative.
Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer: True or False?
True, unequivocally, unless we live indoors and/or otherwise never go about under sunlight.
“But our ancestors—” lived under the same sun we do, and either used sunscreen or got advanced skin aging and cancer.
Sunscreen of times past ranged from mud to mineral lotions, but it’s pretty much always existed. Even non-human animals that have skin and don’t have fur or feathers, tend to take mud-baths in sunny parts of the world.
If you’d like to avoid oxybenzone and other chemicals, though, you might have your reasons. Maybe you’re allergic, or maybe you read that it’s a potential endocrine disruptor with estrogen-like and anti-androgenic properties that you don’t want.
There are other options, to include physical blockers containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective ingredients.
If you’re interested, you can even make your own sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays (UVA is what causes skin cancer; UVB is “milder” and is what causes sunburn):
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Should You Soak Your Nuts?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝hi. how many almonds should one eat per day? do they need to be soaked? thank you.❞
Within reason, however many you like! Given that protein is an appetite suppressant, you’ll probably find it’s not too many.
Dr. Michael Greger, of “How Not To Die” fame, suggests aiming for 30g of nuts per day. Since almonds typically weigh about 1g each, that means 30 if it’s all almonds.
And if you’re wondering about 10 almonds? The name’s a deliberate reference to an old internet hoax about 10 almonds being the equivalent of an aspirin for treating a headache. It’s a reminder to be open-mindedly skeptical about information circulating wildly, and look into the real, evidence-based, science of things.
- Sometimes, the science validates claims, and we’re excited to share that!
- Sometimes, the science just shoots claims down, and it’s important to acknowledge when that happens too.
On which note, about soaking…
Short version: soaking can improve the absorption of some nutrients, but not much more than simply chewing thoroughly. See:
- A review of the impact of processing on nutrient bioaccessibility and digestion of almonds
- Mastication of almonds: effects of lipid bioaccessibility, appetite, and hormone response
Soaking does reduce certain “antinutrients” (compounds that block absorption of other nutrients), such as phytic acid. However, even a 24-hour soak reduces them only by about 5%:
If you don’t want to take 24-hours to get a 5% benefit, there’s good news! A 12-hour soak can result in 4% less phytic acid in chopped (but not whole) almonds:
The Effect of Soaking Almonds and Hazelnuts on Phytate and Mineral Concentrations
Lest that potentially underwhelming benefit leave a bitter taste in your mouth, one good thing about soaking almonds (if you don’t like bitter tastes, anyway) is that it will reduce their bitterness:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: