How Useful Is Hydrotherapy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hyyyyyyydromatic…
Hydrotherapy is a very broad term, and refers to any (external) use of water as part of a physical therapy. Today we’re going to look at some of the top ways this can be beneficial—maybe you’ll know them all already, but maybe there’s something you hadn’t thought about or done decently; let’s find out!
Notwithstanding the vague nature of the umbrella term, some brave researchers have done a lot of work to bring us lots of information about what works and what doesn’t, so we’ll be using this to guide us today. For example:
Scientific Evidence-Based Effects of Hydrotherapy on Various Systems of the Body
Swimming (and similar)
An obvious one, this can for most people be a very good full-body exercise, that’s exactly as strenuous (or not) as you want/need it to be.
It can be cardio, it can be resistance, it can be endurance, it can be high-intensity interval training, it can be mobility work, it can be just support for an aching body that gets to enjoy being in the closest to zero-gravity we can get without being in freefall or in space.
See also: How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Depending on what’s available for you locally (pool with a shallow area, for example), it can also be a place to do some exercises normally performed on land, but with your weight being partially supported (and as a counterpoint, a little resistance added to movement), and no meaningful risk of falling.
Tip: check out your local facilities, to see if they offer water aerobics classes; because the water necessitates slow movement, this can look a lot like tai chi to watch, but it’s great for mobility and balance.
Water circuit therapy
This isn’t circuit training! Rather, it’s a mixture of thermo- and cryotherapy, that is to say, alternating warm and cold water immersion. This can also be interspersed with the use of a sauna, of course.
See also:
- Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
- Saunas: Health Benefits (& Caveats)
- The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
this last one is about thermal shock-mediated hormesis, which sounds drastic, but it’s what we’re doing here with the hot and cold, and it’s good for most people!
Pain relief
Most of the research for this has to do with childbirth pain rather than, for example, back pain, but the science is promising:
Post-exercise recovery
It can be tempting to sink into a hot bath, or at least enjoy a good hot shower, after strenuous exercise. But does it help recovery too? The answer is probably yes:
Effect of hot water immersion on acute physiological responses following resistance exercise
For more on that (and other means of improving post-exercise recovery), check out our previous main feature:
How To Speed Up Recovery After A Workout (According To Actual Science)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Treat Your Own Knee – by Robin McKenzie
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, a note about the author: he’s a physiotherapist and not a doctor, but with 40 years of practice to his name and 33 letters after his name (CNZM OBE FCSP (Hon) FNZSP (Hon) Dip MDT Dip MT), he seems to know his stuff.
The book covers recognizing the difference between arthritis, degeneration, or normal wear and tear, before narrowing down what your actual problem is and what can be done about it.
While there are many possible causes of knee pain (and by causes, we mean the first-level cause, such as “bad posture” or “old sports injury” or “inflammatory diet” or “repetitive strain” etc, not second-level causes that are also symptoms, like inflammation), McKenzie’s approach involves customizing his system to your body’s specific problems and needs. That’s what most of the book is about.
The style is direct and to-the-point; there’s no sensationalization here nor a feel of being sold anything. There’s lots of science scattered throughout, but all with the intent of enabling the reader to understand what’s going on with the problems, processes, and solutions, and why/how the things that work, work. Where there are exercises offered they are clearly-described and well-illustrated.
Bottom line: this is not a fancy book but it is an effective one. If you have knee pain, this is a very worthwhile one to read.
Click here to check out Treat Your Own Knee, and treat your own knee!
PS: if you have musculoskeletal problems elsewhere in your body, you might want to check out the rest of his body parts series (back, hip, neck, wrist, ankle, etc) for the one that’s tailored to your specific problem.
Share This Post
-
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do we need animal products to be healthy?
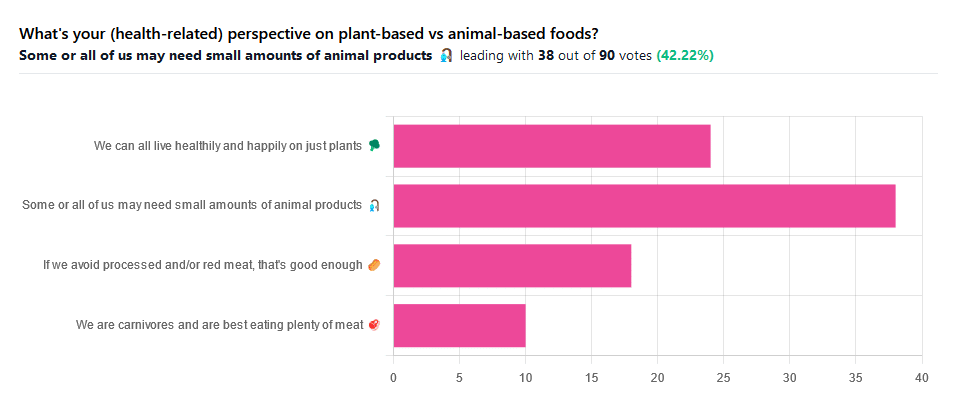
We asked you for your (health-related) perspective on plant-based vs anima-based foods, and got the above-pictured spread of answers.
“Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products” came out on top with more votes than the two more meat-eatery options combined, and the second most popular option was the hard-line “We can all live healthily and happily on just plants”.
Based on these answers, it seems our readership has quite a lot of vegans, vegetarians, and perhaps “flexitarians” who just have a little of animal products here and there.
Perhaps we should have seen this coming; the newsletter is “10almonds”, not “10 rashers of bacon”, after all.
But what does the science say?
We are carnivores and are best eating plenty of meat: True or False?
False. Let’s just rip the band-aid off for this one.
In terms of our anatomy and physiology, we are neither carnivores nor herbivores:
- We have a mid-length digestive tract (unlike carnivores and herbivores who have short and long ones, respectively)
- We have a mouthful of an assortment of teeth; molars and premolars for getting through plants from hard nuts to tough fibrous tubers, and we have incisors for cutting into flesh and (vestigial, but they’re there) canines that really serve us no purpose now but would have been a vicious bite when they were bigger, like some other modern-day primates.
- If we look at our closest living relatives, the other great apes, they are mostly frugivores (fruit-eaters) who supplement their fruity diet with a small quantity of insects and sometimes other small animals—of which they’ll often eat only the fatty organ meat and discard the rest.
And then, there’s the health risks associated with meat. We’ll not linger on this as we’ve talked about it before, but for example:
- Processed Meat Consumption and the Risk of Cancer: A Critical Evaluation of the Constraints of Current Evidence from Epidemiological Studies
- Red Meat Consumption (Heme Iron Intake) and Risk for Diabetes and Comorbidities?
- Health Risks Associated with Meat Consumption: A Review of Epidemiological Studies
- Associations of Processed Meat, Unprocessed Red Meat, Poultry, or Fish Intake With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality
- Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010-2020) evidences
If we avoid processed and/or red meat, that’s good enough: True or False?
True… Ish.
Really this one depends on one’s criteria for “good enough”. The above-linked studies, and plenty more like them, give the following broad picture:
- Red and/or processed meats are unequivocally terrible for the health in general
- Other mammalian meats, such as from pigs, are really not much better
- Poultry, on the other hand, the science is less clear on; the results are mixed, and thus so are the conclusions. The results are often barely statistically significant. In other words, when it comes to poultry, in the matter of health, the general consensus is that you can take it or leave it and will be fine. Some studies have found firmly for or against it, but the consensus is a collective scientific shrug.
- Fish, meanwhile, has almost universally been found to be healthful in moderation. You may have other reasons for wanting to avoid it (ethics, environmentalism, personal taste) but those things are beyond the scope of this article.
Some or all of us may need small amounts of animal products: True or False?
True! With nuances.
Let’s divide this into “some” and “all”. Firstly, some people may have health conditions and/or other mitigating circumstances that make an entirely plant-based diet untenable.
We’re going light on quotations from subscriber comments today because otherwise this article will get a bit long, but here’s a great example that’s worth quoting, from a subscriber who voted for this option:
❝I have a rare genetic disease called hereditary fructose intolerance. It means I lack the enzyme, Aldolase B, to process fructose. Eating fruits and veggies thus gives me severe hypoglycemia. I also have anemia caused by two autoimmune diseases, so I have to eat meat for the iron it supplies. I also supplement with iron pills but the pills alone can’t fix the problem entirely.❞
And, there’s the thing. Popular vegan talking-points are very good at saying “if you have this problem, this will address it; if you have that problem, that will address it”, etc. For every health-related objection to a fully plant-based diet there’s a refutation… Individually.
But actual real-world health doesn’t work like that; co-morbidities are very common, and in some cases, like our subscriber above, one problem undermines the solution to another. Add a third problem and by now you really just have to do what you need to do to survive.
For this reason, even the Vegan Society’s definition of veganism includes the clause “so far as is possible and practicable”.
Now, as for the rest of us “all”.
What if we’re really healthy and are living in optimal circumstances (easy access to a wide variety of choice of food), can we live healthily and happily just on plants?
No—on a technicality.
Vegans famously need to supplement vitamin B12, which is not found in plants. Ironically, much of the B12 in animal products comes from the animals themselves being given supplements, but that’s another matter. However, B12 can also be enjoyed from yeast. Popular options include the use of yeast extract (e.g. Marmite) and/or nutritional yeast in cooking.
Yeast is a single-celled microorganism that’s taxonomically classified as a fungus, even though in many ways it behaves like an animal (which series of words may conjure an amusing image, but we mean, biologically speaking).
However, it’s also not technically a plant, hence the “No—on a technicality”
Bottom line:
By nature, humans are quite versatile generalists when it comes to diet:
- Most of us can live healthily and happily on just plants if we so choose.
- Some people cannot, and will require varying kinds (and quantities) of animal products.
- As for red and/or processed meats, we’re not the boss of you, but from a health perspective, the science is clear: unless you have a circumstance that really necessitates it, just don’t.
- Same goes for pork, which isn’t red and may not be processed, but metabolically it’s associated with the same problems.
- The jury is out on poultry, but it strongly appears to be optional, healthwise, without making much of a difference either way
- Fish is roundly considered healthful in moderation. Enjoy it if you want, don’t if you don’t.
Share This Post
-
How to Eat (And Still Lose Weight) – by Dr. Andrew Jenkinson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: what diet is he recommending?
The answer is: some guiding principles aside…. He’s not recommending a diet, per se.
What this book does instead is outline why we eat too much ← link is to where we previously had this author as a spotlight featured expert on this topic! Check it out!
He goes into a lot more detail than we ever could have in our little article, though, and this book is one of those where the reader may feel as though we have had a few classes at medical school. The style, however, is very comprehensible and accessible; there’s no obfuscating jargon here.
Once we understand the signalling that goes on in terms of hunger/satiety, and the signalling that goes on in terms of fat storage/metabolism, we can simply choose to not give our bodies the wrong signals. Yes, it’s really that simple. It feels quite like a cheat code!
Bottom line: if you’d like a better understanding of what regulates our body’s “set point” in weight/adiposity, and what can change it (for better or for worse), then this is the book for you.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What does lion’s mane mushroom actually do, anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may know it as an ingredient in nootropic supplements. You may have heard of lion’s mane mushroom coffee. You may know it as the big shaggy white mushroom that grows in nature and can look very impressive.
What’s special about it?
The lion’s mane mushroom, or Hericium erinaceus (we mention, as studies we’ll cite often use the botanical name) is an adaptogenic agent that has an established ability to promote nerve regeneration through nerve growth factor neurotrophic activity. In other words, it helps (re)grow neurons.
In a 2023 study, researchers wondered if its abilities (well-established in the peripheral nervous system) would work in the central nervous system too, namely the brain, specifically the hippocampus (responsible for memory).
To boil what they found down to a single line, they concluded:
❝[Lion’s mane extract] therefore acts through a novel pan-neurotrophic signaling pathway, leading to improved cognitive performance.❞
You can read the full study for yourself (with pictures!) here:
Limitations of the study
It’s worth noting that the above study was performed on mice brains, not those of humans. As there is a shortage of human volunteers willing to have their brains sliced and examined under microscopes, we do not expect this study to be repeated with humans any time soon.
So, are there human studies that have been done?
There are! Particularly promising was this 2020 study of people with Alzheimer’s disease, wherein supplementation with 1g of lion’s mane mushroom daily for 49 weeks significantly increased cognitive test scores compared with a placebo; you can read about it here:
Additionally, this 2019 study showed that taking 1.2g daily for eight weeks helped relieve depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders in overweight or obese patiences:
Are there other health benefits?
It seems so! Unfortunately, most of its other health claims are only supported by animal studies so far, aside from one small study funded by a supplement company for their supplement that contained mostly Agaricus blazei (a different mushroom) with 14% lion’s mane.
However, in animal studies, lion’s mane has also shown promise:
- For digestion
- Against inflammation
- For cardiovascular health
- For diabetes management
- Against cancer
- Against aging
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it (or anything else, for that matter) but if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product for your convenience:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What families should know about whooping cough
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Whooping cough is a bacterial respiratory illness that can cause long-term symptoms and even death.
- Two types of vaccines protect against it: The DTap vaccine is given to babies and children up to 6 years old, while the Tdap vaccine is given to children 7 years and older and adults.
- If you or your child has symptoms of whooping cough, isolate them from vulnerable family members and seek treatment early to reduce the risk of serious illness.
Whooping cough, also called pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that’s particularly dangerous for babies. Cases are now at least four times as high as they were at this time last year. Fortunately, vaccines are extremely effective at preventing the disease across age groups.
Read on to learn about the symptoms and risks of whooping cough, who should get vaccinated, and what to do when symptoms appear.What are the symptoms of whooping cough?
Early symptoms of whooping cough typically appear five to 10 days after exposure and may include a runny or stuffy nose, a low fever, and a mild cough. One to two weeks later, some people may experience extreme coughing fits that can cause shortness of breath, trouble sleeping, vomiting, fatigue, and rib fractures. These fits usually last one to six weeks, but they can last up to 10 weeks after infection.
About one in three babies under 1 year old who contract whooping cough require hospitalization, as they may experience life-threatening pauses in breathing (called apnea), pneumonia, and other complications. Children and adults who have asthma or are immunocompromised are also more likely to develop severe symptoms.
Which vaccines protect against whooping cough, and who is eligible?
Two types of vaccines protect against whooping cough: The DTap vaccine is given to babies and children up to 6 years old, while the Tdap vaccine is given to children 7 years and older and adults. Both vaccines protect against infections from diptheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that pregnant people receive a single dose of the Tdap vaccine between 27 and 36 weeks of pregnancy, as this lowers the risk of whooping cough in babies younger than 2 months old by 78 percent.
Multiple doses are required for the best protection. Learn more about DTaP and Tdap vaccine schedules from the CDC, and talk to your health care provider about how many doses you and your children need.
What should families do when whooping cough symptoms appear?
If you or your child has symptoms of whooping cough, isolate the infected person from vulnerable family members. It’s also important to seek treatment early to reduce the risk of serious illness. Health care providers typically prescribe antibiotics to those recovering at home.
Over-the-counter cough and cold medicine is not recommended for children under 4 years old. However, limiting smoke, dust, and chemical fumes at home and using a humidifier can reduce coughing. If you are caring for someone with whooping cough who exhibits pauses in breathing or develops gray or blue skin, call 911 immediately.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Mind-Gut Connection – by Dr. Emeran Mayer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed books about the mind-gut connection before, so what makes this one stand out?
Firstly, it’s a lot more comprehensive than the usual “please, we’re begging you, eat some fiber”.
And yes, of course that’s part of it. Prebiotics, probiotics, reduce fried and processed foods, reduce sugar/alcohol, reduce meat, and again, eat some greenery.
But where this book really comes into its own is looking more thoroughly at the gut microbiota and their function. Dr. Mayer goes well beyond “there are good and bad bacteria” and looks at the relationship each of them have with the body’s many hormones, and especially neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
He also looks at the two-way connection between brain and gut. Yes, our gut gives us “gut feelings”, but 10% of communication between the brain and gut is in the other direction; he explores what that means for us, too.
Finally, he does give a lot of practical advice, not just dietary but also behavioral, to make the most of our mind-gut connection and make it work for our health, rather than against it.
Bottom line: this is the best book on the brain-gut connection that this reviewer has read so far, and certainly the most useful if you already know about gut-healthy nutrition, and are looking to take your understanding to the next level.
Click here to check out The Mind-Gut Connection, and start making yours work for your benefit!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: