Healthy Butternut Macaroni Cheese
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A comfort food classic, healthy and plant-based, without skimping on the comfort.
You will need
- ½ butternut squash, peeled and cut into small pieces (if buying ready-chopped, this should be about 1 lb)
- 1 onion, chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 12 oz (or thereabouts) wholegrain macaroni, or similar pasta shape (even penne works fine—which is good, as it’s often easier to buy wholegrain penne than wholegrain macaroni) (substitute with a gluten-free pasta such as buckwheat pasta, if avoiding gluten)
- 6 oz (or thereabouts) cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 15 minutes (but longer is better)
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend hazelnut for its mellow nutty flavor)
- 3 tbsp nutritional yeast
- Juice of ½ lemon
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: smoked paprika, to serve
Note: if you are allergic to nuts, please accept our apologies that there’s no substitution available in this one. Simply put, removing the cashews would mean changing most of the rest of the recipe to compensate, so there’s no easy “or substitute with…” that we can mention. We’ll have to find/develop a good healthy plant-based no-nuts recipe for you at a later date.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the butternut squash, onion, and garlic with the olive oil, in a large roasting tin, tossing thoroughly to ensure an even coat of oil. Roast them for about 25 minutes until soft.
3) Cook the macaroni while you wait (this should take about 10 minutes or so in salted water), drain, and rinse thoroughly in cold water, before setting aside. This cooling increases the pasta’s resistant starch content (that’s good, for your gut and for your blood sugars, and thus also for your heart and brain), and it will maintain this benefit even when we reheat it later.
4) Drain the cashews, and tip them into a high-speed blender with the milk, and process until smooth. Add the roasted vegetables and the remaining ingredients apart from the pasta, and continue to process until again smooth. You can add a little more milk if you need to, but go easy with it.
5) Heat the sauce (that you just made in the food processor) gently in a saucepan, and refresh the pasta by pouring a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander.
6) Optional: combine the pasta and sauce in an ovenproof dish or cast iron pan, and give it a few minutes under the hottest grill (or browning iron, if you have such) your oven can muster. Alternatively, use a culinary blowtorch, if you have one.
7) Serve; and if you didn’t do the optional step above, this means combining the pasta and sauce. You can also dust the top with some extra seasonings if you like. Smoked paprika works well for this.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Butternut Squash vs Pumpkin – Which is Healthier?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10 Oft-Ignored Symptoms Of Diabetes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Due in part to its prevalence and manageability, diabetes is often viewed as more of an inconvenience than an existential threat. While very few people in countries with decent healthcare die of diabetes directly (such as by diabetic ketoacidosis, which is very unpleasant, and happens disproportionately in the US where insulin is sold with a 500%–3000% markup in price compared to other countries), many more die of complications arising from comorbidities, and as for what comorbidities come with diabetes, well, it increases your risk for almost everything.
So, while for most people diabetes is by no means a death sentence, it is something that means you’ll now have to watch out for pretty much everything else too. On which note, Dr. Siobhan Deshauer is here with things to be aware of:
More than your waistline
Some of these are early symptoms (even appearing in the prediabetic stage, so can be considered an early warning for diabetes), some are later risks (it’s unlikely you’ll lose your feet from diabetic neuropathy complications before noticing that you are diabetic), but all and any of them are good reason to speak with your doctor sooner rather than later:
- Polyuria: waking up multiple times at night to urinate due to excess glucose spilling into the urine.
- Increased thirst: dehydration from frequent urination leads to excessive thirst, creating a cycle.
- Acanthosis nigricans: dark, velvety patches on areas like the neck, armpits, or groin, signalling insulin resistance.
- Skin tags: multiple skin tags in areas of friction may indicate insulin resistance.
- Recurrent Infections: high blood sugar weakens the immune system, making skin infections, UTIs, and yeast infections more common.
- Diabetic stiff hand syndrome: stiffness in hands, limited movement, or a “positive prayer sign” caused by sugar binding to skin and tendon proteins.
- Frozen shoulder and trigger finger: pain and limited movement in the shoulder or fingers, with a snapping sensation when moving inflamed tendons.
- Neuropathy: numbness, tingling, or pain in hands and feet due to nerve and blood vessel damage, often leading to foot deformities like Charcot foot.
- Diabetic foot infections: poor sensation, weakened immune response, and slow healing can result in severe infections and potential amputations.
- Gastroparesis: damage to stomach nerves causes delayed digestion, leading to bloating, nausea, and erratic blood sugar levels.
For more on all of these, plus some visuals of the things like what exactly is a “positive prayer sign”, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Cost of Insulin by Country 2024 ← after the US, the next most expensive country is Chile, at around 1/5 of the price; the cheapest listed is Turkey, at around 1/33 of the price.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Doctor’s Kitchen – by Dr. Rupy Aujla
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve featured Dr. Aujla before as an expert-of-the-week, and now it’s time to review a book by him. What’s his deal, and what should you expect?
Dr. Aujla first outlines the case for food as medicine. Not just “eat nutritionally balanced meals”, but literally, “here are the medicinal properties of these plants”. Think of some of the herbs and spices we’ve featured in our Monday Research Reviews, and add in medicinal properties of cancer-fighting cruciferous vegetables, bananas with dopamine and dopamine precursors, berries full of polyphenols, hemp seeds that fight cognitive decline, and so forth.
Most of the book is given over to recipes. They’re plant-centric, but mostly not vegan. They’re consistent with the Mediterranean diet, but mostly Indian. They’re economically mindful (favoring cheap ingredients where reasonable) while giving a nod to where an extra dollar will elevate the meal. They don’t give calorie values etc—this is a feature not a bug, as Dr. Aujla is of the “positive dieting” camp that advocates for us to “count colors, not calories”. Which, we have to admit, makes for very stress-free cooking, too.
Dr. Aujla is himself an Indian Brit, by the way, which gives him two intersecting factors for having a taste for spices. If you don’t share that taste, just go easier on the pepper etc.
As for the medicinal properties we mentioned up top? Four pages of references at the back, for any who are curious to look up the science of them. We at 10almonds do love references!
Bottom line: if you like tasty food and you’re looking for a one-stop, well-rounded, food-as-medicine cookbook, this one is a top-tier choice.
Share This Post
-
Hospitals worldwide are short of saline. We can’t just switch to other IV fluids – here’s why
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Last week, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration added intravenous (IV) fluids to the growing list of medicines in short supply. The shortage is due to higher-than-expected demand and manufacturing issues.
Two particular IV fluids are affected: saline and compound sodium lactate (also called Hartmann’s solution). Both fluids are made with salts.
There are IV fluids that use other components, such as sugar, rather than salt. But instead of switching patients to those fluids, the government has chosen to approve salt-based solutions by other overseas brands.
So why do IV fluids contain different chemicals? And why can’t they just be interchanged when one runs low?
Pavel Kosolapov/Shutterstock We can’t just inject water into a vein
Drugs are always injected into veins in a water-based solution. But we can’t do this with pure water, we need to add other chemicals. That’s because of a scientific principle called osmosis.
Osmosis occurs when water moves rapidly in and out of the cells in the blood stream, in response to changes to the concentration of chemicals dissolved in the blood plasma. Think salts, sugars, nutrients, drugs and proteins.
Too high a concentration of chemicals and protein in your blood stream leads it to being in a “hypertonic” state, which causes your blood cells to shrink. Not enough chemicals and proteins in your blood stream causes your blood cells to expand. Just the right amount is called “isotonic”.
Mixing the drug with the right amount of chemicals, via an injection or infusion, ensures the concentration inside the syringe or IV bag remains close to isotonic.
Australia is currently short on two salt-based IV fluids. sirnength88/Shutterstock What are the different types of IV fluids?
There are a range of IV fluids available to administer drugs. The two most popular are:
- 0.9% saline, which is an isotonic solution of table salt. This is one of the IV fluids in short supply
- a 5% solution of the sugar glucose/dextrose. This fluid is not in short supply.
There are also IV fluids that combine both saline and glucose, and IV fluids that have other salts:
- Ringer’s solution is an IV fluid which has sodium, potassium and calcium salts
- Plasma-Lyte has different sodium salts, as well as magnesium
- Hartmann’s solution (compound sodium lactate) contains a range of different salts. It is generally used to treat a condition called metabolic acidosis, where patients have increased acid in their blood stream. This is in short supply.
What if you use the wrong solution?
Some drugs are only stable in specific IV fluids, for instance, only in salt-based IV fluids or only in glucose.
Putting a drug into the wrong IV fluid can potentially cause the drug to “crash out” of the solution, meaning patients won’t get the full dose.
Or it could cause the drug to decompose: not only will it not work, but it could also cause serious side effects.
An example of where a drug can be transformed into something toxic is the cancer chemotherapy drug cisplatin. When administered in saline it is safe, but administration in pure glucose can cause life-threatening damage to a patients’ kidneys.
What can hospitals use instead?
The IV fluids in short supply are saline and Hartmann’s solution. They are provided by three approved Australian suppliers: Baxter Healthcare, B.Braun and Fresenius Kabi.
The government’s solution to this is to approve multiple overseas-registered alternative saline brands, which they are allowed to do under current legislation without it going through the normal Australian quality checks and approval process. They will have received approval in their country of manufacture.
The government is taking this approach because it may not be effective or safe to formulate medicines that are meant to be in saline into different IV fluids. And we don’t have sufficient capacity to manufacture saline IV fluids here in Australia.
The Australian Society of Hospital Pharmacists provides guidance to other health staff about what drugs have to go with which IV fluids in their Australian Injectable Drugs Handbook. If there is a shortage of saline or Hartmann’s solution, and shipments of other overseas brands have not arrived, this guidance can be used to select another appropriate IV fluid.
Why don’t we make it locally?
The current shortage of IV fluids is just another example of the problems Australia faces when it is almost completely reliant on its critical medicines from overseas manufacturers.
Fortunately, we have workarounds to address the current shortage. But Australia is likely to face ongoing shortages, not only for IV fluids but for any medicines that we rely on overseas manufacturers to produce. Shortages like this put Australian lives at risk.
In the past both myself, and others, have called for the federal government to develop or back the development of medicines manufacturing in Australia. This could involve manufacturing off-patent medicines with an emphasis on those medicines most used in Australia.
Not only would this create stable, high technology jobs in Australia, it would also contribute to our economy and make us less susceptible to future global drug supply problems.
Nial Wheate, Professor and Director Academic Excellence, Macquarie University and Shoohb Alassadi, Casual academic, pharmaceutical sciences, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Olive Oil vs Coconut Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing extra virgin olive oil to cold-pressed coconut oil, we picked the olive oil.
Why?
While the cold-pressed coconut oil may offer some health benefits due to its lauric acid content, its 80–90% saturated fat content isn’t great for most people. It’s a great oil when applied topically for healthy skin and hair, though!
The extra virgin olive oil has a much more uncontroversially healthy blend of triglycerides, and (in moderation) is universally recognized as very heart-healthy.
Your local supermarket, most likely, has a good extra virgin olive oil, but if you’d like to get some online, here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The “Five Tibetan Rites” & Why To Do Them!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Spinning Around
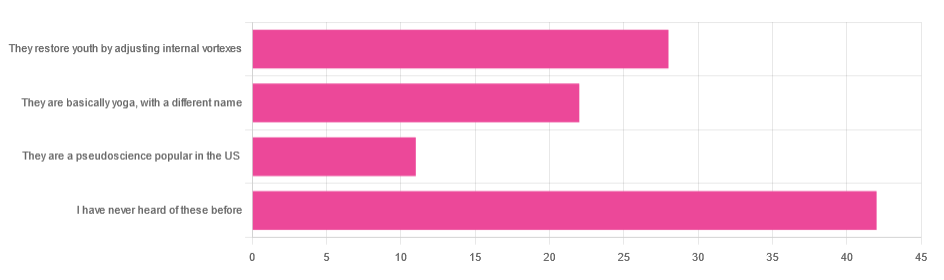
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of the “Five Tibetan Rites”, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 41% said “I have never heard of these before”
- About 27% said “they restore youth by adjusting internal vortexes”
- About 22% said “they are basically yoga, by a different name”
- About 11% said “they are a pseudoscience popular in the US”
So what does the science say?
The Five Tibetan Rites are five Tibetan rites: True or False?
False, though this is more question of social science than of health science, so we’ll not count it against them for having a misleading name.
The first known mentioning of the “Five Tibetan Rites” is by an American named Peter Kelder, who in 1939 published, through a small LA occult-specialized publishing house, a booklet called “The Eye of Revelation”. This work was then varyingly republished, repackaged, and occasionally expanded upon by Kelder or other American authors, including Chris Kilham’s popular 1994 book “The Five Tibetans”.
The “Five Tibetan Rites” are unknown as such in Tibet, except for what awareness of them has been raised by people asking about them in the context of the American phenomenon.
Here’s a good history book, for those interested:
The author didn’t originally set out to “debunk” anything, and is himself a keen spiritualist (and practitioner of the five rites), but he was curious about the origins of the rites, and ultimately found them—as a collection of five rites, and the other assorted advices given by Kelder—to be an American synthesis in the whole, each part inspired by various different physical practices (some of them hatha yoga, some from the then-popular German gymnastics movement, some purely American spiritualism, all available in books that were popular in California in the early 1900s).
You may be wondering: why didn’t Kelder just say that, then, instead of telling stories of an ancient Tibetan tradition that empirically does not exist? The answer to this lies again in social science not health science, but it’s been argued that it’s common for Westerners to “pick ‘n’ mix” ideas from the East, champion them as inscrutably mystical, and (since they are inscrutable) then simply decide how to interpret and represent them. Here’s an excellent book on this, if you’re interested:
(in Kelder’s case, this meant that “there’s a Tibetan tradition, trust me” was thus more marketable in the West than “I read these books in LA”)
They are at least five rites: True or False?
True! If we use the broad definition of “rite” as “something done repeatedly in a solemn fashion”. And there are indeed five of them:
- Spinning around (good for balance)
- Leg raises (this one’s from German gymnastics)
- Kneeling back bend (various possible sources)
- Tabletop (hatha yoga, amongst others)
- Pendulum (hatha yoga, amongst others) ← you may recognize this one from the Sun Salutation
You can see them demonstrated here:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Kelder also advocated for what was basically the Hay Diet (named not for the substance but for William Hay; it involved separating foods into acid and alkali, not necessarily according to the actual pH of the foods, and combining only “acid” foods or only “alkali” foods at a time), which was popular at the time, but has since been rejected as without scientific merit. Kelder referred to this as “the sixth rite”.
The Five Rites restore youth by adjusting internal vortexes: True or False?
False, in any scientific sense of that statement. Scientifically speaking, the body does not have vortexes to adjust, therefore that is not the mechanism of action.
Spiritually speaking, who knows? Not us, a humble health science publication.
The Five Rites are a pseudoscience popular in the US: True or False?
True, if 27% of those who responded of our mostly North American readership can be considered as representative of what is popular.
However…
“Pseudoscience” gets thrown around a lot as a bad word; it’s often used as a criticism, but it doesn’t have to be. Consider:
A small child who hears about “eating the rainbow” and mistakenly understands that we are all fuelled by internal rainbows that need powering-up by eating fruits and vegetables of different colors, and then does so…
…does not hold a remotely scientific view of how things are happening, but is nevertheless doing the correct thing as recommended by our best current science.
It’s thus a little similar with the five rites. Because…
The Five Rites are at least good for our health: True or False?
True! They are great for the health.
The first one (spinning around) is good for balance. Science would recommend doing it both ways rather than just one way, but one is not bad. It trains balance, trains our stabilizing muscles, and confuses our heart a bit (in a good way).
See also: Fall Special (How To Not Fall, And Not Get Injured If You Do)
The second one (leg raises) is excellent for core strength, which in turn helps keep our organs where they are supposed to be (this is a bigger health issue than most people realise, because “out of sight, out of mind”), which is beneficial for many aspects of our health!
See also: Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← visceral fat is the fat that surrounds your internal organs; too much there becomes a problem!
The third, fourth, and fifth ones stretch our spine (healthily), strengthen our back, and in the cases of the fourth and fifth ones, are good full-body exercises for building strength, and maintaining muscle mass and mobility.
See also: Building & Maintaining Mobility
So in short…
If you’ve been enjoying the Five Rites, by all means keep on doing them; they might not be Tibetan (or an ancient practice, as presented), and any mystical aspect is beyond the scope of our health science publication, but they are great for the health in science-based ways!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Parsnips vs Potatoes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing parsnips to potatoes, we picked the parsnips.
Why?
To be more specific, we’re looking at russet potatoes, and in both cases we’re looking at cooked without fat or salt, skin on. In other words, the basic nutritional values of these plants in edible form, without adding anything. With this in mind, once we get to the root of things, there’s a clear winner:
Looking at the macros first, potatoes have more carbs while parsnips have more fiber. Potatoes do have more protein too, but given the small numbers involved when it comes to protein we don’t think this is enough of a plus to outweigh the extra fiber in the parsnips.
In the category of vitamins, again a champion emerges: parsnips have more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B9, C, E, and K, while potatoes have more of vitamins B3, B6, and choline. So, a 7:3 win for parsnips.
When it comes to minerals, parsnips have more calcium copper, manganese, selenium, and zinc, while potatoes have more iron and potassium. Potatoes do also have more sodium, but for most people most of the time, this is not a plus, healthwise. Disregarding the sodium, this category sees a 5:2 win for parsnips.
In short: as with most starchy vegetables, enjoy both in moderation if you feel so inclined, but if you’re picking one, then parsnips are the nutritionally best choice here.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: