Health Nut: A Feel-Good Cookbook – by Jess Damuck
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is a classically trained chef (worked with Martha Stewart for a long time!), and while health is the focus here, it’s not the be-all-and-end-all, so there’s a lot of attention given to pleasure also. Which, after all, is not a zero-sum game—we can have both!
So, the title and subtitle together sum up the ethos of the book pretty well.
The recipes themselves are divided into categories by meal-type, snacks, desserts, etc. They’re varied enough to suit most moods and seasons, as well as being equally appropriate for cooking for one, or a family, or entertaining. Many (but not all) of the recipes are vegan, though where they’re not, the substitutions are mostly easy and obvious, or explained, or else alternative recipes are given (for example a vegan “tuna” recipe).
In terms of complexity, these are not very complex, yet include everything they need to to make things interesting. That said, the ingredients are also not obscure, and should be easy to find in any reasonably well-stocked supermarket.
One small downside is that many of the recipes are not illustrated, but the instructions are clear enough that this isn’t really a problem, in this reviewer’s opinion.
Bottom line: if you’d like to broaden your kitchen repertoire with plants-forward cooking from an accomplished chef, then this is a good book for that.
Click here to check out Health Nut, and enjoy the feel-good food!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Magic Of Mindful Self-Awareness − by Matt Tenny
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As the author is not a Dr. Matt Tenny, you may wonder his qualifications. In this case, the answer is summed up in the title of the first part of the book, “How I discovered unconditional happiness on my journey from prisoner to monk to social entrepreneur”. In other words, this one’s about personal experience of changing his life considerably.
Part two, however, is where the actual practical content starts, with such topics as:
- How to be free from your thoughts so you can stop overthinking and enjoy the present moment
- How to clear your mind and make the practice of self-awareness (almost) effortless
- How to transform mundane activities into magical moments and be happy 95% of the time
You may be wondering about the other 5%; i.e. will this not work for some things? The answer is rather that sometimes we will experience emotions that are considered negative, and that’s ok. It need not be much of the time, but if we didn’t experience them at all, we’d just normalize a new set point and consider the least enjoyable 5% of that to be negative.
And indeed, part three is “how to be at peace during the 5% of life that is truly painful, and live a deeply meaningful life”.
Which, honestly, is a very important life skill, and this alone is worth the price of the book if you don’t already have this skill (and if you do, then condolences for however you got it, but congratulations on having it).
The style is quite personal and direct, and—unlike that of a lot of CEO-monk types—surprisingly down-to-earth and (actually!) mindfully self-aware.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be at peace in life with more practical advice than just “practice some mindfulness meditation”, then this book could be just the turning point you need.
Share This Post
-
Statins: His & Hers?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Hidden Complexities of Statins and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
This is Dr. Barbara Roberts. She’s a cardiologist and the Director of the Women’s Cardiac Center at one of the Brown University Medical School teaching hospitals. She’s an Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine and takes care of patients, teaches medical students, and does clinical research. She specializes in gender-specific aspects of heart disease, and in heart disease prevention.
We previously reviewed Dr. Barbara Roberts’ excellent book “The Truth About Statins: Risks and Alternatives to Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs”. It prompted some requests to do a main feature about Statins, so we’re doing it today. It’s under the auspices of “Expert Insights” as we’ll be drawing almost entirely from Dr. Roberts’ work.
So, what are the risks of statins?
According to Dr. Roberts, one of the biggest risks is not just drug side-effects or anything like that, but rather, what they simply won’t treat. This is because statins will lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, without necessarily treating the underlying cause.
Imagine you got Covid, and it’s one of the earlier strains that’s more likely deadly than “merely” debilitating.
You’re coughing and your throat feels like you gargled glass.
Your doctor gives you a miracle cough medicine that stops your coughing and makes your throat feel much better.
(Then a few weeks later, you die, because this did absolutely nothing for the underlying problem)
You see the problem?
Are there problematic side-effects too, though?
There can be. But of course, all drugs can have side effects! So that’s not necessarily news, but what’s relevant here is the kind of track these side-effects can lead one down.
For example, Dr. Roberts cites a case in which a woman’s LDL levels were high and she was prescribed simvastatin (Zocor), 20mg/day. Here’s what happened, in sequence:
- She started getting panic attacks. So, her doctor prescribed her sertraline (Zoloft) (a very common SSRI antidepressant) and when that didn’t fix it, paroxetine (Paxil). This didn’t work either… because the problem was not actually her mental health. The panic attacks got worse…
- Then, while exercising, she started noticing progressive arm and leg weakness. Her doctor finally took her off the simvastatin, and temporarily switched to ezetimibe (Zetia), a less powerful nonstatin drug that blocks cholesterol absorption, which change eased her arm and leg problem.
- As the Zetia was a stopgap measure, the doctor put her on atorvastatin (Lipitor). Now she got episodes of severe chest pressure, and a skyrocketing heart rate. She also got tremors and lost her body temperature regulation.
- So the doctor stopped the atorvastatin and tried rosovastatin (Crestor), on which she now suffered exhaustion (we’re not surprised, by this point) and muscle pains in her arms and chest.
- So the doctor stopped the rosovastatin and tried lovastatin (Mevacor), and now she had the same symptoms as before, plus light-headedness.
- So the doctor stopped the lovastatin and tried fluvastatin (Lescol). Same thing happened.
- So he stopped the fluvastatin and tried pravastatin (Pravachol), without improvement.
- So finally he took her off all these statins because the high LDL was less deleterious to her life than all these things.
- She did her own research, and went back to the doctor to ask for cholestyramine (Questran), which is a bile acid sequestrent and nothing to do with statins. She also asked for a long-acting niacin. In high doses, niacin (one of the B-vitamins) raises HDL (good) cholesterol, lowers LDL, and lowers tryglycerides.
- Her own non-statin self-prescription (with her doctor’s signature) worked, and she went back to her life, her work, and took up running.
Quite a treatment journey! Want to know more about the option that actually worked?
Read: Bile Acid Resins or Sequestrants
What are the gender differences you/she mentioned?
Actually mostly sex differences, since this appears to be hormonal (which means that if your hormones change, so will your risk). A lot of this is still pending more research—basically it’s a similar problem in heart disease to one we’ve previously talked about with regard to diabetes. Diabetes disproportionately affects black people, while diabetes research disproportionately focuses on white people.
In this case, most heart disease research has focused on men, with women often not merely going unresearched, but also often undiagnosed and untreated until it’s too late. And the treatments, if prescribed? Assumed to be the same as for men.
Dr. Roberts tells of how medicine is taught:
❝When I was in medical school, my professors took the “bikini approach” to women’s health: women’s health meant breasts and reproductive organs. Otherwise the prototypical patient was presented as a man.❞
There has been some research done with statins and women, though! Just, still not a lot. But we do know for example that some statins can be especially useful for treating women’s atherosclerosis—with a 50% success rate, rather than 31% for men.
For lowering LDL itself, however, it can work but is generally not so hot in women.
Fun fact:
In men:
- High total cholesterol
- High non-HDL cholesterol
- High LDL cholesterol
- Low HDL cholesterol
…are all significantly associated with an increased risk of death from CVD.
In women:
…levels of LDL cholesterol even more than 190 were associated with only a small, statistically insignificant increased risk of dying from CVD.
So…
The fact that women derive less benefit from a medicine that mainly lowers LDL cholesterol, may be because elevated LDL cholesterol is less harmful to women than it is to men.
And also: Treatment and Response to Statins: Gender-related Differences
And for that matter: Women Versus Men: Is There Equal Benefit and Safety from Statins?*
Definitely a case where Betteridge’s Law of Headlines applies!
What should women do to avoid dying of CVD, then?
First, quick reminder of our general disclaimer: we can’t give medical advice and nothing here comprises such. However… One particularly relevant thing we found illuminating in Dr. Roberts’ work was this observation:
The metabolic syndrome is diagnosed if you have three (or more) out of five of the following:
- Abdominal obesity (waist >35″ if a woman or >40″ if a man)
- Fasting blood sugars of 100mg/dl or more
- Fasting triglycerides of 150mg/dl or more
- Blood pressure of 130/85 or higher
- HDL <50 if a woman or <40 if a man
And yet… because these things can be addressed with exercise and a healthy diet, which neither pharmaceutical companies nor insurance companies have a particular stake in, there’s a lot of focus instead on LDL levels (since there are a flock of statins that can be sold be lower them)… Which, Dr. Roberts says, is not nearly as critical for women.
So women end up getting prescribed statins that cause panic attacks and all those things we mentioned earlier… To lower our LDL, which isn’t nearly as big a factor as the other things.
In summary:
Statins do have their place, especially for men. They can, however, mask underlying problems that need treatment—which becomes counterproductive.
When it comes to women, statins are—in broad terms—statistically not as good. They are a little more likely to be helpful specifically in cases of atherosclerosis, whereby they have a 50/50 chance of helping.
For women in particular, it may be worthwhile looking into alternative non-statin drugs, and, for everyone: diet and exercise.
Further reading: How Can I Safely Come Off Statins?
Share This Post
-
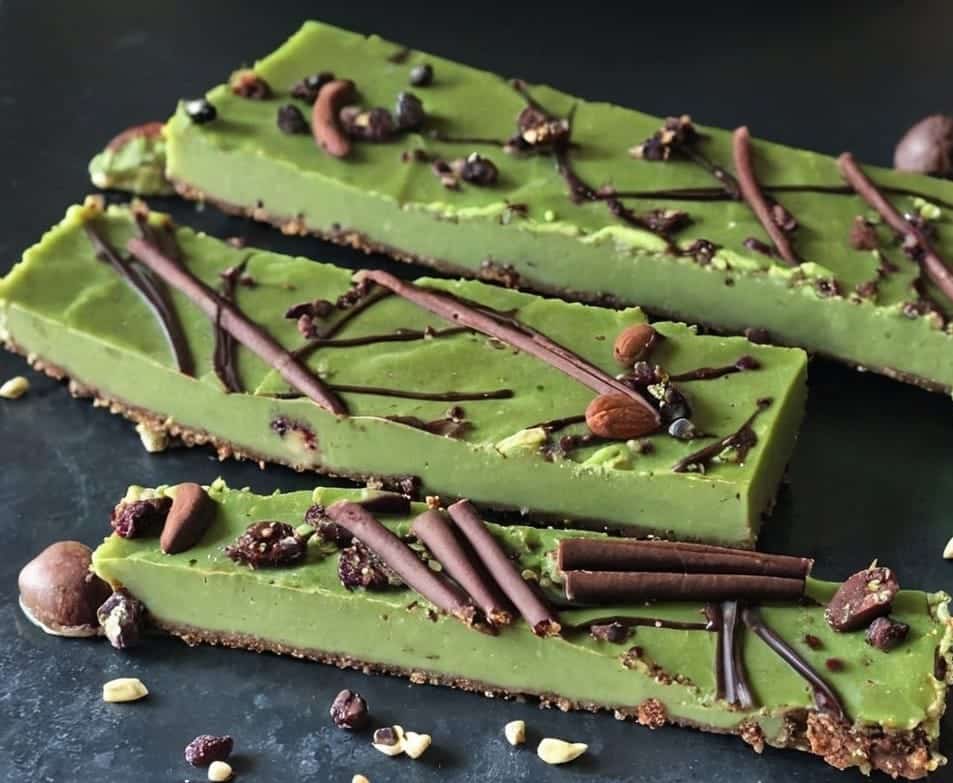
Antioxidant Matcha Snack Bars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The antioxidants in this come not just from the matcha, but also the cacao nibs and chocolate, as well as lots of nutrients from the hazelnuts and cashews. If you’re allergic to nuts, we’ll give you substitutions that will change the nutritional profile (and flavor), but still work perfectly well and be healthy too.
You will need
For the base:
- ⅔ cup roasted hazelnuts (if allergic, substitute dessicated coconut)
- ⅔ cup chopped dates
For the main part:
- 1 cup raw cashews (if allergic, substitute raw coconut, chopped)
- ½ cup almond milk (or your preferred milk of any kind)
- ½ cup cacao nibs
- 2 tbsp lime juice
- 1 tbsp matcha powder
- 1 tbsp maple syrup (omit if you don’t care for sweetness)
For the topping (optional):
- 2oz dark chocolate, melted (and if you like, tempered—but this isn’t necessary; it’ll just make it glossier if you do)
- Spare cacao nibs, chopped nuts, or anything else you might want on there
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the base ingredients in a food processor until it has a coarse sticky texture, but isn’t yet a paste or dough.
2) Line a cake pan with baking paper and spread the base mix on the base; press it down to compact it a little and ensure it is flat. If there’s room, put this in the freezer while you do the next bit. If not, the fridge will suffice.
3) Blend the main part ingredients apart from the cacao nibs, until smooth. Stir in the cacao nibs with a spoon.
4) Spread the main part evenly over the base, and allow everything you’ve built (in this recipe, not in life in general) to chill in the fridge for at least 4 hours.
5) Cut it into blocks of the size and shape you want to eat them, and (if adding the optional topping) separate the blocks slightly from each other, before drizzling with the chocolate topping. Put it back in the fridge to cool this too; an hour should be sufficient.
6) Serve!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Tea Is Best, By Science?
- Which Plant Milk?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Other Significant Others – by Rhaina Cohen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we get older, it’s a function of statistics that increasingly many of us are divorced or widowed. While some will—after whatever time seems right to them—get back into dating, what about those of us who decide that we won’t?
Rhaina Cohen explores the importance of friendship, mutual support, and (Platonic!) closeness and yes, even kinds of intimacy (for that too can be Platonic!) as we go on.
Even from a purely evolutionary approach, we are fundamentally social creatures, and while as individuals we may exist on a spectrum from reclusive to extroverted, we all thrive better when we at least have access to community and friends.
The style of the book is easy-reading and exploratory, and is very compelling as a call-to-arms for those who may wish to give/receive support to/from those with whom we are not necessarily sleeping.
Because at the end of the day, why should sex and/or romance be a required feature for legal protections? Aren’t we adults who can make our own decisions about whom we trust to care for us?
Bottom line: if you’re happily partnered and expect to pre-decease your partner, this book might not be directly important for you (it might for your partner, though). Everyone else? This book may be important at some point. That point might even be now already; only you know.
Click here to check out The Other Significant Others, and make your own choices in life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Castor Oil: All-Purpose Life-Changer, Or Snake Oil?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As “trending” health products go, castor oil is enjoying a lot of popularity presently, lauded as a life-changing miracle-worker, and social media is abuzz with advice to put it everywhere from your eyes to your vagina.
But:
- what things does science actually say it’s good for,
- what things lack evidence, and
- what things go into the category of “wow definitely do not do that”?
We don’t have the space to go into all of its proposed uses (there are simply far too many), but we’ll examine some common ones:
To heal/improve the skin barrier
Like most oils, it’s functional as a moisturizer. In particular, its high (90%!) ricinoleic fatty acid content does indeed make it good at that, and furthermore, has properties that can help reduce skin inflammation and promote wound healing:
Bioactive polymeric formulations for wound healing ← there isn’t a conveniently quotable summary we can just grab here, but you can see the data and results, from which we can conclude:
- formulations with ricinoleic acid (such as with castor oil) performed very well for topical anti-inflammatory purposes
- they avoided the unwanted side effects associated with some other contenders
- they consistently beat other preparations in the category of wound-healing
To support hair growth and scalp health
There is no evidence that it helps. We’d love to provide a citation for this, but it’s simply not there. There’s also no evidence that it doesn’t help. For whatever reason, despite its popularity, peer-reviewed science has simply not been done for this, or if it has, it wasn’t anywhere publicly accessible.
It’s possible that if a person is suffering hair loss specifically as a result of prostaglandin D2 levels, that ricinoleic acid will inhibit the PGD2, reversing the hair loss, but even this is hypothetical so far, as the science is currently only at the step before that:
However, due to some interesting chemistry, the combination of castor oil and warm water can result in acute (and irreversible) hair felting, in other words, the strands of hair suddenly glue together to become one mass which then has to be cut off:
“Castor Oil” – The Culprit of Acute Hair Felting
👆 this is a case study, which is generally considered a low standard of evidence (compared to high-quality Randomized Controlled Trials as the highest standard of evidence), but let’s just say, this writer (hi, it’s me) isn’t risking her butt-length hair on the off-chance, and doesn’t advise you to, either. There are other hair-oils out there; argan oil is great, coconut oil is totally fine too.
As a laxative
This time, there’s a lot of evidence, and it’s even approved for this purpose by the FDA, but it can be a bit too good, insofar as taking too much can result in diarrhea and uncomfortable cramping (the cramps are a feature not a bug; the mechanism of action is stimulatory, i.e. it gets the intestines squeezing, but again, it can result in doing that too much for comfort):
Castor Oil: FDA-Approved Indications
To soothe dry eyes
While putting oil in your eyes may seem dubious, this is another one where it actually works:
❝Castor oil is deemed safe and tolerable, with strong anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, analgesic, antioxidant, wound healing and vasoconstrictive properties.
These can supplement deficient physiological tear film lipids, enabling enhanced lipid spreading characteristics and reducing aqueous tear evaporation.
Studies reveal that castor oil applied topically to the ocular surface has a prolonged residence time, facilitating increased tear film lipid layer thickness, stability, improved ocular surface staining and symptoms.❞
Source: Therapeutic potential of castor oil in managing blepharitis, meibomian gland dysfunction and dry eye
Against candidiasis (thrush)
We couldn’t find science for (or against) castor oil’s use against vaginal candidiasis, but here’s a study that investigated its use against oral candidiasis:
…in which castor oil was the only preparation that didn’t work against the yeast.
Summary
We left a lot unsaid today (so many proposed uses, it feels like a shame to skip them), but in few words: it’s good for skin (including wound healing) and eyes; but we’d give it a miss for hair, candidiasis, and digestive disorders.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Air-Fried Food Really Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Air-frying has a reputation for being healthy—and it generally is, provided it’s used carefully:
Just one thing to watch out for
An air-fryer is basically a small convection oven that uses circulating air rather than immersion in oil to cook food. The smallness of an air-fryer is a feature not a bug—if you get an air-fryer over a certain size, then congratulations, you just have a convection oven. The small size it what helps it to cook so efficiently. This is one reason that they’re not really used in industrial settings.
The documentary-makers from this video had their food (chicken, fish, and fries) lab-tested (for fat, cholesterol, and acrylamide), and found:
- Air-frying significantly reduced saturated fat (38–53%) and trans fats (up to 55%) in some foods.
- Cholesterol reduction varied depending on the food type.
- Acrylamide levels in air-fried potatoes were much higher due to cooking time and temperature.
About that acrylamide: acrylamide forms in starchy foods at high temperatures and may pose cancer risks (the research is as yet unclear, with conflicting evidence). Air-frying can cause higher acrylamide levels if cooking is prolonged or temperatures are too high.
Recommendations to reduce acrylamide:
- Soak potatoes before cooking.
- Use lower temperatures (e.g. 180℃/350℉) and shorter cooking times.
- Avoid over-browning food.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Unlock Your Air-Fryer’s Potential!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: