Hardwiring Happiness – by Dr. Rick Hanson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Publishers are very excitable about “the new science of…”, and it’s almost never actually a new science of. But what about in this case?
No, it isn’t. It’s the very well established science of! And that’s a good thing, because it means this book is able to draw on quite a lot of research and established understanding of how neuroplasticity works, to leverage that and provide useful guidance.
A particular strength of this book is that while it polarizes the idea that some people have “happy amygdalae” and some people have “sad amygdalae”, it acknowledges that it’s not just a fated disposition and is rather the result of the lives people have led… And then provides advice on upgrading from sad to happy, based on the assumption that the reader is quite possibly coming from a non-ideal starting point.
The bookdoes an excellent job of straddling neuroscience and psychology, which sounds like not much of a straddle (the two are surely very connected, after all, right?) but this does mean that we’re hearing about the chemical structure of DNA inside the nuclei of the neurons of the insula, not long after reading an extended gardening metaphor about growth, choices, and vulnerabilities.
Bottom line: if you’d like a guide to changing your brain for the better (happier) that’s not just “ask yourself: what if it goes well?” and similar CBTisms, then this is a fine book for you.
Click here to check out Hardwiring Happiness, and indeed hardwire happiness!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bird flu has been detected in a pig in the US. Why does that matter?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
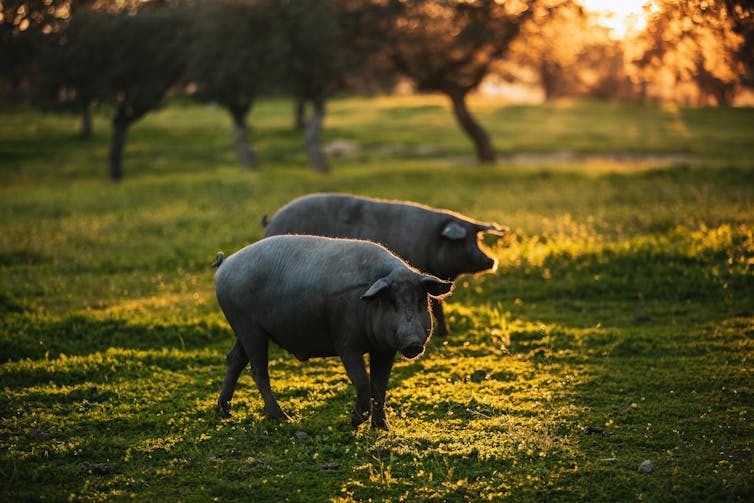
The United States Department of Agriculture last week reported that a pig on a backyard farm in Oregon was infected with bird flu.
As the bird flu situation has evolved, we’ve heard about the A/H5N1 strain of the virus infecting a range of animals, including a variety of birds, wild animals and dairy cattle.
Fortunately, we haven’t seen any sustained spread between humans at this stage. But the detection of the virus in a pig marks a worrying development in the trajectory of this virus.
David MG/Shutterstock How did we get here?
The most concerning type of bird flu currently circulating is clade 2.3.4.4b of A/H5N1, a strain of influenza A.
Since 2020, A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b has spread to a vast range of birds, wild animals and farm animals that have never been infected with bird flu before.
While Europe is a hotspot for A/H5N1, attention is currently focused on the US. Dairy cattle were infected for the first time in 2024, with more than 400 herds affected across at least 14 US states.
Bird flu has enormous impacts on farming and commercial food production, because infected poultry flocks have to be culled, and infected cows can result in contaminated diary products. That said, pasteurisation should make milk safe to drink.
While farmers have suffered major losses due to H5N1 bird flu, it also has the potential to mutate to cause a human pandemic.
Birds and humans have different types of receptors in their respiratory tract that flu viruses attach to, like a lock (receptors) and key (virus). The attachment of the virus allows it to invade a cell and the body and cause illness. Avian flu viruses are adapted to birds, and spread easily among birds, but not in humans.
So far, human cases have mainly occurred in people who have been in close contact with infected farm animals or birds. In the US, most have been farm workers.
The concern is that the virus will mutate and adapt to humans. One of the key steps for this to happen would be a shift in the virus’ affinity from the bird receptors to those found in the human respiratory tract. In other words, if the virus’ “key” mutated to better fit with the human “lock”.
A recent study of a sample of A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b from an infected human had worrying findings, identifying mutations in the virus with the potential to increase transmission between human hosts.
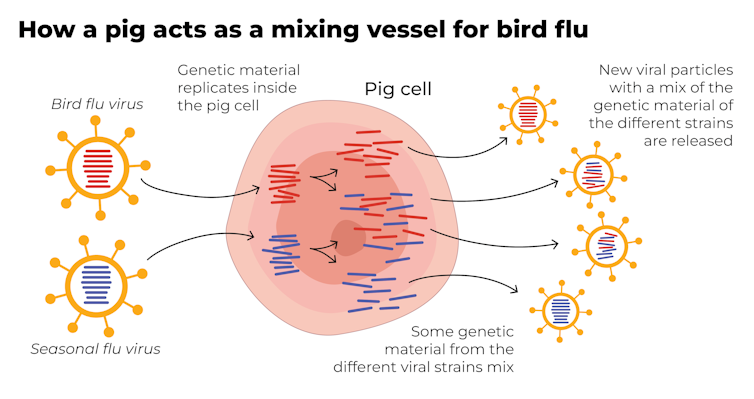
Why are pigs a problem?
A human pandemic strain of influenza can arise in several ways. One involves close contact between humans and animals infected with their own specific flu viruses, creating opportunities for genetic mixing between avian and human viruses.
Pigs are the ideal genetic mixing vessel to generate a human pandemic influenza strain, because they have receptors in their respiratory tracts which both avian and human flu viruses can bind to.
This means pigs can be infected with a bird flu virus and a human flu virus at the same time. These viruses can exchange genetic material to mutate and become easily transmissible in humans.
The Conversation, CC BY-SA Interestingly, in the past pigs were less susceptible to A/H5N1 viruses. However, the virus has recently mutated to infect pigs more readily.
In the recent case in Oregon, A/H5N1 was detected in a pig on a non-commercial farm after an outbreak occurred among the poultry housed on the same farm. This strain of A/H5N1 was from wild birds, not the one that is widespread in US dairy cows.
The infection of a pig is a warning. If the virus enters commercial piggeries, it would create a far greater level of risk of a pandemic, especially as the US goes into winter, when human seasonal flu starts to rise.
How can we mitigate the risk?
Surveillance is key to early detection of a possible pandemic. This includes comprehensive testing and reporting of infections in birds and animals, alongside financial compensation and support measures for farmers to encourage timely reporting.
Strengthening global influenza surveillance is crucial, as unusual spikes in pneumonia and severe respiratory illnesses could signal a human pandemic. Our EPIWATCH system looks for early warnings of such activity, which can speed up vaccine development.
If a cluster of human cases occurs, and influenza A is detected, further testing (called subtyping) is essential to ascertain whether it’s a seasonal strain, an avian strain from a spillover event, or a novel pandemic strain.
Early identification can prevent a pandemic. Any delay in identifying an emerging pandemic strain enables the virus to spread widely across international borders.
Australia’s first human case of A/H5N1 occurred in a child who acquired the infection while travelling in India, and was hospitalised with illness in March 2024. At the time, testing revealed Influenza A (which could be seasonal flu or avian flu), but subtyping to identify A/H5N1 was delayed.
This kind of delay can be costly if a human-transmissible A/H5N1 arises and is assumed to be seasonal flu because the test is positive for influenza A. Only about 5% of tests positive for influenza A are subtyped further in Australia and most countries.
In light of the current situation, there should be a low threshold for subtyping influenza A strains in humans. Rapid tests which can distinguish between seasonal and H5 influenza A are emerging, and should form part of governments’ pandemic preparedness.
A higher risk than ever before
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the current risk posed by H5N1 to the general public remains low.
But with H5N1 now able to infect pigs, and showing worrying mutations for human adaptation, the level of risk has increased. Given the virus is so widespread in animals and birds, the statistical probability of a pandemic arising is higher than ever before.
The good news is, we are better prepared for an influenza pandemic than other pandemics, because vaccines can be made in the same way as seasonal flu vaccines. As soon as the genome of a pandemic influenza virus is known, the vaccines can be updated to match it.
Partially matched vaccines are already available, and some countries such as Finland are vaccinating high-risk farm workers.
C Raina MacIntyre, Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney and Haley Stone, Research Associate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute & CRUISE lab, Computer Science and Engineering, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Anti-Stress Herb That Also Fights Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What does Rhodiola rosea actually do, anyway?
Rhodiola rosea (henceforth, “rhodiola”) is a flowering herb whose roots have adaptogenic properties.
In the cold, mountainous regions of Europe and Asia where it grows, it has been used in herbal medicine for centuries to alleviate anxiety, fatigue, and depression.
What does the science say?
Well, let’s just say the science is more advanced than the traditional use:
❝In addition to its multiplex stress-protective activity, Rhodiola rosea extracts have recently demonstrated its anti-aging, anti-inflammation, immunostimulating, DNA repair and anti-cancer effects in different model systems❞
Nor is how it works a mystery, as the same paper explains:
❝Molecular mechanisms of Rhodiola rosea extracts’s action have been studied mainly along with one of its bioactive compounds, salidroside. Both Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside have contrasting molecular mechanisms on cancer and normal physiological functions.
For cancer, Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside inhibit the mTOR pathway and reduce angiogenesis through down-regulation of the expression of HIF-1α/HIF-2α.
For normal physiological functions, Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside activate the mTOR pathway, stimulate paracrine function and promote neovascularization by inhibiting PHD3 and stabilizing HIF-1α proteins in skeletal muscles❞
~ Ibid.
And, as for the question of “do the supplements work?”,
❝In contrast to many natural compounds, salidroside is water-soluble and highly bioavailable via oral administration❞
~ Ibid.
And as to how good it is:
❝Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside can impose cellular and systemic benefits similar to the effect of positive lifestyle interventions to normal physiological functions and for anti-cancer❞
~ Ibid.
Source: Rhodiola rosea: anti-stress, anti-aging, and immunostimulating properties for cancer chemoprevention
But that’s not all…
We can’t claim this as a research review if we only cite one paper (even if that paper has 144 citations of its own), and besides, it didn’t cover all the benefits yet!
Let’s first look at the science for the “traditional use” trio of benefits:
When you read those, what are your first thoughts?
Please don’t just take our word for things! Reading even just the abstracts (summaries) at the top of papers is a very good habit to get into, if you don’t have time (or easy access) to read the full text.
Reading the abstracts is also a very good way to know whether to take the time to read the whole paper, or whether it’s better to skip onto a different one.
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for anxiety was quite a small study.
- The fact is, while we found mountains of evidence for rhodiola’s anxiolytic (antianxiety) effects, they were all small and/or animal studies. So we picked a human study and went with it as illustrative.
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for fatigue pertained mostly to stress-related fatigue.
- This, we think, is a feature not a bug. After all, most of us experience fatigue because of the general everything of life, not because we just ran a literal marathon.
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for depression said it didn’t work as well as sertraline (a very common pharmaceutical SSRI antidepressant).
- But, it worked almost as well and it had far fewer adverse effects reported. Bear in mind, the side effects of antidepressants are the reason many people avoid them, or desist in taking them. So rhodiola working almost as well as sertraline for far fewer adverse effects, is quite a big deal!
Bonus features
Rhodiola also putatively offers protection against Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and cerebrovascular disease in general:
Rosenroot (Rhodiola): Potential Applications in Aging-related Diseases
It may also be useful in the management of diabetes (types 1 and 2), but studies so far have only been animal studies, and/or in vitro studies. Here are two examples:
- Antihyperglycemic action of rhodiola-aqeous extract in type 1 diabetic rats
- Evaluation of Rhodiola crenulata and Rhodiola rosea for management of type 2 diabetes and hypertension
How much to take?
Dosages have varied a lot in studies. However, 120mg/day seems to cover most bases. It also depends on which of rhodiola’s 140 active compounds a particular benefit depends on, though salidroside and rosavin are the top performers.
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else) but here’s an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
- Perhaps you noticed that the paper we cited for anxiety was quite a small study.
-
What’s the difference between Alzheimer’s and dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
Changes in thinking and memory as we age can occur for a variety of reasons. These changes are not always cause for concern. But when they begin to disrupt daily life, it could indicate the first signs of dementia.
Another term that can crop up when we’re talking about dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, or Alzheimer’s for short.
So what’s the difference?
Lightspring/Shutterstock What is dementia?
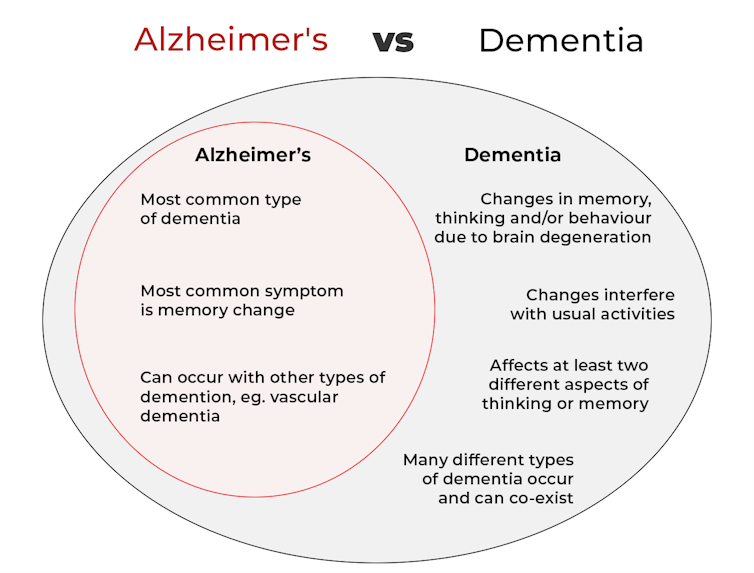
Dementia is an umbrella term used to describe a range of syndromes that result in changes in memory, thinking and/or behaviour due to degeneration in the brain.
To meet the criteria for dementia these changes must be sufficiently pronounced to interfere with usual activities and are present in at least two different aspects of thinking or memory.
For example, someone might have trouble remembering to pay bills and become lost in previously familiar areas.
It’s less-well known that dementia can also occur in children. This is due to progressive brain damage associated with more than 100 rare genetic disorders. This can result in similar cognitive changes as we see in adults.
So what’s Alzheimer’s then?
Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of cases.
So it’s not surprising many people use the terms dementia and Alzheimer’s interchangeably.
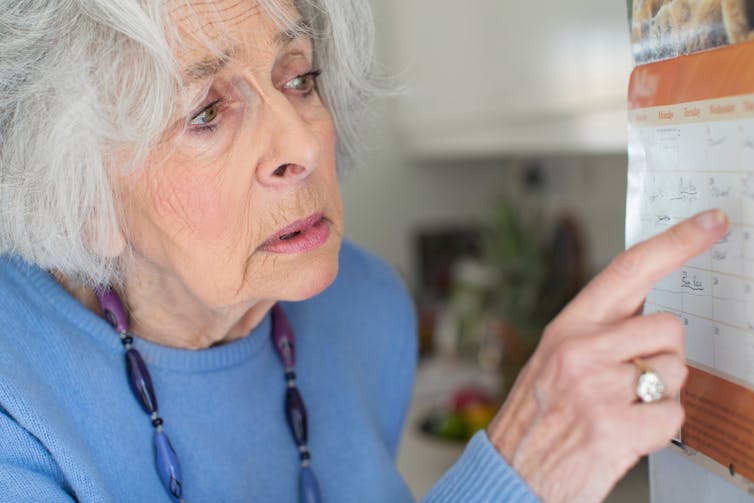
Changes in memory are the most common sign of Alzheimer’s and it’s what the public most often associates with it. For instance, someone with Alzheimer’s may have trouble recalling recent events or keeping track of what day or month it is.
People with dementia may have trouble keeping track of dates. Daisy Daisy/Shutterstock We still don’t know exactly what causes Alzheimer’s. However, we do know it is associated with a build-up in the brain of two types of protein called amyloid-β and tau.
While we all have some amyloid-β, when too much builds up in the brain it clumps together, forming plaques in the spaces between cells. These plaques cause damage (inflammation) to surrounding brain cells and leads to disruption in tau. Tau forms part of the structure of brain cells but in Alzheimer’s tau proteins become “tangled”. This is toxic to the cells, causing them to die. A feedback loop is then thought to occur, triggering production of more amyloid-β and more abnormal tau, perpetuating damage to brain cells.
Alzheimer’s can also occur with other forms of dementia, such as vascular dementia. This combination is the most common example of a mixed dementia.
Vascular dementia
The second most common type of dementia is vascular dementia. This results from disrupted blood flow to the brain.
Because the changes in blood flow can occur throughout the brain, signs of vascular dementia can be more varied than the memory changes typically seen in Alzheimer’s.
For example, vascular dementia may present as general confusion, slowed thinking, or difficulty organising thoughts and actions.
Your risk of vascular dementia is greater if you have heart disease or high blood pressure.
Frontotemporal dementia
Some people may not realise that dementia can also affect behaviour and/or language. We see this in different forms of frontotemporal dementia.
The behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia is the second most common form (after Alzheimer’s disease) of younger onset dementia (dementia in people under 65).
People living with this may have difficulties in interpreting and appropriately responding to social situations. For example, they may make uncharacteristically rude or offensive comments or invade people’s personal space.
Semantic dementia is also a type of frontotemporal dementia and results in difficulty with understanding the meaning of words and naming everyday objects.
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies results from dysregulation of a different type of protein known as α-synuclein. We often see this in people with Parkinson’s disease.
So people with this type of dementia may have altered movement, such as a stooped posture, shuffling walk, and changes in handwriting. Other symptoms include changes in alertness, visual hallucinations and significant disruption to sleep.
Do I have dementia and if so, which type?
If you or someone close to you is concerned, the first thing to do is to speak to your GP. They will likely ask you some questions about your medical history and what changes you have noticed.
Sometimes it might not be clear if you have dementia when you first speak to your doctor. They may suggest you watch for changes or they may refer you to a specialist for further tests.
There is no single test to clearly show if you have dementia, or the type of dementia. A diagnosis comes after multiple tests, including brain scans, tests of memory and thinking, and consideration of how these changes impact your daily life.
Not knowing what is happening can be a challenging time so it is important to speak to someone about how you are feeling or to reach out to support services.
Dementia is diverse
As well as the different forms of dementia, everyone experiences dementia in different ways. For example, the speed dementia progresses varies a lot from person to person. Some people will continue to live well with dementia for some time while others may decline more quickly.
There is still significant stigma surrounding dementia. So by learning more about the various types of dementia and understanding differences in how dementia progresses we can all do our part to create a more dementia-friendly community.
The National Dementia Helpline (1800 100 500) provides information and support for people living with dementia and their carers. To learn more about dementia, you can take this free online course.
Nikki-Anne Wilson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA), UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Total Fitness After 40 – by Nick Swettenham
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Time may march relentlessly on, but can we retain our youthful good health?
The answer is that we can… to a degree. And where we can’t, we can and should adapt what we do as we age.
The key, as Swettenham illustrates, is that there are lifestyle factors that will help us to age more slowly, thus retaining our youthful good health for longer. At the same time, there are factors of which we must simply be mindful, and take care of ourselves a little differently now than perhaps we did when we were younger. Here, Swettenham acts guide and instructor.
A limitation of the book is that it was written with the assumption that the reader is a man. This does mean that anything relating to hormones is assuming that we have less testosterone as we’re getting older and would like to have more, which is obviously not the case for everyone. However, happily, the actual advice remains applicable regardless.
Swettenham covers the full spread of what he believes everyone should take into account as we age:
- Mindset changes (accepting that physical changes are happening, without throwing our hands in the air and giving up)
- Focus on important aspects such as:
- strength
- flexibility
- mobility
- agility
- endurance
- Some attention is also given to diet—nothing you won’t have read elsewhere, but it’s a worthy mention.
All in all, this is a fine book if you’re thinking of taking up or maintaining an exercise routine that doesn’t stick its head in the sand about your aging body, but doesn’t just roll over and give up either. A worthy addition to anyone’s bookshelf!
Check Out Fitness After 40 On Amazon Today!
Looking for a more women-centric equivalent book? Vonda Wright M.D. has you covered (and her bio is very impressive)!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
“You Just Need to Lose Weight” And 19 Other Myths About Fat People – by Aubrey Gordon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed another book by this author, “What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat”, and this time, she’s doing some important mythbusting.
The titular “you just need to lose weight” is a commonly-taken easy-out for many doctors, to avoid having to dispense actual treatment for an actual condition. Whether or not weight loss would help in a given situation is often immaterial; “kicking the can down the road” is the goal.
Most of the book is divided into 20 chapters, each of them devoted to debunking one myth. Think of it like 10almonds’ “Mythbusting Friday” edition (indeed, we did one about obesity), but with an entire book, and as much room as she needs to provide much more detail than we can ever get into in a single article.
And far from being a mere polemic, she does indeed provide that detail—this is clearly a very well-researched book, above and beyond the author’s own personal experience. Further, all the key points are illustrated and articulated clearly, making the book’s ideas very comprehensible.
The style is pop-science, but with frequent bibliographical references for relevant sources.
Bottom line: for some readers, this book will come as a great validation; for others, it may be eye-opening. Either way, it’s a very worthwhile read.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
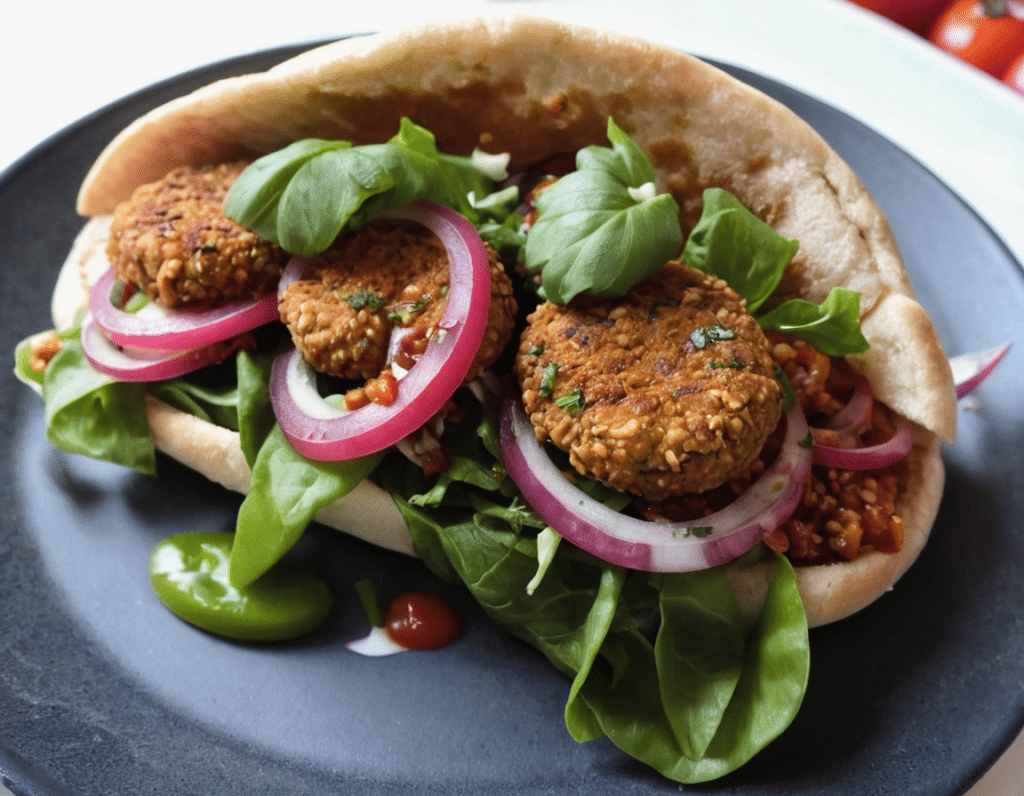
Healthy Harissa Falafel Patties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You can make these as regular falafel balls if you prefer, but patties are quicker and easier to cook, and are great for popping in a pitta.
You will need
For the falafels:
- 1 can chickpeas, drained, keep the chickpea water (aquafaba)
- 1 red onion, roughly chopped
- 2 tbsp chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- 1 bunch parsley
- 1 tbsp harissa paste
- Extra virgin olive oil for frying
For the harissa sauce:
- ½ cup crème fraîche or plant-based equivalent (you can use our Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese recipe and add the juice of 1 lemon)*
- 1 tbsp harissa paste (or adjust this quantity per your heat preference)
*if doing this, rather than waste the zest of the lemon, you can add the zest to the falafels if you like, but it’s by no means necessary, just an option
For serving:
- Wholegrain pitta or other flatbread (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe)
- Salad (your preference; we recommend some salad leaves, sliced tomato, sliced cucumber, maybe some sliced onion, that sort of thing)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the chickpeas, 1 oz of the aquafaba, the onion, the parsley, and the harissa paste, until smooth. Then add in the chickpea flour until you get a thick batter. If you overdo it with the chickpea flour, add a little more of the aquafaba to equalize. Refrigerate the mixture for at least 30 minutes.
2) Heat some oil in a skillet, and spoon the falafel mixture into the pan to make the patties, cooking on both sides (you can use a spatula to gently turn them), and set them aside.
3) Mix the harissa sauce ingredients in a small bowl.
4) Assemble; best served warm, but enjoy it however you like!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in more of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Hero Homemade Hummus ← another great option
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: