Gymnema Sylvestre: The “Sugar Destroyer”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Leaf That Stops Sugar From “Working”
Gymnema sylvestre, whose botanical name in Greek and Latin means “naked thread of the woods”, and is in various Indian languages referred to be names that translate as “sugar destroyer”, has the most prosaic name in Australia: the Australian cowplant.
In English it’s mostly called by the Greek “gymnema” though, so that’s what we’ll call it here.
You may be wondering: “the sugar destroyer?”
And no, it doesn’t actually destroy sugar. But it does do quite a bit of sugar-related stuff. Here’s the science for it…
Blocks sugar receptors in your tongue
This is what it is most well-known for, and it is a topical effect, so you won’t get this from a pill, but you will get this from the leaves, or from drinking it as a tea made from the leaves.
The effect last several hours, during which time your ability to taste sweetness will be reduced, which not only makes sweet foods less appealing because they’re no longer tasting sweet, but also, once you get used to it, when you actually do taste sweet foods, they will now taste too sweet.
So, it doesn’t just temporarily curb cravings; it offers a long-term escape from such, too.
You may be wondering: “what about artificially sweetened foods and drinks?”
And the answer is: yes, it blocks perception of the sweetness of those too:
Effects of sweetness perception and caloric value of a preload on short term intake ← this study used gymnema as the sweetness-blocker, testing sugary drinks, aspartame-sweetened drinks, and unsweetened drinks
Blocks sugar receptors in the gut, too
Long story short: this slows down the absorption of sugars from the gut, thus resulting in a gentler blood sugar curve, minimizing spikes, and (because of the body’s use of blood sugars as it goes) overall lower blood sugar levels.
Want the long version? Here it is:
Benefits beyond sugar-blocking
It also prevents the accumulation of triglycerides in muscles and the liver, as well as decreasing fatty acid accumulation in the blood. In simpler terms: it lowers LDL (“bad” cholesterol”, including VLDL). As a bonus, it increases HDL (“good” cholesterol) while it’s at it.
The vast majority of the studies for this are on rats and mice though, of which you can see very many listed in the “similar articles” under this systematic review of studies:
A systematic review of Gymnema sylvestre in obesity and diabetes management
We did find one good quality human RCT, testing gymnema along with several other treatments (they found that each worked, and/but using a combination yielded the best results):
(the title says “on weight loss”, but rest assured the study also gives information about its effects on total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, overall triglycerides, and serum leptin levels, as well as excretion of urinary fat metabolites—suffice it to say, they were thorough)
Is it safe?
It has a good safety profile in general, but if you are diabetic, proceed with caution and discuss it with your endocrinologist, since it will be affecting your blood sugar levels and insulin levels. While it’s probably not enough to replace metformin or similar, it is enough that taking it carelessly could result in an unexpected hypo.
Similarly, if you have any heart condition and especially if you are being treated for that with medication, do speak with your cardiologist since its antilipemic action could potentially lower your cholesterol more than expected, and doctors don’t like surprises.
As ever, no list of contraindications will be exhaustive, and we can’t speak for your specific situation, so checking with your pharmacist/doctor is always a good idea.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon ← we’ve linked to a tea version of it so you can enjoy the full effects; if you prefer capsule form, you can click through from there to shop around 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do Breathe – by Michael Williams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever felt you could get everything in your life in order, if you could just get a little breathing room first?
Notwithstanding the title, this is mostly not a book about breathing exercises. It does cover that too, but there’s a lot more.
The author’s advices draw from a variety of high quality sources. Well-read readers will certainly recognise sections that are straight from David Allen’s “Getting Things Done”, and Mihaly Czikszentmihalyi’s “Flow”, for example, as well as Francesco Cirillo’s “Pomodoro Technique”, and James Clear’s “Atomic Habits”.
We also learn about how even simple yoga can help us, and good sleep, and a healthy diet.
In short, if you’ve been reading 10almonds for a while, you might not actually learn much new! But it’s very nice to have all these things in one book, for sure, and it’s a pleasant, easy read too.
Bottom line: if you’d like to streamline your life and not have to buy a whole stack of different books to do it, this book is a great composite that will enable you to get the job done efficiently.
Share This Post
-
Could Just Two Hours Sleep Per Day Be Enough?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Polyphasic Sleep… Super-Schedule Or An Idea Best Put To Rest?
What is it?
Let’s start by defining some terms:
- Monophasic sleep—sleeping in one “chunk” per day. For example, a good night’s “normal” sleep.
- Biphasic sleep—sleeping in two “chunks” per day. Typically, a shorter night’s sleep, with a nap usually around the middle of the day / early afternoon.
- Polyphasic sleep—sleeping in two or more “chunks per day”. Some people do this in order to have more hours awake per day, to do things. The idea is that sleeping this way is more efficient, and one can get enough rest in less time. The most popular schedules used are:
- The Überman schedule—six evenly-spaced 20-minute naps, one every four hours, throughout the 24-hour day. The name is a semi-anglicized version of the German word Übermensch, “Superman”.
- The Everyman schedule—a less extreme schedule, that has a three-hours “long sleep” during the night, and three evenly-spaced 20-minute naps during the day, for a total of 4 hours sleep.
There are other schedules, but we’ll focus on the most popular ones here.
Want to learn about the others? Visit: Polyphasic.Net (a website by and for polyphasic sleep enthusiasts)
Some people have pointed to evidence that suggests humans are naturally polyphasic sleepers, and that it is only modern lifestyles that have forced us to be (mostly) monophasic.
There is at least some evidence to suggest that when environmental light/dark conditions are changed (because of extreme seasonal variation at the poles, or, as in this case, because of artificial changes as part of a sleep science experiment), we adjust our sleeping patterns accordingly.
The counterpoint, of course, is that perhaps when at the mercy of long days/nights at the poles, or no air-conditioning to deal with the heat of the day in the tropics, that perhaps we were forced to be polyphasic, and now, with modern technology and greater control, we are free to be monophasic.
Either way, there are plenty of people who take up the practice of polyphasic sleep.
Ok, But… Why?
The main motivation for trying polyphasic sleep is simply to have more hours in the day! It’s exciting, the prospect of having 22 hours per day to be so productive and still have time over for leisure.
A secondary motivation for trying polyphasic sleep is that when the brain is sleep-deprived, it will prioritize REM sleep. Here’s where the Überman schedule becomes perhaps most interesting:
The six evenly-spaced naps of the Überman schedule are each 20 minutes long. This corresponds to the approximate length of a normal REM cycle.
Consequently, when your head hits the pillow, you’ll immediately begin dreaming, and at the end of your dream, the alarm will go off.
Waking up at the end of a dream, when one hasn’t yet entered a non-REM phase of sleep, will make you more likely to remember it. Similarly, going straight into REM sleep will make you more likely to be aware of it, thus, lucid dreaming.
Read: Sleep fragmentation and lucid dreaming (actually a very interesting and informative lucid dreaming study even if you don’t want to take up polyphasic sleep)
Six 20-minute lucid-dreaming sessions per day?! While awake for the other 22 hours?! That’s… 24 hours per day of wakefulness to use as you please! What sorcery is this?
Hence, it has quite an understandable appeal.
Next Question: Does it work?
Can we get by without the other (non-REM) kinds of sleep?
According to Überman cycle enthusiasts: Yes! The body and brain will adapt.
According to sleep scientists: No! The non-REM slow-wave phases of sleep are essential
Read: Adverse impact of polyphasic sleep patterns in humans—Report of the National Sleep Foundation sleep timing and variability consensus panel
(if you want to know just how bad it is… the top-listed “similar article” is entitled “Suicidal Ideation”)
But what about, for example, the Everman schedule? Three hours at night is enough for some non-REM sleep, right?
It is, and so it’s not as quickly deleterious to the health as the Überman schedule. But, unless you are blessed with rare genes that allow you to operate comfortably on 4 hours per day (you’ll know already if that describes you, without having to run any experiment), it’s still bad.
Adults typically need 7–9 hours of sleep per night, and if you don’t get it, you’ll accumulate a sleep debt. And, importantly:
When you accumulate sleep debt, you are borrowing time at a very high rate of interest!
And, at risk of laboring the metaphor, but this is important too:
Not only will you have to pay it back soon (with interest), you will be hounded by the debt collection agents—decreased cognitive ability and decreased physical ability—until you pay up.
In summary:
- Polyphasic sleep is really very tempting
- It will give you more hours per day (for a while)
- It will give the promised lucid dreaming benefits (which is great until you start micronapping between naps, this is effectively a mini psychotic break from reality lasting split seconds each—can be deadly if behind the wheel of a car, for instance!)
- It is unequivocally bad for the health and we do not recommend it
Bottom line:
Some of the claimed benefits are real, but are incredibly short-term, unsustainable, and come at a cost that’s far too high. We get why it’s tempting, but ultimately, it’s self-sabotage.
(Sadly! We really wanted it to work, too…)
Share This Post
-
How to Find Happiness In Yourself – by Michelle Mann
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of books about happiness tell you what to pursue, generally. What things to focus on, and that’s good, but incomplete. This book does cover those things too (complete with academic sources to back up what really works), but also goes further:
Michelle Mann gives 25 key habits that will cumulatively build happiness, which is what it’s really about. After all:
- If you watch your favourite movie, you’ll be happy for 90 minutes (or 9 hours if it’s The Lord of the Rings).
- If you build daily habits that add happiness to you, your surroundings, and those around you, you’ll be happy for life.
They do also cover happiness while going through difficult times, such as divorce, job loss, illness, or bereavement.
Sometimes, knowing what we “should” do in theory is the easy part. Where Mann excels here is in providing explanations of each habit. This means that rather than it being some platitude, the principles underlying it are truly understood… and thus motivate us to actually apply the advice and build the habits into our life.
While the explanations are therefore the greatest value of the book, we do recommend copying out the 25 habits (which are effectively subchapter headings) and putting them somewhere to read often.
Bottom line: we recommend getting yourself (and/or your loved ones!) a copy of this book. You (and/or they) will be happy you did!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
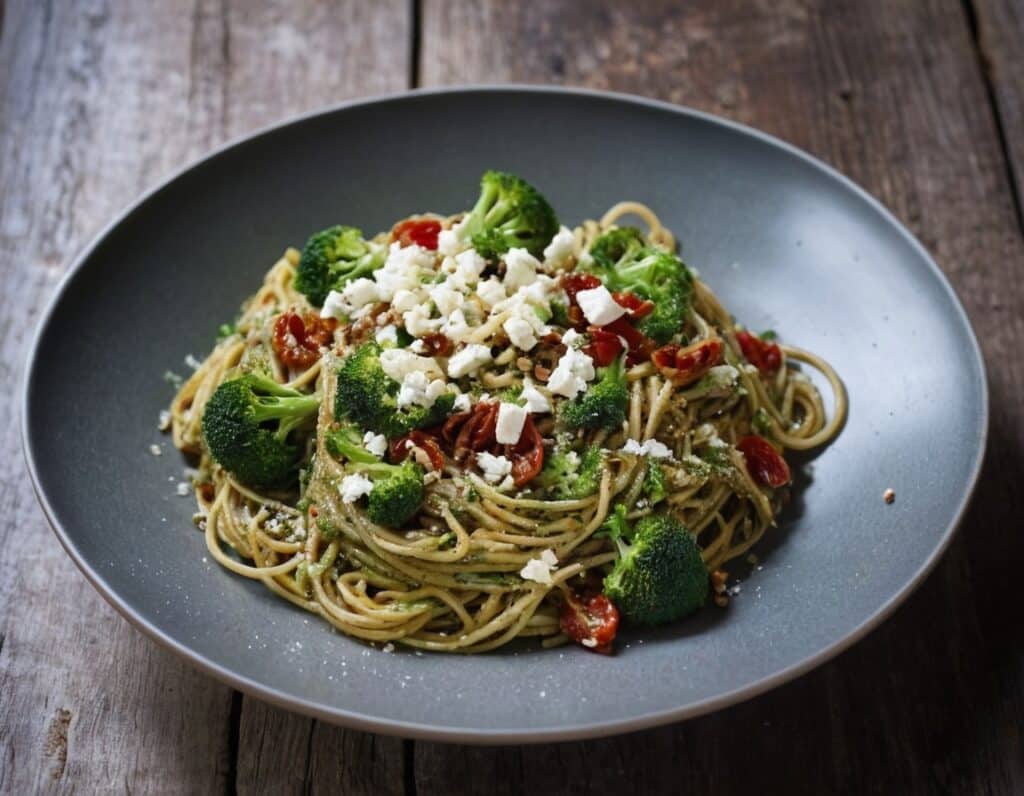
Gut-Healthy Spaghetti Chermoula
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chermoula is a Maghreb relish/marinade (it’s used for both purposes); it’s a little like chimichurri but with distinctly N. African flavors. The gut-healthiness starts there (it’s easy to forget that olives—unless fresh—are a fermented food full of probiotic Lactobacillus sp. and thus great for the gut even beyond their fiber content), and continues in the feta, the vegetables, and the wholewheat nature of the pasta. The dish can be enjoyed at any time, but it’s perfect for warm summer evenings—perhaps dining outside, if you’ve place for that.
You will need
- 9oz wholewheat spaghetti (plus low-sodium salt for its water)
- 10oz broccoli, cut into small florets
- 3oz cilantro (unless you have the soap gene)
- 3oz parsley (whether or not you included the cilantro)
- 3oz green olives, pitted, rinsed
- 1 lemon, pickled, rinsed
- 1 bulb garlic
- 3 tbsp pistachios, shelled
- 2 tbsp mixed seeds
- 1 tsp cumin
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- ½ cup extra virgin olive oil
- For the garnish: 3oz feta (or plant-based equivalent), crumbled, 3oz sun-dried tomatoes, diced, 1 tsp cracked black pepper
Note: why are we rinsing the things? It’s because while picked foods are great for the gut, the sodium can add up, so there’s no need to bring extra brine with them too. By doing it this way, there’ll be just the right amount for flavor, without overdoing it.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the spaghetti as you normally would, but when it’s a minute or two from being done, add the broccoli in with it. When it’s done, drain and rinse thoroughly to get rid of excess starch and salt, and also because cooling it even temporarily (as in this case) lowers its glycemic index.
2) Put the rest of the ingredients into a food processor (except the olive oil and the garnish), and blitz thoroughly until no large coarse bits remain. When that’s done, add the olive oil, and pulse it a few times to combine. We didn’t add the olive oil previously, because blending it so thoroughly in that state would have aerated it in a way we don’t want.
3) Put ⅔ of the chermoula you just made into the pan you used for cooking the spaghetti, and set it over a medium heat. When it starts bubbling, return the spaghetti and broccoli to the pan, mixing gently but thoroughly. If the pasta threatens to stick, you can add a little more chermoula, but go easy on it. Any leftover chermoula that you didn’t use today, can be kept in the fridge and used later as a pesto.
4) Serve! Add the garnish as you do.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Less Obvious Probiotics Benefits
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- What Matters Most For Your Heart? ← spoiler: this is why, while we do watch the sodium, we care more about the fiber
- All about Olive Oil: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
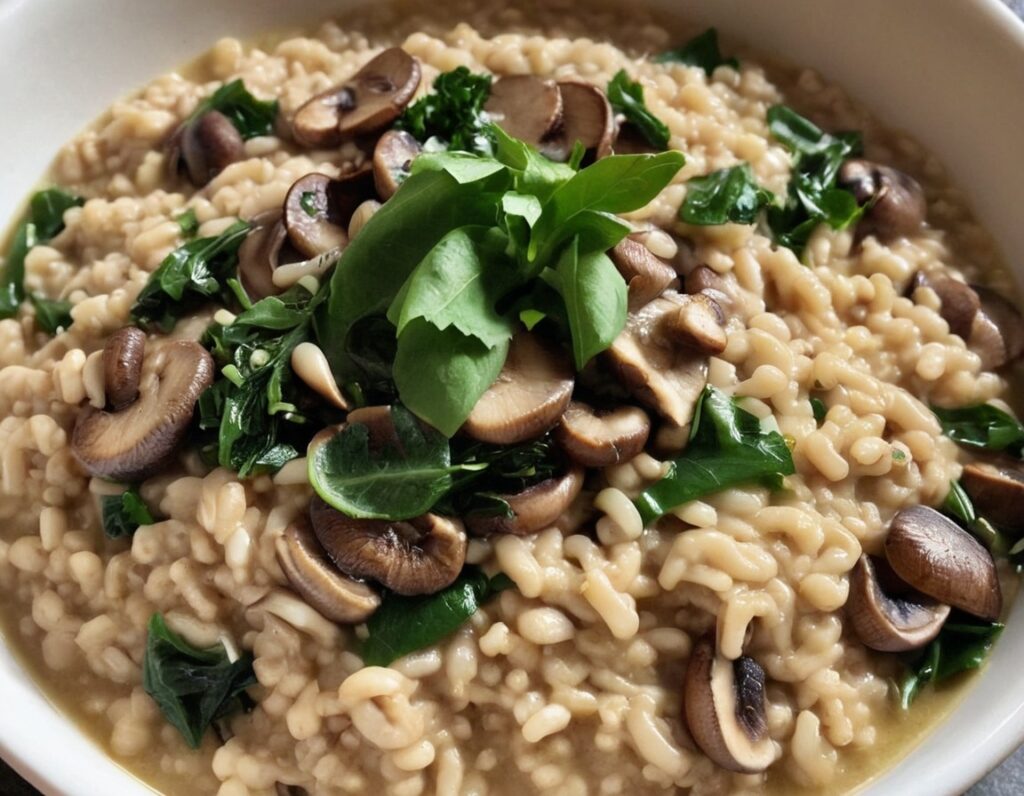
Luxurious Longevity Risotto
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pearl barley is not only tasty and fiber-rich, but also, it contains propionic acid, which lowers cholesterol. The fiber content also lowers cholesterol too, of course, by the usual mechanism. The dish’s health benefits don’t end there, though; check out the science section at the end of the recipe!
You will need
- 2 cups pearl barley
- 3 cups sliced chestnut mushrooms
- 2 onions, finely chopped
- 6 large leaves collard greens, shredded
- ½ bulb garlic, finely chopped
- 8 spring onions, sliced
- 1½ quarts low-sodium vegetable stock
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp MSG or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- 1 tsp rosemary
- 1 tsp thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
- Optional garnish: fresh basil leaves
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat a little oil in a large sauté pan; add the onions and garlic and cook for 5 minutes; add the mushrooms and cook for another 5 minutes.
2) Add the pearl barley and a cup of the vegetable stock. Cook, stirring, until the liquid is nearly all absorbed, and add more stock every few minutes, as per any other risotto. You may or may not use all the stock you had ready. Pearl barley takes longer to cook than rice, so be patient—it’ll be worth the wait!
Alternative: an alternative is to use a slow cooker, adding a quart of the stock at once and coming back about 4 hours later—thus, it’ll take a lot longer, but will require minimal/no supervision.
3) When the pearl barley has softened, become pearl-like, and the dish is taking on a creamy texture, stir in the rest of the ingredients. Once the greens have softened, the dish is done, and it’s time to serve. Add the garnish if using one:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Magic Of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Metabolic Health Roadmap – by Brenda Wollenberg
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The term “roadmap” is often used in informative books, but in this case, Wollenberg (a nutritionist with decades of experience) really does deliver what can very reasonably be described as a roadmap:
She provides chapters in the form of legs of a journey [to better metabolic health], and those legs are broadly divided into an “information center” to deliver new information, a “rest stop” for reflection, “roadwork” to guide the reader through implementing the information we just learned, in a practical fashion, and finally “traveller assistance” to give additional support / resources, as well as any potential troubleshooting, etc.
The information and guidance within are all based on very good science; a lot is what you will have read already about blood sugar management (generally the lynchpin of metabolic health in general), but there’s also a lot about leveraging epigenetics for our benefit, rather than being sabotaged by such.
There’s a little guidance that falls outside of nutrition (sleep, exercise, etc), but for the most part, Wollenberg stays within her own field of expertise, nutrition.
The style is idiosyncratic; it’s very clear that her goal is providing the promised roadmap, and not living up to any editor’s wish or publisher’s hope of living up to industry standard norms of book formatting. However, this pays off, because her delivery is clear and helpful while remaining personable and yet still bringing just as much actual science, and this makes for a very pleasant and informative read.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your metabolic health, as well as get held-by-the-hand through your health-improvement journey by a charming guide, this is very much the book for you!
Click here to check out the Metabolic Health Roadmap, and start taking steps!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: