The Fruit That Can Specifically Reduce Belly Fat
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gambooge: Game-Changer Or Gamble?
The gambooge, also called the gummi-gutta, whence its botanical name Garcinia gummi-gutta (formerly Gardinia cambogia), is also known as the Malabar tamarind, and it even got an English name, the brindle berry.
It’s a fruit that looks like a small pale yellow pumpkin in shape, but it grows on trees and has a taste so sour, that it’s usually used only in cooking, and not eaten raw which makes this writer really want to try it raw now.
Its active phytochemical compound hydroxycitric acid (HCA) rose to popularity as a supplement in the US based on a paid recommendation from Dr. Oz, and then became a controversy as supplements associated with it, were in turn associated with hepatotoxicity (more on this in the “Is it safe?” section below).
What do people use it for?
Simply put: it’s a weight loss supplement.
Less simply put: least interestingly, it’s a mild appetite suppressant:
Safety and mechanism of appetite suppression by a novel hydroxycitric acid extract (HCA-SX) ← this talks more about the biochemistry, but isn’t a human study. Human studies have been small and with mixed results. It seems likely that (as in the rat studies discussed above) the mechanism of action is largely about increasing serotonin, which itself is a well-established appetite suppressant. Therefore, the results will depend somewhat on a person’s brain’s serotonergic system.
We’ll revisit that later, but first let’s look at…
Even less simply put: its other mechanism of action is much more interesting; it actually blocks the production of fat (especially: visceral fat) in the body, by inhibiting citrate lyase, which enzyme plays a significant role in fat production:
Effects of (−)-hydroxycitrate on net fat synthesis as de novo lipogenesis
More illustratively, here’s another study, which found:
❝G cambogia reduced abdominal fat accumulation in subjects, regardless of sex, who had the visceral fat accumulation type of obesity. No rebound effect was observed.
It is therefore expected that G cambogia may be useful for the prevention and reduction of accumulation of visceral fat. ❞
~ Dr. Norihiro Shigematsu et al.
As to why this is particularly important, and far more important than mere fat loss in general, see our previous main feature:
Visceral Belly Fat (And How To Lose It)
Is it safe?
It has shown a good safety profile up to large doses (2.8g/day):
Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of hydroxycitric acid or Garcinia cambogia extracts in humans
There have been some fears about hepatotoxicity, but they appear to be unfounded, and based on products that did not, in fact, contain HCA (and were merely sold by a company that used a similar name in their marketing):
No evidence demonstrating hepatotoxicity associated with hydroxycitric acid
However, as it has a serotoninergic effect, it could cause problems for anyone at risk of serotonin syndrome, which means caution is advisable if you are taking SSRIs (which reduce the rate at which the brain can scrub serotonin, with the usually laudable goal of having more serotonin in the brain—but it is possible to have too much of a good thing, and serotonin syndrome isn’t fun).
As ever, do check with your pharmacist and/or doctor, to be sure, since they can advise with regard to your specific situation and any medications you may be taking.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caloric Restriction with Optimal Nutrition
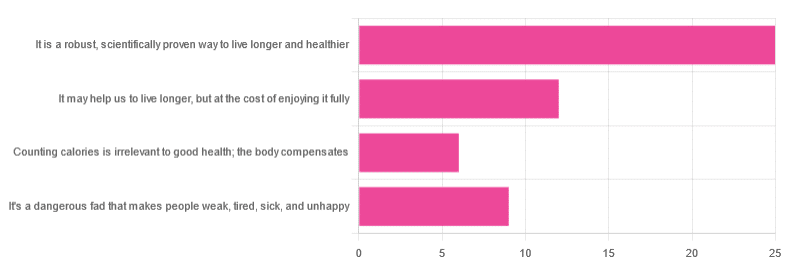
Yesterday, we asked you “What is your opinion of caloric restriction as a health practice?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- 48% said “It is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier”
- 23% said “It may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully”
- 17% said “It’s a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy”
- 12% said “Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates”
So… What does the science say?
A note on terms, first
“Caloric restriction” (henceforth: CR), as a term, sees scientific use to mean anything from a 25% reduction to a 50% reduction, compared to metabolic base rate.
This can also be expressed the other way around, “dropping to 60% of the metabolic base rate” (i.e., a 40% reduction).
Here we don’t have the space to go into much depth, so our policy will be: if research papers consider it CR, then so will we.
A quick spoiler, first
The above statements about CR are all to at least some degree True in one way or another.
However, there are very important distinctions, so let’s press on…
CR is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier: True or False?
True! This has been well-studied and well-documented. There’s more science for this than we could possibly list here, but here’s a good starting point:
❝Calorie restriction (CR), a nutritional intervention of reduced energy intake but with adequate nutrition, has been shown to extend healthspan and lifespan in rodent and primate models.
Accumulating data from observational and randomized clinical trials indicate that CR in humans results in some of the same metabolic and molecular adaptations that have been shown to improve health and retard the accumulation of molecular damage in animal models of longevity.
In particular, moderate CR in humans ameliorates multiple metabolic and hormonal factors that are implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, the leading causes of morbidity, disability and mortality❞
Source: Ageing Research Reviews | Calorie restriction in humans: an update
See also: Caloric restriction in humans reveals immunometabolic regulators of health span
We could devote a whole article (or a whole book, really) to this, but the super-short version is that it lowers the metabolic “tax” on the body and allows the body to function better for longer.
CR may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully: True or False?
True or False, contingently, depending on what’s important to you. And that depends on psychology as much as physiology, but it’s worth noting that there is often a selection bias in the research papers; people ill-suited to CR drop out of the studies and are not counted in the final data.
Also, relevant for a lot of our readers, most (human-based) studies recruit people over 18 and under 60. So while it is reasonable to assume the same benefits will be carried over that age, there is not nearly as much data for it.
Studies into CR and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) have been promising, and/but have caveats:
❝In non-obese adults, CR had some positive effects and no negative effects on HRQoL.❞
❝We do not know what degree of CR is needed to achieve improvements in HRQoL, but we do know it requires an extraordinary amount of support.
Therefore, the incentive to offer this intervention to a low-risk, normal or overweight individual is lacking and likely not sustainable in practice.❞
CR a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy: True or False?
True if it is undertaken improperly, and/or without sufficient support. Many people will try CR and forget that the idea is to reduce metabolic load while still getting good nutrition, and focus solely on the calorie-counting.
So for example, if a person “saves” their calories for the day to have a night out in a bar where they drink their calories as alcohol, then this is going to be abysmal for their health.
That’s an extreme example, but lesser versions are seen a lot. If you save your calories for a pizza instead of a night of alcoholic drinks, then it’s not quite so woeful, but for example the nutrition-to-calorie ratio of pizza is typically not great. Multiply that by doing it as often as not, and yes, someone’s health is going to be in ruins quite soon.
Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates: True or False?
True if by “good health” you mean weight loss—which is rarely, if ever, what we mean by “good health” here at 10almonds (unless we clarify such), but it’s a very common association and indeed, for some people it’s a health goal. You cannot sustainably and healthily lose weight by CR alone, especially if you’re not getting optimal nutrition.
Your body will notice that you are starving, and try to save you by storing as much fat as it can, amongst other measures that will similarly backfire (cortisol running high, energy running low, etc).
For short term weight loss though, yes, it’ll work. At a cost. That we don’t recommend.
❝By itself, decreasing calorie intake will have a limited short-term influence.❞
Source: Reducing Calorie Intake May Not Help You Lose Body Weight
See also…
❝Caloric restriction is a commonly recommended weight-loss method, yet it may result in short-term weight loss and subsequent weight regain, known as “weight cycling”, which has recently been shown to be associated with both poor sleep and worse cardiovascular health❞
Source: Dieting Behavior Characterized by Caloric Restriction
In summary…
Caloric restriction is a well-studied area of health science. We know:
- Practised well, it can extend not only lifespan, but also healthspan
- Practised well, it can improve mood, energy, sexual function, and the other things people fear losing
- Practised badly, it can be ruinous to the health—it is critical to practise caloric restriction with optimal nutrition.
- Practised badly, it can lead to unhealthy weight loss and weight regain
One final note…
If you’ve tried CR and hated it, and you practised it well (e.g., with optimal nutrition), then we recommend just not doing it.
You could also try intermittent fasting instead, for similar potential benefits. If that doesn’t work out either, then don’t do that either!
Sometimes, we’re just weird. It can often be because of a genetic or epigenetic quirk. There are usually workarounds, and/but not everything that’s right for most people will be right for all of us.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Seven Sins Of Memory – by Dr. Daniel Schacter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we get older, we often become more forgetful—despite remembering many things clearly from decades past. Why?
Dr. Daniel Shacter takes us on a tour of the brain, and also through evolution, to show how memory is not just one thing, but many. And furthermore, it’s not just our vast memory that’s an evolutionary adaptation, but also, our capacity to forget.
He does also discusses disease that affect memory, including Alzheimer’s, and explores the biological aspects of memory too.
The “seven sins” of the title are seven ways our (undiseased, regular) memory “lets us down”, and why, and how that actually benefits us as individuals and as a species, and/but also how we can modify that if we so choose.
The book’s main strength is in how it separates—or bids us separate for ourselves—what is important to us and our lives and what is not. How and why memory and information processing are often at odds with each other (and what that means for us). And, on a practical note, how we can tip the scales for or against certain kinds of memory.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand human memory in all its glorious paradoxes, and put into place practical measures to make it work for you the way you want, this is a fine book for you.
Click here to check out The Seven Sins of Memory, and get managing yours!
Share This Post
-
How To Be 7.5x More Likely To Develop Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what is it?
Many more people have chronic fatigue, which is the symptom of being exhausted all the time, than have chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) which is the illness of myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME).
This is because fatigue can be a symptom of many, many other conditions, and can be heavily influenced by lifestyle factors too.
A lot of the advice for dealing with chronic fatigue is often the same in both cases, but some will be different, because for example:
- If your fatigue is from some other condition, that condition probably impacts what lifestyle factors you are (and are not) able to change, too
- If your fatigue is from lifestyle factors, that hopefully means you can change those and enjoy less fatigue…
- But if it’s not from lifestyle factors, as in ME/CFS, then advice to “exercise more” etc is not going to help so much.
There are ways to know the difference though:
Check out: Do You Have Chronic Fatigue Syndrome?
The chronic disease pipeline
While it had been strongly suspected that COVID infection could lead to CFS, with long COVID having chronic fatigue as one of its characteristic symptoms, a research team led by Dr. Suzanne Vernon has now established the nature of the relationship.
It was a large (n=13,224) longitudinal observational cohort study of people with no pre-existing ME/CFS, grouped according to their COVID infection status:
- acute infected, enrolled within 30 days of infection or enrolled as uninfected who became infected (n=4,515)
- post-acute infected, enrolled greater than 30 days after infection (n=7,270)
- uninfected (n=1,439).
(to be clear, that last means “never infected”, or else they would be in group 2)
Note: people who had COVID and were hospitalized for it were excluded from the study, so this risk is the risk represented by even just more “moderate” infections.
What they found:
❝The proportion of all RECOVER-Adult participants that met criteria for ME/CFS following SARS-CoV-2 infection was 4.5% (531 of 11,785) compared to 0.6% (9 of 1439) in uninfected participants.❞
There are then different numbers if we look per 100 person-years, as the study also did—in which case, we get a re-modelled increase in risk of 5x instead of 7.5x, but a) that’s still not good b) the “here-and-now” figures of 4.5% vs 0.6% are also relevant.
Read in full: Incidence and Prevalence of Post-COVID-19 Myalgic Encephalomyelitis: A Report from the Observational RECOVER-Adult Study
The killer nobody wants to talk about anymore
Of course, as we all know the pandemic is over, because politicians declared it so, which is very reassuring.
Nevertheless, COVID is currently the still 4th leading cause of death in the US, placing it higher than stroke, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and others.
See also: Emergency or Not, Covid Is Still Killing People. Here’s What Doctors Advise to Stay Safe
So, while it’s very good to take care of our hearts, brains, blood sugars, and so forth, let’s at the very least continue to keep on top of our vaccinations, avoid enclosed crowded spaces where possible, etc.
And for extra boosts to one’s chances: Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
What if I do get (or already have) long COVID and/or ME/CFS?
Well, that is definitely going to suck, but there are still some things that can be done.
Here’s a big one: How To Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue ← this will not, of course, cure you, but it’s a way of getting maximum nutrition for minimum effort, given that for someone with chronic fatigue, effort is a very finite resource that must be used sparingly
Finally, here are some further resources:
Support For Long COVID & Chronic Fatigue
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Dentists Debunk 15 Teeth Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dentists Dr. John Yoo and Dr. Jason Lin leave no gaps in the truth:
The tooth, the whole tooth, and nothing but the tooth
Not only is there no tooth fairy (we are shocked), but also…
- “Baby teeth aren’t important.”
False! Baby teeth act as space holders for permanent teeth, affect speech development, and influence a child’s psychological well-being. - “Acidic fruits will whiten your smile.”
False! In any practical sense, anyway: acidic fruits may temporarily make teeth appear whiter by dispersing stains but cause enamel erosion and weaken teeth over time. - “Fillings last forever.”
False! Fillings can wear down, fail, or develop cavities underneath if oral hygiene isn’t maintained, requiring replacement over time. - “Cavities are irreversible.”
False! Cavities in the enamel can be reversed with fluoride and good oral hygiene, but cavities that reach the dentin are typically irreversible. - “Braces are just for crooked teeth.”
False! Braces also correct functional issues like overbites, underbites, crossbites, and prevent future complications like tooth impaction. - “A knocked-out tooth is gone for good.”
False! A knocked-out tooth can be reimplanted if done quickly (ideally within an hour); storing it in whole milk or saliva helps preserve it. - “Diet sodas won’t give you cavities.”
False! Diet sodas can still cause cavities due to their acidic pH, which erodes enamel, even without sugar. - “Dental cleanings aren’t necessary.”
False! Dental cleanings help remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing can’t, and allow for regular oral health checkups. - “Retainers aren’t for life.”
False! To maintain teeth alignment after braces, retainers should be worn long-term as teeth can shift even years later. - “You should floss before brushing.”
False! The order doesn’t matter, but do floss regularly. - “Everyone has wisdom teeth.”
False! Not everyone is born with wisdom teeth; they are the most commonly missing teeth, and not everyone needs them removed. - “Hydrogen peroxide and baking soda are good toothpaste replacements.”
False! While they are common components in toothpaste, they lack fluoride, which is essential for remineralizing and protecting enamel. - “You’re too old to get braces.”
False! There’s no age limit for braces or aligners; adults often seek them for both aesthetic and functional reasons. - “Teeth that have had root canals can’t feel.”
False! Teeth with root canals can’t feel pain from nerves, but you can still sense pressure due to surrounding ligaments. - “You’ll inevitably lose all your teeth when you’re old.”
False! Good oral hygiene and regular dental care can preserve natural teeth into old age, though genetics also play a role.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- “Baby teeth aren’t important.”
-
The End of Alzheimer’s – by Dr. Dale Bredesen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one didn’t use the “The New Science Of…” subtitle that many books do, and this one actually is a “new science of”!
Which is exciting, and/but comes with the caveat that the overall protocol itself is still undergoing testing, but the results so far are promising. The constituent parts of the protocol are for the most already well-established, but have not previously been put together in this way.
Dr. Bredesen argues that Alzheimer’s Disease is not one condition but three (medical consensus agrees at least that it is a collection of conditions, but different schools of thought slice them differently), and outlines 36 metabolic factors that are implicated, and the good news is, most of them are within our control.
Since there’s a lot to put together, he also offers many workarounds and “crutches”, making for very practical advice.
The style of the book is on the hard end of pop-science, that is to say while the feel and tone is very pop-sciencey, there are nevertheless a lot of words that you might know but your spellchecker probably wouldn’t. He does explain everything along the way, but this does mean that if you’re not already well-versed, you can’t just dip in to a later point without reading the earlier parts.
Bottom line: even if you only implement half the advice in this book, you’ll be doing your long-term cognitive health a huge favor.
Click here to check out The End of Alzheimer’s, and keep cognitive decline at bay!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Reclaiming Body Trust – by Hilary Kinavey & Dana Sturtevant
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Authored by a therapist and a dietician, this book draws from both of their extensive professional clinical experiences, to explore how we can (often early in our lives) be led into disordered thinking when it comes to food and our bodies, and how we can “take back that which has been stolen from us”.
More prosaically: the presented goal here is for us to each figure out where we are with our own body, and how we might build our relationship with same going forwards, in the way that will work the best for us.
The style is relaxed and conversational, while taking care to cover topics that are often tricky with no less seriousness. Chapter headings such as “Your coping is rooted in wisdom”, “What does grief have to do with it?” and “Allowing for pleasure and satisfaction” give an idea of the flavors at hand here.
Bottom line: if you think your relationship with food and your body could be better, not only are you probably right, but also, this book can help.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: