Eye Exercises That Measurably Improve Your Vision
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our eyesight, like most of the rest of our body’s functions, will decline if not adequately maintained. Modern lifestyles see most of us indoors for most of the day (which means a reduced maximum focal length) and often looking at screens (even further reduced focal length), which means that part of our eyes responsible for focus will tend to atrophy and wither. And if we want to see something better, we adjust the settings instead of adjusting our eyes. However, it is perfectly possible to recover our clear youthful vision:
See the results for yourself (and see them clearly!)
The exercises that gave him the results he showed between the two tests, are:
- Blink for 30 seconds
- Focus on something in front and (keeping your focus on that stationary point) move your head left & right, upwards & downwards, and diagonally
- Take a break and blink for 30 seconds
- Keep your head still while you move your eyes left & right, upwards & downwards, and diagonally
- Focus on something in front while you move move your head left & right, upwards & downwards, and diagonally
This should temporarily improve your vision immediately, because of what has been going on in the capillaries in and around your eyes, but sustained results require sustained (i.e. daily) practice. This is because the vasculature is only part of the mechanism; it’s also a matter of improving the muscles responsible for focusing the eyes—and like any muscles, it’s not a case of “do it once and enjoy the results forever”. So, even just 2–3 minutes each day is recommended.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Are Your Glasses Making Your Eyesight Worse?
or, if you are very serious about having excellent vision for life:
Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider ← this one’s a book, and a very good one at that
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Piperine, a compound found in Piper nigrum (black pepper, to its friends), has many health benefits. It’s included as a minor ingredient in some other supplements, because it boosts bioavailability. In its form as a kitchen spice, it’s definitely a superfood.
What does it do?
First, three things that generally go together:
These things often go together for the simple reason that oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer often go together. In each case, it’s a matter of cellular wear-and-tear, and what can mitigate that.
For what it’s worth, there’s generally a fourth pillar: anti-aging. This is again for the same reason. That said, black pepper hasn’t (so far as we could find) been studied specifically for its anti-aging properties, so we can’t cite that here as an evidence-based claim.
Nevertheless, it’s a reasonable inference that something that fights oxidation, inflammation, and cancer, will often also slow aging.
Special note on the anti-cancer properties
We noticed two very interesting things while researching piperine’s anti-cancer properties. It’s not just that it reduces cancer risk and slows tumor growth in extant cancers (as we might expect from the above-discussed properties). Let’s spotlight some studies:
It is selectively cytotoxic (that’s a good thing)
Piperine was found to be selectively cytotoxic to cancerous cells, while not being cytotoxic to non-cancerous cells. To this end, it’s a very promising cancer-sniper:
Piperine as a Potential Anti-cancer Agent: A Review on Preclinical Studies
It can reverse multi-drug resistance in cancer cells
P-glycoprotein, found in our body, is a drug-transporter that is known for “washing out” chemotherapeutic drugs from cancer cells. To date, no drug has been approved to inhibit P-glycoprotein, but piperine has been found to do the job:
Targeting P-glycoprotein: Investigation of piperine analogs for overcoming drug resistance in cancer
What’s this about piperine analogs, though? Basically the researchers found a way to “tweak” piperine to make it even more effective. They called this tweaked version “Pip1”, because calling it by its chemical name,
((2E,4E)-5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1-(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1 H)-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one)
…got a bit unwieldy.
The upshot is: Pip1 is better, but piperine itself is also good.
Other benefits
Piperine does have other benefits too, but the above is what we were most excited to talk about today. Its other benefits include:
- Neuroprotective effects (against Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and more)
- Blood-sugar balancing / antidiabetic effect
- Good for gut microbiome diversity
- Heart health benefits, including cholesterol-balancing
- Boosts bioavailability of other nutrients/drugs
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Professional-Style Dental Cleaning At Home?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You know the scene: your dentist is rummaging around inside your mouth with an implement that looks like a medieval torture device; you wince at a sudden sharp pain, only to be told “if you flossed, you wouldn’t be bleeding now”.
For most of us, going to the dentist isn’t near the top of our “favorite things to do” list, but it is of course a necessity of (healthy) life.
So, what can we do to minimize suffering in the dentist’s chair?
First, the basics
Of course, good oral hygiene is the absolute baseline, but with so many choices out there, which is best? We examined an array of options in this three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing Without Flossing?
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← we recommend the miswak! Not only does it clean the teeth as well as or better than traditional brushing, but also it changes the composition of saliva to improve the oral microbiome, effectively turning your saliva into a biological mouthwash that kills unwanted microbes and is comfortable for the ones that should be there.
In fact, caring for the composition of one’s saliva, and thus one’s oral microbiome, is so important that we did a main feature on that, a little later:
Make Your Saliva Better For Your Teeth ← this is especially important if you take any meds that affect the composition of your saliva (scroll down to the table of meds). Your medications’ leaflets won’t tell you that it does that directly, but they will list “dry mouth” as one of the potential side effects (and you’ll probably know if you have a medication that gives you a dry mouth).
Next, level up
For this one, we’ll drop some links to some videos we’ve featured (for those who prefer text, worry not, your faithful writer has added text-based overviews):
- How To Regrow Receding Gums
- Tooth Remineralization: How To Heal Your Teeth Naturally
- Tartar Removal At Home & How To Prevent Tartar
Now, that last one sounds slightly more exciting than it is—it is about using chemical processes to gradually lessen the tartar over time, with a six-month timeframe.
So, what if you want to do one better than that?
Finally… Buckle up, this one’s fun
Ok, so “fun” and “dental care” don’t usually go hand-in-hand, and maybe your sense of fun differs from this writer’s, but hey. The thing is, we’re going to get hands-on with dental tools.
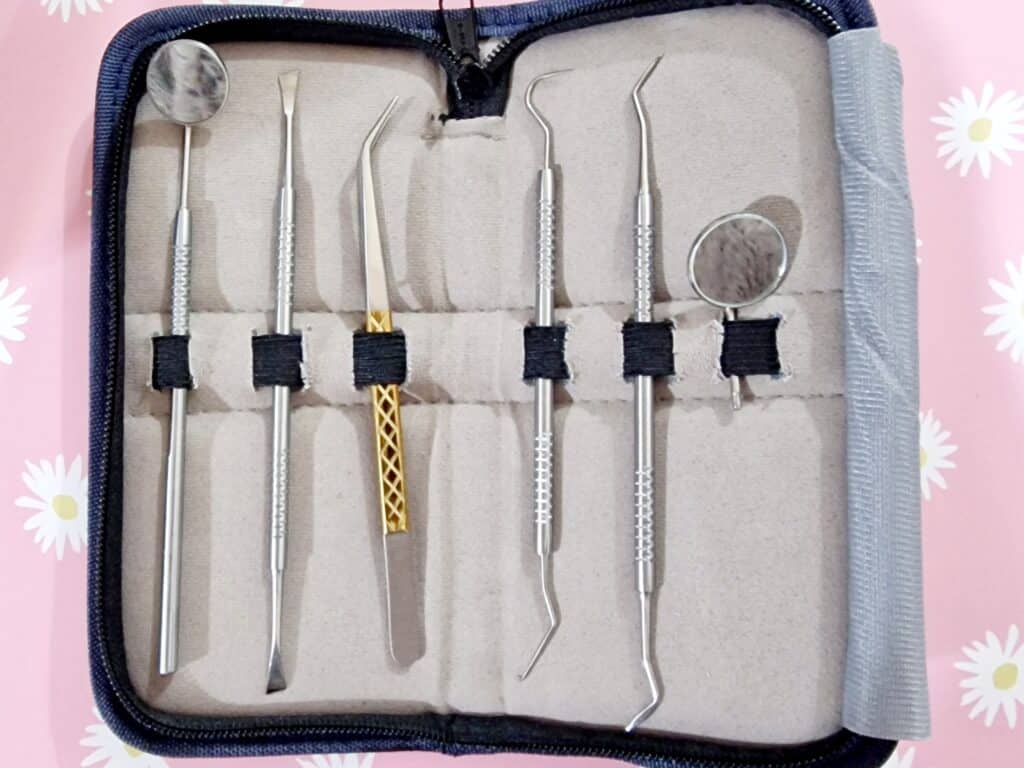
Specifically, these dental tools:
👆 these are literally the tools this writer has; if you look in the specula (the round mirror bits), you can see the reflection of the fluffy gray bathrobe I was wearing when I took the picture!
You can get tools like these easily online; here’s an example product on Amazon; do also shop around of course, and we recommend checking the reviews to ensure good quality.
Writer’s story on why I have these: once upon a time, a wisdom tooth came through at 45°, ploughing through the molar next to it, which then needed removing.
However, my teeth have the interesting anatomical quirk that I have hooked/barbed roots, which does not make tooth extraction easy; it had to come out sidewise, and the process was somewhat bungled by an inexperienced dental surgeon.
When the anesthetic wore off, it was the most pain I’ve ever been in in my life.
After that, I wasn’t a very regular returner to the dentist, and in 2013, I fell into a very deep depression for unrelated reasons, and during that period, I got some plaque/tartar buildup on some of my teeth due to lack of care, that then just stayed until I decided to take care of it more recently, which I am happy to say, I’ve now done (my teeth are the happiest and healthiest they’ve ever been), and I’m going to share how, with you.
So, here’s how to do it… First, you’ll need those tools, of course.
You will also want a good quality backlit magnifying mirror. Again, here’s an example product on Amazon ← this is the exact kind this writer has, and it’s very good.
You may be thinking: “wait a minute, this is scary, those are dangerous and I’m not a dentist!”
If so, then a few quick things to bear in mind:
- If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
- These things do look scarier than they are once you get used to them. Do you use metal silverware when eating? Technically you could stab yourself with a fork any time, or damage your teeth with it, but when was the last time you did that?
- With regard to manual dexterity, if you have the manual dexterity required to paint your nails, floss your teeth, sew by hand, or write with a pen, then you have the manual dexterity to do this, too.
Now, about the tools:
- Speculum / magnifying speculum: the one with the mirror. This is useful for looking at the backs of teeth.
- Tweezers: the one with the gold grip in the photo above. You probably won’t need to use these, but we’re sure you know how to use tweezers in general.
- Dental explorer: the one with the big wicked-looking hook on one end, and a tiny (almost invisible in the photo) hook on the other end. This is for examining cavities, not for manipulating things. Best leave that to your dentist if you have cavities.
- Dental pick: this is the one to the right of the dental explorer, and it is for cleaning in the crevices between teeth. One end is quite blunt; the other is pointier, and you can choose which end to use depending on what fits into the shape of the crevice between your teeth.
- Dental scraper: this is the one with chisel ends. One end curves very slightly to the left, the other, very slightly to the right. This is for ergonomics depending on which hand you’re using, and which side you’re scraping (you’ll become very aware that your teeth, even if they look straight, curve very slightly at the edges.
You’ll be using these last two for the actual tartar removal, selecting the tool appropriate to cleaning the flat surface of a tooth, or the crevice where the teeth meet (not like flossing! That part, yes, but under no circumstances is this thing going all the way through to the other side, it’s just for getting into to nook that the scraper can’t so easily clean, that’s all).
A word on using metal against your teeth: a scary prospect, initially! However…
While steel is indeed harder than the enamel of your teeth, the enamel of your teeth is much harder than the plaque/tartar/calculus that you will be removing. Therefore, the technique to use is very gently scrape, starting as gently as humanly possible until you get a feel for it.
Unlike the dentist, you will have an advantage here in that you have biofeedback, and bone conduction of the sounds in your mouth, so you can exercise much more restraint than your dentist can. With the correct minimum of pressure, the tool should glide smoothly down enamel, but when it’s scraping tartar, it should make a very fine sandpapery noise.
This is why “or write with a pen” was one of the skills we mentioned earlier; it’s the same thing; you don’t press with a pen so hard that it goes through the paper, so don’t press so hard with the tool that it damages your enamel, that’s all.
Because of the differential in hardness between the tartar and the enamel, it’s really very easy to remove the tartar without harming the enamel, provided one is gentle.
Final word of warning; we’ll repeat: If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
Also, while this kind of cleaning can be done safely at home, we recommend against doing anything more complicated than that.
See for example: Can You Repair Your Own Teeth At Home? ← the short answer is “no”, or not beyond tooth remineralization, anyway, and kits that say otherwise are potentially misleading, or stop-gap solutions at best.
One last time: always consult with a professional and get their advice (ours is not advice; it’s just information).
Take care!
Share This Post
-
7 Signs of Undiagnosed Autism in Adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to adults and autism, there are two kinds of person in the popular view: those who resemble the Rain Man, and those who are making it up. But, it’s not so, as Paul Micallef explains:
The signs
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Social interaction difficulties: such a person may struggle with understanding social cues, leading to awkwardness, isolation, or appearing eccentric.
- Need for structure and routine: either highly structured or disorganized, both of which stem from executive function challenges. The former, of course, is a coping mechanism, while the latter is the absence of same.
- Sensory sensitivities: can include sensitivities or insensitivities to light, sound, temperature, smells, tastes, and so forth.
- Spiky skillset: extreme strengths in certain areas, coupled with significant difficulties in others, leading to uneven abilities. May be able to dismantle and rebuild a PC, while not knowing how to arrange an Über.
- Emotional regulation issues: experiences of meltdowns, shutdowns, or withdrawal as coping mechanisms when overwhelmed. Not that this is “or”, not necessarily “and”. The latter goes especially unnoticed as an emotional regulation issue, because for everyone else, it’s something that’s not there to see.
- Unusual associations: making mental connections or associations that seem random or uncommon compared to others. The mind went to 17 places quickly and while everyone else got from idea A to idea B, this person is already at idea Q.
- Being “just different”: a general sense of being the odd one out, standing out in subtle or distinct ways. This is rather a catch-all, but if there’s someone who fits this, there’s a good chance, the other things apply too.
For more on all of these, whether pertaining to yourself or a loved one (or both!), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- 16 Overlooked Autistic Traits In Women
- What is AuDHD? 5 important things to know when someone has both autism and ADHD
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Ultimate Booster
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Winning The Biological Arms Race
The human immune system (and indeed, other immune systems, but we are all humans here, after all) is in a constant state of war with pathogens, and that war is a constant biological arms race:
- We improve our defenses and destroy the attackers; the 1% of pathogens that survived now “know” how to counter that trick.
- The pathogens wreak havoc in our systems; the n% of us that survive now have immune systems that “know” how to counter that trick.
Vaccines are a mighty tool in our favor here, because they’re the technology that stops our n% from also being a very low number.
With vaccines, we can effectively pass on established defenses onto the population at large, as this cute video explains very well and very simply in 57 seconds:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
The problem with vaccines
The problem is that this accelerates the arms race. It’s like a chess game where we are able to respond to every move quickly (which is good for us), and/but this means passing the move over to our opponent sooner.
That problem’s hard to avoid, because the alternative has always been “let people die in much larger numbers”.
Traditional vs mRNA vaccines
A quick refresher before we continue to the big news of the day:
- Traditional vaccines use a disabled version of a pathogen to trigger an immune response that will teach the body to recognize the pathogen ready for when the full version shows up
- mRNA vaccines use a custom-made bit of genetic information to tell the body to make its own harmless fake pathogen and then respond to the harmless fake pathogen it made.
Note: this happens independently of the host’s DNA, so no, it does not change your DNA
See also: The Truth About Vaccines
Here’s a more detailed explainer (with a helpful diagram) using the COVID mRNA vaccine as an example:
Genome.gov | How does an mRNA vaccine work?
However, this still leaves us “chasing strains”, because as the pathogen (in this case, a virus) adapts, the vaccine has to be updated too, hence all the boosters.
This is a lot like a security update for your computer’s antivirus software. They’re annoying, but they do an important job.
No more “chasing strains”
The press conference soundbite on this sums it up well:
❝Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised.❞
Read in full: Vaccine breakthrough means no more chasing strains
You may be wondering: what makes this one effective against any strain?
❝What I want to emphasize about this vaccine strategy is that it is broad.
It is broadly applicable to any number of viruses, broadly effective against any variant of a virus, and safe for a broad spectrum of people. This could be the universal vaccine that we have been looking for.
Viruses may mutate in regions not targeted by traditional vaccines. However, we are targeting their whole genome with thousands of small RNAs. They cannot escape this.❞
Importantly, this means it can be applied not just to one disease, let alone just one strain of COVID. Rather, it can be used for a wide variety of viruses that have similar viral functions—COVID / SARS in general, including influenza, and even viruses such as dengue.
How it does this: the above article explains in more detail, but in few words: it targets tiny strings of the genome that are present in all strains of the virus.
Illustrative example: if you wanted to block 10almonds (please don’t), you could block our email address.
But if we were malicious (we’re not) we could be sneaky and change it, so you’d have to block the new one, and the cycle repeats.
But if you were block all emails containing the tiny string of characters “10almonds”, changing our email address would no longer penetrate your defenses.
Now imagine also blocking strings such as “One-Minute Book Review” and “Today’s almonds have been activated by” and other strings we use in every email.
Now multiply this by thousands of strings (because genomes are much larger than our little newsletter), and you see its effectiveness!
Great! How can I get this?
It’s still in the testing stages for now; this is “breaking news” science, after all.
The study itself
…is paywalled for now, sadly, but if you happen to have institutional access, here it is:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Train For The Event Of Your Life!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mobility As A Sporting Pursuit
As we get older, it becomes increasingly important to treat life like a sporting event. By this we mean:
As an “athlete of life”, there are always events coming up for which we need to train. Many of these events will be surprise tests!
Such events/tests might include:
- Not slipping in the shower and breaking a hip (or worse)
- Reaching an item from a high shelf without tearing a ligament
- Getting out of the car at an awkward angle without popping a vertebra
- Climbing stairs without passing out light-headed at the top
- Descending stairs without making it a sled-ride-without-a-sled
…and many more.
Train for these athletic events now
Not necessarily this very second; we appreciate you finishing reading first. But, now generally in your life, not after the first time you fail such a test; it can (and if we’re not attentive: will) indeed happen to us all.
With regard to falling, you might like to revisit our…
…which covers how to not fall, and to not injure yourself if you do.
You’ll also want to be able to keep control of your legs (without them buckling) all the way between standing and being on the ground.
Slav squats or sitting squats (same exercise, different names, amongst others) are great for building and maintaining this kind of strength and suppleness:
(Click here for a refresher if you haven’t recently seen Zuzka’s excellent video explaining how to do this, especially if it’s initially difficult for you, “The Most Anti-Aging Exercise”)
this exercise is, by the way, great for pretty much everything below the waist!
You will also want to do resistance exercises to keep your body robust:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And as for those shoulders? If it is convenient for you to go swimming, then backstroke is awesome for increasing and maintaining shoulder mobility (and strength).
If swimming isn’t a viable option for you, then doing the same motion with your arms, while standing, will build the same flexibility. If you do it while holding a small weight (even just 1kg is fine, but feel free to increase if you so wish and safely can) in each hand will build the necessary strength as you go too.
As for why even just 1kg is fine: read on
About that “and strength”, by the way…
Stretching is not everything. Stretching is great, but mobility without strength (in that joint!) is just asking for dislocation.
You don’t have to be built like the Terminator, but you do need to have the structural integrity to move your body and then a little bit more weight than that (or else any extra physical work could be enough to tip you to breaking point) without incurring damage from the strain. So, it needs to not be a strain! See again, the aforementioned resistance exercises.
That said, even very gentle exercise helps too; see for example the impact of walking on osteoporosis:
Living near green spaces linked to higher bone density and lower osteoporosis risk
and…
So you don’t have to run marathons—although you can if you want:
Marathons in Mid- and Later-Life
…to keep your hips and more in good order.
Want to test yourself now?
Check out:
Building & Maintaining Mobility
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Apple vs Apricot – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple to apricot, we picked the apricot.
Why?
In terms of macros, there’s not too much between them; apples are higher in carbs and only a little higher in fiber, which disparity makes for a slightly higher glycemic index, but it’s not a big difference and they are both low GI foods.
Micronutrients, however, set these two fruits apart:
In the category of vitamins, apple is a tiny bit higher in choline, while apricots are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, and K—in most cases, by quite large margins, too. All in all, a clear and easy win for apricots.
When it comes to minerals, apples are not higher in any minerals, while apricots are higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. There’s simply no contest here.
In short, if an apple a day keeps the doctor away, then an apricot will give the doctor a nice weekend break somewhere.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: