Eat Real Food and Love It – by Kari McCloskey
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Half the battle of healthy eating is enjoying it—because once you do, it’s no longer a battle!
So that’s what this book focuses on. The author, a Registered Nutritionist, does indeed dispense nutritional advice, as you might expect, but also bids us pay attention to what nature’s foods do for us, and notice what less healthy foods take from us. She goes through these category by category, quite comprehensively, before moving on to the more “active” parts of the book.
There’s a lot about training our senses, and about taking a holistic approach to eating, as well as renewing not just our relationship with food, but also various other parts of our life that are inextricably linked to it (from sleep and exercise, to social considerations, and medical issues that healthier eating will help us to avoid or at least tame).
The style is… Joyful. Much like this reviewer, the author loves food, and it shows. She also (again much like this reviewer) cares deeply about the impact food has on her, and (for a third time: like this reviewer!) wants to share that joy and care with the reader. The priority is readability and helpfulness; scientific references are still provided wherever appropriate, though.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your eating but it seems like a chore, this book can help turn it into an excitingly enjoyable journey instead.
Click here to check out Eat Real Food And Love It, and eat real food and love it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To April Fool Yourself Into Having A Nutrient-Dense Diet!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These nutrient-dense foods pack such a punch you only need a bit added to your meal…
- “Have 5 servings of fruit per day”—popular wisdom in the West
- “Have 7 servings of fruit per day!”—generally held as the norm in Japan
- “Have these 12 things that are mostly fruit & veg & nuts each day”—Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen
- “Does the pickle that comes with a burger count?”—an indication of how much many people struggle.
For what it’s worth: pickles are a good source of some minerals (and some healthy gut bacteria too), but are generally too high in sodium to be healthy for most people beyond in the most modest moderation.
But! It can be a lot easier, and without sitting down to a salad buffet every day!
Here are some sneaky tips:
(call it our nod to April Fool’s Day, because tricking yourself into eating more healthily is a top-tier prank)
Beyond soups and smoothies
Soups and smoothies are great, because we can take a lot of nutrients that way without actually oing much eating. And if we’ve a want or need to hide something, blending it does a fine job. However, we’re confident you already know how to make soups and smoothies. So…
Sauces are another excellent place to put nutrients—and as a bonus, homemade sauces will mean skipping on the store-bought sauces whose ingredients all-too-often look something like “sugar, water, spirit vinegar, glucose-fructose syrup, modified maize starch, maltodextrin, salt…”
Top things to use as a main base ingredient in sauces:
- Tomato purée—so much lycopene, and great vitamins too! Modest flavour, but obviously only sensible for what you intend to be a tomato-based sauce. Use it to make anything from marinara sauce to ketchup, sweet-and-sour to smoky barbecue.
- Lentils/beans—if unsure, red lentils or haricot beans have a very mild taste, and edamame beans are almost not-there, flavor-wise. But cooked and blended smooth, these are high-protein, iron-rich, flavonoid-heavy, and a good source of fiber too. Can be used as the base of so many savory creamy sauces!
- Corn—that yellow color? It’s all the lutein. Home-made creamed corn goes great as a dipping sauce! Added spices optional.
Vegetables that punch above their weight
Sometimes, you might not want to eat much veg, but a small edible side-dish could be appealing, or even a generous garnish. In those cases, if you choose wisely, you can have a lot of nutrients in a tiny portion. Here are some that have an absurd nutrient-to-size ratio:
Cacao nibs—one for the dessert-lovers here, but can also garnish a frothy coffee, your morning overnight oats, or if we’re honest, can also just be snacked on! And they keep for ages. Botanically technically a fruit, but we’re going to throw it in here. As for health qualities? Where to begin…
They:
- are full of antioxidants and fight inflammation
- boost immune health
- help control blood sugar levels
- improve vascular function and heart health
- and even fight cancer, which is a many-headed beast, but for example:
…which is starting to look like a pattern, isn’t it? It’s good against cancer.
Brussels sprouts—if your knee-jerk reaction here wasn’t one of great appeal, then consider: these are delicious if done right.
Buy them fresh, not frozen (nothing nutritionally wrong with frozen if you like them—we’re just doing the extra-level tastiness here). Wash them and peel them, then cut twice from the top to almost-the-bottom, to quarter them in a way that they still stay in one piece. Rub them (or if you’re going easier on the fats, spray them) with a little olive oil, a tiny touch of lemon juice, and sprinkle a little cracked black pepper. Sautée them. We know people will advise roasting, which is also great, but try the sautée approach, and thank us later.
Four sprouts is already a sufficient daily serving of cruciferous vegetables, and provides so many health benefits, with not just a stack of vitamins and minerals, but also have anti-cancer properties, are great for your heart in multiple ways, and reduce inflammation too. They’re literally one of the healthiest foods out there and you only need a tiny portion to benefit.
Kale—Don’t like the taste/texture? That’s OK, read on… No surprises here, but it’s crammed with vitamins and minerals.
- If you don’t care for the bitter taste, cooking it (such as by steaming it) takes that away.
- If you don’t care for the texture, baking it with a little sprayed-on olive oil changes that completely (and is how “kale chips” are made).
- If you don’t care for either? Do the “kale chips” thing mentioned above, but do it on a lower heat for longer—dry it out, basically. Then either blend it in a food processor, or by hand with a pestle and mortar (it turns to powder very easily, so this won’t be hard work), and you now have a very nutrient-dense powder that tastes of very little. While fries are not a health food, an example here is that you can literally dust fries with it and they won’t taste any different but you got a bunch of vitamins and minerals added from a whole food source.
- If going for the above approach, do it in batch and make yourself a jar of it to keep handy with your seasonings collection!
Bell peppers—Working hard to justify their high prices in the grocery store, these are very high in vitamins, especially rich in carotenoids, including lutein, and as a bonus, they’re also full of antioxidants. So, slice some and throw them at whatever else you’re cooking, and you’ve added a lot of nutrients for negligible effort.
Garlic—once you’ve done the paperwork, garlic not only makes bland meals delicious, but is also a treasure trove of micronutrients. It has a stack of vitamins and minerals, and also contains allicin. If you’ve not heard of that one, it’s the compound in garlic that is so good for blood pressure and heart health. See for example:
- Lipid-lowering effects of time-released garlic
- Garlic extract lowers blood pressure in patients with hypertension
- Garlic extract reduces blood pressure in hypertensives
If an apple a day keeps the doctor away, just imagine what a bulb of garlic can do (come on, we can’t be the only ones who measure garlic by the bulb instead of by the clove, right?)!
But in seriousness: measure garlic with your heart—have lots or a little, per your preference. The whole point here is that even a little of these superfoods can make a huge difference to your health!
Share This Post
-
Top 10 Unhealthy Foods: How Many Do You Eat?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The items on this list won’t come as a shocking surprise to you, but it can be a good opportunity to do a quick tally and see how many of these have snuck into your diet:
The things that take away health instead of adding it
Without further ado, they are…
- Alcohol: not only is it high in empty calories, but also it’s bad for pretty much everything, especially increasing the risks of liver disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
- Processed snacks: low in nutrition; contain unhealthy fats, refined sugars, and artificial additives that often aren’t great.
- Potato chips: get their own category for being especially high in fat, sodium, and empty calories; contribute to heart disease and weight gain.
- Processed cheese: some kinds of cheese are gut-healthy in moderation, but this isn’t. Instead, it’s just loaded with saturated fats, sodium, and sugars, and is pretty much heart disease in a slice.
- Donuts: deep-fried, sugary, and made with refined flour; cause blood sugar spikes and crashes, and what’s bad for your blood sugars is bad for almost everything else.
- French fries & similar deep-fried foods: high in saturated fats and sodium; contribute to obesity and heart issues, are not great for blood sugars either.
- White bread: made with refined flour; cause blood sugar spikes and metabolic woes.
- Sodas: high in sugar or artificial sweeteners; can easily lead to weight gain, diabetes, and tooth decay.
- Processed meats: high in calories and salt; strongly associated with heart disease and cancer.
- Hot dogs & fast food burgers: get their own category for being the absolute worst of the above-mentioned processed meats.
This writer scored: no / rarely / no / no / no / rarely / rarely / rarely / no / no
How about you?
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What happens in my brain when I get a migraine? And what medications can I use to treat it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Migraine is many things, but one thing it’s not is “just a headache”.
“Migraine” comes from the Greek word “hemicrania”, referring to the common experience of migraine being predominantly one-sided.
Some people experience an “aura” preceding the headache phase – usually a visual or sensory experience that evolves over five to 60 minutes. Auras can also involve other domains such as language, smell and limb function.
Migraine is a disease with a huge personal and societal impact. Most people cannot function at their usual level during a migraine, and anticipation of the next attack can affect productivity, relationships and a person’s mental health.
Francisco Gonzelez/Unsplash What’s happening in my brain?
The biological basis of migraine is complex, and varies according to the phase of the migraine. Put simply:
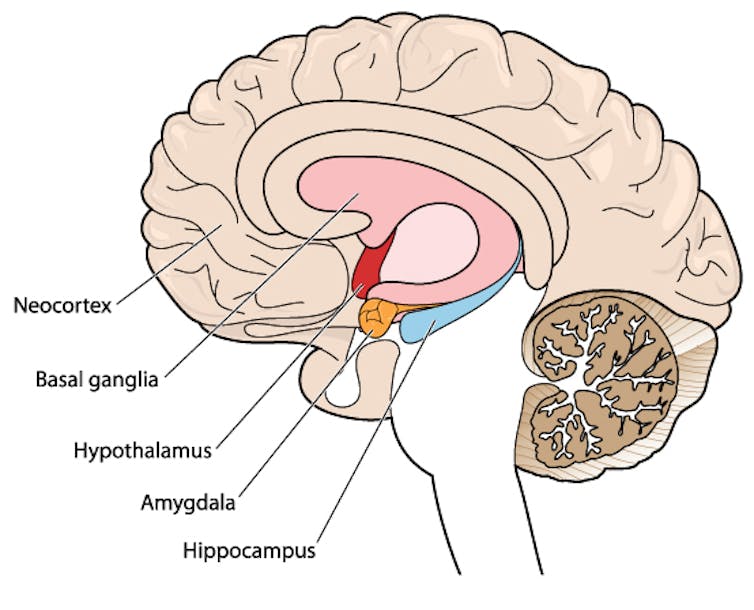
The earliest phase is called the prodrome. This is associated with activation of a part of the brain called the hypothalamus which is thought to contribute to many symptoms such as nausea, changes in appetite and blurred vision.
The hypothalamus is shown here in red. Blamb/Shutterstock Next is the aura phase, when a wave of neurochemical changes occur across the surface of the brain (the cortex) at a rate of 3–4 millimetres per minute. This explains how usually a person’s aura progresses over time. People often experience sensory disturbances such as flashes of light or tingling in their face or hands.
In the headache phase, the trigeminal nerve system is activated. This gives sensation to one side of the face, head and upper neck, leading to release of proteins such as CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide). This causes inflammation and dilation of blood vessels, which is the basis for the severe throbbing pain associated with the headache.
Finally, the postdromal phase occurs after the headache resolves and commonly involves changes in mood and energy.
What can you do about the acute attack?
A useful way to conceive of migraine treatment is to compare putting out campfires with bushfires. Medications are much more successful when applied at the earliest opportunity (the campfire). When the attack is fully evolved (into a bushfire), medications have a much more modest effect.
Aspirin
For people with mild migraine, non-specific anti-inflammatory medications such as high-dose aspirin, or standard dose non-steroidal medications (NSAIDS) can be very helpful. Their effectiveness is often enhanced with the use of an anti-nausea medication.
Triptans
For moderate to severe attacks, the mainstay of treatment is a class of medications called “triptans”. These act by reducing blood vessel dilation and reducing the release of inflammatory chemicals.
Triptans vary by their route of administration (tablets, wafers, injections, nasal sprays) and by their time to onset and duration of action.
The choice of a triptan depends on many factors including whether nausea and vomiting is prominent (consider a dissolving wafer or an injection) or patient tolerability (consider choosing one with a slower onset and offset of action).
As triptans constrict blood vessels, they should be used with caution (or not used) in patients with known heart disease or previous stroke.
Triptans should be used cautiously in patients with heart disease. CDC/Unsplash Gepants
Some medications that block or modulate the release of CGRP, which are used for migraine prevention (which we’ll discuss in more detail below), also have evidence of benefit in treating the acute attack. This class of medication is known as the “gepants”.
Gepants come in the form of injectable proteins (monoclonal antibodies, used for migraine prevention) or as oral medication (for example, rimegepant) for the acute attack when a person has not responded adequately to previous trials of several triptans or is intolerant of them.
They do not cause blood vessel constriction and can be used in patients with heart disease or previous stroke.
Ditans
Another class of medication, the “ditans” (for example, lasmiditan) have been approved overseas for the acute treatment of migraine. Ditans work through changing a form of serotonin receptor involved in the brain chemical changes associated with the acute attack.
However, neither the gepants nor the ditans are available through the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) for the acute attack, so users must pay out-of-pocket, at a cost of approximately A$300 for eight wafers.
What about preventing migraines?
The first step is to see if lifestyle changes can reduce migraine frequency. This can include improving sleep habits, routine meal schedules, regular exercise, limiting caffeine intake and avoiding triggers such as stress or alcohol.
Despite these efforts, many people continue to have frequent migraines that can’t be managed by acute therapies alone. The choice of when to start preventive treatment varies for each person and how inclined they are to taking regular medication. Those who suffer disabling symptoms or experience more than a few migraines a month benefit the most from starting preventives.
Some people will take medicines to prevent migraines. Tbel Abuseridze/Unsplash Almost all migraine preventives have existing roles in treating other medical conditions, and the physician would commonly recommend drugs that can also help manage any pre-existing conditions. First-line preventives include:
- tablets that lower blood pressure (candesartan, metoprolol, propranolol)
- antidepressants (amitriptyline, venlafaxine)
- anticonvulsants (sodium valproate, topiramate).
Some people have none of these other conditions and can safely start medications for migraine prophylaxis alone.
For all migraine preventives, a key principle is starting at a low dose and increasing gradually. This approach makes them more tolerable and it’s often several weeks or months until an effective dose (usually 2- to 3-times the starting dose) is reached.
It is rare for noticeable benefits to be seen immediately, but with time these drugs typically reduce migraine frequency by 50% or more.
‘Nothing works for me!’
In people who didn’t see any effect of (or couldn’t tolerate) first-line preventives, new medications have been available on the PBS since 2020. These medications block the action of CGRP.
The most common PBS-listed anti-CGRP medications are injectable proteins called monoclonal antibodies (for example, galcanezumab and fremanezumab), and are self-administered by monthly injections.
These drugs have quickly become a game-changer for those with intractable migraines. The convenience of these injectables contrast with botulinum toxin injections (also effective and PBS-listed for chronic migraine) which must be administered by a trained specialist.
Up to half of adolescents and one-third of young adults are needle-phobic. If this includes you, tablet-form CGRP antagonists for migraine prevention are hopefully not far away.
Data over the past five years suggest anti-CGRP medications are safe, effective and at least as well tolerated as traditional preventives.
Nonetheless, these are used only after a number of cheaper and more readily available first-line treatments (all which have decades of safety data) have failed, and this also a criterion for their use under the PBS.
Mark Slee, Associate Professor, Clinical Academic Neurologist, Flinders University and Anthony Khoo, Lecturer, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cucumber vs Lychee – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cucumber to lychee, we picked the lychee.
Why?
In terms of macros, the lychee has more carbs and more fiber, but both are low glycemic index foods. Functionally a tie, though we could consider it a nominal win for cucumber.
In the category of vitamins, cucumber has more of vitamins A, B1, B5, and K, while lychee has more of vitamins B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, and choline. In particular, cucumber has a lot more vitamin K and lychee has a lot more vitamin C. Nevertheless, in terms of overall vitamin coverage, lychee is the clear winner here.
Looking at minerals, cucumber has more calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while lychee has more copper (especially rich in this), iron, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. Another clear win for lychee.
Both have an abundance of anti-inflammatory polyphenols, but we could find no strong argument for one being better than the other in this category, just different.
In short, both are fine options, but the more nutritionally dense is the lychee, so that’s our choice!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Total Recovery – by Dr. Gary Kaplan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, know: Dr. Kaplan is an osteopath, and as such, will be mostly approaching things from that angle. That said, he is also board certified in other things too, including family medicine, so he’s by no means a “one-trick pony”, nor are there “when your only tool is a hammer, everything starts to look like a nail” problems to be found here. Instead, the scope of the book is quite broad.
Dr. Kaplan talks us through the diagnostic process that a doctor goes through when presented with a patient, what questions need to be asked and answered—and by this we mean the deeper technical questions, e.g. “what do these symptoms have in common”, and “what mechanism was at work when the pain become chronic”, not the very basic questions asked in the initial debriefing with the patient.
He also asks such questions (and questions like these get chapters devoted to them) as “what if physical traumas build up”, and “what if physical and emotional pain influence each other”, and then examines how to interrupt the vicious cycles that lead to deterioration of one’s condition.
The style of the book is very pop-science and often narrative in its presentation, giving lots of anecdotes to illustrate the principles. It’s a “sit down and read it cover-to-cover” book—or a chapter a day, whatever your preferred pace; the point is, it’s not a “dip directly to the part that answers your immediate question” book; it’s not a textbook or manual.
Bottom line: a lot of this work is about prompting the reader to ask the right questions to get to where we need to be, but there are many illustrative possible conclusions and practical advices to be found and given too, making this a useful read if you and/or a loved one suffers from chronic pain.
Click here to check out Total Recovery, and solve your own mysteries!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Scheduling Tips for Overrunning Tasks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Your Questions, Our Answers!
Q: Often I schedule time for things, but the task takes longer than I think, or multiplies while I’m doing it, and then my schedule gets thrown out. Any ideas?
A: A relatable struggle! Happily, there are remedies:
- Does the task really absolutely need to be finished today? If not, just continue it in scheduled timeslots until it’s completed.
- Some tasks do indeed need to be finished today (hi, writer of a daily newsletter here!), so it can be useful to have an idea of how long things really take, in advance. While new tasks can catch us unawares, recurring or similar-to-previous tasks can be estimated based on how long they took previously. For this reason, we recommend doing a time audit every now and again, to see how you really use your time.
- A great resource that you should include in your schedule is a “spare” timeslot, ideally at least one per day. Call it a “buffer” or a “backup” or whatever (in my schedule it’s labelled “discretionary”), but the basic idea is that it’s a scheduled timeslot with nothing scheduled in it, and it works as an “overflow” catch-all.
Additionally:
- You can usually cut down the time it takes you to do tasks by setting “Deep Work” rules for yourself. For example: cut out distractions, single-task, work in for example 25-minute bursts with 5-minute breaks, etc
- You can also usually cut down the time it takes you to do tasks by making sure you’re prepared for them. Not just task-specific preparation, either! A clear head on, plenty of energy, the resources you’ll need (including refreshments!) to hand, etc can make a huge difference to efficiency.
See Also: Time Optimism and the Planning Fallacy
Do you have a question you’d like to see answered here? Hit reply or use the feedback widget at the bottom; we’d love to hear from you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: