Easy Ways To Fix Brittle, Dry, Wiry Hair
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Sam Ellis, a dermatologist, specializes in skin, hair, and nail care—and she’s here with professional knowledge:
Tackling the problem at the root
As we age, hair becomes less shiny, more brittle, coarse, wiry, or gray. More concerningly for many, hair thinning and shedding increases due to shortened growth phases and hormonal changes.
The first set of symptoms there are largely because sebum production decreases, leading to dry hair. It’s worth bearing in mind though, that factors like UV radiation, smoking, stress, and genetics contribute to hair aging too. So while we can’t do much about genetics, the modifiable factors are worth addressing.
Menopause and the corresponding “andropause” impact hair health, and hormonal shifts, not just aging, drive many hair changes. Which is good to know, because it means that HRT (mostly: topping up estrogen or testosterone as appropriate) can make a big difference. Additionally, topical/oral minoxidil and DHT blockers (such as finasteride or dutasteride) can boost hair density. These things come with caveats though, so do research any possible treatment plan before embarking on it, to be sure you are comfortable with all aspects of it—including that if you use minoxidil, while on the one hand it indeed works wonders, on the other hand, you’ll then have to keep using minoxidil for the rest of your life or your hair will fall out when you stop. So, that’s a commitment to be thought through before beginning.
Nutritional deficiencies (iron, zinc, vitamin D) and insufficient protein intake hinder hair growth, so ensure proper nutrition, with sufficient protein and micronutrients.
While we’re on the topic of “from the inside” things: take care to manage stress healthily, as stress negatively affects hair health.
Now, as for “from the outside”…
Dr. Ellis recommends moisturizing shampoos/conditioners; Virtue and Dove brands she mentions positively. She also recommends bond repair products (such as K18 and Olaplex) that restore hair integrity, and heat protectants (she recommends: Unite 7 Seconds) as well as hair oils in general that improve hair condition.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
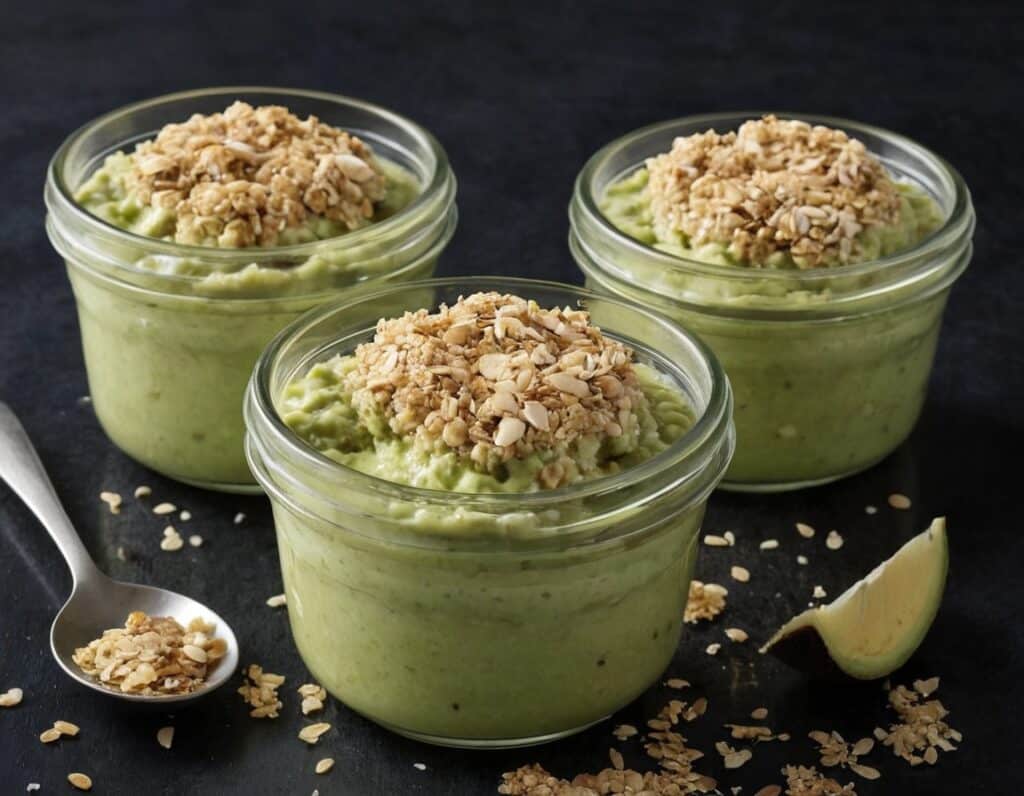
Avocado, Coconut & Lime Crumble Pots
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one’s a refreshing snack or dessert, whose ingredients come together to make a very good essential fatty acid supplement. Coconut is a good source of MCTs, avocados are rich in omega 3, 6, and 9, while chia seeds are a great ALA omega 3 food, topping up the healthy balance.
You will need
- flesh of 2 large ripe avocados
- grated zest and juice of 2 limes
- 3 tbsp coconut oil
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 2 tsp honey (omit if you prefer a less sweet dish)
- 1 tsp desiccated coconut
- 4 low-sugar oat biscuits
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the avocado, lime juice, coconut oil, honey, and half the desiccated coconut, in a food processor.
2) Scoop the mixture into 4 ramekins (or equivalent-sized glasses), making sure to leave a ½” gap at the top. Refrigerate for at least 2–4 hours (longer is fine if you’re not ready to serve yet).
3) Assemble, by crumbling the oat biscuits and sprinkling on top of each serving, along with the other half of the desiccated coconut, the lime zest, and the chia seeds.
4) Serve immediately:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What causes the itch in mozzie bites? And why do some people get such a bad reaction?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you one of these people who loathes spending time outdoors at dusk as the weather warms and mosquitoes start biting?
Female mosquitoes need blood to develop their eggs. Even though they take a tiny amount of our blood, they can leave us with itchy red lumps that can last days. And sometimes something worse.
So why does our body react and itch after being bitten by a mosquito? And why are some people more affected than others?
Arthur Poulin/Unsplash What happens when a mosquito bites?
Mosquitoes are attracted to warm blooded animals, including us. They’re attracted to the carbon dioxide we exhale, our body temperatures and, most importantly, the smell of our skin.
The chemical cocktail of odours from bacteria and sweat on our skin sends out a signal to hungry mosquitoes.
Some people’s skin smells more appealing to mosquitoes, and they’re more likely to be bitten than others.
Once the mosquito has made its way to your skin, things get a little gross.
The mosquito pierces your skin with their “proboscis”, their feeding mouth part. But the proboscis isn’t a single, straight, needle-like tube. There are multiple tubes, some designed for sucking and some for spitting.
Once their mouth parts have been inserted into your skin, the mosquito will inject some saliva. This contains a mix of chemicals that gets the blood flowing better.
There has even been a suggestion that future medicines could be inspired by the anti-blood clotting properties of mosquito saliva.
A common pest mosquito around the world, Culex quinquefasciatus. Cameron Webb (NSW Health Pathology), CC BY It’s not the stabbing of our skin by the mosquito’s mouth parts that hurts, it’s the mozzie spit our bodies don’t like.
Are some people allergic to mosquito spit?
Once a mosquito has injected their saliva into our skin, a variety of reactions can follow. For the lucky few, nothing much happens at all.
For most people, and irrespective of the type of mosquito biting, there is some kind of reaction. Typically there is redness and swelling of the skin that appears within a few hours, but often more quickly, after just a few minutes.
Occasionally, the reaction can cause pain or discomfort. Then comes the itchiness.
Some people do suffer severe reactions to mosquito bites. It’s a condition often referred to as “skeeter syndrome” and is an allergic reaction caused by the protein in the mosquito’s saliva. This can cause large areas of swelling, blistering and fever.
The chemistry of mosquito spit hasn’t really been well studied. But it has been shown that, for those who do suffer allergic reactions to their bites, the reactions may differ depending on the type of mosquito biting.
We all probably get more tolerant of mosquito bites as we get older. Young children are certainly more likely to suffer more following mosquito bites. But as we get older, the reactions are less severe and may pass quickly without too much notice.
How best to treat the bites?
Research into treating bites has yet to provide a single easy solution.
There are many myths and home remedies about what works. But there is little scientific evidence supporting their use.
The best way to treat mosquito bites is by applying a cold pack to reduce swelling and to keep the skin clean to avoid any secondary infections. Antiseptic creams and lotions may also help.
There is some evidence that heat may alleviate some of the discomfort.
It’s particularly tough to keep young children from scratching at the bite and breaking the skin. This can form a nasty scab that may end up being worse than the bite itself.
Applying an anti-itch cream may help. If the reactions are severe, antihistamine medications may be required.
To save the scratching, stop the bites
Of course, it’s better not to be bitten by mosquitoes in the first place. Topical insect repellents are a safe, effective and affordable way to reduce mosquito bites.
Covering up with loose fitted long sleeved shirts, long pants and covered shoes also provides a physical barrier.
Mosquito coils and other devices can also assist, but should not be entirely relied on to stop bites.
There’s another important reason to avoid mosquito bites: millions of people around the world suffer from mosquito-borne diseases. More than half a million people die from malaria each year.
In Australia, Ross River virus infects more than 5,000 people every year. And in recent years, there have been cases of serious illnesses caused by Japanese encephalitis and Murray Valley encephalitis viruses.
Cameron Webb, Clinical Associate Professor and Principal Hospital Scientist, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
If you’re worried about inflammation, stop stressing about seed oils and focus on the basics
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’ve probably seen recent claims online seed oils are “toxic” and cause inflammation, cancer, diabetes and heart disease. But what does the research say?
Overall, if you’re worried about inflammation, cancer, diabetes and heart disease there are probably more important things to worry about than seed oils.
They may or may not play a role in inflammation (the research picture is mixed). What we do know, however, is that a high-quality diet rich in unprocessed whole foods (fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, grains and lean meats) is the number one thing you can to do reduce inflammation and your risk of developing diseases.
Rather than focusing on seed oils specifically, reduce your intake of processed foods more broadly and focus on eating fresh foods. So don’t stress out too much about using a bit of seed oils in your cooking if you are generally focused on all the right things.
What are seed oils?
Seed oils are made from whole seeds, such as sunflower seeds, flax seeds, chia seeds and sesame seeds. These seeds are processed to extract oil.
The most common seed oils found at grocery stores include sesame oil, canola oil, sunflower oil, flaxseed oil, corn oil, grapeseed oil and soybean oil.
Seed oils are generally affordable, easy to find and suitable for many dishes and cuisines as they often have a high smoke point.
However, most people consume seed oils in larger amounts through processed foods such as biscuits, cakes, chips, muesli bars, muffins, dipping sauces, deep-fried foods, salad dressings and margarines.
These processed foods are “discretionary”, meaning they’re OK to have occasionally. But they are not considered necessary for a healthy diet, nor recommended in our national dietary guidelines, the Australian Guide for Healthy Eating.
Seed oils often have a high smoke point.
Gleb Usovich/ShutterstockI’ve heard people say seed oils ‘promote inflammation’. Is that true?
There are two essential types of omega fatty acids: omega-3 and omega-6. These are crucial for bodily functions, and we must get them through our diet since our bodies cannot produce them.
While all oils contain varying levels of fatty acids, some argue an excessive intake of a specific omega-6 fatty acid in seed oils called “linoleic acid” may contribute to inflammation in the body.
There is some evidence linoleic acid can be converted to arachidonic acid in the body and this may play a role in inflammation. However, other research doesn’t support the idea reducing dietary linoleic acid affects the amount of arachidonic acid in your body. The research picture is not clear cut.
But if you’re keen to reduce inflammation, the best thing you can do is aim for a healthy diet that is:
- high in antioxidants (found in fruits and vegetables)
- high in “healthy”, unsaturated fatty acids (found in fatty fish, some nuts and olive oil, for example)
high in fibre (found in carrots, cauliflower, broccoli and leafy greens) and prebiotics (found in onions, leeks, asparagus, garlic and legumes)
low in processed foods.
If reducing inflammation is your goal, it’s probably more meaningful to focus on these basics than on occasional use of seed oils.
Choose foods high in fibre (like many vegetables) and prebiotics (like legumes).
Kiian Oksana/ShutterstockWhat about seed oils and heart disease, cancer or diabetes risk?
Some popular arguments against seed oils come from data from single studies on this topic. Often these are observational studies where researchers do not make changes to people’s diet or lifestyle.
To get a clearer picture, we should look at meta-analyses, where scientists combine all the data available on a topic. This helps us get a better overall view of what’s going on.
A 2022 meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials investigated the relationship between supplementation with omega-6 fatty acid (often found in seed oils) and cardiovascular disease risk (meaning disease relating to the heart and blood vessels).
The researchers found omega-6 intake did not affect the risk for cardiovascular disease or death but that further research is needed for firm conclusions. Similar findings were observed in a 2019 review on this topic.
The World Health Organization published a review and meta-analysis in 2022 of observational studies (considered lower quality evidence compared to randomised controlled trials) on this topic.
They looked at omega-6 intake and risk of death, cardiovascular disease, breast cancer, mental health conditions and type 2 diabetes. The findings show both advantages and disadvantages of consuming omega-6.
The findings reported that, overall, higher intakes of omega-6 were associated with a 9% reduced risk of dying (data from nine studies) but a 31% increased risk of postmenopausal breast cancer (data from six studies).
One of the key findings from this review was about the ratio of omega-3 fatty acids to omega-6 fatty acids. A higher omega 6:3 ratio was associated with a greater risk of cognitive decline and ulcerative colitis (an inflammatory bowel condition).
A higher omega 3:6 ratio was linked to a 26% reduced risk of depression. These mixed outcomes may be a cause of confusion among health-conscious consumers about the health impact of seed oils.
Overall, the evidence suggests that a high intake of omega-6 fatty acids from seed oils is unlikely to increase your risk of death and disease.
However, more high-quality intervention research is needed.
The importance of increasing your omega-3 fatty acids
On top of the mixed outcomes, there is clear evidence increasing the intake of omega-3 fatty acids (often found in foods such as fatty fish and walnuts) is beneficial for health.
While some seed oils contain small amounts of omega-3s, they are not typically considered rich sources.
Flaxseed oil is an exception and is one of the few seed oils that is notably high in alpha-linolenic acid (sometimes shortened to ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid.
If you are looking to increase your omega-3 intake, it’s better to focus on other sources such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and algae-based supplements. These foods are known for their higher omega-3 content compared to seed oils.
The bottom line
At the end of the day, it’s probably OK to include small quantities of seed oils in your diet, as long as you are mostly focused on eating fresh, unprocessed foods.
The best way to reduce your risk of inflammation, heart disease, cancer or diabetes is not to focus so much on seed oils but rather on doing your best to follow the Australian Guide for Healthy Eating.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Emily Burch, Lecturer, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Truth About Statins – by Barbara H. Roberts, M.D.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All too often, doctors looking to dispense a “quick fix” will prescribe from their playbook of a dozen or so “this will get you out of my office” drugs. Most commonly, things that treat symptoms rather than the cause. Sometimes, this can be fine! For example, in some cases, painkillers and antidepressants can make a big improvement to people’s lives. What about statins, though?
Prescribed to lower cholesterol, they broadly do exactly that. However…
Dr. Roberts wants us to know that we could be missing the big picture of heart health, and making a potentially fatal mistake.
This is not to say that the book argues that statins are necessarily terrible, or that they don’t have their place. Just, we need to understand what they will and won’t do, and make an informed choice.
To which end, she does advise regards when statins can help the most, and when they may not help at all. She also covers the questions to ask if your doctor wants to prescribe them. And—all so frequently overlooked—the important differences between men’s and women’s heart health, and the implications these have for the efficacy (or not) of statins.
With regard to the “alternatives to cholesterol-lowering drugs” promised in the subtitle… we won’t keep any secrets here:
Dr. Roberts (uncontroversially) recommends the Mediterranean diet. She also provides two weeks’ worth of recipes for such, in the final part of the book.
All in all, an important book to read if you or a loved one are taking, or thinking of taking, statins.
Pick up your copy of The Truth About Statins on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Do the Work – by Dr. Nicole LaPera
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We have reviewed some self-therapy books before, and they chiefly have focused on CBT and mindfulness, which are great. This one’s different.
Dr. Nicole LaPera has a bolder vision for what we can do for ourselves. Rather than giving us some worksheets for unraveling cognitive distortions or clearing up automatic negative thoughts, she bids us treat the cause, rather than the symptom.
For most of us, this will be the life we have led. Now, we cannot change the parenting style(s) we received (or didn’t), get a redo on childhood, avoid mistakes we made in our adolescence, or face adult life with the benefit of experience we gained right after we needed it most. But we can still work on those things if we just know how.
The subtitle of this book promsies that the reader can/will “recognise your patterns, heal from your past, and create your self”.
That’s accurate, for the content of the book and the advice it gives.
Dr. LaPera’s focus is on being our own best healer, and reparenting our own inner child. Giving each of us the confidence in ourself; the love and care and/but also firm-if-necessary direction that a (good) parent gives a child, and the trust that a secure child will have in the parent looking after them. Doing this for ourselves, Dr. LaPera holds, allows us to heal from traumas we went through when we perhaps didn’t quite have that, and show up for ourselves in a way that we might not have thought about before.
If the book has a weak point, it’s that many of the examples given are from Dr. LaPera’s own life and experience, so how relatable the specific examples will be to any given reader may vary. But, the principles and advices stand the same regardless.
Bottom line: if you’d like to try self-therapy on a deeper level than CBT worksheets, this book is an excellent primer.
Click here to check out How To Do The Work, and empower yourself to indeed do the work!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What causes the itch in mozzie bites? And why do some people get such a bad reaction?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you one of these people who loathes spending time outdoors at dusk as the weather warms and mosquitoes start biting?
Female mosquitoes need blood to develop their eggs. Even though they take a tiny amount of our blood, they can leave us with itchy red lumps that can last days. And sometimes something worse.
So why does our body react and itch after being bitten by a mosquito? And why are some people more affected than others?
Arthur Poulin/Unsplash What happens when a mosquito bites?
Mosquitoes are attracted to warm blooded animals, including us. They’re attracted to the carbon dioxide we exhale, our body temperatures and, most importantly, the smell of our skin.
The chemical cocktail of odours from bacteria and sweat on our skin sends out a signal to hungry mosquitoes.
Some people’s skin smells more appealing to mosquitoes, and they’re more likely to be bitten than others.
Once the mosquito has made its way to your skin, things get a little gross.
The mosquito pierces your skin with their “proboscis”, their feeding mouth part. But the proboscis isn’t a single, straight, needle-like tube. There are multiple tubes, some designed for sucking and some for spitting.
Once their mouth parts have been inserted into your skin, the mosquito will inject some saliva. This contains a mix of chemicals that gets the blood flowing better.
There has even been a suggestion that future medicines could be inspired by the anti-blood clotting properties of mosquito saliva.
A common pest mosquito around the world, Culex quinquefasciatus. Cameron Webb (NSW Health Pathology), CC BY It’s not the stabbing of our skin by the mosquito’s mouth parts that hurts, it’s the mozzie spit our bodies don’t like.
Are some people allergic to mosquito spit?
Once a mosquito has injected their saliva into our skin, a variety of reactions can follow. For the lucky few, nothing much happens at all.
For most people, and irrespective of the type of mosquito biting, there is some kind of reaction. Typically there is redness and swelling of the skin that appears within a few hours, but often more quickly, after just a few minutes.
Occasionally, the reaction can cause pain or discomfort. Then comes the itchiness.
Some people do suffer severe reactions to mosquito bites. It’s a condition often referred to as “skeeter syndrome” and is an allergic reaction caused by the protein in the mosquito’s saliva. This can cause large areas of swelling, blistering and fever.
The chemistry of mosquito spit hasn’t really been well studied. But it has been shown that, for those who do suffer allergic reactions to their bites, the reactions may differ depending on the type of mosquito biting.
We all probably get more tolerant of mosquito bites as we get older. Young children are certainly more likely to suffer more following mosquito bites. But as we get older, the reactions are less severe and may pass quickly without too much notice.
How best to treat the bites?
Research into treating bites has yet to provide a single easy solution.
There are many myths and home remedies about what works. But there is little scientific evidence supporting their use.
The best way to treat mosquito bites is by applying a cold pack to reduce swelling and to keep the skin clean to avoid any secondary infections. Antiseptic creams and lotions may also help.
There is some evidence that heat may alleviate some of the discomfort.
It’s particularly tough to keep young children from scratching at the bite and breaking the skin. This can form a nasty scab that may end up being worse than the bite itself.
Applying an anti-itch cream may help. If the reactions are severe, antihistamine medications may be required.
To save the scratching, stop the bites
Of course, it’s better not to be bitten by mosquitoes in the first place. Topical insect repellents are a safe, effective and affordable way to reduce mosquito bites.
Covering up with loose fitted long sleeved shirts, long pants and covered shoes also provides a physical barrier.
Mosquito coils and other devices can also assist, but should not be entirely relied on to stop bites.
There’s another important reason to avoid mosquito bites: millions of people around the world suffer from mosquito-borne diseases. More than half a million people die from malaria each year.
In Australia, Ross River virus infects more than 5,000 people every year. And in recent years, there have been cases of serious illnesses caused by Japanese encephalitis and Murray Valley encephalitis viruses.
Cameron Webb, Clinical Associate Professor and Principal Hospital Scientist, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: