Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does This Practice Really Hold A Candle To Evidence-Based Medicine?
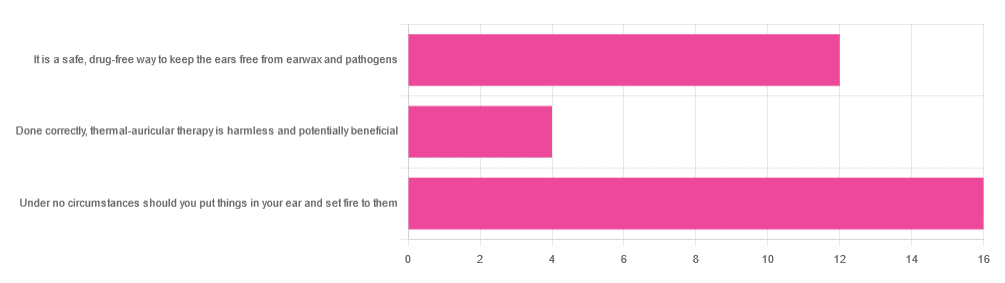
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion of ear candling, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- Exactly 50% said “Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them”
- About 38% said “It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens”
- About 13% said “Done correctly, thermal-auricular therapy is harmless and potentially beneficial”
This means that if we add the two positive-to-candling answers together, it’s a perfect 50:50 split between “do it” and “don’t do it”.
(Yes, 38%+13%=51%, but that’s because we round to the nearest integer in these reports, and more precisely it was 37.5% and 12.5%)
So, with the vote split, what does the science say?
First, a quick bit of background: nobody seems keen to admit to having invented this. One of the major manufacturers of ear candles refers to them as “Hopi” candles, which the actual Hopi tribe has spent a long time asking them not to do, as it is not and never has been used by the Hopi people. Other proposed origins offered by advocates of ear candling include Traditional Chinese Medicine (not used), Ancient Egypt (no evidence of such whatsoever), and Atlantis:
Quackwatch | Why Ear Candling Is Not A Good Idea
It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens: True or False?
False! In a lot of cases of alternative therapy claims, there’s an absence of evidence that doesn’t necessarily disprove the treatment. In this case, however, it’s not even an open matter; its claims have been actively disproven by experimentation:
- It doesn’t remove earwax; on the contrary, experimentation “showed no removal of cerumen from the external auditory canal. Candle wax was actually deposited in some“
- It doesn’t remove pathogens, and the proposed mechanism of action for removing pathogens, that of the “chimney effect”: the idea that the burning candle creates a vacuum that draws wax out of the ear along with debris and bacteria, simply does not work; on the contrary, “Tympanometric measurements in an ear canal model demonstrated that ear candles do not produce negative pressure”.
- It isn’t safe; on the contrary, “Ear candles have no benefit in the management of cerumen and may result in serious injury”
In a medium-sized survey (n=122), the following injuries were reported:
- 13 x burns
- 7 x occlusion of the ear canal
- 6 x temporary hearing loss
- 3 x otitis externa (this also called “swimmer’s ear”, and is an inflammation of the ear, accompanied by pain and swelling)
- 1 x tympanic membrane perforation
Indeed, authors of one paper concluded:
❝Ear candling appears to be popular and is heavily advertised with claims that could seem scientific to lay people. However, its claimed mechanism of action has not been verified, no positive clinical effect has been reliably recorded, and it is associated with considerable risk.
No evidence suggests that ear candling is an effective treatment for any condition. On this basis, we believe it can do more harm than good and we recommend that GPs discourage its use❞
Source: Canadian Family Physician | Ear Candling
Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them: True or False?
True! It’s generally considered good advice to not put objects in general in your ears.
Inserting flaming objects is a definite no-no. Please leave that for the Cirque du Soleil.
You may be thinking, “but I have done this and suffered no ill effects”, which seems reasonable, but is an example of survivorship bias in action—it doesn’t make the thing in question any safer, it just means you were one of the one of the ones who got away unscathed.
If you’re wondering what to do instead… Ear oils can help with the removal of earwax (if you don’t want to go get it sucked out at a clinic—the industry standard is to use a suction device, which actually does what ear candles claim to do). For information on safely getting rid of earwax, see our previous article:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tofu to seitan, we picked the tofu.
Why?
This one is not close!
In terms of macros, seitan does have about 2x the protein, but it also has 6x the carbs and 6x the sodium of tofu, as well as less fiber than tofu.. So we’ll call it a tie on macros. But…
Seitan is also much more processed than tofu, as tofu has usually just been fermented and possibly pressed (depending on kind). Seitan, in contrast, is processed gluten that has been extracted from wheat and usually had lots of things happen to it on the way (depending on kind).
About that protein… Tofu is a complete protein, meaning it has all of the essential amino acids. Seitain, meanwhile, is lacking in lysine.
When it comes to vitamins and minerals, again tofu easily comes out on top; tofu has 5x the calcium, similar iron, more magnesium, 2x the phosphorous, 150% of the potassium, and contains several other nutrients that seitan doesn’t, such as folate and choline.
So, easy winning for tofu across the board on micronutrients.
Tofu is also rich in isoflavones, antioxidant phytonutrients, while seitan has no such benefits.
So, another win for tofu.
There are two reasons you might choose seitan:
- prioritizing bulk protein above all other health considerations
- you are allergic to soy and not allergic to gluten
If neither of those things are the case, then tofu is the healthier choice!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Tempeh vs Tofu – Which is Healthier? ← tempeh is, nutritionally speaking, tofu but better. Of course on a culinary level, there are many recipes where tofu will work and tempeh wouldn’t, though.
- Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Counterintuitive Dos and Don’ts of Nail Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I take a vitamin supplement for strengthening my nails (particularly one of my big toes!) – but they are running out! What do you recommend for strengthening nails? What is/are the key ingredient(s)?❞
Vitamin-wise, biotin (vitamin B7) is an underrated and very important one. As a bonus, it’s really good for your hair too (hair and nails being made of fundamentally the same “stuff”. Because it has exceptionally low toxicity, it can be taken up to 10,000% of the NRV, so if shopping for supplements, a high biotin content is better than a low one.
A lot of products marketed as for “skin, hair, and nails” focus on vitamins A and E, which are good for the skin but aren’t so relevant for nails.
Nutritionally, getting plenty of protein (whatever form you normally take it is fine) is also important since keratin (as nails are made of) is a kind of protein.
Outside of nutritional factors, a few other considerations:
- Testosterone strengthens nails, and declining testosterone levels (as experienced by most men over the age of 45) can result in weaker nails. So for men over 45 especially, a diet that favors testosterone (think foods rich in magnesium and zinc) is good.
- Because estrogen doesn’t do for women’s nails what testosterone does for men’s nails, increasing our magnesium and zinc intake won’t help our nails (but it’s still good for other things, including energy levels in the day and good sleep at night, and most people are deficient in magnesium anyway)
- Those of us who enjoy painted nails would do well to let our nails go without polish sometimes, as it can dry them out. And, acrylic nails are truly ruinous to nail health, as are gel nails (the kind that use a UV lamp to harden them—which is also bad for the skin)
- When nails are brittle, it can be tempting to soak them to reduce their brittleness. However, this is actually counterproductive, as the water will leech nutrients from the nails, and by the time you’ve been out of the footbath (for example) for about an hour, your nails will bemore brittle than before you soaked them.
- Use a moisturizing lotion or nail-oil instead—bonus if it contains biotin, keratin, and/or other helpful nutrients.
- Keep yourself hydrated, too! Hydration that comes to your nails from the inside will deliver nutrients, rather than removing them.
About those supplements: we don’t sell them (or anything else) but for your convenience, here are some great ones (this writer takes pretty much the same, just a different brand because I’m in a different country):
Magnesium Gummies (600mg) & Biotin Gummies (10,000µg)
Enjoy!
❝I was wondering whether there were very simple, clear bullet points or instructions on things to be wary of in Yoga.❞
That’s quite a large topic, and not one that lends itself well to being conveyed in bullet points, but first we’ll share the article you sent us when sending this question:
Tips for Avoiding Yoga Injuries
…and next we’ll recommend the YouTube channel @livinleggings, whose videos we feature here from time to time. She (Liv) has a lot of good videos on problems/mistakes/injuries to avoid.
Here’s a great one to get you started:
! Share This Post
-
Ozempic’s cousin drug liraglutide is about to get cheaper. But how does it stack up?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
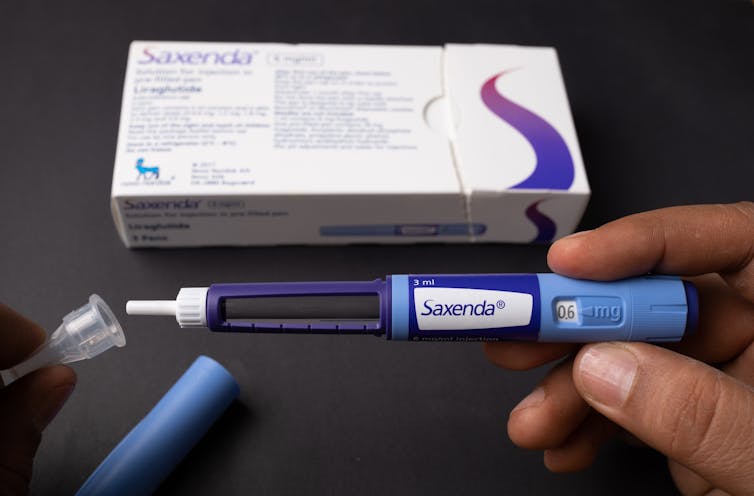
Fourteen years ago, the older drug cousin of semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) came onto the market. The drug, liraglutide, is sold under the brand names Victoza and Saxenda.
Patents for Victoza and Saxenda have now expried. So other drug companies are working to develop “generic” versions. These are likely be a fraction of current cost, which is around A$400 a month.
So how does liraglutide compare with semaglutide?
Halfpoint/Shutterstock How do these drugs work?
Liraglutide was not originally developed as a weight-loss treatment. Like semaglutide (Ozempic), it originally treated type 2 diabetes.
The class of drugs liraglutide and semaglutide belong to are known as GLP-1 mimetics, meaning they mimic the natural hormone GLP-1. This hormone is released from your small intestines in response to food and acts in several ways to improve the way your body handles glucose (sugar).
How do they stop hunger?
Liraglutide acts in several regions of the unconscious part of your brain, specifically the hypothalamus, which controls metabolism, and parts of the brain stem responsible for communicating your body’s nutrient status to the hypothalamus.
Its actions here appear to reduce hunger in two different ways. First, it helps you to feel full earlier, making smaller meals more satisfying. Second, it alters your “motivational salience” towards food, meaning it reduces the amount of food you seek out.
Liraglutide’s original formulation, designed to treat type 2 diabetes, was marketed as Victoza. Its ability to cause weight loss was evident soon after it entered the market.
Shortly after, a stronger formulation, called Saxenda, was released, which was intended for weight loss in people with obesity.
How much weight can you lose with liraglutide?
People respond differently and will lose different amounts of weight. But here, we’ll note the average weight loss users can expect. Some will lose more (sometimes much more), others will lose less, and a small proportion won’t respond.
The first GLP-1 mimicking drug was exenatide (Bayetta). It’s still available for treating type 2 diabetes, but there are currently no generics. Exenatide does provide some weight loss, but this is quite modest, typically around 3-5% of body weight.
For liraglutide, those using the drug to treat obesity will use the stronger one (Saxenda), which typically gives about 10% weight loss.
Semaglutide, with the stronger formulation called Wegovy, typically results in 15% weight loss.
The newest GLP-1 mimicking drug on the market, tirzepatide (Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes and Zepbound for weight loss), results in weight loss of around 25% of body weight.
What happens when you stop taking them?
Despite the effectiveness of these medications in helping with weight loss, they do not appear to change people’s weight set-point.
So in many cases, when people stop taking them, they experience a rebound toward their original weight.
People often regain weight when when they stop taking the drug. Mohammed_Al_Ali/Shutterstock What is the dose and how often do you need to take it?
Liraglutide (Victoza) for type 2 diabetes is exactly the same drug as Saxenda for weight loss, but Saxenda is a higher dose.
Although the target for each formulation is the same (the GLP-1 receptor), for glucose control in type 2 diabetes, liraglutide has to (mainly) reach the pancreas.
But to achieve weight loss, it has to reach parts of the brain. This means crossing the blood-brain barrier – and not all of it makes it, meaning more has to be taken.
All the current formulations of GLP-1 mimicking drug are injectables. This won’t change when liraglutide generics hit the market.
However, they differ in how frequently they need to be injected. Liraglutide is a once-daily injection, whereas semaglutide and tirzepatide are once-weekly. (That makes semaglutide and tirzepatide much more attractive, but we won’t see semaglutide as a generic until 2033.)
What are the side effects?
Because all these medicines have the same target in the body, they mostly have the same side effects.
The most common are a range of gastrointestinal upsets including nausea, vomiting, bloating, constipation and diarrhoea. These occur, in part, because these medications slow the movement of food out of the stomach, but are generally managed by increasing the dose slowly.
Recent clinical data suggests the slowing in emptying of the stomach can be problematic for some people, and may increase the risk of of food entering the lungs during operations, so it is important to let your doctor know if you are taking any of these drugs.
Because these are injectables, they can also lead to injection-site reactions.
Gastrointestinal side effects are most common. Halfpoint/Shutterstock During clinical trials, there were some reports of thyroid disease and pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). However, it is not clear that these can be attributed to GLP-1 mimicking drugs.
In animals, GLP-1 mimicking drugs drugs have been found to negatively alter the growth of the embryo. There is currently no controlled clinical trial data on their use during pregnancy, but based on animal data, these medicines should not be used during pregnancy.
Who can use them?
The GLP-1 mimicking drugs for weight loss (Wegovy, Saxenda, Zepbound/Mounjaro) are approved for use by people with obesity and are meant to only be used in conjunction with diet and exercise.
These drugs must be prescribed by a doctor and for obesity are not covered by the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, which is one of the reasons why they are expensive. But in time, generic versions of liraglutide are likely to be more affordable.
Sebastian Furness, ARC Future Fellow, School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What are heart rate zones, and how can you incorporate them into your exercise routine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you spend a lot of time exploring fitness content online, you might have come across the concept of heart rate zones. Heart rate zone training has become more popular in recent years partly because of the boom in wearable technology which, among other functions, allows people to easily track their heart rates.
Heart rate zones reflect different levels of intensity during aerobic exercise. They’re most often based on a percentage of your maximum heart rate, which is the highest number of beats your heart can achieve per minute.
But what are the different heart rate zones, and how can you use these zones to optimise your workout?
The three-zone model
While there are several models used to describe heart rate zones, the most common model in the scientific literature is the three-zone model, where the zones may be categorised as follows:
- zone 1: 55%–82% of maximum heart rate
- zone 2: 82%–87% of maximum heart rate
- zone 3: 87%–97% of maximum heart rate.
If you’re not sure what your maximum heart rate is, it can be calculated using this equation: 208 – (0.7 × age in years). For example, I’m 32 years old. 208 – (0.7 x 32) = 185.6, so my predicted maximum heart rate is around 186 beats per minute.
There are also other models used to describe heart rate zones, such as the five-zone model (as its name implies, this one has five distinct zones). These models largely describe the same thing and can mostly be used interchangeably.
What do the different zones involve?
The three zones are based around a person’s lactate threshold, which describes the point at which exercise intensity moves from being predominantly aerobic, to predominantly anaerobic.
Aerobic exercise uses oxygen to help our muscles keep going, ensuring we can continue for a long time without fatiguing. Anaerobic exercise, however, uses stored energy to fuel exercise. Anaerobic exercise also accrues metabolic byproducts (such as lactate) that increase fatigue, meaning we can only produce energy anaerobically for a short time.
On average your lactate threshold tends to sit around 85% of your maximum heart rate, although this varies from person to person, and can be higher in athletes.
Wearable technology has taken off in recent years. Ketut Subiyanto/Pexels In the three-zone model, each zone loosely describes one of three types of training.
Zone 1 represents high-volume, low-intensity exercise, usually performed for long periods and at an easy pace, well below lactate threshold. Examples include jogging or cycling at a gentle pace.
Zone 2 is threshold training, also known as tempo training, a moderate intensity training method performed for moderate durations, at (or around) lactate threshold. This could be running, rowing or cycling at a speed where it’s difficult to speak full sentences.
Zone 3 mostly describes methods of high-intensity interval training, which are performed for shorter durations and at intensities above lactate threshold. For example, any circuit style workout that has you exercising hard for 30 seconds then resting for 30 seconds would be zone 3.
Striking a balance
To maximise endurance performance, you need to strike a balance between doing enough training to elicit positive changes, while avoiding over-training, injury and burnout.
While zone 3 is thought to produce the largest improvements in maximal oxygen uptake – one of the best predictors of endurance performance and overall health – it’s also the most tiring. This means you can only perform so much of it before it becomes too much.
Training in different heart rate zones improves slightly different physiological qualities, and so by spending time in each zone, you ensure a variety of benefits for performance and health.
So how much time should you spend in each zone?
Most elite endurance athletes, including runners, rowers, and even cross-country skiers, tend to spend most of their training (around 80%) in zone 1, with the rest split between zones 2 and 3.
Because elite endurance athletes train a lot, most of it needs to be in zone 1, otherwise they risk injury and burnout. For example, some runners accumulate more than 250 kilometres per week, which would be impossible to recover from if it was all performed in zone 2 or 3.
Of course, most people are not professional athletes. The World Health Organization recommends adults aim for 150–300 minutes of moderate intensity exercise per week, or 75–150 minutes of vigorous exercise per week.
If you look at this in the context of heart rate zones, you could consider zone 1 training as moderate intensity, and zones 2 and 3 as vigorous. Then, you can use heart rate zones to make sure you’re exercising to meet these guidelines.
What if I don’t have a heart rate monitor?
If you don’t have access to a heart rate tracker, that doesn’t mean you can’t use heart rate zones to guide your training.
The three heart rate zones discussed in this article can also be prescribed based on feel using a simple 10-point scale, where 0 indicates no effort, and 10 indicates the maximum amount of effort you can produce.
With this system, zone 1 aligns with a 4 or less out of 10, zone 2 with 4.5 to 6.5 out of 10, and zone 3 as a 7 or higher out of 10.
Heart rate zones are not a perfect measure of exercise intensity, but can be a useful tool. And if you don’t want to worry about heart rate zones at all, that’s also fine. The most important thing is to simply get moving.
Hunter Bennett, Lecturer in Exercise Science, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Coconut Milk vs Soy Milk – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing coconut milk to soy milk, we picked the soy.
Why?
First, because there are many kinds of both, let’s be clear which ones we’re comparing. For both, we picked the healthiest options commonly available, which were:
- Soy milk, unsweetened, fortified
- Coconut milk, raw (liquid expressed from grated meat and water)
Macronutrients are our first consideration; coconut milk has about 3x the carbs and about 14x the fat. Now, the fats are famously healthy medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), but still, one cup of coconut milk contains about 2.5x the recommended daily amount of saturated fat, so it’s wise to go easy on that. Coconut milk also has about 4x the fiber, but still, because the saturated fat difference, we’re calling this one a win for soy milk.
In the category of vitamins, the fortified soy milk wins. In case you’re curious: milk in general (animal or plant) is generally fortified with vitamin D (in N. America, anyway; other places may vary), and vitamin B12. In this case, the soy milk has those, plus some natural vitamins, meaning it has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and D, while coconut milk has more of vitamins B3, B5, and C. A fair win for soy milk.
When it comes to minerals, the only fortification for the soy milk is calcium, of which it has more than 7x what coconut milk has. The coconut milk, however, has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium. An easy win for coconut milk.
Adding up the sections gives us a win for soy milk—but if consumed in moderation as part of a diet otherwise low in saturated fat, a case could be made for the coconut.
The real take-away here today is not this specific head-to-head but rather: milks (animal or plant) vary a lot, have a lot of different fortifications and/or additives, and yes that goes even for brands (cow milk brands do this a lot) who don’t advertise their additives because their branding is going for a “natural” look. So, read labels, and make informed decisions about which additives you do or don’t want.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
We analysed almost 1,000 social media posts about 5 popular medical tests. Most were utterly misleading
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Kim Kardashian posted on Instagram about having had a full-body MRI, she enthused that the test can be “life saving”, detecting diseases in the earliest stages before symptoms arise.
What Kardashian neglected to say was there’s no evidence this expensive scan can bring benefits for healthy people. She also didn’t mention it can carry harms including unnecessary diagnoses and inappropriate treatments.
With this post in mind, we wanted to explore what influencers are telling us about medical tests.
In a new study published today in JAMA Network Open, we analysed nearly 1,000 Instagram and TikTok posts about five popular medical tests which can all do more harm than good to healthy people, including the full-body MRI scan.
We found the overwhelming majority of these posts were utterly misleading.
C-R-V/Shutterstock 5 controversial tests
Before we get into the details of what we found, a bit about the five tests included in our study.
While these tests can be valuable to some, all five carry the risk of overdiagnosis for generally healthy people. Overdiagnosis is the diagnosis of a condition which would have never caused symptoms or problems. Overdiagnosis leads to overtreatment, which can cause unnecessary side effects and stress for the person, and wasted resources for the health system.
As an example, estimates suggest 29,000 cancers a year are overdiagnosed in Australia alone.
Overdiagnosis is a global problem, and it’s driven in part by healthy people having tests like these. Often, they’re promoted under the guise of early screening, as a way to “take control” of your health. But most healthy people simply don’t need them.
These are the five tests we looked at:
The full-body MRI scan claims to test for up to 500 conditions, including cancer. Yet there is no proven benefit of the scan for healthy people, and a real risk of unnecessary treatment from “false alarm” diagnoses.
The “egg timer” test (technically known as the AMH, or anti-mullarian hormone test) is often falsely promoted as a fertility test for healthy women. While it may be beneficial for women within a fertility clinic setting, it cannot reliably predict the chance of a woman conceiving, or menopause starting. However, low results can increase fear and anxiety, and lead to unnecessary and expensive fertility treatments.
Multi-cancer early detection blood tests are being heavily marketed as the “holy grail of cancer detection”, with claims they can screen for more than 50 cancers. In reality, clinical trials are still a long way from finished. There’s no good evidence yet that the benefits will outweigh the harms of unnecessary cancer diagnoses.
The gut microbiome test of your stool promises “wellness” via early detection of many conditions, from flatulence to depression, again without good evidence of benefit. There’s also concern that test results can lead to wasted resources.
Testosterone testing in healthy men is not supported by any high-quality evidence, with concerns direct-to-consumer advertising leads men to get tested and take testosterone replacement therapy unnecessarily. Use of testosterone replacement therapy carries its own risk of potential harms with the long-term safety in relation to heart disease and mortality still largely unknown.
Multi-cancer early detection blood tests are heavily marketed. Yuri A/Shutterstock What we found
Together with an international group of health researchers, we analysed 982 posts pertaining to the above tests from across Instagram and TikTok. The posts we looked at came from influencers and account holders with at least 1,000 followers, some with a few million followers. In total, the creators of the posts we included had close to 200 million followers.
Even discounting the bots, that’s a massive amount of influence (and likely doesn’t reflect their actual reach to non-followers too).
The vast majority of posts were misleading, failing to even mention the possibility of harm arising from taking one of these tests. We found:
- 87% of posts mentioned test benefits, while only 15% mentioned potential harms
- only 6% of posts mentioned the risk of overdiagnosis
- only 6% of posts discussed any scientific evidence, while 34% of posts used personal stories to promote the test
- 68% of influencers and account holders had financial interests in promoting the test (for example, a partnership, collaboration, sponsorship or selling for their own profit in some way).
Further analysis revealed medical doctors were slightly more balanced in their posts. They were more likely to mention the harms of the test, and less likely to have a strongly promotional tone.
The vast majority of posts we looked at were misleading. DimaBerlin/Shutterstock As all studies do, ours had some limitations. For example, we didn’t analyse comments connected to posts. These may give further insights into the information being provided about these tests, and how social media users perceive them.
Nonetheless, our findings add to the growing body of evidence showing misleading medical information is widespread on social media.
What can we do about it?
Experts have proposed a range of solutions including pre-bunking strategies, which means proactively educating the public about common misinformation techniques.
However, solutions like these often place responsibility on the individual. And with all the information on social media to navigate, that’s a big ask, even for people with adequate health literacy.
What’s urgently needed is stronger regulation to prevent misleading information being created and shared in the first place. This is especially important given social media platforms including Instagram are moving away from fact-checking.
In the meantime, remember that if information about medical tests promoted by influencers sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
Brooke Nickel, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, University of Sydney; Joshua Zadro, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, Sydney Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney, and Ray Moynihan, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences & Medicine, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: