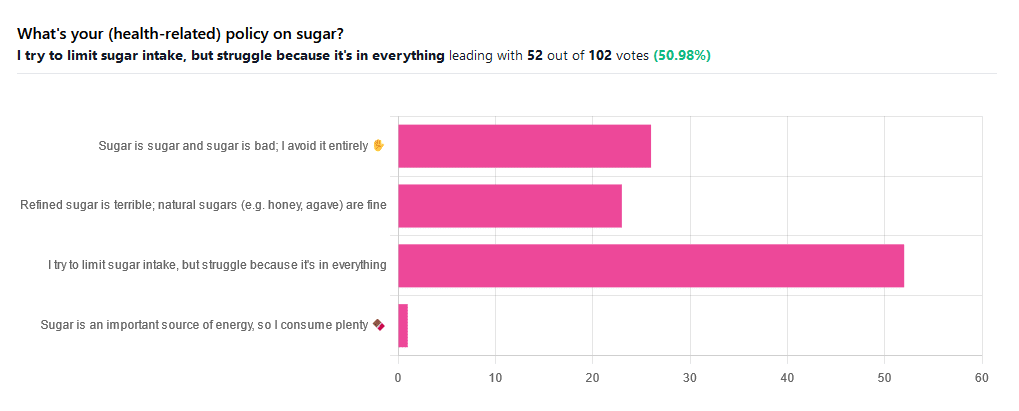
Diet Tips for Crohn’s Disease
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Doctors are great at saving lives like mine. I’m a two time survivor of colon cancer and have recently been diagnosed with Chron’s disease at 62. No one is the health system can or is prepared to tell me an appropriate diet to follow or what to avoid. Can you?❞
Congratulations on the survivorship!
As to Crohn’s, that’s indeed quite a pain, isn’t it? In some ways, a good diet for Crohn’s is the same as a good diet for most other people, with one major exception: fiber
…and unfortunately, that changes everything, in terms of a whole-foods majority plant-based diet.
What stays the same:
- You still ideally want to eat a lot of plants
- You definitely want to avoid meat and dairy in general
- Eating fish is still usually* fine, same with eggs
- Get plenty of water
What needs to change:
- Consider swapping grains for potatoes or pasta (at least: avoid grains)
- Peel vegetables that are peelable; discard the peel or use it to make stock
- Consider steaming fruit and veg for easier digestion
- Skip spicy foods (moderate spices, like ginger, turmeric, and black pepper, are usually fine in moderation)
Much of this latter list is opposite to the advice for people without Crohn’s Disease.
*A good practice, by the way, is to keep a food journal. There are apps that you can get for free, or you can do it the old-fashioned way on paper if prefer.
But the important part is: make a note not just of what you ate, but also of how you felt afterwards. That way, you can start to get a picture of patterns, and what’s working (or not) for you, and build up a more personalized set of guidelines than anyone else could give to you.
We hope the above pointers at least help you get going on the right foot, though!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The S.T.E.P.S. To A Healthier Heart
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Stepping Into Better Heart Health
This is Dr. Jennifer H. Mieres, FACC, FAHA, MASNC. she’s an award-winning (we counted 9 major awards) professor of cardiology, and a leading advocate for women’s heart health. This latter she’s done via >70 scientific publications, >100 research presentations at national and international conferences, 3 books so far, and 4 documentaries, including the Emmy-nominated “A Woman’s Heart”.
What does she want us to know?
A lot of her work is a top-down approach, working to revolutionize the field of cardiology in its application, to result in far fewer deaths annually. Which is fascinating, but unless you’re well-placed in that industry, not something too actionable as an individual (if you are well-placed in that industry, do look her up, of course).
For the rest of us…
Dr. Mieres’ S.T.E.P.S. to good heart health
She wants us to do the following things:
1) Stock your kitchen with heart health in mind
This is tied to the third item in the list of course, but it’s a critical step not to be overlooked. It’s all very well to know “eat more fiber; eat less red meat” and so forth, but if you go to your kitchen and what’s there is not conducive to heart health, you’re just going to do the best with what’s available.
Instead, actually buy foods that are high in fiber, and preferably, foods that you like. Not a fan of beans? Don’t buy them. Love pasta? Go wholegrain. Like leafy greens in principle, but they don’t go with what you cook? Look up some recipes, and then buy them.
Love a beef steak? Well we won’t lie to you, that is not good for your heart, but make it a rare option—so to speak—and enjoy it mindfully (see also: mindful eating) once in a blue moon for a special occasion, rather than “I don’t know what to cook tonight, so sizzle sizzle I guess”.
Meal planning goes a long way for this one! And if meal-planning sounds like an overwhelming project to take on, then consider trying one of the many healthy-eating meal kit services that will deliver ingredients (and their recipes) to your door—opting for a plants-forward plan, and the rest should fall into place.
2) Take control of your activity
Choose to move! Rather than focusing on what you can’t do (let’s say, those 5am runs, or your regularly-scheduled, irregularly attended, gym sessions), focus on what you can do, and do it.
See also: No-Exercise Exercise!
3) Eat for a healthier heart
This means following through on what you did on the first step, and keeping it that way. Buying fresh fruit and veg is great, but you also have to actually eat it. Do not let the perishables perish!
For you too, dear reader, are perishable (and would presumably like to avoid perishing).
This item in the list may seem flippant, but actually this is about habit-forming, and without it, the whole plan will grind to a halt a few days after your first heart-health-focused shopping trip.
See also: Where Nutrition Meets Habits!
4) Partner with your doctor, family, and friends
Good relationships, both professional and personal, count for a lot. Draw up a plan with your doctor; don’t just guess at when to get this or that checked—or what to do about it if the numbers aren’t to your liking.
Partnership with your doctor goes both ways, incidentally. Read up, have opinions, discuss them! Doing so will ultimately result in better care than just going in blind and coming out with a recommendation you don’t understand and just trust (but soon forget, because you didn’t understand).
And as for family and friends, this is partly about social factors—we tend to influence, and be influenced by, those around us. It can be tricky to be on a health kick if your partner wants take-out every night, so some manner of getting everyone on the same page is important, be it by compromise or, in an ideal world, gradually trending towards better health. But any such changes must come from a place of genuine understanding and volition, otherwise at best they won’t stick, and at worst they’ll actively create a pushback.
Same goes for exercise as for diet—exercising together is a good way to boost commitment, especially if it’s something fun (dance classes are a fine example that many couples enjoy, for example).
5) Sleep more, stress less, savor life
These things matter a lot! Many people focus on cutting down salt or saturated fat, and that can be good if otherwise consumed to excess, but for most people they’re not the most decisive factors:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt ← sleep features here!
Stress is also a huge one, and let’s put it this way: people more often have heart attacks during a moment of excessive emotional stress—not during a moment when they had a bit too much butter on their toast.
It’s not even just that acute stress is the trigger, it’s that chronic stress is a contributory factor that erodes the body’s ability to handle the acute stress.
Changing this may seem “easier said than done” because often the stressors are external (e.g. work pressure, financial worries, caring for a sick relative, relationship troubles, major life change, etc), but it is possible to find peace even in the chaos of life:
Want to know more from Dr. Mieres?
You might like this book of hers, which goes into each of the above items in much more depth than we have room to here:
Heart Smarter for Women: Six Weeks to a Healthier Heart – by Dr. Jennifer Mieres
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Celery vs Cucumber – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to cucumber, we picked the celery.
Why?
They are both great, of course! But celery came out on top:
Their macros are very comparable; they’re both 95% water with just enough other things to hold them together, and those other things are in approximately the same proportions in both celery and cucumber.
In the category of vitamins, however, celery has a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B9, E, and K, as well as slightly more vitamin C. Cucumber, meanwhile, only boasts slightly higher vitamin B1.
An easy win for celery on the vitamin front!
Minerals are closer, but celery still comes out on top with its notably higher calcium and potassium content. Cucumber has more iron and zinc, but the margin is smaller.
As a point in cucumber’s favor, it has been noted for its anti-inflammatory effect in ways that celery hasn’t, but we don’t think this is enough to say it wins over celery sweeping the vitamins category and coming out top for minerals too.
However! They are both great, so enjoy them both, of course.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety ← both celery and cucumber are great for this
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs
We asked you for your (health-related) policy on sugar. The trends were as follows:
- About half of all respondents voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Refined sugar is terrible; natural sugars (e.g. honey, agave) are fine”
- About a quarter of all respondents voted for “Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad; I avoid it entirely”
- One (1) respondent voted for “Sugar is an important source of energy, so I consume plenty”
Writer’s note: I always forget to vote in these, but I’d have voted for “I try to limit sugar intake, but struggle because it’s in everything”.
Sometimes I would like to make my own [whatever] to not have the sugar, but it takes so much more time, and often money too.
So while I make most things from scratch (and typically spend about an hour cooking each day), sometimes store-bought is the regretfully practical timesaver/moneysaver (especially when it comes to condiments).
So, where does the science stand?
There has, of course, been a lot of research into the health impact of sugar.
Unfortunately, a lot of it has been funded by sugar companies, which has not helped. Conversely, there are also studies funded by other institutions with other agendas to push, and some of them will seek to make sugar out to be worse than it is.
So for today’s mythbusting overview, we’ve done our best to quality-control studies for not having financial conflicts of interest. And of course, the usual considerations of favoring high quality studies where possible Large sample sizes, good method, human subjects, that sort of thing.
Sugar is sugar and sugar is bad: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
- Sucrose is sucrose, and is generally bad.
- Fructose is fructose, and is worse.
Both ultimately get converted into glycogen (if not used immediately for energy), but for fructose, this happens mostly* in the liver, which a) taxes it b) goes very unregulated by the pancreas, causing potentially dangerous blood sugar spikes.
This has several interesting effects:
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, it doesn’t cause insulin insensitivity (yay)
- Because fructose doesn’t directly affect insulin levels, this leaves hyperglycemia untreated (oh dear)
- Because fructose is metabolized by the liver and converted to glycogen which is stored there, it’s one of the main contributors to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (at this point, we’re retracting our “yay”)
Read more: Fructose and sugar: a major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
*”Mostly” in the liver being about 80% in the liver. The remaining 20%ish is processed by the kidneys, where it contributes to kidney stones instead. So, still not fabulous.
Fructose is very bad, so we shouldn’t eat too much fruit: True or False?
False! Fruit is really not the bad guy here. Fruit is good for you!
Fruit does contain fructose yes, but not actually that much in the grand scheme of things, and moreover, fruit contains (unless you have done something unnatural to it) plenty of fiber, which mitigates the impact of the fructose.
- A medium-sized apple (one of the most sugary fruits there is) might contain around 11g of fructose
- A tablespoon of high-fructose corn syrup can have about 27g of fructose (plus about 3g glucose)
Read more about it: Effects of high-fructose (90%) corn syrup on plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and normal subjects
However! The fiber content (in fruit) mitigates the impact of the fructose almost entirely anyway.
And if you take fruits that are high in sugar and/but high in polyphenols, like berries, they now have a considerable net positive impact on glycemic health:
- Polyphenols and Glycemic Control
- Polyphenols and their effects on diabetes management: A review
- Dietary polyphenols as antidiabetic agents: Advances and opportunities
You may be wondering: what was that about “unless you have done something unnatural to it”?
That’s mostly about juicing. Juicing removes much (or all) of the fiber, and if you do that, you’re basically back to shooting fructose into your veins:
- Effect of Fruit Juice on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials
- Intake of Fruit, Vegetables, and Fruit Juices and Risk of Diabetes in Women
Natural sugars like honey, agave, and maple syrup, are healthier than refined sugars: True or False?
True… Sometimes, and sometimes marginally.
This is partly because of the glycemic index and glycemic load. The glycemic index scores tail off thus:
- table sugar = 65
- maple syrup = 54
- honey = 46
- agave syrup = 15
So, that’s a big difference there between agave syrup and maple syrup, for example… But it might not matter if you’re using a very small amount, which means it may have a high glycemic index but a low glycemic load.
Note, incidentally, that table sugar, sucrose, is a disaccharide, and is 50% glucose and 50% fructose.
The other more marginal health benefits come from that fact that natural sugars are usually found in foods high in other nutrients. Maple syrup is very high in manganese, for example, and also a fair source of other minerals.
But… Because of its GI, you really don’t want to be relying on it for your nutrients.
Wait, why is sugar bad again?
We’ve been covering mostly the more “mythbusting” aspects of different forms of sugar, rather than the less controversial harms it does, but let’s give at least a cursory nod to the health risks of sugar overall:
- Obesity and associated metabolic risk
- Main contributor to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Insulin resistance and diabetes risk
- Cellular aging (shortened telomeres)
- 95% increased cancer risk
That last one, by the way, was a huge systematic review of 37 large longitudinal cohort studies. Results varied depending on what, specifically, was being examined (e.g. total sugar, fructose content, sugary beverages, etc), and gave up to 200% increased cancer risk in some studies on sugary beverages, but 95% increased risk is a respectable example figure to cite here, pertaining to added sugars in foods.
And finally…
The 56 Most Common Names for Sugar (Some Are Tricky)
How many did you know?
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why ’10almonds’? Newsletter Name Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: Why is your newsletter called 10almonds? Maybe I missed it in the intro email, but my curiosity wants to know the significance. Thanks!”
It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was online… So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a tongue-in-cheek reference to that story… but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Grain Brain – by Dr. David Perlmutter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re a regular 10almonds reader, you probably know that refined flour, and processed food in general, is not great for the health. So, what does this book offer more?
Dr. Perlmutter sets out the case against (as the subtitle suggests) wheat, carbs, and sugar. Yes, including wholegrain wheat, and including starchy vegetables such as potatoes and parsnips. Fruit does also come under scrutiny, a clear distinction is made between whole fruits and juices. In the latter case, the lack of fiber (along with the more readily absorbable liquid state) allows for those sugars to zip straight into our blood.
The book includes lots of stats and facts, and many study citations, along with infographics and clear explanations.
If the book has a weakness, it’s when it forgets to clarify something that was obvious to the author. For example, when he talks about our ancestors’ diets being 75% fat and 5% carbs, he neglects to mention that this is 75% by calorie count, not by mass or volume. This makes a huge difference! It’s the difference between a fat-guzzling engine, and someone who eats mostly fruit and oily nuts but also some very high-fat meat/organs.
The book’s strengths, on the other hand, are found in its explanation, backed by good science, of what wheat, along with excessive carbohydrates (especially sugar) can do to our body, including (and most focusedly, hence the title) our brain, leading the way to not just obvious metabolic disorders like diabetes, but also inflammatory diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Bottom line: you don’t have to completely revamp your diet if it’s working for you, but data is data, and this book has lots, making it well-worth a read.
Click here to check out Grain Brain, and learn about how to avoid inflaming yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How light can shift your mood and mental health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
It’s spring and you’ve probably noticed a change in when the Sun rises and sets. But have you also noticed a change in your mood?
We’ve known for a while that light plays a role in our wellbeing. Many of us tend to feel more positive when spring returns.
But for others, big changes in light, such as at the start of spring, can be tough. And for many, bright light at night can be a problem. Here’s what’s going on.
llaszlo/Shutterstock An ancient rhythm of light and mood
In an earlier article in our series, we learned that light shining on the back of the eye sends “timing signals” to the brain and the master clock of the circadian system. This clock coordinates our daily (circadian) rhythms.
“Clock genes” also regulate circadian rhythms. These genes control the timing of when many other genes turn on and off during the 24-hour, light-dark cycle.
But how is this all linked with our mood and mental health?
Circadian rhythms can be disrupted. This can happen if there are problems with how the body clock develops or functions, or if someone is routinely exposed to bright light at night.
When circadian disruption happens, it increases the risk of certain mental disorders. These include bipolar disorder and atypical depression (a type of depression when someone is extra sleepy and has problems with their energy and metabolism).
Light on the brain
Light may also affect circuits in the brain that control mood, as animal studies show.
There’s evidence this happens in humans. A brain-imaging study showed exposure to bright light in the daytime while inside the scanner changed the activity of a brain region involved in mood and alertness.
Another brain-imaging study found a link between daily exposure to sunlight and how the neurotransmitter (or chemical messenger) serotonin binds to receptors in the brain. We see alterations in serotonin binding in several mental disorders, including depression.
Our mood can lift in sunlight for a number of reasons, related to our genes, brain and hormones. New Africa/Shutterstock What happens when the seasons change?
Light can also affect mood and mental health as the seasons change. During autumn and winter, symptoms such as low mood and fatigue can develop. But often, once spring and summer come round, these symptoms go away. This is called “seasonality” or, when severe, “seasonal affective disorder”.
What is less well known is that for other people, the change to spring and summer (when there is more light) can also come with a change in mood and mental health. Some people experience increases in energy and the drive to be active. This is positive for some but can be seriously destabilising for others. This too is an example of seasonality.
Most people aren’t very seasonal. But for those who are, seasonality has a genetic component. Relatives of people with seasonal affective disorder are more likely to also experience seasonality.
Seasonality is also more common in conditions such as bipolar disorder. For many people with such conditions, the shift into shorter day-lengths during winter can trigger a depressive episode.
Counterintuitively, the longer day-lengths in spring and summer can also destabilise people with bipolar disorder into an “activated” state where energy and activity are in overdrive, and symptoms are harder to manage. So, seasonality can be serious.
Alexis Hutcheon, who experiences seasonality and helped write this article, told us:
[…] the season change is like preparing for battle – I never know what’s coming, and I rarely come out unscathed. I’ve experienced both hypomanic and depressive episodes triggered by the season change, but regardless of whether I’m on the ‘up’ or the ‘down’, the one constant is that I can’t sleep. To manage, I try to stick to a strict routine, tweak medication, maximise my exposure to light, and always stay tuned in to those subtle shifts in mood. It’s a time of heightened awareness and trying to stay one step ahead.
So what’s going on in the brain?
One explanation for what’s going on in the brain when mental health fluctuates with the change in seasons relates to the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine.
Serotonin helps regulate mood and is the target of many antidepressants. There is some evidence of seasonal changes in serotonin levels, potentially being lower in winter.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in reward, motivation and movement, and is also a target of some antidepressants. Levels of dopamine may also change with the seasons.
But the neuroscience of seasonality is a developing area and more research is needed to know what’s going on in the brain.
How about bright light at night?
We know exposure to bright light at night (for instance, if someone is up all night) can disturb someone’s circadian rhythms.
This type of circadian rhythm disturbance is associated with higher rates of symptoms including self-harm, depressive and anxiety symptoms, and lower wellbeing. It is also associated with higher rates of mental disorders, such as major depression, bipolar disorder, psychotic disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (or PTSD).
Why is this? Bright light at night confuses and destabilises the body clock. It disrupts the rhythmic regulation of mood, cognition, appetite, metabolism and many other mental processes.
But people differ hugely in their sensitivity to light. While still a hypothesis, people who are most sensitive to light may be the most vulnerable to body clock disturbances caused by bright light at night, which then leads to a higher risk of mental health problems.
Bright light at night disrupts your body clock, putting you at greater risk of mental health issues. Ollyy/Shutterstock Where to from here?
Learning about light will help people better manage their mental health conditions.
By encouraging people to better align their lives to the light-dark cycle (to stabilise their body clock) we may also help prevent conditions such as depression and bipolar disorder emerging in the first place.
Healthy light behaviours – avoiding light at night and seeking light during the day – are good for everyone. But they might be especially helpful for people at risk of mental health problems. These include people with a family history of mental health problems or people who are night owls (late sleepers and late risers), who are more at risk of body clock disturbances.
Alexis Hutcheon has lived experience of a mental health condition and helped write this article.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Jacob Crouse, Research Fellow in Youth Mental Health, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney; Emiliana Tonini, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney, and Ian Hickie, Co-Director, Health and Policy, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: