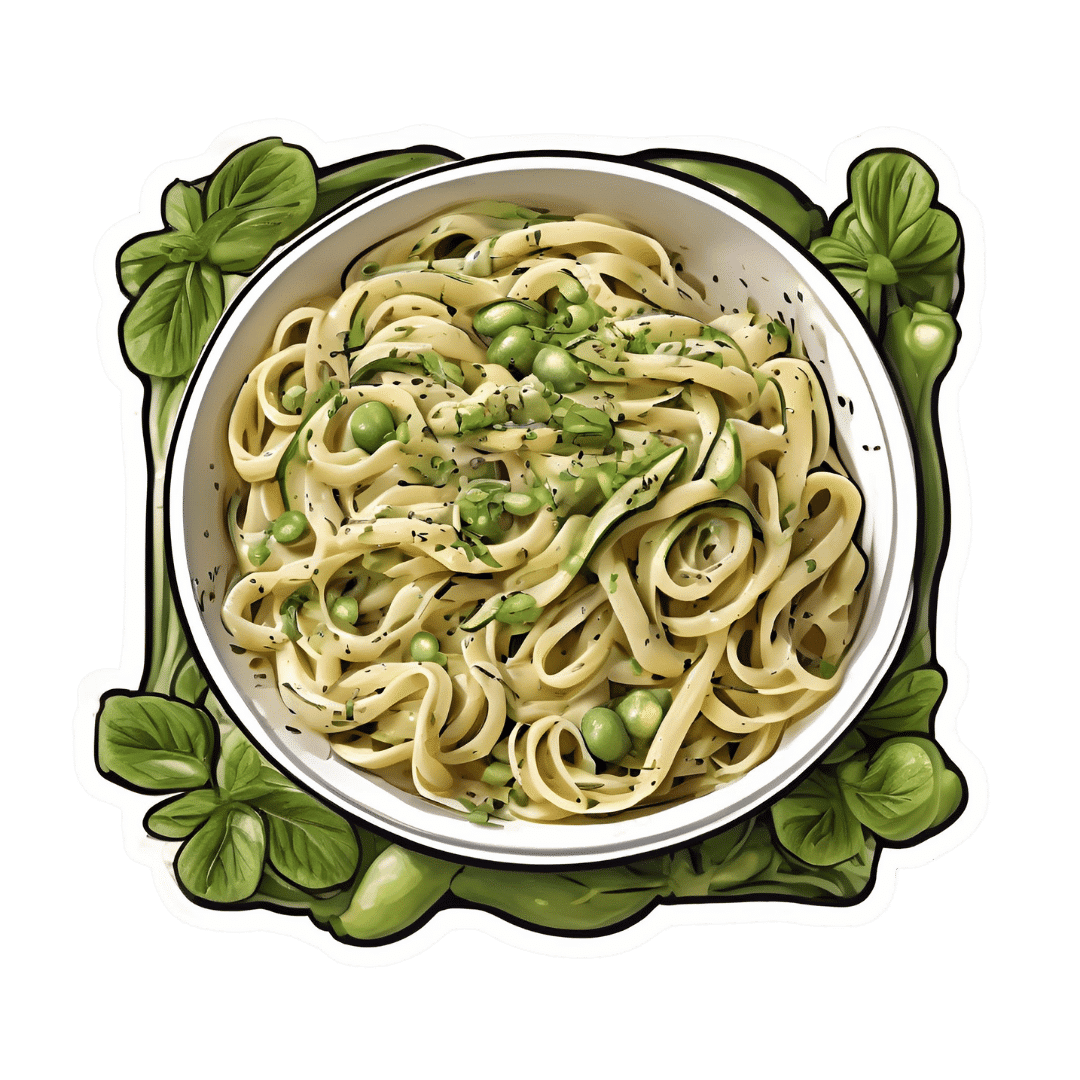
Creamy Zucchini, Edamame, & Asparagus Linguine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein, fiber, and polyphenols are the dish of the day here:
You will need
- 1½ cups milk (your choice what kind; we recommend soy for its neutral taste, though hazelnut’s nutty flavor would also work in this recipe)
- 6 oz wholegrain linguine (or your pasta of choice)
- 2 zucchini, thinly sliced
- 5 oz edamame beans (frozen is fine)
- 5 oz asparagus tips, cut into 2″ lengths
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 small handful arugula
- 1 small handful parsley, chopped
- A few mint leaves, chopped
- Juice of ½ lemon
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a sauté pan or similar, over a low to medium heat. Add the zucchini and cook for 5 minutes until they start to soften.
2) Add the garlic and continue cooking for 1 minute, stirring gently.
3) Add the milk, bring to the boil, and add the past, chia seeds (the resistant starch from the pasta will help thicken the sauce, as will the chia seeds), and MSG or salt.
4) Reduce the heat, cover, and simmer for 8 minutes.
5) Add the edamame beans and asparagus, and cook for a further 2 minutes, or until the pasta is cooked but still firm to the bite. The sauce should be quite thick now.
6) Stir in the remaining ingredients and serve, adding a garnish if you wish.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Daily, Weekly, Monthly: Habits Against Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Anil Rajani has advice on restoring/retaining youthfulness. Two out of three of the sections are on skincare specifically, which may seem a vanity, but it’s also worth remembering that our skin is a very large and significant organ, and makes a big difference for the rest of our physical health, as well as our mental health. So, it’s worthwhile to look after it:
The recommendations
Daily: meditation practice
Meditation reduces stress, which reduction in turn protects telomere length, slowing the overall aging process in every living cell of the body.
Weekly: skincare basics
Dr. Rajani recommends a combination of retinol and glycolic acid. The former to accelerate cell turnover, stimulate collagen production, and reduce wrinkles; the latter, to exfoliate dead cells, allowing the retinol to do its job more effectively.
We at 10almonds would like to add: wearing sunscreen with SPF50 is a very good thing to do on any day that your phone’s weather app says the UV index is “moderate” or higher.
Monthly: skincare extras
Here are the real luxuries; spa visits, microneedling (stimulates collagen production), and non-ablative laser therapy. He recommends creating a home spa if possible for monthly skincare treatments, investing in high-quality devices for long-term benefits.
For more on all of these things, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
- No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
- The Evidence-Based Skincare That Beats Product-Specific Hype
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Is More Likely Than You Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): More Likely Than You Think
COPD is not so much one disease, as rather a collection of similar (and often overlapping) diseases. The main defining characteristic is that they are progressive lung diseases. Historically the most common have been chronic bronchitis and emphysema, though Long COVID and related Post-COVID conditions appear to have been making inroads.
Lung cancer is generally considered separately, despite being a progressive lung disease, but there is crossover too:
COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history
COPD can be quite serious:
“But I don’t smoke”
Great! In fact we imagine our readership probably has disproportionately few smokers compared to the general population, being as we all are interested in our health.
But, it’s estimated that 30,000,000 Americans have COPD, and approximately half don’t know it. Bear in mind, the population of the US is a little over 340,000,000, so that’s a little under 9% of the population.
Click here to see a state-by-state breakdown (how does your state measure up?)
How would I know if I have it?
It typically starts like any mild respiratory illness. Likely shortness of breath, especially after exercise, a mild cough, and a frequent need to clear your throat.
Then it will get worse, as the lungs become more damaged; each of those symptoms might become stronger, as well as chest tightness and a general lack of energy.
Later stages, you guessed it, the same but worse, and—tellingly—weight loss.
The reason for the weight loss is because you are getting less oxygen per breath, making carrying your body around harder work, meaning you burn more calories.
What causes it?
Lots of things, with smoking being up at the top, or being exposed to a lot of second-hand smoke. Working in an environment with a lot of air pollution (for example, working around chemical fumes) can cause it, as can inhaling dust. New Yorkers: yes, that dust too. It can also develop from other respiratory illnesses, and some people even have a genetic predisposition to it:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: a commonly overlooked cause of lung disease
Is it treatable?
Treatment varies depending on what form of it you have, and most of the medical interventions are beyond the scope of this article. Suffice it to say, there are medications that can be taken (including bronchodilators taken via an inhaler device), corticosteroids, antibiotics and antivirals of various kinds if appropriate. This is definitely a “see your doctor” item though, because there are is far too much individual variation for us to usefully advise here.
However!
There are habits we can do to a) make COPD less likely and b) make COPD at least a little less bad if we get it.
Avoiding COPD:
- Don’t smoke. Just don’t.
- Avoid second-hand smoke if you can
- Avoid inhaling other chemicals/dust that may be harmful
- Breathe through your nose, not your mouth; it filters the air in a whole bunch of ways
- Seriously, we know it seems like nostril hairs surely can’t do much against tiny particles, but tiny particles are attracted to them and get stuck in mucous and dealt with by our immune system, so it really does make a big difference
Managing COPD:
- Continue the above things, of course
- Exercise regularly, even just light walking helps; we realize it will be difficult
- Maintain a healthy weight if you can
- This means both ways; COPD causes weight loss and that needs to be held in check. But similarly, you don’t want to be carrying excessive weight either; that will tire you even more.
- Look after the rest of your health; everything else will now hit you harder, so even small things need to be taken seriously
- If you can, get someone to help / do your household cleaning for you, ideally while you are not in the room.
Where can I get more help/advice?
As ever, speak to your doctor if you are concerned this may be affecting you. You can also find a lot of resources via the COPD Foundation’s website.
Take care of yourself!
Share This Post
- Don’t smoke. Just don’t.
-
How To Get More Nutrition From The Same Food
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Get More Out Of What’s On Your Plate
Where does digestion begin? It’s not the stomach. It’s not even the mouth.
It’s when we see and smell our food; maybe even hear it! “Sell the sizzle, not the steak” has a biological underpinning.
At that point, when we begin to salivate, that’s just one of many ways that our body is preparing itself for what we’re about to receive.
When we grab some ready-meal and wolf it down, we undercut that process. In the case of ready-meals, they often didn’t have much nutritional value, but even the most nutritious food isn’t going to do us nearly as much good if it barely touches the sides on the way down.
We’re not kidding about the importance of that initial stage of our external senses, by the way:
- Food perception primes hepatic endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis via melanocortin-dependent control of mTOR activation
- Olfaction regulates organismal proteostasis and longevity via microRNA-dependent signalling
So, mindful eating is not just something for Instagrammable “what I eat in a day” aesthetic photos, nor is just for monks atop cold mountains. There is actual science here, and a lot of it.
It starts with ingredients
“Eating the rainbow” (no, Skittles do not count) is great health advice for getting a wide variety of micronutrients, but it’s also simply beneficial for our senses, too. Which, as above-linked, makes a difference to digestion and nutrient absorption.
Enough is enough
That phrase always sounds like an expression of frustration, “Enough is enough!”. But, really:
Don’t overcomplicate your cooking, especially if you’re new to this approach. You can add in more complexities later, but for now, figure out what will be “enough”, and let it be enough.
The kitchen flow
Here we’re talking about flow in the Csikszentmihalyi sense of the word. Get “into the swing of things” and enjoy your time in the kitchen. Schedule more time than you need, and take it casually. Listen to your favourite music. Dance while you cook. Taste things as you go.
There are benefits, by the way, not just to our digestion (in being thusly primed and prepared for eating), but also to our cognition:
In The Zone: Flow State and Cognition in Older Adults
Serve
No, not just “put the food on the table”, but serve.
Have a pleasant environment; with sensory pleasures but without too many sensory distractions. Think less “the news on in the background” and more smooth jazz or Mozart or whatever works for you. Use your favourite (small!) plates/bowls, silverware, glasses. Have a candle if you like (unscented!).
Pay attention to presentation on the plate / in the bowl / in any “serve yourself” serving-things. Use a garnish (parsley is great if you want to add a touch of greenery without changing the flavor much). Crack that black pepper at the table. Make any condiments count (less “ketchup bottle” and more “elegant dip”).
Take your time
Say grace if that fits with your religious traditions, and/or take a moment to reflect on gratitude.
In many languages there’s a pre-dinner blessing that most often translates to “good appetite”. This writer is fond of the Norwegian “Velbekommen”, and it means more like “May good come of it for you”, or “May it do you good”.
Then, enjoy the food.
For the most even of blood sugar levels, consider eating fiber, protein/fat, carbs, in that order.
Why? See: 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Chew adequately and mindfully. Put your fork (or spoon, or chopsticks, or whatever) down between bites. Drink water alongside your meal.
Try to take at least 20 minutes to enjoy your meal, and/but any time you go to reach for another helping, take a moment to check in with yourself with regard to whether you are actually still hungry. If you’re not, and are just eating for pleasure, consider deferring that pleasure by saving the food for later.
At this point, people with partners/family may be thinking “But it won’t be there later! Someone else will eat it!”, and… That’s fine! Be happy for them. You can cook again tomorrow. You prepared delicious wholesome food that your partner/family enjoyed, and that’s always a good thing.
Want to know more about the science of mindful eating?
Check out Harvard’s Dr. Lilian Cheung on Mindful Eating here!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Whole-Body Approach to Osteoporosis – by Keith McCormick
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably already know to get enough calcium and vitamin D, and do some resistance training. What does this book offer beyond that advice?
It’s pretty comprehensive, as it turns out. It covers the above, plus the wide range of medications available, what supplements help or harm or just don’t have enough evidence either way yet, things like that.
Amongst the most important offerings are the signs and symptoms that can help monitor your bone health (things you can do at home! Like examinations of your fingernails, hair, skin, tongue, and so forth, that will reveal information about your internal biochemical make-up), as well as what lab tests to ask for. Which is important, as osteoporosis is one of those things whereby we often don’t learn something is wrong until it’s too late.
The author is a chiropractor, which doesn’t always have a reputation as the most robustly science-based of physical therapy options, but he…
- doesn’t talk about chiropractic
- did confer with a flock of experts (osteopaths, nutritionists, etc) to inform/check his work
- does refer consistently to good science, and explains it well
- includes 16 pages of academic references, and yes, they are very reputable publications
Bottom line: this one really does give what the subtitle promises: a whole body approach to avoiding (or reversing) osteoporosis.
Click here to check out The Whole Body Approach To Osteoporosis; sooner is better than later!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How community health screenings get more people of color vaccinated
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
U.S. preventive health screening rates dropped drastically at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. They have yet to go back to pre-pandemic levels, especially for Black and Latine communities.
Screenings, or routine medical checkups, are important ways to avoid and treat disease. They’re key to finding problems early on and can even help save people’s lives.
Community health workers say screenings are also a key to getting more people vaccinated. Screening fairs provide health workers the chance to build rapport and trust with the communities they serve, while giving their clients the chance to ask questions and get personalized recommendations according to their age, gender, and family history.
But systemic barriers to health care can often keep people from marginalized communities from accessing recommended screenings, exacerbating racial health disparities.
Public Good News spoke with Dr. Marie-Jose Francois, president and chief executive officer, and April Johnson, outreach coordinator, at the Center for Multicultural Wellness and Prevention (CMWP), in Central Florida, to learn how they promote the benefits of screening and leverage screenings for vaccination outreach among their diverse communities.
Here’s what they said.
[Editor’s note: This content has been edited for clarity and length.]
PGN: What is CMWP’s mission? How does vaccine outreach fit into the work you do in the communities you serve?
Dr. Marie-Jose Francois: Since 1995, our mission has been to enhance the health, wellness, and quality of life for diverse populations in Central Florida. At the beginning, our main focus was education, wellness, and screening for HIV/AIDS, and we continue to do case management for HIV screening and testing.
When the issue of COVID-19 came into the picture, we included COVID-19 information and education and stressed the importance of screening and receiving vaccinations during all of our outreach activities.
We try to meet the community where they are. Because there is so much misconception—and taboo—in regard to immunization.
April Johnson: So our job is to disperse accurate information. And how we do that is we go into rural communities. We build partnerships with local apartment complexes, hair salons, nail salons, laundromats, and provide a little community engagement, where people just hang out in different areas.
We build gatekeepers in those communities because you first have to get in there. You have to know that they trust you. Being in this field for about 30 years, I’ve [learned that] flexibility is key. Because sometimes you can’t get them from 9 to 5, or [from] Monday through Friday. So, you have to be very flexible in doing the outreach portion in order to get what you need.
I’ve built collaborations with senior citizen centers, community centers, schools, clinics, churches in Orlando and [in] different areas in Orange, Osceola, Seminole, and Lake counties. And we also partner with other community-based organizations to try to make it like a one-stop shop. So, partnership is a big thing.
PGN: How do you promote the importance of preventive screenings in the communities you serve?
M.F.: We try to make them view their health in a more comprehensive way, for them to understand the importance of screening. [That] self care is key, and for them to not be afraid.
We empower them to know what to ask when they go to the doctor. We ask them, ‘Do you know your status? Do you know your numbers?’
For example, if you go to the doctor, do you know your blood pressure? If you’re diabetic? Do you know your hemoglobin (A1C)? Do you know your cholesterol levels?
And now, [we also ask them]: ‘Have you received your flu shot for the year? Have you received all of your vaccine doses for COVID-19?’ We are even adding the mpox vaccine now, based on risk factors.
[We recommend they] ask their provider. For women, [we ask], ‘When do you need to have your mammogram?’ For the men, ‘You need to ask about your PSA and also about when and when to have your colonoscopy based on your age.’
We also try to explain to the community that the more they know their family history, the more they can engage in their own health. Because sometimes you have mom and dad who have a history of cancer. They have a history of diabetes or blood pressure—and they don’t talk to their children. So, we try to [recommend they] talk to their children. Your own family needs to know what’s going on so they can be proactive in their screenings.
PGN: What strategies or methods have you found most effective in getting people screened?
M.F.: Not everybody wants to be screened, not everybody wants to receive vaccines.
But with patience, just give them the facts. It goes right back to education, people have to be assured.
When you talk to them about COVID, or even HIV, you may hear them say, ‘Oh, I don’t see myself at risk for HIV.’ But we have to repeat to them that the more they get screened to make sure they’re OK, the better it is for them. ‘The more you use condoms, [the] safer it is for you.’
In Haitian culture, they listen to the radio. So we use the radio as a tool to educate and deliver information [to] get vaccinated, wash your hands. ‘If you’re coughing, cover your mouth. If you have a fever, wear your masks. Call your doctor.’
In our target population, we have people who have chronic conditions. We have people with HIV. So, we have to motivate them to receive the flu vaccine, to receive the COVID vaccine, to receive that RSV [vaccine], or to get the mpox vaccine. We have people with diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, depressed immune systems. We have people with lupus, we have people with sickle cell disease.
So, this is a way to [ensure that] whomever you’re talking to one-on-one understands the value of being safe.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why is pain so exhausting?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One of the most common feelings associated with persisting pain is fatigue and this fatigue can become overwhelming. People with chronic pain can report being drained of energy and motivation to engage with others or the world around them.
In fact, a study from the United Kingdom on people with long-term health conditions found pain and fatigue are the two biggest barriers to an active and meaningful life.
But why is long-term pain so exhausting? One clue is the nature of pain and its powerful effect on our thoughts and behaviours.
simona pilolla 2/Shutterstock Short-term pain can protect you
Modern ways of thinking about pain emphasise its protective effect – the way it grabs your attention and compels you to change your behaviour to keep a body part safe.
Try this. Slowly pinch your skin. As you increase the pressure, you’ll notice the feeling changes until, at some point, it becomes painful. It is the pain that stops you squeezing harder, right? In this way, pain protects us.
When we are injured, tissue damage or inflammation makes our pain system become more sensitive. This pain stops us from mechanically loading the damaged tissue while it heals. For instance, the pain of a broken leg or a cut under our foot means we avoid walking on it.
The concept that “pain protects us and promotes healing” is one of the most important things people who were in chronic pain tell us they learned that helped them recover.
But long-term pain can overprotect you
In the short term, pain does a terrific job of protecting us and the longer our pain system is active, the more protective it becomes.
But persistent pain can overprotect us and prevent recovery. People in pain have called this “pain system hypersensitivity”. Think of this as your pain system being on red alert. And this is where exhaustion comes in.
When pain becomes a daily experience, triggered or amplified by a widening range of activities, contexts and cues, it becomes a constant drain on one’s resources. Going about life with pain requires substantial and constant effort, and this makes us fatigued.
About 80% of us are lucky enough to not know what it is like to have pain, day in day out, for months or years. But take a moment to imagine what it would be like.
Imagine having to concentrate hard, to muster energy and use distraction techniques, just to go about your everyday tasks, let alone to complete work, caring or other duties.
Whenever you are in pain, you are faced with a choice of whether, and how, to act on it. Constantly making this choice requires thought, effort and strategy.
Mentioning your pain, or explaining its impact on each moment, task or activity, is also tiring and difficult to get across when no-one else can see or feel your pain. For those who do listen, it can become tedious, draining or worrying.
Concentrating hard, mustering energy and using distraction techniques can make everyday life exhausting. PRPicturesProduction/Shutterstock No wonder pain is exhausting
In chronic pain, it’s not just the pain system on red alert. Increased inflammation throughout the body (the immune system on red alert), disrupted output of the hormone cortisol (the endocrine system on red alert), and stiff and guarded movements (the motor system on red alert) also go hand in hand with chronic pain.
Each of these adds to fatigue and exhaustion. So learning how to manage and resolve chronic pain often includes learning how to best manage the over-activation of these systems.
Loss of sleep is also a factor in both fatigue and pain. Pain causes disruptions to sleep, and loss of sleep contributes to pain.
In other words, chronic pain is seldom “just” pain. No wonder being in long-term pain can become all-consuming and exhausting.
What actually works?
People with chronic pain are stigmatised, dismissed and misunderstood, which can lead to them not getting the care they need. Ongoing pain may prevent people working, limit their socialising and impact their relationships. This can lead to a descending spiral of social, personal and economic disadvantage.
So we need better access to evidence-based care, with high-quality education for people with chronic pain.
There is good news here though. Modern care for chronic pain, which is grounded in first gaining a modern understanding of the underlying biology of chronic pain, helps.
The key seems to be recognising, and accepting, that a hypersensitive pain system is a key player in chronic pain. This makes a quick fix highly unlikely but a program of gradual change – perhaps over months or even years – promising.
Understanding how pain works, how persisting pain becomes overprotective, how our brains and bodies adapt to training, and then learning new skills and strategies to gradually retrain both brain and body, offers scientifically based hope; there’s strong supportive evidence from clinical trials.
Every bit of support helps
The best treatments we have for chronic pain take effort, patience, persistence, courage and often a good coach. All that is a pretty overwhelming proposition for someone already exhausted.
So, if you are in the 80% of the population without chronic pain, spare a thought for what’s required and support your colleague, friend, partner, child or parent as they take on the journey.
More information about chronic pain is available from Pain Revolution.
Michael Henry, Physiotherapist and PhD candidate, Body in Mind Research Group, University of South Australia and Lorimer Moseley, Professor of Clinical Neurosciences and Foundation Chair in Physiotherapy, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: