Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
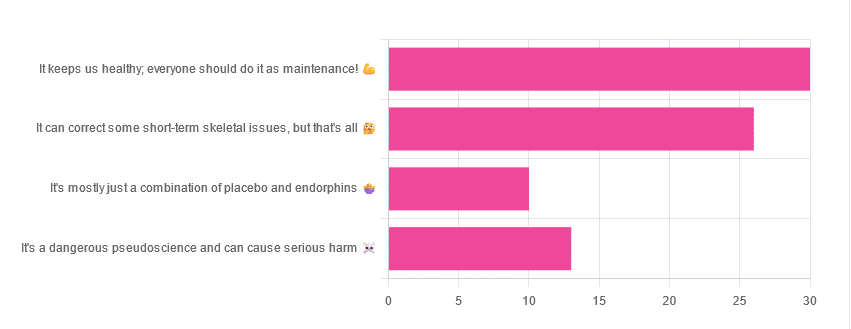
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on chiropractic medicine, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- 38% of respondents said it keeps us healthy, and everyone should do it as maintenance
- 33% of respondents said it can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all
- 16% of respondents said that it’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause serious harm
- 13% of respondents said that it’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins
Respondents also shared personal horror stories of harm done, personal success stories of things cured, and personal “it didn’t seem to do anything for me” stories.
What does the science say?
It’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause harm: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
That is to say, chiropractic in its simplest form that makes the fewest claims, is not a pseudoscience. If somebody physically moves your bones around, your bones will be physically moved. If your bones were indeed misaligned, and the chiropractor is knowledgeable and competent, this will be for the better.
However, like any form of medicine, it can also cause harm; in chiropractic’s case, because it more often than not involves manipulation of the spine, this can be very serious:
❝Twenty six fatalities were published in the medical literature and many more might have remained unpublished.
The reported pathology usually was a vascular accident involving the dissection of a vertebral artery.
Conclusion: Numerous deaths have occurred after chiropractic manipulations. The risks of this treatment by far outweigh its benefit.❞
Source: Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases
From this, we might note two things:
- The abstract doesn’t note the initial sample size; we would rather have seen this information expressed as a percentage. Unfortunately, the full paper is not accessible, and nor are many of the papers it cites.
- Having a vertebral artery fatally dissected is nevertheless not an inviting prospect, and is certainly a very reasonable cause for concern.
It’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins: True or False?
True or False, depending on what you went in for:
- If you went in for a regular maintenance clunk-and-click, then yes, you will get your clunk-and-click and feel better for it because you had a ritualized* experience and endorphins were released.
- If you went in for something that was actually wrong with your skeletal alignment, to get it corrected, and this correction was within your chiropractor’s competence, then yes, you will feel better because a genuine fault was corrected.
*this is not implying any mysticism, by the way. Rather it means simply that placebo effect is strongest when there is a ritual associated with it. In this case it means going to the place, sitting in a pleasant waiting room, being called in, removing your shoes and perhaps some other clothes, getting the full attention of a confident and assured person for a while, this sort of thing.
With regard to its use to combat specifically spinal pain (i.e., perhaps the most obvious thing to treat by chiropractic spinal manipulation), evidence is slightly in favor, but remains unclear:
❝Due to the low quality of evidence, the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulation compared with a placebo or no treatment remains uncertain. ❞
Source: Clinical Effectiveness and Efficacy of Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation for Spine Pain
It can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all: True or False?
Probably True.
Why “probably”? The effectiveness of chiropractic treatment for things other than short-term skeletal issues has barely been studied. From this, we may wish to keep an open mind, while also noting that it can hardly claim to be evidence-based—and it’s had hundreds of years to accumulate evidence. In all likelihood, publication bias has meant that studies that were conducted and found inconclusive or negative results were simply not published—but that’s just a hypothesis on our part.
In the case of using chiropractic to treat migraines, a very-related-but-not-skeletal issue, researchers found:
❝Pre-specified feasibility criteria were not met, but deficits were remediable. Preliminary data support a definitive trial of MCC+ for migraine.❞
Translating this: “it didn’t score as well as we hoped, but we can do better. We got some positive results, and would like to do another, bigger, better trial; please fund it”
Source: Multimodal chiropractic care for migraine: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Meanwhile, chiropractors’ claims for very unrelated things have been harshly criticized by the scientific community, for example:
Misinformation, chiropractic, and the COVID-19 pandemic
About that “short-term” aspect, one of our subscribers put it quite succinctly:
❝Often a skeletal correction is required for initial alignment but the surrounding fascia and muscles also need to be treated to mobilize the joint and release deep tissue damage surrounding the area. In combination with other therapies chiropractic support is beneficial.❞
This is, by the way, very consistent with what was said in the very clinically-dense book we reviewed yesterday, which has a chapter on the short-term benefits and limitations of chiropractic.
A truism that holds for many musculoskeletal healthcare matters, holds true here too:
❝In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win❞
In other words…
Chiropractic can definitely help put misaligned bones back where they should be. However, once they’re there, if the cause of their misalignment is not treated, they will just re-misalign themselves shortly after you walking out of your session.
This is great for chiropractors, if it keeps you coming back for endless appointments, but it does little for your body beyond give you a brief respite.
So, by all means go to a chiropractor if you feel so inclined (and you do not fear accidental arterial dissection etc), but please also consider going to a physiotherapist, and potentially other medical professions depending on what seems to be wrong, to see about addressing the underlying cause.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why We Get Sick – by Dr. Benjamin Bikman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a slightly buried lede here in that the title doesn’t offer this spoiler, but we will: the book is about insulin resistance.
However, unlike the books we’ve reviewed about blood sugar management, this time the focus is really and truly on insulin itself—and that makes some important differences:
Dr. Bikman makes the case that while indeed hyper- or hypoglycemia bring their problems, mostly these are symptoms rather than causes, and the real culprit is insulin resistance, and this is important for two main reasons:
- Insulin resistance occurs well before the other symptoms set in (which means: it is the thing that truly needs to be nipped in the bud; if your fasting blood sugars are rising, then you missed “nipping it in the bud” likely by a decade or more)
- Insulin resistance causes more problems than “mere” hyperglycemia (the most commonly-known result of insulin resistance) does, so again, it really needs to be considered separately from blood sugar management.
This latter, Dr. Bikman goes into in great detail, linking insulin resistance (even if blood sugar levels are normal) to all manner of diseases (hence the title).
You may be wondering: how can blood sugar levels be normal, if we have insulin resistance?
And the answer is that for as long as it is still able, your pancreas will just faithfully crank out more and more insulin to deal with the blood sugar levels that would otherwise be steadily rising. Since people measure blood sugar levels much more regularly than anyone checks for actual insulin levels, this means that one can be insulin resistant for years without knowing it, until finally the pancreas is no longer able to keep up with the demand—then that’s when people finally notice.
The book is divided into sections:
- The Problem: What Is Insulin Resistance
- The Cause: What Makes Us Insulin Resistant
- How We Can Fight Insulin Resistance
The first two parts are essential for the reader’s understanding, but the third part is the practical part, with appropriately practical advice on the most insulin-friendly ways to exercise, eat, fast, and more. He also talks drugs, and discusses the pros and cons of various interventions—but of course, far better is the lifestyle management of insulin.
The style is mostly very pop-science in overall presentation, and then occasionally gets very dense at times, but when that happens, he will then tend to follow it with an easier-to-understand explanation, to ensure that nothing remains opaque.
Bottom line: if you care about your metabolic health and don’t mind reading a book where you may have to read a paragraph or two twice sometimes, then this is a top-tier book on insulin resistance and how to prevent/reverse it.
Click here to check out Why We Get Sick, and stay well instead!
Share This Post
-
Cilantro vs Parsley – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cilantro to parsley, we picked the parsley.
Why?
Notwithstanding that some of our recipes include “cilantro, or if you have the this-tastes-like-soap gene, parsley”, that choice is more for the taste profile than the nutrition profile. Both are good, though, and it is quite close!
Like many herbs, they’re both full of vitamins and minerals and assorted phytochemicals.
In the category of vitamins, they’re both very good sources of vitamins A, C, and K, but parsley has more of each (and in vitamin K’s case, 4–5 times more). Parsley also has about twice as much folate. For the other vitamins, they’re mostly quite equal except that cilantro has more vitamin E.
When it comes to minerals, again they’re both good but again parsley is better on average, with several times more iron, and about twice as much calcium, zinc, and magnesium. Cilantro only wins noticeably for selenium.
Both have an array of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals, and each boasts antioxidants with anticancer potential.
Both have mood-improving qualities and have research for their anxiolytic and antidepressant effects—sufficient that these deserve their own main feature sometime.
For now though, we’ll say: healthwise, these two wonderful herbs are equal on most things, except that parsley has the better micronutrient profile.
Enjoy!
Further reading
You might also enjoy:
Herbs For (Evidence-Based) Health & Healing
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Figs vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing figs to passion fruit, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
Both are top-tier fruits! But the passion fruit is just that bit more passionate about delivering healthy nutrients:
In terms of macros, passion fruit has slightly more carbs, notably more protein, and a lot more fiber, giving it the win in this category.
In the category of vitamins, figs have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, C, and choline, making for a marginal win by the numbers for passion fruit here.
When it comes to minerals, figs have more calcium, manganese, and zinc, while passion fruit has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. A clearer win for passion fruit this time.
Adding up the sections makes for an easy overall win for passion fruit, but again, figs are really a top-tier fruit too; passion fruit just beats them! By all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← figs have antitumor effects specifically, while removing carcinogens too, and additionally sensitizing cancer cells to light therapy
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Who you are and where you live shouldn’t determine your ability to survive cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Canada, nearly everyone has a cancer story to share. It affects one in every two people, and despite improvements in cancer survivorship, one out of every four people affected by cancer still will die from it.
As a scientist dedicated to cancer care, I work directly with patients to reimagine a system that was never designed for them in the first place – a system in which your quality of care depends on social drivers like your appearance, your bank statements and your postal code.
We know that poverty, poor nutrition, housing instability and limited access to education and employment can contribute to both the development and progression of cancer. Quality nutrition and regular exercise reduce cancer risk but are contingent on affordable food options and the ability to stay active in safe, walkable neighbourhoods. Environmental hazards like air pollution and toxic waste elevate the risk of specific cancers, but are contingent on the built environment, laws safeguarding workers and the availability of affordable housing.
On a health-system level, we face implicit biases among care providers, a lack of health workforce competence in addressing the social determinants of health, and services that do not cater to the needs of marginalized individuals.
Indigenous peoples, racialized communities, those with low income and gender diverse individuals face the most discrimination in health care, resulting in inadequate experiences, missed diagnosis and avoidance of care. One patient living in subsidized housing told me, “You get treated like a piece of garbage – you come out and feel twice as bad.”
As Canadians, we benefit from a taxpayer funded health-care system that encompasses cancer care services. The average Canadian enjoys a life expectancy of more than 80 years and Canada boasts high cancer survival rates. While we have made incredible strides in cancer care, we must work together to ensure these benefits are equally shared amongst all people in Canada. We need to redesign systems of care so that they are:
- Anti-oppressive. We must begin by understanding and responding to historical and systemic racism that shapes cancer risk, access to care and quality of life for individuals facing marginalizing conditions. Without tackling the root causes, we will never be able to fully close the cancer care gap. This commitment involves undoing intergenerational trauma and harm through public policies that elevate the living and working conditions of all people.
- Patient-centric. We need to prioritize patient needs, preferences and values in all aspects of their health-care experience. This means tailoring treatments and services to individual patient needs. In policymaking, it involves creating policies that are informed by and responsive to the real-life experiences of patients. In research, it involves engaging patients in the research process and ensuring studies are relevant to and respectful of their unique perspectives and needs. This holistic approach ensures that patients’ perspectives are central to all aspects of health care.
- Socially just. We must strive for a society in which everyone has equal access to resources, opportunities and rights, and systemic inequalities and injustices are actively challenged and addressed. When redesigning the cancer care system, this involves proactive practices that create opportunities for all people, particularly those experiencing the most marginalization, to become involved in systemic health-care decision-making. A system that is responsive to the needs of the most marginalized will ultimately work better for all people.
Who you are, how you look, where you live and how much money you make should never be the difference between life and death. Let us commit to a future in which all people have the resources and support to prevent and treat cancer so that no one is left behind.
This article is republished from HealthyDebate under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can kimchi really help you lose weight? Hold your pickle. The evidence isn’t looking great
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fermented foods have become popular in recent years, partly due to their perceived health benefits.
For instance, there is some evidence eating or drinking fermented foods can improve blood glucose control in people with diabetes. They can lower blood lipid (fats) levels and blood pressure in people with diabetes or obesity. Fermented foods can also improve diarrhoea symptoms.
But can they help you lose weight, as a recent study suggests? Let’s look at the evidence.
Remind me, what are fermented foods?
Fermented foods are ones prepared when microbes (bacteria and/or yeast) ferment (or digest) food components to form new foods. Examples include yoghurt, cheese, kefir, kombucha, wine, beer, sauerkraut and kimchi.
As a result of fermentation, the food becomes acidic, extending its shelf life (food-spoilage microbes are less likely to grow under these conditions). This makes fermentation one of the earliest forms of food processing.
Fermentation also leads to new nutrients being made. Beneficial microbes (probiotics) digest nutrients and components in the food to produce new bioactive components (postbiotics). These postbiotics are thought to contribute to the health benefits of the fermented foods, alongside the health benefits of the bacteria themselves.
What does the evidence say?
A study published last week has provided some preliminary evidence eating kimchi – the popular Korean fermented food – is associated with a lower risk of obesity in some instances. But there were mixed results.
The South Korean study involved 115,726 men and women aged 40-69 who reported how much kimchi they’d eaten over the previous year. The study was funded by the World Institute of Kimchi, which specialises in researching the country’s national dish.
Eating one to three servings of any type of kimchi a day was associated with a lower risk of obesity in men.
Men who ate more than three serves a day of cabbage kimchi (baechu) were less likely to have obesity and abdominal obesity (excess fat deposits around their middle). And women who ate two to three serves a day of baechu were less likely to have obesity and abdominal obesity.
Eating more radish kimchi (kkakdugi) was associated with less abdominal obesity in both men and women.
However, people who ate five or more serves of any type of kimchi weighed more, had a larger waist sizes and were more likely to be obese.
The study had limitations. The authors acknowledged the questionnaire they used may make it difficult to say exactly how much kimchi people actually ate.
The study also relied on people to report past eating habits. This may make it hard for them to accurately recall what they ate.
This study design can also only tell us if something is linked (kimchi and obesity), not if one thing causes another (if kimchi causes weight loss). So it is important to look at experimental studies where researchers make changes to people’s diets then look at the results.
How about evidence from experimental trials?
There have been several experimental studies looking at how much weight people lose after eating various types of fermented foods. Other studies looked at markers or measures of appetite, but not weight loss.
One study showed the stomach of men who drank 1.4 litres of fermented milk during a meal took longer to empty (compared to those who drank the same quantity of whole milk). This is related to feeling fuller for longer, potentially having less appetite for more food.
Another study showed drinking 200 millilitres of kefir (a small glass) reduced participants’ appetite after the meal, but only when the meal contained quickly-digested foods likely to make blood glucose levels rise rapidly. This study did not measure changes in weight.
Kefir, a fermented milk drink, reduced people’s appetite.
Ildi Papp/ShutterstockAnother study looked at Indonesian young women with obesity. Eating tempeh (a fermented soybean product) led to changes in an appetite hormone. But this did not impact their appetite or whether they felt full. Weight was not measured in this study.
A study in South Korea asked people to eat about 70g a day of chungkookjang (fermented soybean). There were improvements in some measures of obesity, including percentage body fat, lean body mass, waist-to-hip ratio and waist circumference in women. However there were no changes in weight for men or women.
A systematic review of all studies that looked at the impact of fermented foods on satiety (feeling full) showed no effect.
What should I do?
The evidence so far is very weak to support or recommend fermented foods for weight loss. These experimental studies have been short in length, and many did not report weight changes.
To date, most of the studies have used different fermented foods, so it is difficult to generalise across them all.
Nevertheless, fermented foods are still useful as part of a healthy, varied and balanced diet, particularly if you enjoy them. They are rich in healthy bacteria, and nutrients.
Are there downsides?
Some fermented foods, such as kimchi and sauerkraut, have added salt. The latest kimchi study said the average amount of kimchi South Koreans eat provides about 490mg of salt a day. For an Australian, this would represent about 50% of the suggested dietary target for optimal health.
Eating too much salt increases your risk of high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
CBD Oil
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Q&A with the 10almonds Team
Q: Very interested in this article on CBD oil in the states. hope you do another one in the future with more studies done on people and more information on what’s new as far as CBD oil goes
A: We’re glad you enjoyed it! We’ll be sure to revisit CBD in the future—partly because it was a very popular article, and partly because, as noted, there is a lot going on there, research-wise!
And yes, we prefer human studies rather than mouse/rat studies where possible, too, and try to include those where we find them. In some cases, non-human animal studies allow us to know things that we can’t know from human studies… because a research institution’s ethics board will greenlight things for mice that it’d never* greenlight for humans.
Especially: things that for non-human animals are considered “introduction of external stressors” while the same things done to humans would be unequivocally called “torture”.
Animal testing in general is of course a moral quagmire, precisely because of the suffering it causes for animals, while the research results (hopefully) can be brought to bear to reduce to suffering of humans. We’re a health and productivity newsletter, not a philosophical publication, but all this to say: we’re mindful of such too.
And yes, we agree, when studies are available on humans, they’re always going to be better than the same study done on mice and rats.
As a topical aside, did you know there’s a monument to laboratory mice and all they’ve (however unintentionally) done for us?
❝The quirky statue depicts an anthropomorphic mouse as an elderly woman, complete with glasses balanced atop its nose. Emerging from two knitting needles in its hands is the recognizable double-helix of a strand of DNA.❞
~ Smithsonian Magazine
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: