Everything you need to know about cervical cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Every year, around 11,500 new cases of cervical cancer are diagnosed in the U.S. While cervical cancer used to be one of the most common causes of cancer death for U.S. women, the vaccine against the human papillomavirus (HPV), and increased early screening and detection have resulted in a decrease in rates.
“Cervical cancer is almost always preventable and typically diagnosed in patients who have either never had a screening test or have gone many years without one,” says Fred Wyand, director of communications at the American Sexual Health Association, which includes the National Cervical Cancer Coalition.
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, so we spoke to experts to learn more about what it is, its symptoms, and what you can do to prevent it.
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the cervix—the lower part of the uterus that connects the vagina to the uterus. Cervical cancer can affect anyone with a cervix but is most frequently diagnosed in women ages 35 to 44, according to the American Cancer Society.
There are two types:
- Squamous cell carcinoma: Cervical cancer that starts in the thin squamous cells on the outside of the cervix. This is the most common type of cervical cancer.
- Adenocarcinoma: Cervical cancer that starts in glandular cells that line the inside of the cervix. This type of cervical cancer is less common.
In some cases, cervical cancer has features of both types.
What causes cervical cancer?
Almost all cases of cervical cancer are caused by high-risk cases of HPV, a virus that is spread through sexual activity or other close skin-to-skin contact. But don’t panic: HPV is very common, and getting HPV doesn’t always mean you’ll get cervical cancer. Around 85 percent of people in the U.S. will get an HPV infection in their lifetime, but for most people, the virus clears on its own.
However, there are many strains of HPV, and some are linked to cervical cancer. In those cases, when the virus does not clear on its own and the HPV infection persists, it can cause a range of cancers in both men and women, including cancers of the cervix, anus, penis, throat, and vagina.
That’s why HPV vaccination is so important for all people: It can help prevent many types of cancer, including cervical cancer caused by those high-risk HPV infections.
What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer doesn’t usually have symptoms in its early stages, but once cancer begins to spread, the symptoms can include:
- Vaginal bleeding between periods, after sexual intercourse, or after menopause.
- Heavier and longer menstrual periods than usual.
- Vaginal discharge that has a strong odor and is watery.
- Pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse.
In more advanced stages, symptoms of cervical cancer can include:
- Leg swelling.
- Difficult or painful bowel movements or bleeding during a bowel movement.
- Blood in urine or difficulty urinating.
- Back pain.
“Most women present with no symptoms,” Dr. Kristina A. Butler, gynecologic oncologist at Mayo Clinic, tells PGN. “Therefore, the checkups with visualization of the cervix, speaking with your provider, and having a Pap smear are so important.”
How can you help prevent or reduce your risk for cervical cancer?
Vaccination: Cervical cancer is highly preventable. The most effective way to help protect yourself from it is by getting the HPV vaccine. The HPV vaccine is most effective before a person is first exposed to HPV, typically before becoming sexually active.
“If we are able to vaccinate children before they become adults [and] are subsequently exposed, those individuals are maximally protected against the [worst effects] of the virus, which could ultimately be cancer,” Butler adds.
You’re eligible to get the vaccine if you’re between 9 and 45 years old, but there are specific guidelines for each age group. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends HPV vaccination for children ages 11 or 12 (though it can start at 9 years).
The CDC says that you can get catch-up doses until you’re 26 if you didn’t get vaccinated earlier, but if you’re between 26 and 45 years old, you should talk to your health care provider about your individual risk for HPV and to see if you should get the vaccine.
Screenings: This is another effective way to prevent cervical cancer.
Dr. Deanna Gerber, a gynecologic oncologist at NYU Langone’s Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center, tells PGN that regular screenings can catch HPV before it has a chance to become cancer.
“Now that we’re encouraging people to see their gynecologist and get screening more regularly, we’re catching cancer at earlier stages,” she says.
Screenings for cervical cancer include:
- Pap smear: During a Pap smear, also known as a Pap test, cells are collected from your cervix to find precancerous or cervical cancer cells. Pap smears should start at 21 years old, regardless of when you start having sex.
If you’re between 21 and 29, you should get a Pap smear every three years. If you’re 30 to 65 years old, it’s recommended you get one every three years, a Pap and HPV test together every five years, or an HPV test alone every five years.
- HPV test: During an HPV test, cells are collected from your cervix to look for infection with high-risk HPV strains that can cause cervical cancer. If you’re between 21 and 30 years old, it’s only recommended that you get an HPV test if you had an abnormal Pap smear result. After 30, an HPV test is recommended with a Pap smear every five years, as long as other results were normal.
(People over 65 years old should talk to their health care provider about whether they need screening.)
Not smoking: Avoiding smoking can reduce your risk of developing cervical cancer because “HPV and smoking tobacco work together to accelerate the negative effects of HPV,” says Gerber.
Wearing condoms: Although condoms don’t completely prevent HPV infection, they provide some protection. And according to the CDC, the use of condoms has been associated with a lower rate of cervical cancer.
There is hope with early detection
There is hope for people diagnosed with cervical cancer. “Compared to the survival [rates] 10 years ago, women survive much longer now with the great treatments we have,” adds Butler.
Some of those treatments and advances include radiation, chemotherapy, and surgical therapy.
And while there may be some stigma surrounding sexual health, it’s important to advocate for yourself, says Gerber.
“Being comfortable and bold talking to your doctor about your health or any concerns that you have, feeling comfortable with your provider by asking all these questions is really the best thing you can do.”
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hospitals worldwide are short of saline. We can’t just switch to other IV fluids – here’s why
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Last week, the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration added intravenous (IV) fluids to the growing list of medicines in short supply. The shortage is due to higher-than-expected demand and manufacturing issues.
Two particular IV fluids are affected: saline and compound sodium lactate (also called Hartmann’s solution). Both fluids are made with salts.
There are IV fluids that use other components, such as sugar, rather than salt. But instead of switching patients to those fluids, the government has chosen to approve salt-based solutions by other overseas brands.
So why do IV fluids contain different chemicals? And why can’t they just be interchanged when one runs low?
Pavel Kosolapov/Shutterstock We can’t just inject water into a vein
Drugs are always injected into veins in a water-based solution. But we can’t do this with pure water, we need to add other chemicals. That’s because of a scientific principle called osmosis.
Osmosis occurs when water moves rapidly in and out of the cells in the blood stream, in response to changes to the concentration of chemicals dissolved in the blood plasma. Think salts, sugars, nutrients, drugs and proteins.
Too high a concentration of chemicals and protein in your blood stream leads it to being in a “hypertonic” state, which causes your blood cells to shrink. Not enough chemicals and proteins in your blood stream causes your blood cells to expand. Just the right amount is called “isotonic”.
Mixing the drug with the right amount of chemicals, via an injection or infusion, ensures the concentration inside the syringe or IV bag remains close to isotonic.
Australia is currently short on two salt-based IV fluids. sirnength88/Shutterstock What are the different types of IV fluids?
There are a range of IV fluids available to administer drugs. The two most popular are:
- 0.9% saline, which is an isotonic solution of table salt. This is one of the IV fluids in short supply
- a 5% solution of the sugar glucose/dextrose. This fluid is not in short supply.
There are also IV fluids that combine both saline and glucose, and IV fluids that have other salts:
- Ringer’s solution is an IV fluid which has sodium, potassium and calcium salts
- Plasma-Lyte has different sodium salts, as well as magnesium
- Hartmann’s solution (compound sodium lactate) contains a range of different salts. It is generally used to treat a condition called metabolic acidosis, where patients have increased acid in their blood stream. This is in short supply.
What if you use the wrong solution?
Some drugs are only stable in specific IV fluids, for instance, only in salt-based IV fluids or only in glucose.
Putting a drug into the wrong IV fluid can potentially cause the drug to “crash out” of the solution, meaning patients won’t get the full dose.
Or it could cause the drug to decompose: not only will it not work, but it could also cause serious side effects.
An example of where a drug can be transformed into something toxic is the cancer chemotherapy drug cisplatin. When administered in saline it is safe, but administration in pure glucose can cause life-threatening damage to a patients’ kidneys.
What can hospitals use instead?
The IV fluids in short supply are saline and Hartmann’s solution. They are provided by three approved Australian suppliers: Baxter Healthcare, B.Braun and Fresenius Kabi.
The government’s solution to this is to approve multiple overseas-registered alternative saline brands, which they are allowed to do under current legislation without it going through the normal Australian quality checks and approval process. They will have received approval in their country of manufacture.
The government is taking this approach because it may not be effective or safe to formulate medicines that are meant to be in saline into different IV fluids. And we don’t have sufficient capacity to manufacture saline IV fluids here in Australia.
The Australian Society of Hospital Pharmacists provides guidance to other health staff about what drugs have to go with which IV fluids in their Australian Injectable Drugs Handbook. If there is a shortage of saline or Hartmann’s solution, and shipments of other overseas brands have not arrived, this guidance can be used to select another appropriate IV fluid.
Why don’t we make it locally?
The current shortage of IV fluids is just another example of the problems Australia faces when it is almost completely reliant on its critical medicines from overseas manufacturers.
Fortunately, we have workarounds to address the current shortage. But Australia is likely to face ongoing shortages, not only for IV fluids but for any medicines that we rely on overseas manufacturers to produce. Shortages like this put Australian lives at risk.
In the past both myself, and others, have called for the federal government to develop or back the development of medicines manufacturing in Australia. This could involve manufacturing off-patent medicines with an emphasis on those medicines most used in Australia.
Not only would this create stable, high technology jobs in Australia, it would also contribute to our economy and make us less susceptible to future global drug supply problems.
Nial Wheate, Professor and Director Academic Excellence, Macquarie University and Shoohb Alassadi, Casual academic, pharmaceutical sciences, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Seed Saving Secrets – by Alice Mirren
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that home-grown is best, and yet many of us are not exactly farmers (this reviewer tries with mixed results—hardy crops survive; others, not so much). While it’s easy to blame the acidic soil, the harsh climate, or not having enough time and money (this reviewer blames all of the above), the fact remains that a skilled gardener can produce a good crop in any conditions.
That’s where this book helps; right from the beginning, from the seeds. Have you ever bought a pack of seeds, excitedly sown them, and then had a germination rate of zero or something close to that (this reviewer has)?
Alice Mirren takes us on a tour of how to save seeds from plants you know are regionally viable (not the product of some vast globalized industry that doesn’t know you live in an ancient bog with a cold south-east wind blowing in from Siberia), and then how to care for and curate them, how to store them for future years, how to keep a self-perpetuating seed bank.
She goes beyond that, though. Regular 10almonds readers might remember about the supercentenarian “Blue Zones”, and how big factors in healthy longevity include community and purpose; Mirren advocates for organizing community seed banks, which will also mean that everyone (including you) has access to much more diverse seeds, and when it comes to the perils of natural selection, diversity means survival. Otherwise, if you have just one seed type, a single blight can wipe out everything pretty much overnight.
Bottom line: if you grow your own food or would like to, this is a “bible of…” level book that you absolutely should have to hand.
Click here to check out Seed Saving Secrets, and see the results in your kitchen and on your plate!
Share This Post
-
Why do I poo in the morning? A gut expert explains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
No, you’re not imagining it. People really are more likely to poo in the morning, shortly after breakfast. Researchers have actually studied this.
But why mornings? What if you tend to poo later in the day? And is it worth training yourself to be a morning pooper?
To understand what makes us poo when we do, we need to consider a range of factors including our body clock, gut muscles and what we have for breakfast.
Here’s what the science says.
H_Ko/Shutterstock So morning poos are real?
In a UK study from the early 1990s, researchers asked nearly 2,000 men and women in Bristol about their bowel habits.
The most common time to poo was in the early morning. The peak time was 7-8am for men and about an hour later for women. The researchers speculated that the earlier time for men was because they woke up earlier for work.
About a decade later, a Chinese study found a similar pattern. Some 77% of the almost 2,500 participants said they did a poo in the morning.
But why the morning?
There are a few reasons. The first involves our circadian rhythm – our 24-hour internal clock that helps regulate bodily processes, such as digestion.
For healthy people, our internal clock means the muscular contractions in our colon follow a distinct rhythm.
There’s minimal activity in the night. The deeper and more restful our sleep, the fewer of these muscle contractions we have. It’s one reason why we don’t tend to poo in our sleep.
Your lower gut is a muscular tube that contracts more strongly at certain times of day. Vectomart/Shutterstock But there’s increasing activity during the day. Contractions in our colon are most active in the morning after waking up and after any meal.
One particular type of colon contraction partly controlled by our internal clock are known as “mass movements”. These are powerful contractions that push poo down to the rectum to prepare for the poo to be expelled from the body, but don’t always result in a bowel movement. In healthy people, these contractions occur a few times a day. They are more frequent in the morning than in the evening, and after meals.
Breakfast is also a trigger for us to poo. When we eat and drink our stomach stretches, which triggers the “gastrocolic reflex”. This reflex stimulates the colon to forcefully contract and can lead you to push existing poo in the colon out of the body. We know the gastrocolic reflex is strongest in the morning. So that explains why breakfast can be such a powerful trigger for a bowel motion.
Then there’s our morning coffee. This is a very powerful stimulant of contractions in the sigmoid colon (the last part of the colon before the rectum) and of the rectum itself. This leads to a bowel motion.
How important are morning poos?
Large international surveys show the vast majority of people will poo between three times a day and three times a week.
This still leaves a lot of people who don’t have regular bowel habits, are regular but poo at different frequencies, or who don’t always poo in the morning.
So if you’re healthy, it’s much more important that your bowel habits are comfortable and regular for you. Bowel motions do not have to occur once a day in the morning.
Morning poos are also not a good thing for everyone. Some people with irritable bowel syndrome feel the urgent need to poo in the morning – often several times after getting up, during and after breakfast. This can be quite distressing. It appears this early-morning rush to poo is due to overstimulation of colon contractions in the morning.
Can you train yourself to be regular?
Yes, for example, to help treat constipation using the gastrocolic reflex. Children and elderly people with constipation can use the toilet immediately after eating breakfast to relieve symptoms. And for adults with constipation, drinking coffee regularly can help stimulate the gut, particularly in the morning.
A disturbed circadian rhythm can also lead to irregular bowel motions and people more likely to poo in the evenings. So better sleep habits can not only help people get a better night’s sleep, it can help them get into a more regular bowel routine.
A regular morning coffee can help relieve constipation. Caterina Trimarchi/Shutterstock Regular physical activity and avoiding sitting down a lot are also important in stimulating bowel movements, particularly in people with constipation.
We know stress can contribute to irregular bowel habits. So minimising stress and focusing on relaxation can help bowel habits become more regular.
Fibre from fruits and vegetables also helps make bowel motions more regular.
Finally, ensuring adequate hydration helps minimise the chance of developing constipation, and helps make bowel motions more regular.
Monitoring your bowel habits
Most of us consider pooing in the morning to be regular. But there’s a wide variation in normal so don’t be concerned if your poos don’t follow this pattern. It’s more important your poos are comfortable and regular for you.
If there’s a major change in the regularity of your bowel habits that’s concerning you, see your GP. The reason might be as simple as a change in diet or starting a new medication.
But sometimes this can signify an important change in the health of your gut. So your GP may need to arrange further investigations, which could include blood tests or imaging.
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Hearing voices is common and can be distressing. Virtual reality might help us meet and ‘treat’ them
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever heard something that others cannot – such as your name being called? Hearing voices or other noises that aren’t there is very common. About 10% of people report experiencing auditory hallucinations at some point in their life.
The experience of hearing voices can be very different from person to person, and can change over time. They might be the voice of someone familiar or unknown. There might be many voices, or just one or two. They can be loud or quiet like a whisper.
For some people these experiences are positive. They might represent a spiritual or supernatural experience they welcome or a comforting presence. But for others these experiences are distressing. Voices can be intrusive, negative, critical or threatening. Difficult voices can make a person feel worried, frightened, embarrassed or frustrated. They can also make it hard to concentrate, be around other people and get in the way of day-to-day activities.
Although not everyone who hears voices has a mental health problem, these experiences are much more common in people who do. They have been considered a hallmark symptom of schizophrenia, which affects about 24 million people worldwide.
However, such experiences are also common in other mental health problems, particularly in mood- and trauma-related disorders (such as bipolar disorder or depression and post-traumatic stress disorder) where as many as half of people may experience them.
Rawpixel/Shutterstock Why do people hear voices?
It is unclear exactly why people hear voices but exposure to prolonged stress, trauma or depression can increase the chances.
Some research suggests people who hear voices might have brains that are “wired” differently, particularly between the hearing and speaking parts of the brain. This may mean parts of our inner speech can be experienced as external voices. So, having the thought “you are useless” when something goes wrong might be experienced as an external person speaking the words.
Other research suggests it may relate to how our brains use past experiences as a template to make sense of and make predictions about the world. Sometimes those templates can be so strong they lead to errors in how we experience what is going on around us, including hearing things our brain is “expecting” rather than what is really happening.
What is clear is that when people tell us they are hearing voices, they really are! Their brain perceives voice experiences as if someone were talking in the room. We could think of this “mistake” as working a bit like being susceptible to common optical tricks or visual illusions.
There may be differences in the brains of people who hear voices. Triff/Shutterstock Coping with hearing voices
When hearing voices is getting in the way of life, treatment guidelines recommend the use of medications. But roughly a third of people will experience ongoing distress. As such, treatment guidelines also recommend the use of psychological therapies such as cognitive behavioural therapy.
The next generation of psychological therapies are beginning to use digital technologies and virtual reality offers a promising new medium.
Avatar therapy allows a person to create a virtual representation of the voice or voices, which looks and sounds like what they are experiencing. This can help people regain power in the “relationship” as they interact with the voice character, supported by a therapist.
Jason’s experience
Aged 53, Jason (not his real name) had struggled with persistent voices since his early 20s. Antipsychotic medication had helped him to some extent over the years, but he was still living with distressing voices. Jason tried out avatar therapy as part of a research trial.
He was initially unable to stand up to the voices, but he slowly gained confidence and tested out different ways of responding to the avatar and voices with his therapist’s support.
Jason became more able to set boundaries, such as not listening to them for periods throughout the day. He also felt more able to challenge what they said and make his own choices.
Over a couple of months, Jason started to experience some breaks from the voices each day and his relationship with them started to change. They were no longer like bullies, but more like critical friends pointing out things he could consider or be aware of.
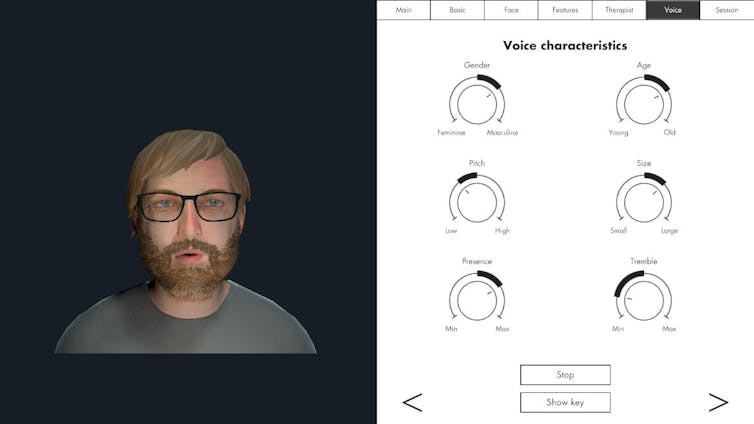
A screenshot from HekaVR, the software used in the Australian AMETHYST trial. HekaVR, CC BY-ND Gaining recognition
Following promising results overseas and its recommendation by the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, our team has begun adapting the therapy for an Australian context.
We are trialling delivering avatar therapy from our specialist voices clinic via telehealth. We are also testing whether avatar therapy is more effective than the current standard therapy for hearing voices, based on cognitive behavioural therapy.
As only a minority of people with psychosis receive specialist psychological therapy for hearing voices, we hope our trial will support scaling up these new treatments to be available more routinely across the country.
We would like to acknowledge the advice and input of Dr Nadine Keen (consultant clinical psychologist at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust, UK) on this article.
Leila Jameel, Trial Co-ordinator and Research Therapist, Swinburne University of Technology; Imogen Bell, Senior Research Fellow and Psychologist, The University of Melbourne; Neil Thomas, Professor of Clinical Psychology, Swinburne University of Technology, and Rachel Brand, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Psychology, University of the Sunshine Coast
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Prevent And Reverse Type 2 Diabetes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Turn back the clock on insulin resistance
This is Dr. Jason Fung. He’s a world-leading expert on intermittent fasting and low carbohydrate approaches to diet. He also co-founded the Intensive Dietary Management Program, later rebranded to the snappier title: The Fasting Method, a program to help people lose weight and reverse type 2 diabetes. Dr. Fung is certified with the Institute for Functional Medicine, for providing functional medicine certification along with educational programs directly accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME).
Why Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is a well-established, well-evidenced, healthful practice for most people. In the case of diabetes, it becomes complicated, because if one’s blood sugars are too low during a fasting period, it will need correcting, thus breaking the fast.
Note: this is about preventing and reversing type 2 diabetes. Type 1 is very different, and sadly cannot be prevented or reversed in this fashion.
However, these ideas may still be useful if you have T1D, as you have an even greater need to avoid developing insulin resistance; you obviously don’t want your exogenous insulin to stop working.
Nevertheless, please do confer with your endocrinologist before changing your dietary habits, as they will know your personal physiology and circumstances in ways that we (and Dr. Fung) don’t.
In the case of having type 2 diabetes, again, please still check with your doctor, but the stakes are a lot lower for you, and you will probably be able to fast without incident, depending on your diet itself (more on this later).
Intermittent Fasting can be extra helpful for the body in the case of type 2 diabetes, as it helps give the body a rest from high insulin levels, thus allowing the body to become gradually re-sensitised to insulin.
Why low carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates, especially sugars, especially fructose*, cause excess sugar to be quickly processed by the liver and stored there. When the body’s ability to store glycogen is exceeded, the liver stores energy as fat instead. The resultant fatty liver is a major contributor to insulin resistance, when the liver can’t keep up with the demand; the blood becomes spiked full of unprocessed sugars, and the pancreas must work overtime to produce more and more insulin to deal with that—until the body starts becoming desensitized to insulin. In other words, type 2 diabetes.
There are other factors that affect whether we get type 2 diabetes, for example a genetic predisposition. But, our carb intake is something we can control, so it’s something that Dr. Fung focuses on.
*A word on fructose: actual fruits are usually diabetes-neutral or a net positive due to their fiber and polyphenols.
Fructose as an added ingredient, however, not so much. That stuff zips straight into your veins with nothing to slow it down and nothing to mitigate it.
The advice from Dr. Fung is simple here: cut the carbs. If you are already diabetic and do this with no preparation, you will probably simply suffer hypoglycemia, so instead:
- Enjoy a fibrous starter (a salad, some fruit, or perhaps some nuts)
- Load up with protein first, during your main meal—this will start to trigger your feelings of satedness
- Eat carbs last (preferably whole, unprocessed carbohydrates), and stop eating when 80% full.
Adapting Intermittent Fasting to diabetes
Dr. Fung advocates for starting small, and gradually increasing your fasting period, until, ideally, fasting 16 hours per day. You probably won’t be able to do this immediately, and that’s fine.
You also probably won’t be able to do this, if you don’t also make the dietary adjustments that help to give your liver a break, and thus by knock-on-effect, give your pancreas a break too.
With the dietary adjustments too, however, your insulin production-and-response will start to return to its pre-diabetic state, and finally its healthy state, after which, it’s just a matter of maintenance.
Want to hear more from Dr. Fung?
You may enjoy his blog, and for those who like videos, here is his YouTube channel:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Stop Negative Thinking – by Daniel Paul
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Just think positive thoughts” is all well and good, but it doesn’t get much mileage in the real world, does it?
What Daniel Paul offers is a lot better than that. Taking a CBT approach, he recommends tips and tricks, gives explanations and exercises, and in short, puts tools in the reader’s toolbox.
But it doesn’t stop at just stopping negative thinking. Rather, it takes a holistic approach to also improve your general life…
- Bookending your day with a good start and finish
- Scheduling a time for any negative thinking that does need to occur (again with the useful realism!)
- Inviting the reader to take on small challenges, of the kind that’ll have knock-on effects that add and multiply and compound as we go
The format is very easy-reading, and we love that there are clear section headings and chapter summaries, too.
Bottom line: definitely a book with the potential to improve your life from day one, and that’ll keep you coming back to it as a cheatsheet and references source.
Get your copy of “How to Stop Negative Thinking” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: