Carrot vs Kale – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing carrot to kale, we picked the kale.
Why?
These are both known as carotene-containing heavyweights, but kale emerges victorious:
In terms of macros, carrot has more carbs while kale has more protein and fiber. An easy win there for kale.
When it comes to vitamins, both are great! But, carrots contain more of vitamins A, B5, and choline, whereas kale contains more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, and K. And while carrot’s strongest point is vitamin A, a cup of carrots contains around 10x the recommended daily dose of vitamin A, whereas a cup of kale contains “only” 6x the recommended daily dose of vitamin A. So, did we really need the extra in carrots? Probably not. In any case, kale already won on overall vitamin coverage, by a long way.
In the category of minerals, kale again sweeps. On the one hand, carrots contain more sodium. On the other hand, kale contains a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. Not a tricky choice!
But don’t be fooled: carrots really are a nutritional powerhouse and a great food. Kale is just better—nutritionally speaking, in any case. If you’re making a carrot cake, please don’t try substituting kale; it will not work 😉
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
You can’t reverse the ageing process but these 5 things can help you live longer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At this time of year many of us resolve to prioritise our health. So it is no surprise there’s a roaring trade of products purporting to guarantee you live longer, be healthier and look more youthful.
While an estimated 25% of longevity is determined by our genes, the rest is determined by what we do, day to day.
There are no quick fixes or short cuts to living longer and healthier lives, but the science is clear on the key principles. Here are five things you can do to extend your lifespan and improve your health.
1. Eat a predominantly plant-based diet
What you eat has a huge impact on your health. The evidence overwhelmingly shows eating a diet high in plant-based foods is associated with health and longevity.
If you eat more plant-based foods and less meat, processed foods, sugar and salt, you reduce your risk of a range of illnesses that shorten our lives, including heart disease and cancer.
Plant-based foods are rich in nutrients, phytochemicals, antioxidants and fibre. They’re also anti-inflammatory. All of this protects against damage to our cells as we age, which helps prevent disease.
No particular diet is right for everyone but one of the most studied and healthiest is the Mediterranean diet. It’s based on the eating patterns of people who live in countries around the Mediterranean Sea and emphases vegetables, fruits, wholegrains, legumes, nuts and seeds, fish and seafood, and olive oil.
2. Aim for a healthy weight
Another important way you can be healthier is to try and achieve a healthy weight, as obesity increases the risk of a number of health problems that shorten our lives.
Obesity puts strain on all of our body systems and has a whole myriad of physiological effects including causing inflammation and hormonal disturbances. These increase your chances of a number of diseases, including heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, diabetes and a number of cancers.
In addition to affecting us physically, obesity is also associated with poorer psychological health. It’s linked to depression, low self-esteem and stress.
One of the biggest challenges we face in the developed world is that we live in an environment that promotes obesity. The ubiquitous marketing and the easy availability of high-calorie foods our bodies are hard-wired to crave mean it’s easy to consume too many calories.
3. Exercise regularly
We all know that exercise is good for us – the most common resolution we make this time of year is to do more exercise and to get fitter. Regular exercise protects against chronic illness, lowers your stress and improves your mental health.
While one of the ways exercising helps you is by supporting you to control your weight and lowering your body fat levels, the effects are broader and include improving your glucose (blood sugar) use, lowering your blood pressure, reducing inflammation and improving blood flow and heart function.
While it’s easy to get caught up in all of the hype about different exercise strategies, the evidence suggests that any way you can include physical activity in your day has health benefits. You don’t have to run marathons or go to the gym for hours every day. Build movement into your day in any way that you can and do things that you enjoy.
4. Don’t smoke
If you want to be healthier and live longer then don’t smoke or vape.
Smoking cigarettes affects almost every organ in the body and is associated with both a shorter and lower quality of life. There is no safe level of smoking – every cigarette increases your chances of developing a range of cancers, heart disease and diabetes.
Even if you have been smoking for years, by giving up smoking at any age you can experience health benefits almost immediately, and you can reverse many of the harmful effects of smoking.
If you’re thinking of switching to vapes as a healthy long term option, think again. The long term health effects of vaping are not fully understood and they come with their own health risks.
5. Prioritise social connection
When we talk about living healthier and longer, we tend to focus on what we do to our physical bodies. But one of the most important discoveries over the past decade has been the recognition of the importance of spiritual and psychological health.
People who are lonely and socially isolated have a much higher risk of dying early and are more likely to suffer from heart disease, stroke, dementia as well as anxiety and depression.
Although we don’t fully understand the mechanisms, it’s likely due to both behavioural and biological factors. While people who are more socially connected are more likely to engage in healthy behaviours, there also seems to be a more direct physiological effect of loneliness on the body.
So if you want to be healthier and live longer, build and maintain your connections to others.
Hassan Vally, Associate Professor, Epidemiology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
What families should know about whooping cough
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Whooping cough is a bacterial respiratory illness that can cause long-term symptoms and even death.
- Two types of vaccines protect against it: The DTap vaccine is given to babies and children up to 6 years old, while the Tdap vaccine is given to children 7 years and older and adults.
- If you or your child has symptoms of whooping cough, isolate them from vulnerable family members and seek treatment early to reduce the risk of serious illness.
Whooping cough, also called pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that’s particularly dangerous for babies. Cases are now at least four times as high as they were at this time last year. Fortunately, vaccines are extremely effective at preventing the disease across age groups.
Read on to learn about the symptoms and risks of whooping cough, who should get vaccinated, and what to do when symptoms appear.What are the symptoms of whooping cough?
Early symptoms of whooping cough typically appear five to 10 days after exposure and may include a runny or stuffy nose, a low fever, and a mild cough. One to two weeks later, some people may experience extreme coughing fits that can cause shortness of breath, trouble sleeping, vomiting, fatigue, and rib fractures. These fits usually last one to six weeks, but they can last up to 10 weeks after infection.
About one in three babies under 1 year old who contract whooping cough require hospitalization, as they may experience life-threatening pauses in breathing (called apnea), pneumonia, and other complications. Children and adults who have asthma or are immunocompromised are also more likely to develop severe symptoms.
Which vaccines protect against whooping cough, and who is eligible?
Two types of vaccines protect against whooping cough: The DTap vaccine is given to babies and children up to 6 years old, while the Tdap vaccine is given to children 7 years and older and adults. Both vaccines protect against infections from diptheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that pregnant people receive a single dose of the Tdap vaccine between 27 and 36 weeks of pregnancy, as this lowers the risk of whooping cough in babies younger than 2 months old by 78 percent.
Multiple doses are required for the best protection. Learn more about DTaP and Tdap vaccine schedules from the CDC, and talk to your health care provider about how many doses you and your children need.
What should families do when whooping cough symptoms appear?
If you or your child has symptoms of whooping cough, isolate the infected person from vulnerable family members. It’s also important to seek treatment early to reduce the risk of serious illness. Health care providers typically prescribe antibiotics to those recovering at home.
Over-the-counter cough and cold medicine is not recommended for children under 4 years old. However, limiting smoke, dust, and chemical fumes at home and using a humidifier can reduce coughing. If you are caring for someone with whooping cough who exhibits pauses in breathing or develops gray or blue skin, call 911 immediately.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.Share This Post
-
Behind Book Recommendations
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: What’s the process behind the books you recommend? You seem to have a limitless stream of recommendations
We do our best!
The books we recommend are books that…
- are on Amazon—it makes things tidy, consistent, and accessible. And if you end up buying one of the books, we get a small affiliate commission*.
- we have read—we would say “obviously”, but you might be surprised how many people write about books without having read them.
- pertain in at least large part to health and/or productivity.
- are written by humans—bookish people (and especially Kindle Unlimited users) may have noticed lately that there are a lot of low quality AI-written books flooding the market, sometimes with paid 5-star reviews to bolster them. It’s frustrating, but we can tell the difference and screen those out.
- are of a certain level of quality. They don’t have to be “top 5 desert-island books”, because well, there’s one every day and the days keep coming. But they do have to genuinely deliver the value that we describe, and merit a sincere recommendation.
- are varied—we try to not give a run of “samey” books one after another. We will sometimes review a book that covers a topic another previously-reviewed book did, but it must have something about it that makes it different. It may be a different angle or a different writing style, but it needs something to set it apart.
*this is from Amazon and isn’t product-specific, so this is not affecting our choice of what books to review at all—just that they will be books that are available on Amazon.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Are You?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Answering The Most Difficult Question: How Are You?
Today’s feature is aimed at helping mainly two kinds of people:
- “I have so many emotions that I don’t always know what to do with them”
- “What is an emotion, really? I think I felt one some time ago”
So, if either those describe you and/or a loved one, read on…
Alexithymia
Alexi who? Alexithymia is an umbrella term for various kinds of problems with feeling emotions.
That could be “problems feeling emotions” as in “I am unable to feel emotions” or “problems feeling emotions” as in “feeling these emotions is a problem for me”.
It is most commonly used to refer to “having difficulty identifying and expressing emotions”.
There are a lot of very poor quality pop-science articles out there about it, but here’s a decent one with good examples and minimal sensationalist pathologization:
Alexithymia Might Be the Reason It’s Hard to Label Your Emotions
A somatic start
Because a good level of self-awareness is critical for healthy emotional regulation, let’s start there. We’ll write this in the first person, but you can use it to help a loved one too, just switching to second person:
Simplest level first:
Are my most basic needs met right now? Is this room a good temperature? Am I comfortable dressed the way I am? Am I in good physical health? Am I well-rested? Have I been fed and watered recently? Does my body feel clean? Have I taken any meds I should be taking?
Note: If the answer is “no”, then maybe there’s something you can do to fix that first. If the answer is “no” and also you can’t fix the thing for some reason, then that’s unfortunate, but just recognize it anyway for now. It doesn’t mean the thing in question is necessarily responsible for how you feel, but it’s good to check off this list as a matter of good practice.
Bonus question: it’s cliché, but if applicable… What time of the month is it? Because while hormonal mood swings won’t create moods out of nothing, they sure aren’t irrelevant either and should be listened to too.
Bodyscanning next
What do you feel in each part of your body? Are you clenching your jaw? Are your shoulders tense? Do you have a knot in your stomach? What are your hands doing? How’s your posture? What’s your breathing like? How about your heart? What are your eyes doing?
Your observations at this point should be neutral, by the way. Not “my posture is terrible”, but “my posture is stooped”, etc. Much like in mindfulness meditation, this is a time for observing, not for judging.
Narrowing it down
Now, like a good scientist, you have assembled data. But what does the data mean for your emotions? You may have to conduct some experiments to find out.
Thought experiments: what calls to you? What do you feel like doing? Do you feel like curling up in a ball? Breaking something? Taking a bath? Crying?
Maybe what calls to you, or what you feel like doing, isn’t something that’s possible for you to do. This is often the case with anxiety, for example, and perhaps also guilt. But whatever calls to you, notice it, reflect on it, and if it’s something that your conscious mind considers reasonable and safe for you to do, you can even try doing it.
Your body is trying to help you here, by the way! It will try (and usually succeed) to give you a little dopamine spike when you anticipate doing the thing it wants you to do. Warning: it won’t always be right about what’s best for you, so do still make your own decisions about whether it is a good idea to safely do it.
Practical experiments: whether you have a theory or just a hypothesis (if you have neither make up a hypothesis; that is also what scientists do), you can also test it:
If in the previous step you identified something you’d like to do and are able to safely do it, now is the time to try it. If not…
- Find something that is likely to (safely) tip you into emotional expression, ideally, in a cathartic way. But, whatever you can get is good.
- Music is great for this. What songs (or even non-lyrical musical works) make you sad, happy, angry, energized? Try them.
- Literature and film can be good too, albeit they take more time. Grab that tear-jerker or angsty rage-fest, and see if it feels right.
- Other media, again, can be completely unrelated to the situation at hand, but if it evokes the same emotion, it’ll help you figure out “yes, this is it”.
- It could be a love letter or a tax letter, it could be an outrage-provoking news piece or some nostalgic thing you own.
Ride it out, wherever it takes you (safely)
Feelings feel better felt. It doesn’t always seem that way! But, really, they are.
Emotions, just like physical sensations, are messengers. And when a feeling/sensation is troublesome, one of the best ways to get past it is to first fully listen to it and respond accordingly.
- If your body tells you something, then it’s good to acknowledge that and give it some reassurance by taking some action to appease it.
- If your emotions are telling you something, then it’s good to acknowledge that and similarly take some action to appease it.
There is a reason people feel better after “having a good cry”, or “pounding it out” against a punchbag. Even stress can be dealt with by physically deliberately tensing up and then relaxing that tension, so the body thinks that you had a fight and won and can relax now.
And when someone is in a certain (not happy) mood and takes (sometimes baffling!) actions to stay in that mood rather than “snap out of it”, it’s probably because there’s more feeling to be done before the body feels heard. Hence the “ride it out if you safely can” idea.
How much feeling is too much?
While this is in large part a subjective matter, clinically speaking the key question is generally: is it adversely affecting daily life to the point of being a problem?
For example, if you have to spend half an hour every day actively managing a certain emotion, that’s probably indicative of something unusual, but “unusual” is not inherently pathological. If you’re managing it safely and in a way that doesn’t negatively affect the rest of your life, then that is generally considered fine, unless you feel otherwise about it.
If you do think “I would like to not think/feel this anymore”, then there are tools at your disposal too:
- How To Manage Chronic Stress
- How To Set Anxiety Aside
- How To Stop Revisiting Those Memories
- How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
ADHD medication – can you take it long term? What are the risks and do benefits continue?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a condition that can affect all stages of life. Medication is not the only treatment, but it is often the treatment that can make the most obvious difference to a person who has difficulties focusing attention, sitting still or not acting on impulse.
But what happens once you’ve found the medication that works for you or your child? Do you just keep taking it forever? Here’s what to consider.
What are ADHD medications?
The mainstay of medication for ADHD is stimulants. These include methylphenidate (with brand names Ritalin, Concerta) and dexamfetamine. There is also lisdexamfetamine (branded Vyvanse), a “prodrug” of dexamfetamine (it has a protein molecule attached, which is removed in the body to release dexamfetamine).
There are also non-stimulants, in particular atomoxetine and guanfacine, which are used less often but can also be highly effective. Non-stimulants can be prescribed by GPs but this may not always be covered by the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme and could cost more.
How stimulants work
Some stimulants prescribed for ADHD are “short acting”. This means the effect comes on after around 20 minutes and lasts around four hours.
Longer-acting stimulants give a longer-lasting effect, usually by releasing medication more slowly. The choice between the two will be guided by whether the person wants to take medication once a day or prefers to target the medication effect to specific times or tasks.
For the stimulants (with the possible exception of lisdexamfetamine) there is very little carry-over effect to the next day. This means the symptoms of ADHD may be very obvious until the first dose of the morning takes effect.
One of the main aims of treatment is the person with ADHD should live their best life and achieve their goals. In young children it is the parents who have to consider the risks and benefits on behalf of the child. As children mature, their role in decision making increases.
What about side effects?
The most consistent side effects of the stimulants are they suppress appetite, resulting in weight loss. In children this is associated with temporary slowing of the growth rate and perhaps a slight delay in pubertal development. They can also increase the heart rate and may cause a rise in blood pressure. Stimulants often cause insomnia.
These changes are largely reversible on stopping medication. However, there is concern the small rises in blood pressure could accelerate the rate of heart disease, so people who take medication over a number of years might have heart attacks or strokes slightly sooner than would have happened otherwise.
This does not mean older adults should not have their ADHD treated. Rather, they should be aware of the potential risks so they can make an informed decision. They should also make sure high blood pressure and attacks of chest pain are taken seriously.
Stimulants can be associated with stomach ache or headache. These effects may lessen over time or with a reduction in dose. While there have been reports about stimulants being misused by students, research on the risks of long-term prescription stimulant dependence is lacking.
Will medication be needed long term?
Although ADHD can affect a person’s functioning at all stages of their life, most people stop medication within the first two years.
People may stop taking it because they don’t like the way it makes them feel, or don’t like taking medication at all. Their short period on medication may have helped them develop a better understanding of themselves and how best to manage their ADHD.
In teenagers the medication may lose its effectiveness as they outgrow their dose and so they stop taking it. But this should be differentiated from tolerance, when the dose becomes less effective and there are only temporary improvements with dose increases.
Tolerance may be managed by taking short breaks from medication, switching from one stimulant to another or using a non-stimulant.
Medication is usually prescribed by a specialist but rules differ around Australia.
Ground Picture/ShutterstockToo many prescriptions?
ADHD is becoming increasingly recognised, with more people – 2–5% of adults and 5–10% of children – being diagnosed. In Australia stimulants are highly regulated and mainly prescribed by specialists (paediatricians or psychiatrists), though this differs from state to state. As case loads grow for this lifelong diagnosis, there just aren’t enough specialists to fit everyone in.
In November, a Senate inquiry report into ADHD assessment and support services highlighted the desperation experienced by people seeking treatment.
There have already been changes to the legislation in New South Wales that may lead to more GPs being able to treat ADHD. Further training could help GPs feel more confident to manage ADHD. This could be in a shared-care arrangement or independent management of ADHD by GPs like a model being piloted at Nepean Blue Mountains Local Health District, with GPs training within an ADHD clinic (where I am a specialist clinician).
Not every person with ADHD will need or want to take medication. However, it should be more easily available for those who could find it helpful.
Alison Poulton, Senior Lecturer, Brain Mind Centre Nepean, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
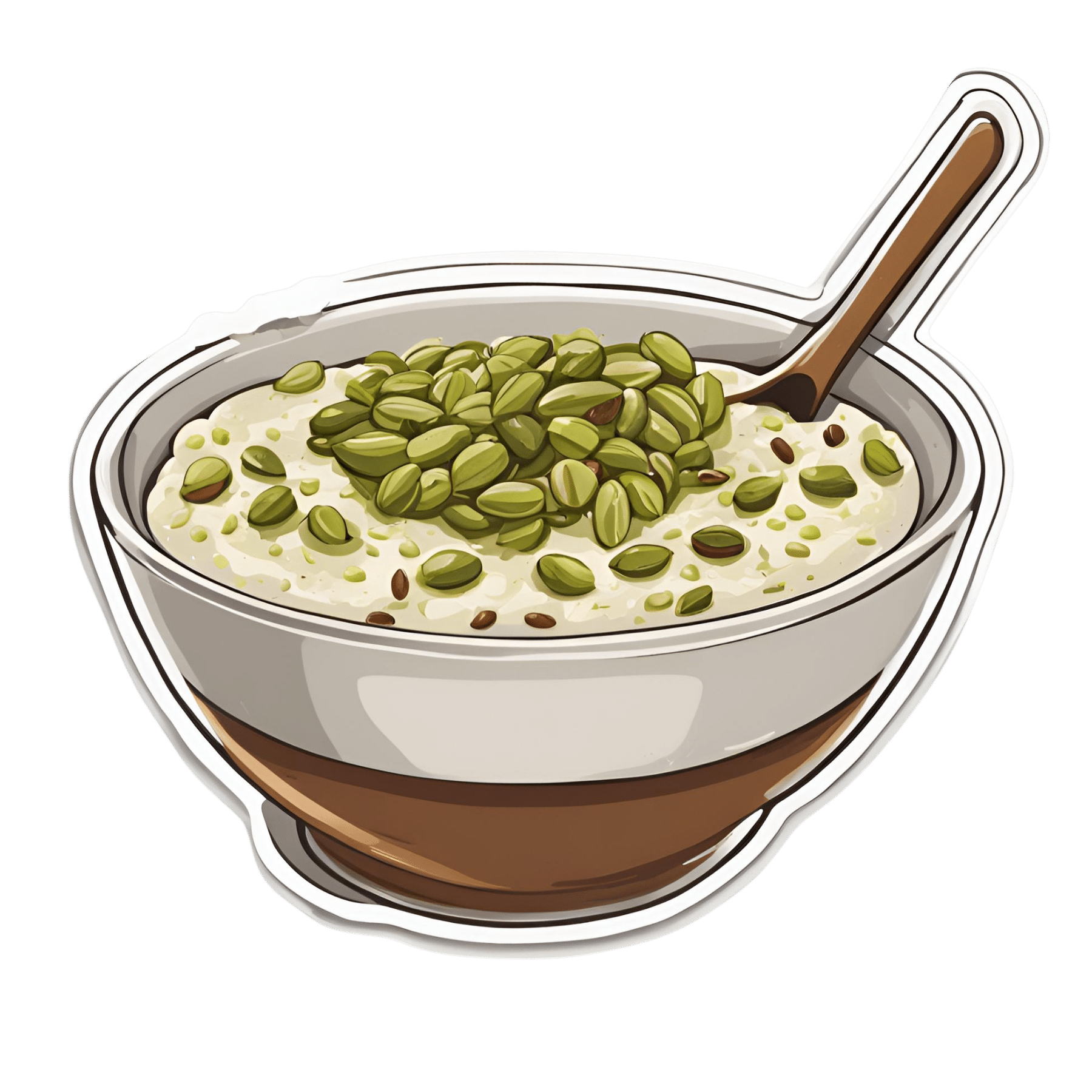
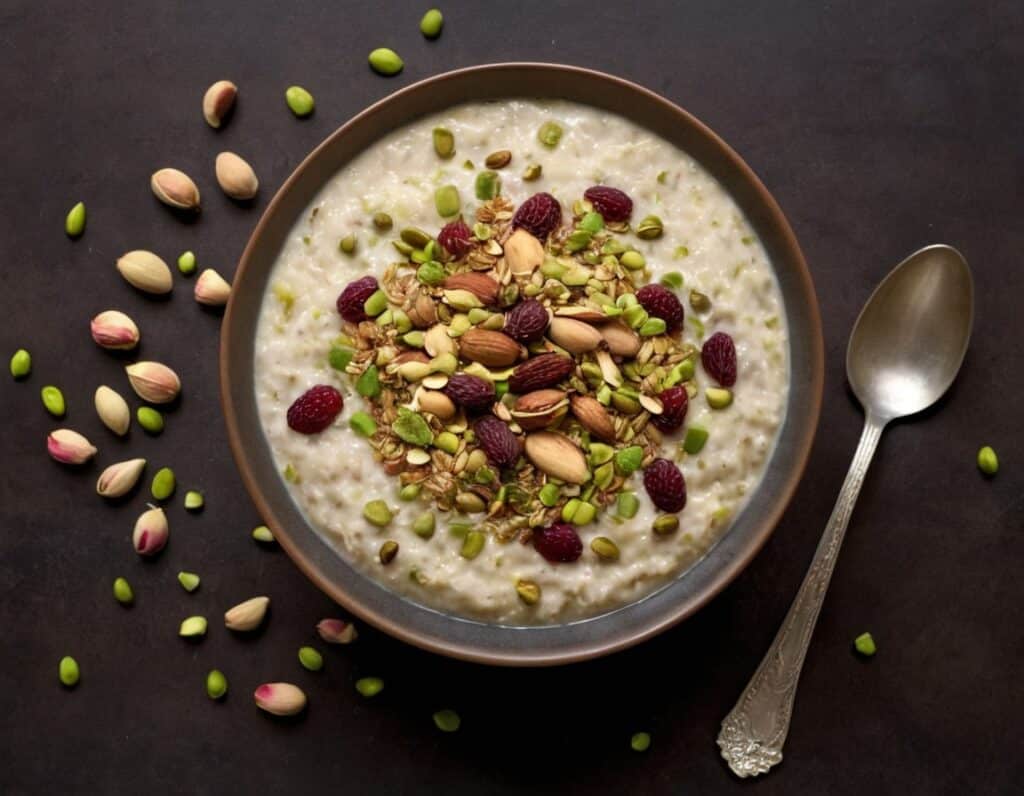
Anti-Cholesterol Cardamom & Pistachio Porridge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This tasty breakfast’s beta-glucan content binds to cholesterol and carries it out of the body; there are lots of other nutritional benefits too!
You will need
- 1 cup coconut milk
- ⅓ cup oats
- 4 tbsp crushed pistachios
- 6 cardamom pods, crushed
- 1 tsp rose water or 4 drops edible rose essential oil
- Optional sweetener: drizzle of honey or maple syrup
- Optional garnishes: rose petals, chopped nuts, dried fruit
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat the coconut milk, adding the oats and crushed cardamom pods. Simmer for 5–10 minutes depending on how cooked you want the oats to be.
2) Stir in the crushed pistachio nuts, as well as the rose water.
3) Serve in a bowl, adding any optional toppings:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s beta-glucan, which is fund abundantly in oats
- Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← coconut can!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: