Blue Cheese vs Brunost – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing blue cheese to brunost, we picked the brunost.
Why?
First, for the unfamiliar, as brunost isn’t necessarily as popular as blue cheese in N. America where most of our readers are:
Brunost, literally “brown cheese” is a traditional Norwegian affair made from aggressively boiling milk, cream, and whey in an iron cauldron. Whereas the blue in blue cheese comes from mold, the brown in brown cheese comes from caramelizing the milk sugars in the cauldron. When we say “cauldron”, yes, there is nowadays mass-produced brunost that is no longer made in something that could be mistaken for a witch’s brew, but the use of cast iron is actually important to the process, and has been the subject of regulatory controversy in Norway; first the cast iron was abandoned, then because that changed the cheese they fortified the product with added iron supplementation, then that was banned, then they reversed it because it affected iron levels in the general population. Nowadays, it is usually made with iron, one way or another.
Ok, so let’s see how they stack up against each other:
In terms of macronutrients, the two cheeses are comparable in fat, but brunost has more carbs—because whereas bacteria (and to a lesser extent, the mold) ate nearly all the carbs in the blue cheese, the caramelization of the milk sugars in brunost meant the result stayed higher in carbs. Both are considered “low GI” foods, but this category is still at least a moderate win for blue cheese.
When it comes to vitamins, brunost is higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B12, while blue cheese is higher in vitamin B9. In other words, a clear and easy win for brunost.
In the category of minerals, brunost has more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. Meanwhile, blue cheese contains more zinc, although we can also mention that blue cheese has about 2x the sodium, which is generally not considered a benefit. The two cheeses are about equal in calcium and selenium. Adding these up makes for another clear and easy win for brunost.
In short, unless you are strongly avoiding [even low-GI foods’] carbs for some reason, brunost wins the day by virtue of its overwhelmingly better vitamin and mineral content.
Still, like most fermented dairy products, both cheeses can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a healthy diet (assuming you don’t have an allergy/intolerance).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Air Purifiers & Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I’ve read that air pollution has a negative effect on sleep quality and duration. Since I live next to a busy road, I was wondering whether I should invest in an air purifier. What are 10Almonds’s views?❞
Going straight to the science, there are two questions here:
- Does air pollution negatively affect sleep quality and duration?
- Does the use of an air purify actually improve the air quality in the way(s) necessary to make a difference?
We thought we’d have to tackle these questions separately, but we did find one study that addressed your question directly. It was a small study (n=30 if you believe the abstract; n=29 if you read the paper itself—one person dropped out); the results were modest but clear:
❝The purifier filter was associated with increased total sleep time for an average of 12 min per night, and increased total time in bed for an average of 19 min per night relative to the placebo.
There were several sleep and mood outcomes for which no changes were observed, and time awake after sleep onset was higher for the purifier filter. Air quality was better during the high-efficiency particulate air filter condition.
These findings offer positive indications that environmental interventions that improve air quality can have benefits for sleep outcomes in healthy populations who are not exhibiting clinical sleep disturbances.❞
In the above-linked paper’s introduction, it does establish the deleterious effect of air pollution on a wide variety of health metrics, including sleep, this latter evidenced per Caddick et al. (2018): A review of the environmental parameters necessary for an optimal sleep environment
Now, you may be wondering: is an extra 12 minutes per night worth it?
That’s your choice to make, but we would argue that it is. We can make many choices in our lives that affect our health slightly for the better or the worse. If we make a stack of choices in a particular direction, the effects will also stack, if not outright compound.
So in the case of sleep, it might be (arbitrary numbers for the sake of illustration):
- Get good exercise earlier in the day (+3%)
- Get good food earlier in the day (+2.5%)
- Practice mindfulness/meditation before bed (+2.5%)
- Have a nice dark room (+5%)
- Have fresh bedding (+2.5%)
- Have an air purifier running (+3%)
Now, those numbers are, as we said, arbitrary*, but remember that percentages don’t add up; they compound. So that “+3%” starts being a lot more meaningful than if it were just by itself.
*Confession: the figure of 3% for the air purifier wasn’t entirely arbitrary; it was based on 100(12/405) = 80/27 ≈ 3, wherein the 405 figure was an approximation of the average total time (in minutes) spent sleeping with placebo, based on a peep at their results graph. There are several ways the average could be reasonably calculated, but 6h45 (i.e., 405 minutes) was an approximate average of those reasonable approximate averages.
So, 12 minutes is a 3% improvement on that.
Don’t have an air purifier and want one?
We don’t sell them, but here’s an example on Amazon, for your convenience
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Plum vs Nectarine – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing plums to nectarines, we picked the nectarines.
Why?
Both are great! But nectarines win at least marginally in each category we look at.
In terms of macros, plums have more carbs while nectarines have more fiber, resulting of course in a lower glycemic index. Plums do have a low GI also; just, nectarines have it better.
When it comes to vitamins, plums have more of vitamins A, B6, C, and K, while nectarines have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, E, and choline.
In the category of minerals, plums are great but not higher in any mineral than nectarines; nectarines meanwhile have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc.
All in all, enjoy both. And if having dried fruit, then prunes (dried plums) are generally more widely available than dried nectarines. But if you’re choosing one fruit or the other, nectarine is the way to go.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Take care!
Share This Post
-
In Vermont, Where Almost Everyone Has Insurance, Many Can’t Find or Afford Care
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
RICHMOND, Vt. — On a warm autumn morning, Roger Brown walked through a grove of towering trees whose sap fuels his maple syrup business. He was checking for damage after recent flooding. But these days, his workers’ health worries him more than his trees’.
The cost of Slopeside Syrup’s employee health insurance premiums spiked 24% this year. Next year it will rise 14%.
The jumps mean less money to pay workers, and expensive insurance coverage that doesn’t ensure employees can get care, Brown said. “Vermont is seen as the most progressive state, so how is health care here so screwed up?”
Vermont consistently ranks among the healthiest states, and its unemployment and uninsured rates are among the lowest. Yet Vermonters pay the highest prices nationwide for individual health coverage, and state reports show its providers and insurers are in financial trouble. Nine of the state’s 14 hospitals are losing money, and the state’s largest insurer is struggling to remain solvent. Long waits for care have become increasingly common, according to state reports and interviews with residents and industry officials.
Rising health costs are a problem across the country, but Vermont’s situation surprises health experts because virtually all its residents have insurance and the state regulates care and coverage prices.
For more than 15 years, federal and state policymakers have focused on increasing the number of people insured, which they expected would shore up hospital finances and make care more available and affordable.
“Vermont’s struggles are a wake-up call that insurance is only one piece of the puzzle to ensuring access to care,” said Keith Mueller, a rural health expert at the University of Iowa.
Regulators and consultants say the state’s small, aging population of about 650,000 makes spreading insurance risk difficult. That demographic challenge is compounded by geography, as many Vermonters live in rural areas, where it’s difficult to attract more health workers to address shortages.
At least part of the cost spike can be attributed to patients crossing state lines for quicker care in New York and Massachusetts. Those visits can be more expensive for both insurers and patients because of long ambulance rides and charges from out-of-network providers.
Patients who stay, like Lynne Drevik, face long waits. Drevik said her doctor told her in April that she needed knee replacement surgeries — but the earliest appointment would be in January for one knee and the following April for the other.
Drevik, 59, said it hurts to climb the stairs in the 19th-century farmhouse in Montgomery Center she and her husband operate as an inn and a spa. “My life is on hold here, and it’s hard to make any plans,” she said. “It’s terrible.”
Health experts say some of the state’s health system troubles are self-inflicted.
Unlike most states, Vermont regulates hospital and insurance prices through an independent agency, the Green Mountain Care Board. Until recently, the board typically approved whatever price changes companies wanted, said Julie Wasserman, a health consultant in Vermont.
The board allowed one health system — the University of Vermont Health Network — to control about two-thirds of the state’s hospital market and allowed its main facility, the University of Vermont Medical Center in Burlington, to raise its prices until it ranked among the nation’s most expensive, she said, citing data the board presented in September.
Hospital officials contend their prices are no higher than industry averages.
But for 2025, the board required the University of Vermont Medical Center to cut the prices it bills private insurers by 1%.
The nonprofit system says it is navigating its own challenges. Top officials say a severe lack of housing makes it hard to recruit workers, while too few mental health providers, nursing homes, and long-term care services often create delays in discharging patients, adding to costs.
Two-thirds of the system’s patients are covered by Medicare or Medicaid, said CEO Sunny Eappen. Both government programs pay providers lower rates than private insurance, which Eappen said makes it difficult to afford rising prices for drugs, medical devices, and labor.
Officials at the University of Vermont Medical Center point to several ways they are trying to adapt. They cited, for example, $9 million the hospital system has contributed to the construction of two large apartment buildings to house new workers, at a subsidized price for lower-income employees.
The hospital also has worked with community partners to open a mental health urgent care center, providing an alternative to the emergency room.
In the ER, curtains separate areas in the hallway where patients can lie on beds or gurneys for hours waiting for a room. The hospital also uses what was a storage closet as an overflow room to provide care.
“It’s good to get patients into a hallway, as it’s better than a chair,” said Mariah McNamara, an ER doctor and associate chief medical officer with the hospital.
For the about 250 days a year when the hospital is full, doctors face pressure to discharge patients without the ideal home or community care setup, she said. “We have to go in the direction of letting you go home without patient services and giving that a try, because otherwise the hospital is going to be full of people, and that includes people that don’t need to be here,” McNamara said.
Searching for solutions, the Green Mountain Care Board hired a consultant who recommended a number of changes, including converting four rural hospitals into outpatient facilities, in a worst-case scenario, and consolidating specialty services at several others.
The consultant, Bruce Hamory, said in a call with reporters that his report provides a road map for Vermont, where “the health care system is no match for demographic, workforce, and housing challenges.”
But he cautioned that any fix would require sacrifice from everyone, including patients, employers, and health providers. “There is no simple single policy solution,” he said.
One place Hamory recommended converting to an outpatient center only was North Country Hospital in Newport, a village in Vermont’s least populated region, known as the Northeast Kingdom.
The 25-bed hospital has lost money for years, partly because of an electronic health record system that has made it difficult to bill patients. But the hospital also has struggled to attract providers and make enough money to pay them.
Officials said they would fight any plans to close the hospital, which recently dropped several specialty services, including pulmonology, neurology, urology, and orthopedics. It doesn’t have the cash to upgrade patient rooms to include bathroom doors wide enough for wheelchairs.
On a recent morning, CEO Tom Frank walked the halls of his hospital. The facility was quiet, with just 14 admitted patients and only a couple of people in the ER. “This place used to be bustling,” he said of the former pulmonology clinic.
Frank said the hospital breaks even treating Medicare patients, loses money treating Medicaid patients, and makes money from a dwindling number of privately insured patients.
The state’s strict regulations have earned it an antihousing, antibusiness reputation, he said. “The cost of health care is a symptom of a larger problem.”
About 30 miles south of Newport, Andy Kehler often worries about the cost of providing health insurance to the 85 workers at Jasper Hill Farm, the cheesemaking business he co-owns.
“It’s an issue every year for us, and it looks like there is no end in sight,” he said.
Jasper Hill pays half the cost of its workers’ health insurance premiums because that’s all it can afford, Kehler said. Employees pay $1,700 a month for a family, with a $5,000 deductible.
“The coverage we provide is inadequate for what you pay,” he said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
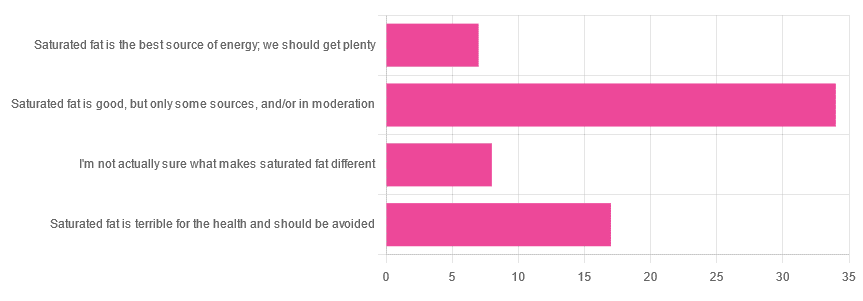
We asked you for your health-related opinion of saturated fat, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of results.
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
- This is an easy one to vote for, because of the “and/or in moderation” part, which tends to be a “safe bet” for most things.
- Next most popular was “Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided”
- About half as many recorded votes were for “I’m not actually sure what makes saturated fat different”, which is a very laudable option to click. Admitting when we don’t know things (and none of us know everything) is a very good first step to learning about them!
- Fewest recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty”.
So, what does the science say?
First, a bit of physics, chemistry, and biology
You may be wondering what, exactly, saturated fats are “saturated” with. That’s a fair question, so…
All fats have a molecular structure made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen, and thus have only single bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated fats have at least one double-bond between carbon atoms).
The observable effect this has on them, is that fats that are saturated with hydrogen are solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. Their different properties also make for different interactions inside the human body, including how likely or not they are to (for example) clog arteries.
See also: Could fat in your bloodstream cause blood clots?
Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty: True or False?
False, in any reasonable interpretation, anyway. That is to say, if your idea of “plenty” is under 13g (e.g: two tablespoons of butter, and no saturated fat from other sources, e.g. meat) per day, then yes, by all means feel free to eat plenty. More than that, though, and you might want to consider trimming it down a bit.
The American Heart Association has this to say:
❝When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fats, which are found in butter, cheese, red meat and other animal-based foods, and tropical oils.
Decades of sound science has proven it can raise your “bad” cholesterol and put you at higher risk for heart disease.❞
Source: The American Heart Association Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations on Saturated Fat
The British Heart Foundation has a similar statement:
❝Despite what you read in the media, our advice is clear: replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats and avoid trans fats. Saturated fat is the kind of fat found in butter, lard, ghee, fatty meats and cheese. This is linked to an increased risk of heart and circulatory disease❞
Source: British Heart Foundation: What does fat do and what is saturated fat?
As for the World Health Organization:
❝1. WHO strongly recommends that adults and children reduce saturated fatty acid intake to 10% of total energy intake
2. WHO suggests further reducing saturated fatty acid intake to less than 10% of total energy intake
3. WHO strongly recommends replacing saturated fatty acids in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids; monounsaturated fatty acids from plant sources; or carbohydrates from foods containing naturally occurring dietary fibre, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses.❞
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
Please note, organizations such as the AHA, the BHF, and the WHO are not trying to sell us anything, and just would like us to not die of heart disease, the world’s #1 killer.
As for “the best source of energy”…
We evolved to eat (much like our nearest primate cousins) a diet consisting mostly of fruits and other edible plants, with a small supplementary amount of animal-source protein and fats.
That’s not to say that because we evolved that way we have to eat that way—we are versatile omnivores. But for example, we are certainly not complete carnivores, and would quickly sicken and die if we tried to live on only meat and animal fat (we need more fiber, more carbohydrates, and many micronutrients that we usually get from plants)
The closest that humans tend to come to doing such is the ketogenic diet, which focuses on a high fat, low carbohydrate imbalance, to promote ketosis, in which the body burns fat for energy.
The ketogenic diet does work, and/but can cause a lot of health problems if a lot of care is not taken to avoid them.
See for example: 7 Keto Risks To Keep In Mind
Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided: True or False?
False, if we are talking about “completely”.
Firstly, it’s practically impossible to cut out all saturated fats, given that most dietary sources of fat are a mix of saturated, unsaturated (mono- and poly-), and trans fats (which are by far the worst, but beyond the scope of today’s main feature).
Secondly, a lot of research has been conducted and found insignificant or inconclusive results, in cases where saturated fat intake was already within acceptable levels (per the recommendations we mentioned earlier), and then cut down further.
Rather than fill up the newsletter with individual studies of this kind here’s a high-quality research review, looking at 19 meta-analyses, each of those meta-analyses having looked at many studies:
Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: a narrative review
Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation: True or False?
True! The moderation part is easy to guess, so let’s take a look at the “but only some sources”.
We were not able to find any convincing science to argue for health-based reasons to favor plant- or animal-sourced saturated fat. However…
Not all saturated fats are created equal (there are many kinds), and also many of the foods containing them have additional nutrients, or harmful compounds, that make a big difference to overall health, when compared gram-for-gram in terms of containing the same amount of saturated fat.
For example:
- Palm oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of palmitic acid, which raises LDL (“bad” cholesterol) without affecting HDL (“good” cholesterol), thus having an overall heart-harmful effect.
- Most animal fats contain a disproportionate amount of stearic acid, which has statistically insignificant effects on LDL and HDL levels, and thus is broadly considered “heart neutral” (in moderation!)
- Coconut oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of lauric acid, which raises total cholesterol, but mostly HDL without affecting LDL, thus having an overall heart-beneficial effect (in moderation!)
Do you know what’s in the food you eat?
Test your knowledge with the BHF’s saturated fat quiz!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
-
Stop Walking on Eggshells – by Randi Kreger & Paul Mason
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As you may gather from the title, the angle here is not “Borderline Personality Disorder is fine and dandy”, but nor is it something anyone chooses to have, and as such, importantly, this book’s advice is also not “and so you should immediately disown, divorce, defenestrate your partner”, either.
Rather, it has a balanced and compassionate approach that examines both the pitfalls and the possibilities, and provides the tools to make your relationship feel (and hopefully, actually be) safe for all concerned.
And yes, ending a relationship is always an option too, even if it can sometimes feel like it’s not, on account of how the relationships of people with BPD often have a lot of “near miss” situations, nearly ending but not quite, or (in the case of a partner who’s amenable to such), off-and-on relationships—either of which can make it seem like it’ll never truly be over.
First, though, the authors do look at a variety of ways of avoiding that outcome; making changes within oneself, setting boundaries and honing related skills, asserting your needs with confidence and clarity, and dealing with the lies, rumor-mongering, and accusations that often come with BPD. For that matter, the authors do also note that not all conflict is abuse (something that many forget), but on the flipside, how to tell when it actually is, too.
The style is very pop-science, light in tone albeit sometimes heavy in content.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one has BPD, or even just has a lot of the same symptoms as such, this book can be very helpful.
Click here to check out Stop Walking On Eggshells, and stop walking on eggshells!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
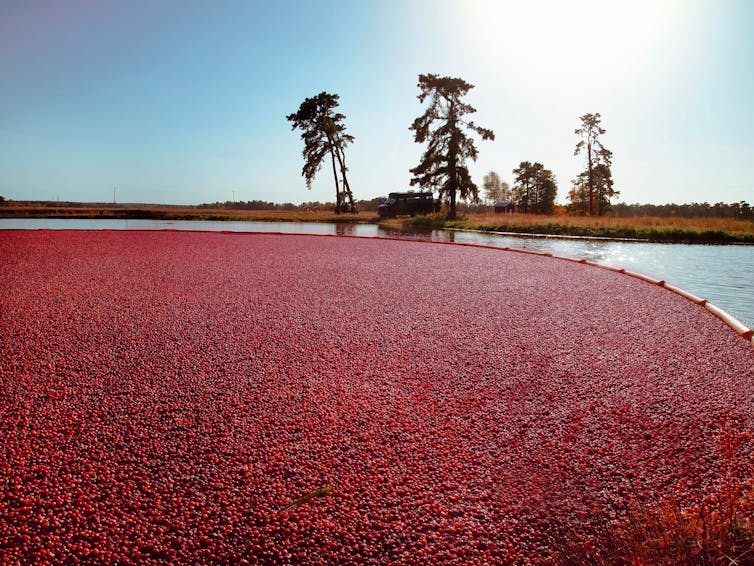
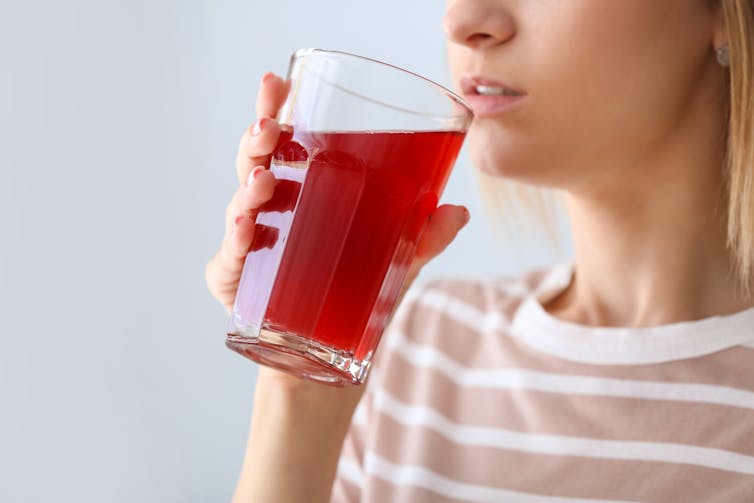
Cranberry juice really can help with UTIs – and reduce reliance on antibiotics
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cranberry juice has been used medicinally for centuries. Our new research indicates it should be a normal aspect of urinary tract infection (UTI) management today.
While some benefits of cranberry compounds for the prevention of UTIs have been suspected for some time, it hasn’t been clear whether the benefits from cranberry juice were simply from drinking more fluid, or something in the fruit itself.
For our study, published this week, we combined and collectively assessed 3,091 participants across more than 20 clinical trials.
Our analysis indicates that increasing liquids reduces the rate of UTIs compared with no treatment, but cranberry in liquid form is even better at reducing UTIs and antibiotic use.
Julie Falk/Flickr, CC BY-NC-ND Are UTIs really that bad?
Urinary tract infections affect more than 50% of women and 20% of men in their lifetime.
Most commonly, UTIs are caused from the bug called Escherichia coli (E.coli). This bug lives harmlessly in our intestines, but can cause infection in the urinary tract. This is why, particularly for women, it is recommended people wipe from front to back after using the toilet.
An untreated UTI can move up to the kidneys and cause even more serious illness.
Even when not managing infection, many people are anxious about contracting a UTI. Sexually active women, pregnant women and older women may all be at increased risk.
Why cranberries?
To cause a UTI, the bacteria need to attach to the wall of the urinary bladder. Increasing fluids helps to flush out bacteria before it attaches (or makes its way up into the bladder).
Some beneficial compounds in cranberry, such as proanthocyanidins (also called condensed tannins), prevent the bacteria from attaching to the wall itself.
While there are treatments, over 90% of the bugs that cause UTIs exhibit some form of microbial resistance. This suggests that they are rapidly changing and some cases of UTI might be left untreatable.
The juice of cranberries has long been thought to have infection-fighting properties. duckeesue/Shutterstock What we found
Our analysis showed a 54% lower rate of UTIs from cranberry juice consumption compared to no treatment. This means that significantly fewer participants who regularly consumed cranberry juice (most commonly around 200 millilitres each day) reported having a UTI during the periods assessed in the studies we analysed.
Cranberry juice was also linked to a 49% lower rate of antibiotic use than placebo liquid and a 59% lower rate than no treatment, based on analysis of indirect and direct effects across six studies. The use of cranberry compounds, whether in drinks or tablet form, also reduced the prevalence of symptoms associated with UTIs.
While some studies we included presented conflicts of interest (such as receiving funding from cranberry companies), we took this “high risk of bias” into account when analysing the data.
The study found extra hydration helped but not to the same extent as cranberry juice. Pixelshot/Shutterstock So, when can cranberry juice help?
We found three main benefits of cranberry juice for UTIs.
1. Reduced rates of infections
Increasing fluids (for example, drinking more water) reduced the prevalence of UTIs, and taking cranberry compounds (such as tablets) was also beneficial. But the most benefits were identified from increasing fluids and taking cranberry compounds at the same time, such as with cranberry juice.
2. Reduced use of antibiotics
The data shows cranberry juice lowers the need to use antibiotics by 59%. This was identified as fewer participants in randomised cranberry juice groups required antibiotics.
Increasing fluid intake also helped reduce antibiotic use (by 25%). But this was not as useful as increasing fluids at the same time as using cranberry compounds.
Cranberry compounds alone (such as tablets without associated increases in fluid intake) did not affect antibiotic use.
3. Reducing symptoms
Taking cranberry compounds (in any form, liquid or tablet) reduced the symptoms of UTIs, as measured in the overall data, by more than five times.
Take home advice
While cranberry juice cannot treat a UTI, it can certainly be part of UTI management.
If you suspect that you have a UTI, see your GP as soon as possible.
Christian Moro, Associate Professor of Science & Medicine, Bond University and Charlotte Phelps, Senior Teaching Fellow, Medical Program, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: