The Brain Alarm Signs That Warn Of Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to predicting age-related cognitive impairment:
First there are genetic factors to take into account (such as the APOE4 gene for Alzheimer’s), as well as things such as age and sex.
When it comes to sex, by the way, what matters here is hormones, which is why [it seems; this as technically as yet unproven with full rigor, but the hypothesis is sound and there is a body of evidence gradually being accumulated to support it] postmenopausal women with untreated menopause get Alzheimer’s at a higher rate and deteriorate more quickly:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Next, there are obviously modifiable lifestyle factors to take into account, things that will reduce your risk such as getting good sleep, good diet, good exercise, and abstaining from alcohol and smoking, as well as oft-forgotten things such as keeping cognitively active and, equally importantly, socially active:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
(the article outlines what matters the most in each of the above areas, by the way, so that you can get the most bang-for-buck in terms of lifestyle adjustments)
Lastly (in the category of risk factors), there are things to watch out for in the blood such as hypertension and high cholesterol.
Nipping it in the blood
In new research (so new it is still ongoing, but being at year 2 of a 4-year prospective study, they have published a paper with their results so far), researchers have:
- started with the premise “dementia is preceded by mild cognitive impairment”
- then, asked the question “what are the biometric signs of mild cognitive impairment?”
Using such tools as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) while the participants performed cognitive tasks, they were able to record changes in plasma levels of extracellular vesicles, assessing them with small-particle flow cytometry.
Translating from sciencese: they gave the participants mental tasks, and while they completed them, the researchers scanned their brains and monitored blood flow and the brain’s ability to compensate for any lack of it.
What they found:
- in young adults, blood flow increased, facilitating neurovascular coupling (this is good)
- in older adults, blood flow did not increase as much, but they engaged other areas of the brain to compensate, by what’s called functional connectivity (this is next best)
- in those with mild cognitive impairment, blood flow was reduced, and they did not have the ability to compensate by functional connectivity (this is not good)
They also performed a liquid biopsy, which sounds alarming but it just means they took some blood, and tested this for density of cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs), which—in more prosaic words—are bits from the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain.
People with mild cognitive impairment had more of these brain bits in their blood than those without.
You can read the paper itself here:
What this means
The science here is obviously still young (being as it is still in progress), but this will likely contribute greatly to early warning signs of dementia, by catching mild cognitive impairment in its early stages, by means of a simple blood test, instead of years of wondering before getting a dementia diagnosis.
And of course, forewarned is forearmed, so if this is something that could be done as a matter of routine upon hitting the age of, say, 65 and then periodically thereafter, it would catch a lot of cases while there’s still more time to turn things around.
As for how to turn things around, well, we imagine you have now read our “How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk” article linked up top (if not, we recommend checking it out), and there is also…
Do Try This At Home: The 12-Week Brain Fitness Program To Measurably Boost Your Brain
Take care!
When it comes to predicting age-related cognitive impairment:
First there are genetic factors to take into account (such as the APOE4 gene for Alzheimer’s), as well as things such as age and sex.
When it comes to sex, by the way, what matters here is hormones, which is why [it seems; this as technically as yet unproven with full rigor, but the hypothesis is sound and there is a body of evidence gradually being accumulated to support it] postmenopausal women with untreated menopause get Alzheimer’s at a higher rate and deteriorate more quickly:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Next, there are obviously modifiable lifestyle factors to take into account, things that will reduce your risk such as getting good sleep, good diet, good exercise, and abstaining from alcohol and smoking, as well as oft-forgotten things such as keeping cognitively active and, equally importantly, socially active:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
(the article outlines what matters the most in each of the above areas, by the way, so that you can get the most bang-for-buck in terms of lifestyle adjustments)
Lastly (in the category of risk factors), there are things to watch out for in the blood such as hypertension and high cholesterol.
Nipping it in the blood
In new research (so new it is still ongoing, but being at year 2 of a 4-year prospective study, they have published a paper with their results so far), researchers have:
- started with the premise “dementia is preceded by mild cognitive impairment”
- then, asked the question “what are the biometric signs of mild cognitive impairment?”
Using such tools as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) while the participants performed cognitive tasks, they were able to record changes in plasma levels of extracellular vesicles, assessing them with small-particle flow cytometry.
Translating from sciencese: they gave the participants mental tasks, and while they completed them, the researchers scanned their brains and monitored blood flow and the brain’s ability to compensate for any lack of it.
What they found:
- in young adults, blood flow increased, facilitating neurovascular coupling (this is good)
- in older adults, blood flow did not increase as much, but they engaged other areas of the brain to compensate, by what’s called functional connectivity (this is next best)
- in those with mild cognitive impairment, blood flow was reduced, and they did not have the ability to compensate by functional connectivity (this is not good)
They also performed a liquid biopsy, which sounds alarming but it just means they took some blood, and tested this for density of cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs), which—in more prosaic words—are bits from the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain.
People with mild cognitive impairment had more of these brain bits in their blood than those without.
You can read the paper itself here:
What this means
The science here is obviously still young (being as it is still in progress), but this will likely contribute greatly to early warning signs of dementia, by catching mild cognitive impairment in its early stages, by means of a simple blood test, instead of years of wondering before getting a dementia diagnosis.
And of course, forewarned is forearmed, so if this is something that could be done as a matter of routine upon hitting the age of, say, 65 and then periodically thereafter, it would catch a lot of cases while there’s still more time to turn things around.
As for how to turn things around, well, we imagine you have now read our “How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk” article linked up top (if not, we recommend checking it out), and there is also…
Do Try This At Home: The 12-Week Brain Fitness Program To Measurably Boost Your Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
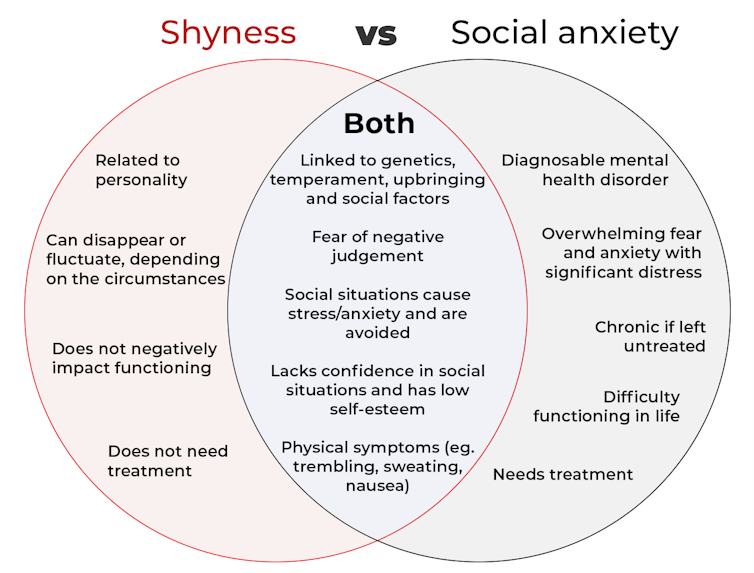
What’s the difference between shyness and social anxiety?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
The terms “shyness” and “social anxiety” are often used interchangeably because they both involve feeling uncomfortable in social situations.
However, feeling shy, or having a shy personality, is not the same as experiencing social anxiety (short for “social anxiety disorder”).
Here are some of the similarities and differences, and what the distinction means.
pathdoc/Shutterstock How are they similar?
It can be normal to feel nervous or even stressed in new social situations or when interacting with new people. And everyone differs in how comfortable they feel when interacting with others.
For people who are shy or socially anxious, social situations can be very uncomfortable, stressful or even threatening. There can be a strong desire to avoid these situations.
People who are shy or socially anxious may respond with “flight” (by withdrawing from the situation or avoiding it entirely), “freeze” (by detaching themselves or feeling disconnected from their body), or “fawn” (by trying to appease or placate others).
A complex interaction of biological and environmental factors is also thought to influence the development of shyness and social anxiety.
For example, both shy children and adults with social anxiety have neural circuits that respond strongly to stressful social situations, such as being excluded or left out.
People who are shy or socially anxious commonly report physical symptoms of stress in certain situations, or even when anticipating them. These include sweating, blushing, trembling, an increased heart rate or hyperventilation.
How are they different?
Social anxiety is a diagnosable mental health condition and is an example of an anxiety disorder.
For people who struggle with social anxiety, social situations – including social interactions, being observed and performing in front of others – trigger intense fear or anxiety about being judged, criticised or rejected.
To be diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, social anxiety needs to be persistent (lasting more than six months) and have a significant negative impact on important areas of life such as work, school, relationships, and identity or sense of self.
Many adults with social anxiety report feeling shy, timid and lacking in confidence when they were a child. However, not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. Also, feeling shy does not necessarily mean a person meets the criteria for social anxiety disorder.
People vary in how shy or outgoing they are, depending on where they are, who they are with and how comfortable they feel in the situation. This is particularly true for children, who sometimes appear reserved and shy with strangers and peers, and outgoing with known and trusted adults.
Individual differences in temperament, personality traits, early childhood experiences, family upbringing and environment, and parenting style, can also influence the extent to which people feel shy across social situations.
Not all shy children go on to develop social anxiety. 249 Anurak/Shutterstock However, people with social anxiety have overwhelming fears about embarrassing themselves or being negatively judged by others; they experience these fears consistently and across multiple social situations.
The intensity of this fear or anxiety often leads people to avoid situations. If avoiding a situation is not possible, they may engage in safety behaviours, such as looking at their phone, wearing sunglasses or rehearsing conversation topics.
The effect social anxiety can have on a person’s life can be far-reaching. It may include low self-esteem, breakdown of friendships or romantic relationships, difficulties pursuing and progressing in a career, and dropping out of study.
The impact this has on a person’s ability to lead a meaningful and fulfilling life, and the distress this causes, differentiates social anxiety from shyness.
Children can show similar signs or symptoms of social anxiety to adults. But they may also feel upset and teary, irritable, have temper tantrums, cling to their parents, or refuse to speak in certain situations.
If left untreated, social anxiety can set children and young people up for a future of missed opportunities, so early intervention is key. With professional and parental support, patience and guidance, children can be taught strategies to overcome social anxiety.
Why does the distinction matter?
Social anxiety disorder is a mental health condition that persists for people who do not receive adequate support or treatment.
Without treatment, it can lead to difficulties in education and at work, and in developing meaningful relationships.
Receiving a diagnosis of social anxiety disorder can be validating for some people as it recognises the level of distress and that its impact is more intense than shyness.
A diagnosis can also be an important first step in accessing appropriate, evidence-based treatment.
Different people have different support needs. However, clinical practice guidelines recommend cognitive-behavioural therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that teaches people practical coping skills). This is often used with exposure therapy (a kind of psychological therapy that helps people face their fears by breaking them down into a series of step-by-step activities). This combination is effective in-person, online and in brief treatments.
Treatment is available online as well as in-person. ImYanis/Shutterstock For more support or further reading
Online resources about social anxiety include:
- This Way Up’s online program for managing excessive shyness and fear of social situations
- Beyond Blue’s resources on social anxiety
- a guide to looking after yourself if you have social anxiety, from the Western Australian health department
- social anxiety online program for children and teens from the University of Queensland
- inroads, a self-guided online program for young adults who drink alcohol to manage their anxiety.
We thank the Black Dog Institute Lived Experience Advisory Network members for providing feedback and input for this article and our research.
Kayla Steele, Postdoctoral research fellow and clinical psychologist, UNSW Sydney and Jill Newby, Professor, NHMRC Emerging Leader & Clinical Psychologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
To Nap Or Not To Nap; That Is The Question
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Is it good to nap in the afternoon, or better to get the famous 7 to 9 hours at night and leave it at that? I’m worried that daytime napping to make up for a shorter night’s sleep will just perpetuate and worsen it in the long run, is there a categorical answer here?❞
Generally considered best is indeed the 7–9 hours at night (yes, including at older ages):
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
…and sleep efficiency does matter too:
Why 7 Hours Sleep Is Not Enough
…which in turn, is influenced by factors other than just length and depth:
The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
However! Knowing what is best in theory does not help at all if it’s unattainable in practice. So, if you’re not getting a good night’s sleep (and we’ll assume you’re already practising good sleep hygiene; fresh bedding, lights-off by a certain time, no alcohol or caffeine before bed, that kind of thing), then a first port-of-call may be sleep remedies:
Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors
If even those don’t work, then napping is now likely your best back-up option. But, napping done incorrectly can indeed cause as many problems as it solves. There’s a difference between:
- “I napped and now I have energy again” and you continue with your day
- “Darkness took me, and I strayed out of thought and time. Stars wheeled overhead, and every day was as long as the life age of the earth—but it was not the end.” and now you’re not sure whether it’s day or night, whose house you’re in, or whether you’ve been drugged.
These two very common napping experiences are influenced by factors that we can control:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
If you still prefer to not risk napping but do need at least some kind of refreshment that’s actually a refreshment and not just taking stimulants, then you might consider this practice (from yoga nidra) that gives some of the same benefits of sleep, without actually sleeping:
Non-Sleep Deep Rest: A Neurobiologist’s Insights
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Robert F. Kennedy Jr says vitamin A protects you from deadly measles. Here’s what the study he cites actually says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Robert F. Kennedy Jr, who oversees the health of more than 340 million Americans, says vitamin A can prevent the worst effects of measles rather than urging more people to get vaccinated.
In an opinion piece for Fox News, the US health secretary said he was “deeply concerned” about the current measles outbreak in Texas. However, he said the decision to vaccinate was a “personal one” and something for parents to discuss with their health-care provider.
Kennedy mentioned updated advice from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) to treat measles with vitamin A. He also cited a study he said shows vitamin A can reduce the risk of dying from measles.
Here’s what the vitamin A study actually says and why public health officials are so concerned about Kennedy’s latest statement.
RobsPhoto/Shutterstock Why is a measles outbreak so worrying?
Measles is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus. It spreads easily including when an infected person breathes, coughs or sneezes.
Measles initially infects the respiratory tract and then the virus spreads throughout the body. Symptoms include a high fever, cough, red eyes, runny nose and a rash all over the body.
Measles can also be severe, can cause complications including blindness and swelling of the brain, and can be fatal. Measles can affect anyone but is most common in children.
The Texan health department has confirmed 150-plus cases of measles and one death of an unvaccinated child during the current outbreak. While this is by far the largest measles outbreak in the US in 2025, the CDC has reported smaller outbreaks in several other states so far this year.
Why vitamin A?
Vitamin A is essential for our overall health. It has many roles in the body, from supporting our growth and reproduction, to making sure we have healthy vision, skin and immune function.
Foods rich in vitamin A or related molecules include orange, yellow and red coloured fruits and vegetables, green leafy vegetables, as well as dairy, egg, fish and meat. You can take it as a supplement.
Vitamin A can also be used therapeutically. In other words, doctors may prescribe vitamin A to treat a deficiency. Vitamin A deficiency has long been associated with more severe cases of infectious disease, including measles. Vitamin A boosts immune cells and strengthens the respiratory tract lining, which is the body’s first defence against infections.
Because of this, the CDC has recently said vitamin A can also be prescribed as part of treatment for children with severe measles – such as those in hospital – under doctor supervision.
One key message from the CDC’s advice is that people are already sick enough with measles to be in hospital. They’re not taking vitamin A to prevent catching measles in the first place.
The other key message is vitamin A is taken under medical supervision, under specific circumstances, where patients can be closely monitored to prevent toxicity from high doses.
Vitamin A toxicity can cause birth defects and increase the risk of fractures in elderly people. Vitamin A and beta-carotene (which the body turns into vitamin A) from supplements may also increase your risk of cancer, especially if you smoke.
Taking too much vitamin A can lead to toxicity and cause birth defects. ChameleonsEye/Shutterstock How about the study Kennedy cites?
Kennedy cites and links to a 2010 study, a type known as a systematic review and meta-analysis. Researchers reviewed and analysed existing studies, which included ones that looked at the effectiveness of vitamin A in preventing measles deaths.
They found three studies that looked at vitamin A treatment by specific dose. There were different doses depending on the age of the children, measured in IU (international units). Having two doses of vitamin A (200,000IU for children over one year of age or 100,000IU for infants below one year) reduced mortality by 62% compared to children who did not have vitamin A.
The 2010 study did not show vitamin A reduced your risk of getting measles from another infected person. To my knowledge no study has shown this.
To be fair, Kennedy did not say that vitamin A stops you from catching measles from another infected person. Instead, he used the following vague statement:
Studies have found that vitamin A can dramatically reduce measles mortality.
It’s easy to see how a reader could misinterpret this as “take vitamin A if you want to avoid dying from measles”.
We know what works – vaccines
The World Health Organization recommends all children receive two doses of measles vaccine.
The CDC states two doses of the measles vaccine (measles-mumps-rubella or MMR vaccine) is 97% effective against getting measles. This means out of every 100 people who are vaccinated only three will get it, and this will be a milder form.
But these facts were missing from Kennedy’s statement. Should we be surprised? Kennedy is well known for his vaccine sceptism and for undermining vaccination efforts, including for the measles vaccine.
As Sue Kressly, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, told the Washington Post:
relying on vitamin A instead of the vaccine is not only dangerous and ineffective […] it puts children at serious risk.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Art of Being Unflappable (Tricks For Daily Life)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Art of Being Unflappable
From Stoicism to CBT, thinkers through the ages have sought the unflappable life.
Today, in true 10almonds fashion, we’re going to distil it down to some concentrated essentials that we can all apply in our daily lives:
Most Common/Impactful Cognitive Distortions To Catch (And Thus Avoid)
These are like the rhetorical fallacies with which you might be familiar (ad hominem, no true Scotsman, begging the question, tu quoque, straw man, etc), but are about what goes on between your own ears, pertaining to your own life.
If we learn about them and how to recognize them, however, we can catch them before they sabotage us, and remain “unflappable” in situations that could otherwise turn disastrous.
Let’s take a look at a few:
Catastrophizing / Crystal Ball
- Distortion: not just blowing something out of proportion, but taking an idea and running with it to its worst possible conclusion. For example, we cook one meal that’s a “miss” and conclude we are a terrible cook, and in fact for this reason a terrible housewife/mother/friend/etc, and for this reason everyone will probably abandon us and would be right to do so
- Reality: by tomorrow, you’ll probably be the only one who even remembers it happened
Mind Reading
- Distortion: attributing motivations that may or may not be there, and making assumptions about other people’s thoughts/feelings. An example is the joke about two partners’ diary entries; one is long and full of feelings about how the other is surely dissatisfied in their marriage, has been acting “off” with them all day, is closed and distant, probably wants to divorce, may be having an affair and is wondering which way to jump, and/or is just wondering how to break the news—the other partner’s diary entry is short, and reads “motorcycle won’t start; can’t figure out why”
- Reality: sometimes, asking open questions is better than guessing, and much better than assuming!
All-or-Nothing Thinking / Disqualifying the Positive / Magnifying the Negative
- Distortion: having a negative bias that not only finds a cloud in every silver lining, but stretches it out so that it’s all that we can see. In a relationship, this might mean that one argument makes us feel like our relationship is nothing but strife. In life in general, it may lead us to feel like we are “naturally unlucky”.
- Reality: those negative things wouldn’t even register as negative to us if there weren’t a commensurate positive we’ve experienced to hold them in contrast against. So, find and remember that positive too.
For brevity, we put a spotlight on (and in some cases, clumped together) the ones we think have the most bang-for-buck to know about, but there are many more.
So for the curious, here’s some further reading:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Brazil Nuts vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Brazil nuts to cashews, we picked the cashews.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, Brazil nuts have more fat and fiber, while cashews have more carbs and protein. So, it really comes down to what you want to prioritize. We’d generally consider fiber the tie-breaker, making this category a subjective marginal win for Brazil nuts—and especially marginal since they are both low glycemic index foods in any case.
When it comes to vitamins, Brazil nuts have more of vitamins C, E, and choline, while cashews have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and K, so while both are great, this category is a clear by-the-numbers win for cashews.
The category of minerals is an interesting one. Brazil nuts have more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and selenium, while cashews have more copper, iron, manganese, and zinc. That would be a 4:4 tie, but let’s take a closer look at those selenium levels:
- A cup of cashews contains 109% of the RDA of selenium. Your hair will be luscious and shiny.
- A cup of Brazil nuts contains 10,456% of the RDA of selenium. This is way past the point of selenium toxicity, and your (luscious, shiny) hair will fall out.
For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
We consider that a point against Brazil nuts.
Adding up the section makes for a win for cashews. Of course, enjoy Brazil nuts too if you will, but in careful moderation please!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Pegan Diet – by Dr. Mark Hyman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First things first: the title of the book is a little misleading. “Pegan” is a portmanteau of “paleo” and “vegan”, making it sound like it will be appropriate for both of those dietary practices. Instead:
- Dr. Hyman offers advice about eating the right grains and legumes (inappropriate for a paleo diet)
- He also offers such advice as “be picky about poultry, eggs, and fish”, and “avoid dairy—mostly” (inappropriate for a vegan diet).
So, since his paleo vegan diet is neither paleo nor vegan, what actually is it?
It’s a whole foods diet that encourages the enjoyment of a lot of plants, and discretion with regard to the quality of animal products.
It’s a very respectable approach to eating, even if it didn’t live up to the title.
The style is somewhat sensationalist, while nevertheless including plenty of actual science in there too—so the content is good, even if the presentation isn’t what this reviewer would prefer.
He has recipes; they can be a little fancy (e.g. “matcha poppy bread with rose water glaze”) which may not be to everyone’s taste, but they are healthy.
Bottom line: the content is good; the style you may love or hate, and again, don’t be misled by the title.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: