Best Salt for Neti Pots?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❓ Q&A With 10almonds Subscribers!
Q: What kind of salt is best for neti pots?
A: Non-iodised salt is usually recommended, but really, any human-safe salt is fine. By this we mean for example:
- Sodium chloride (like most kitchen salts),
- Potassium chloride (as found in “reduced sodium” kitchen salts), or
- Magnesium sulfate (also known as epsom salts).
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Three Critical Kitchen Prescriptions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Three Critical Kitchen Prescriptions
This is Dr. Saliha Mahmood-Ahmed. She’s a medical doctor—specifically, a gastroenterologist. She’s also a chef, and winner of the BBC’s MasterChef competition. So, from her gastroenterology day-job and her culinary calling, she has some expert insights to share on eating well!
❝Food and medicine are inextricably linked to one another, and it is an honour to be a doctor who specialises in digestive health and can both cook, and teach others to cook❞
~ Dr. Saliha Mahmood-Ahmed, after winning MasterChef and being asked if she’d quit medicine to be a full-time chef
Dr. Mahmood-Ahmed’s 3 “Kitchen Prescriptions”
They are:
- Cook, cook, cook
- Feed your gut bugs
- Do not diet
Let’s take a look at each of those…
Cook, cook, cook
We’re the only species on Earth that cooks food. An easy knee-jerk response might be to think maybe we shouldn’t, then, but… We’ve been doing it for at least 30,000 years, which is about 1,500 generations, while a mere 100 generations is generally sufficient for small evolutionary changes. So, we’ve evolved this way now.
More importantly in this context: we, ourselves, should cook our own food, at least per household.
Not ready meals; we haven’t evolved for those (yet! Give it another few hundred generations maybe)
Feed your gut bugs
The friendly ones. Enjoy prebiotics, probiotics, and plenty of fiber—and then be mindful of what else you do or don’t eat. Feeding the friendly bacteria while starving the unfriendly ones may seem like a tricky task, but it actually can be quite easily understood and implemented. We did a main feature about this a few weeks ago:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
Do not diet
Dr. Mahmood-Ahmed is a strong critic of calorie-counting as a weight-loss strategy:
Rather than focusing on the number of calories consumed, try focusing on introducing enough variety of food into your daily diet, and on fostering good microbial diversity within your gut.
It’s a conceptual shift from restrictive weight loss, to prescriptive adding of things to one’s diet, with fostering diversity of microbiota as a top priority.
This, too, she recommends be undertaken gently, though—making small, piecemeal, but sustainable improvements. Nobody can reasonably incorporate, say, 30 new fruits and vegetables into one’s diet in a week; it’s unrealistic, and more importantly, it’s unsustainable.
Instead, consider just adding one new fruit or vegetable per shopping trip!
Share This Post
-
Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
- Myth: you can’t get too much calcium!
- Myth: you must get as much vitamin D as possible!
Let’s tackle calcium first:
❝Calcium is good for you! You need more calcium for your bones! Be careful you don’t get calcium-deficient!❞
Contingently, those comments seem reasonable. Contingently on you not already having the right amount of calcium. Most people know what happens in the case of too little calcium: brittle bones, osteoporosis, and so forth.
But what about too much?
Hypercalcemia
Having too much calcium—or “hypercalcemia”— can lead to problems with…
- Groans: gastrointestinal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis.
- Bones: bone-related pains. Osteoporosis, osteomalacia, arthritis and pathological fractures.
- Stones: kidney stones causing pain.
- Moans: refers to fatigue and malaise.
- Thrones: polyuria, polydipsia, and constipation
- Psychic overtones: lethargy, confusion, depression, and memory loss.
(mnemonic courtesy of Sadiq et al, 2022)
What causes this, and how do we avoid it? Is it just dietary?
It’s mostly not dietary!
Overconsumption of calcium is certainly possible, but not common unless one has an extreme diet and/or over-supplementation. However…
Too much vitamin D
Again with “too much of a good thing”! While keeping good levels of vitamin D is, obviously, good, overdoing it (including commonly prescribed super-therapeutic doses of vitamin D) can lead to hypercalcemia.
This happens because vitamin D triggers calcium absorption into the gut, and acts as gatekeeper to the bloodstream.
Normally, the body only absorbs 10–20% of the calcium we consume, and that’s all well and good. But with overly high vitamin D levels, the other 80–90% can be waved on through, and that is very much Not Good™.
See for yourself:
- Hypercalcemia of Malignancy: An Update on Pathogenesis and Management
- Vitamin D-Mediated Hypercalcemia: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
How much is too much?
The United States’ Office of Dietary Supplements defines 4000 IU (100μg) as a high daily dose of vitamin D, and recommends 600 IU (15μg) as a daily dose, or 800 IU (20μg) if aged over 70.
See for yourself: Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Health Professionals ← there’s quite a bit of extra info there too
Share This Post
-
Mosquitoes can spread the flesh-eating Buruli ulcer. Here’s how you can protect yourself
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Each year, more and more Victorians become sick with a flesh-eating bacteria known as Buruli ulcer. Last year, 363 people presented with the infection, the highest number since 2004.
But it has been unclear exactly how it spreads, until now. New research shows mosquitoes are infected from biting possums that carry the bacteria. Mozzies spread it to humans through their bite.
What is Buruli ulcer?
Buruli ulcer, also known as Bairnsdale ulcer, is a skin infection caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium ulcerans.
It starts off like a small mosquito bite and over many months, slowly develops into an ulcer, with extensive destruction of the underlying tissue.
While often painless initially, the infection can become very serious. If left untreated, the ulcer can continue to enlarge. This is where it gets its “flesh-eating” name.
Thankfully, it’s treatable. A six to eight week course of specific antibiotics is an effective treatment, sometimes supported with surgery to remove the infected tissue.
Where can you catch it?
The World Health Organization considers Buruli ulcer a neglected tropical skin disease. Cases have been reported across 33 countries, primarily in west and central Africa.
However, since the early 2000s, Buruli ulcer has also been increasingly recorded in coastal Victoria, including suburbs around Melbourne and Geelong.
Scientists have long known Australian native possums were partly responsible for its spread, and suspected mosquitoes also played a role in the increase in cases. New research confirms this.
Our efforts to ‘beat Buruli’
Confirming the role of insects in outbreaks of an infectious disease is achieved by building up corroborating, independent evidence.
In this new research, published in Nature Microbiology, the team (including co-authors Tim Stinear, Stacey Lynch and Peter Mee) conducted extensive surveys across a 350 km² area of Victoria.
We collected mosquitoes and analysed the specimens to determine whether they were carrying the pathogen, and links to infected possums and people. It was like contact tracing for mosquitoes.
Aedes notoscriptus was the mosquito identified as carrying the bacteria that caused Buruli ulcer.
Cameron Webb (NSW Health Pathology)Molecular testing of the mosquito specimens showed that of the two most abundant mosquito species, only Aedes notoscriptus (a widespread species commonly known as the Australian backyard mosquito) was positive for Mycobacterium ulcerans.
We then used genomic tests to show the bacteria found on these mosquitoes matched the bacteria in possum poo and humans with Buruli ulcer.
We further analysed mosquito specimens that contained blood to show Aedes notoscriptus was feeding on both possums and humans.
To then link everything together, geospatial analysis revealed the areas where human Buruli ulcer cases occur overlap with areas where both mosquitoes and possums that harbour Mycobacterium ulcerans are active.
Stop its spread by stopping mozzies breeding
The mosquito in this study primarily responsible for the bacteria’s spread is Aedes notoscriptus, a mosquito that lays its eggs around water in containers in backyard habitats.
Controlling “backyard” mosquitoes is a critical part of reducing the risk of many global mosquito-borne disease, especially dengue and now Buruli ulcer.
You can reduce places where water collects after rainfall, such as potted plant saucers, blocked gutters and drains, unscreened rainwater tanks, and a wide range of plastic buckets and other containers. These should all be either emptied at least weekly or, better yet, thrown away or placed under cover.
Mosquitoes can lay eggs in a wide range of water-filled items in the backyard.
Cameron Webb (NSW Health Pathology)There is a role for insecticides too. While residual insecticides applied to surfaces around the house and garden will reduce mosquito populations, they can also impact other, beneficial, insects. Judicious use of such sprays is recommended. But there are ecological safe insecticides that can be applied to water-filled containers (such as ornamental ponds, fountains, stormwater pits and so on).
Recent research also indicates new mosquito-control approaches that use mosquitoes themselves to spread insecticides may soon be available.
How to protect yourself from bites
The first line of defence will remain personal protection measures against mosquito bites.
Covering up with loose fitted long sleeved shirts, long pants, and covered shoes will provide physical protection from mosquitoes.
Applying topical insect repellent to all exposed areas of skin has been proven to provide safe and effective protection from mosquito bites. Repellents should include diethytolumide (DEET), picaridin or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
While the rise in Buruli ulcer is a significant health concern, so too are many other mosquito-borne diseases. The steps to avoid mosquito bites and exposure to Mycobacteriam ulcerans will also protect against viruses such as Ross River, Barmah Forest, Japanese encephalitis, and Murray Valley encephalitis.
Cameron Webb, Clinical Associate Professor and Principal Hospital Scientist, University of Sydney; Peter Mee, Adjunct Associate Lecturer, School of Applied Systems Biology, La Trobe University; Stacey Lynch, Team Leader- Mammalian infection disease research, CSIRO, and Tim Stinear, Professor of Microbiology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saturated Fat: What’s The Truth?
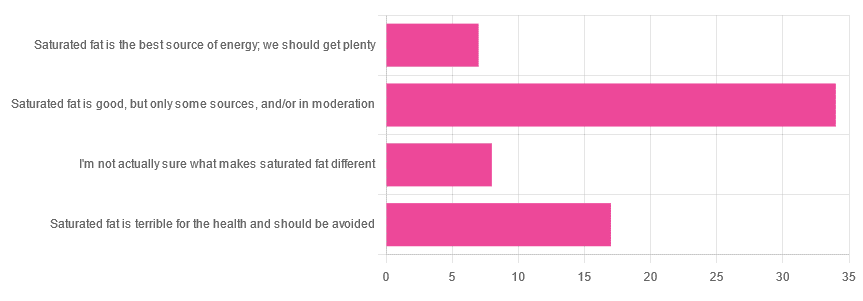
We asked you for your health-related opinion of saturated fat, and got the above-pictured, below-described, set of results.
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
- This is an easy one to vote for, because of the “and/or in moderation” part, which tends to be a “safe bet” for most things.
- Next most popular was “Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided”
- About half as many recorded votes were for “I’m not actually sure what makes saturated fat different”, which is a very laudable option to click. Admitting when we don’t know things (and none of us know everything) is a very good first step to learning about them!
- Fewest recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty”.
So, what does the science say?
First, a bit of physics, chemistry, and biology
You may be wondering what, exactly, saturated fats are “saturated” with. That’s a fair question, so…
All fats have a molecular structure made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Saturated fats are saturated with hydrogen, and thus have only single bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated fats have at least one double-bond between carbon atoms).
The observable effect this has on them, is that fats that are saturated with hydrogen are solid at room temperature, whereas unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. Their different properties also make for different interactions inside the human body, including how likely or not they are to (for example) clog arteries.
See also: Could fat in your bloodstream cause blood clots?
Saturated fat is the best source of energy; we should get plenty: True or False?
False, in any reasonable interpretation, anyway. That is to say, if your idea of “plenty” is under 13g (e.g: two tablespoons of butter, and no saturated fat from other sources, e.g. meat) per day, then yes, by all means feel free to eat plenty. More than that, though, and you might want to consider trimming it down a bit.
The American Heart Association has this to say:
❝When you hear about the latest “diet of the day” or a new or odd-sounding theory about food, consider the source.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fats, which are found in butter, cheese, red meat and other animal-based foods, and tropical oils.
Decades of sound science has proven it can raise your “bad” cholesterol and put you at higher risk for heart disease.❞
Source: The American Heart Association Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations on Saturated Fat
The British Heart Foundation has a similar statement:
❝Despite what you read in the media, our advice is clear: replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats and avoid trans fats. Saturated fat is the kind of fat found in butter, lard, ghee, fatty meats and cheese. This is linked to an increased risk of heart and circulatory disease❞
Source: British Heart Foundation: What does fat do and what is saturated fat?
As for the World Health Organization:
❝1. WHO strongly recommends that adults and children reduce saturated fatty acid intake to 10% of total energy intake
2. WHO suggests further reducing saturated fatty acid intake to less than 10% of total energy intake
3. WHO strongly recommends replacing saturated fatty acids in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids; monounsaturated fatty acids from plant sources; or carbohydrates from foods containing naturally occurring dietary fibre, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses.❞
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
Please note, organizations such as the AHA, the BHF, and the WHO are not trying to sell us anything, and just would like us to not die of heart disease, the world’s #1 killer.
As for “the best source of energy”…
We evolved to eat (much like our nearest primate cousins) a diet consisting mostly of fruits and other edible plants, with a small supplementary amount of animal-source protein and fats.
That’s not to say that because we evolved that way we have to eat that way—we are versatile omnivores. But for example, we are certainly not complete carnivores, and would quickly sicken and die if we tried to live on only meat and animal fat (we need more fiber, more carbohydrates, and many micronutrients that we usually get from plants)
The closest that humans tend to come to doing such is the ketogenic diet, which focuses on a high fat, low carbohydrate imbalance, to promote ketosis, in which the body burns fat for energy.
The ketogenic diet does work, and/but can cause a lot of health problems if a lot of care is not taken to avoid them.
See for example: 7 Keto Risks To Keep In Mind
Saturated fat is terrible for the health and should be avoided: True or False?
False, if we are talking about “completely”.
Firstly, it’s practically impossible to cut out all saturated fats, given that most dietary sources of fat are a mix of saturated, unsaturated (mono- and poly-), and trans fats (which are by far the worst, but beyond the scope of today’s main feature).
Secondly, a lot of research has been conducted and found insignificant or inconclusive results, in cases where saturated fat intake was already within acceptable levels (per the recommendations we mentioned earlier), and then cut down further.
Rather than fill up the newsletter with individual studies of this kind here’s a high-quality research review, looking at 19 meta-analyses, each of those meta-analyses having looked at many studies:
Dietary saturated fat and heart disease: a narrative review
Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation: True or False?
True! The moderation part is easy to guess, so let’s take a look at the “but only some sources”.
We were not able to find any convincing science to argue for health-based reasons to favor plant- or animal-sourced saturated fat. However…
Not all saturated fats are created equal (there are many kinds), and also many of the foods containing them have additional nutrients, or harmful compounds, that make a big difference to overall health, when compared gram-for-gram in terms of containing the same amount of saturated fat.
For example:
- Palm oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of palmitic acid, which raises LDL (“bad” cholesterol) without affecting HDL (“good” cholesterol), thus having an overall heart-harmful effect.
- Most animal fats contain a disproportionate amount of stearic acid, which has statistically insignificant effects on LDL and HDL levels, and thus is broadly considered “heart neutral” (in moderation!)
- Coconut oil’s saturated fat contains a disproportionate amount of lauric acid, which raises total cholesterol, but mostly HDL without affecting LDL, thus having an overall heart-beneficial effect (in moderation!)
Do you know what’s in the food you eat?
Test your knowledge with the BHF’s saturated fat quiz!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Most recorded votes were for “Saturated fat is good, but only some sources, and/or in moderation”
-
Should Men Over 50 Get PSA?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Loved the information on prostate cancer. Do recommend your readers get a PSA or equivalent test annually for over 50 yr old men.❞
(This is about: Prostate Health: What You Should Know)
Yep, or best yet, the much more accurate PSE test! But if PSA test is what’s available, it’s a lot better than nothing. And, much as it’s rarely the highlight of anyone’s day, a prostate exam by a suitably qualified professional is also a good idea.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dandelion Greens vs Collard Greens – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dandelion greens to collard greens, we picked the dandelion greens.
Why?
Collard greens are great—they even beat kale in one of our previous “This or That” articles!—but dandelion greens simply pack more of a nutritional punch:
In terms of macros, dandelions have slightly more carbs (+3g/100g) for the same protein and fiber, and/but the glycemic index is equal (zero), so those carbs aren’t anything to worry about. Nobody is getting metabolic disease by getting their carbs from dandelion leaves. In short, we’re calling it a tie on macros, though it could nominally swing either way if you have an opinion (one way or the other) about the extra 3g of carbs.
In the category of vitamins, things are more exciting: dandelion greens have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, C, E, and K, while collard greens have more vitamin B5. An easy and clear win for dandelions.
Looking at the minerals tells a similar story; dandelion greens have much more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while collard greens have slightly more manganese. Another overwhelming win for dandelions.
One more category, polyphenols. We’d be here until next week if we listed all the polyphenols that dandelion greens have, but suffice it to say, dandelion greens have a total of 385.55mg/100g polyphenols, while collard greens have a total of 0.08mg/100g polyphenols. Grabbing a calculator, we see that this means dandelions have more than 4819x the polyphenol content that collard greens do.
So, “eat leafy greens” is great advice, but they are definitely not all created equal!
Let us take this moment to exhort: if you have any space at home where you can grow dandelions, grow them!
Not only are they great for pollinators, but also they beat the collard greens that beat kale. And you can have as much as you want, for free, right there.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Collard Greens vs Kale – Which is Healthier?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: