Berberine For Metabolic Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Berberine Nature’s Ozempic/Wegovy?
Berberine is a compound found in many plants. Of which, some of them are variations of the barberry, hence the name.
It’s been popular this past couple of years, mostly for weight loss. In and of itself, something being good for weight loss doesn’t mean it’s good for the health (just ask diarrhoea, or cancer).
Happily, berberine’s mechanisms of action appear to be good for metabolic health, including:
- Reduced fasting blood sugar levels
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Reduced LDL and triglycerides
- Increased HDL levels
So, what does the science say?
It’s (mostly!) not nature’s Wegovy/Ozempic
It’s had that title in a number of sensationalist headlines (and a current TikTok trend, apparently), but while both berberine and the popular weight-loss drugs Wegovy/Ozempic act in part on insulin metabolism, they mostly do so by completely different mechanisms.
Wegovy and Ozempic are GLP-1 agonists, which mean they augment the action of glucagon-like-peptide 1, which increases insulin release, decreases glucagon release, and promotes a more lasting feeling of fullness.
Berberine works mostly by other means, not all of which are understood. But, we know that it activates AMP-activated protein kinase, and on the flipside, inhibits proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9.
In less arcane words: it boosts some enzymes and inhibits others.
Each of these boosts/inhibitions has a positive effect on metabolic health.
However, it does also have a slight GLP-1 agonist effect too! Bacteria in the gut can decompose and metabolize berberine into dihydroberberine, thus preventing the absorption of disaccharides in the intestinal tract, and increasing GLP-1 levels.
See: Effects of Berberine on the Gastrointestinal Microbiota
Does it work for weight loss?
Yes, simply put. And if we’re going to put it head-to-head with Wegovy/Ozempic, it works about half as well. Which sounds like a criticism, but for a substance that’s a lot safer (and cheaper, and easier—if we like capsules over injections) and has fewer side effects.
- Weight Loss Outcomes Associated With Semaglutide Treatment for Patients With Overweight or Obesity ← Wegovy and Ozempic are both brand names of semaglutide
- The effect of berberine supplementation on obesity parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials ← a good recent research review giving clear data on many factors
- Lipid-lowering effect of berberine in human subjects and rats ← this is an older study, 2012, but it gives 3-month weight loss percentages rather than discrete values in the abstract, so it’s easier to compare to the semaglutide study without grabbing a calculator
❝But more interestingly, the treatment significantly reduced blood lipid levels (23% decrease of triglyceride and 12.2% decrease of cholesterol levels) in human subjects.
However, there was interestingly, an increase in calcitriol levels seen in all human subjects following berberine treatment (mean 59.5% increase)
Collectively, this study demonstrates that berberine is a potent lipid-lowering compound with a moderate weight loss effect, and may have a possible potential role in osteoporosis treatment/prevention.❞
(click through to read in full)
Is it safe?
It appears to be, with one special caveat: remember that paper about the effects of berberine on the gastrointestinal microbiota? It also has some antimicrobial effects, so you could do harm there if not careful. It’s recommended to give it a break every couple of months, to be sure of allowing your gut microbiota to not get too depleted.
Also, as with anything you might take that’s new, always consult your doctor/pharmacist in case of contraindications based on medications you are taking.
Where can I get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Menopause, & When Not To Let Your Guard Down
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Jessica Shepherd, a physician Fellow of the American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, CEO at Sanctum Medical & Wellness, and CMO at Hers.
She’s most well-known for her expertise in the field of the menopause. So, what does she want us to know?
Untreated menopause is more serious than most people think
Beyond the famous hot flashes, there’s also the increased osteoporosis risk, which is more well-known at least amongst the health-conscious, but oft-neglected is the increased cardiovascular disease risk:
What Menopause Does To The Heart
…and, which a lot of Dr. Shepherd’s work focuses on, it also increases dementia risk; she cites that 60–80% of dementia cases are women, and it’s also established that it progresses more quickly in women than men too, and this is associated with lower estrogen levels (not a problem for men, because testosterone does it for them) which had previously been a protective factor, but in untreated menopause, was no longer there to help:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Treated menopause is safer than many people think
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study, conducted in the 90s and published in 2002, linked HRT to breast cancer, causing fear, but it turned out that this was quite bad science in several ways and the reporting was even worse (even the flawed data did not really support the conclusion, much less the headlines); it was since broadly refuted (and in fact, it can be a protective factor, depending on the HRT regimen), but fearmongering headlines made it to mainstream news, whereas “oopsies, never mind, we take that back” didn’t.
The short version of the current state of the science is: breast cancer risk varies depending on age, HRT type, and dosage; some kinds of HRT can increase the risk marginally in those older than 60, but absolute risk is low compared to placebo, and taking estrogen alone can reduce risk at any age in the event of not having a uterus (almost always because of having had a hysterectomy; as a quirk, it is possible to be born without, though).
It’s worth noting that even in the cases where HRT marginally increased the risk of breast cancer, it significantly decreased the risk of cancers in total, as well fractures and all-cause-mortality compared to the placebo group.
In other words, it might be worth having a 0.12% risk of breast cancer, to avoid the >30% risk of osteoporosis, which can ultimately be just as fatal (without even looking at the other things the HRT is protective against).
However! In the case of those who already have (or have had) breast cancer, increasing estrogen levels can indeed make that worse/return, and it becomes more complicated in cases where you haven’t had it, but there is a family history of it, or you otherwise know you have the gene for it.
You can read more about HRT and breast cancer risk (increases and decreases) here:
…and about the same with regard to HMT, here:
The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
Lifestyle matters, and continues to matter
Menopause often receives the following attention from people:
- Perimenopause: “Is this menopause?”
- Menopause: “Ok, choices to make about HRT or not, plus I should watch out for osteoporosis”
- Postmenopause: “Yay, that’s behind me now, back to the new normal”
The reality, Dr. Shepherd advises, is that “postmenopause” is a misnomer because if it’s not being treated, then the changes are continuing to occur in your body.
This is a simple factor of physiology; your body is always rebuilding itself, will never stop until you die, and in untreated menopause+postmenopause, it’s now doing it without much estrogen.
So, you can’t let your guard down!
Thus, she recommends: focus on maintaining muscle mass, bone health, and cardiovascular health. If you focus on those things, the rest (including your brain, which is highly dependent on cardiovascular health) will mostly take care of itself.
Because falls and fractures, particularly hip fractures, drastically reduce quality and length of life in older adults, it is vital to avoid those, and try to be sufficiently robust so that if you do go A over T, you won’t injure yourself too badly, because your bones are strong. As a bonus, the same things (especially that muscle mass we talked about) will help you avoid falling in the first place, by improving stability.
See also: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And about falls specifically: Fall Special: Be Robust, Mobile, & Balanced!
Want to know more from Dr. Shepherd?
You might like this book of hers that we reviewed not long back:
Generation M – by Dr. Jessica Shepherd
Take care!
Share This Post
-
80-Year-Olds Share Their Biggest Regrets
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Notwithstanding the title, some of these people are a little younger than 80, but this adds to the interest a little as we see the different regrets / learned wisdoms at different stages of later life!
If we could turn back the time…
There are dozens of life regrets / wishes / retroactive advices shared in this video; here are some highlights:
- “My regret was I had a dysfunctional family and I wish I would have learned not to take responsibility.”
- “In my 30s, when I started drinking very heavily, I wish I hadn’t done that because it escalated to drug abuse.”
- “When my parents were old ages, I was working very hard… I didn’t have time to take care of them, not even spend the time with them. That’s my biggest regret.”
- “Live life to the fullest because none of us have any assurance on how old we’re going to be when we’re going to die.”
- “If I could do it over, I would have called home more and realized what my brother was going through.”
- “Spent a lot of years being concerned about what other people thought of me.”
- “You got to be careful what you say to your children because it means a lot.”
For the rest, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Managing Your Mortality Without Regrets
- How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
- Managing Sibling Relationships In Adult Life
- Family Estrangment & How To Fix It
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why Psyllium Is Healthy Through-And-Through
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Psyllium is the powder of the husk of the seed of the plant Plantago ovata.
It can be taken as a supplement, and/or used in cooking.
What’s special about it?
It is fibrous, and the fiber is largely soluble fiber. It’s a “bulk-forming laxative”, which means that (dosed correctly) it is good against both constipation (because it’s a laxative) and diarrhea (because it’s bulk-forming).
See also, because this is Research Review Monday and we provide papers for everything:
In other words, it will tend things towards being a 3 or 4 on the Bristol Stool Scale ← this is not pretty, but it is informative.
Before the bowels
Because of how it increases the viscosity of substances it finds itself in, psyllium slows stomach-emptying, and thus improves feelings of satiety.
Here’s a study in which taking psyllium before breakfast and lunch resulted in increased satiety between meals, and reduction in food-related cravings:
Satiety effects of psyllium in healthy volunteers
Prebiotic benefits
We can’t digest psyllium, but our gut bacteria can—somewhat! Because they can only digest some of the psyllium fibers, that means the rest will have the stool-softening effect, while we also get the usual in-gut benefits from prebiotic fiber first too:
The Effect of Psyllium Husk on Intestinal Microbiota in Constipated Patients and Healthy Controls
Cholesterol-binding
Psyllium can bind to cholesterol during the digestive process. Why only “can”? Well, if you don’t consume cholesterol (for example, if you are vegan), then there won’t be cholesterol in the digestive tract to bind to (yes, we do need some cholesterol to live, but like most animals, we can synthesize it ourselves).
What this cholesterol-binding action means is that the dietary cholesterol thus bound cannot enter the bloodstream, and is simply excreted instead:
Heart health beyond cholesterol
Psyllium supplementation can also help lower high blood pressure but does not significantly lower already-healthy blood pressure, so it can be particularly good for keeping things in safe ranges:
❝Given the overarching benefits and lack of reported side effects, particularly for hypertensive patients, health care providers and clinicians should consider the use of psyllium supplementation for the treatment or abatement of hypertension, or hypertensive symptoms.❞
Read in full: The effect of psyllium supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials ← you can see the concrete numbers here
Is it safe?
Psyllium is first and foremost a foodstuff, and is considered very safe unless you have an allergy (which is rare, but possible).
However, it is still recommended to start at a low dose and work up, because anything that changes your gut microbiota, even if it changes it for the better, will be easiest if done slowly (or else, you will hear about it from your gut).
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Anti-Cholesterol Cardamom & Pistachio Porridge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This tasty breakfast’s beta-glucan content binds to cholesterol and carries it out of the body; there are lots of other nutritional benefits too!
You will need
- 1 cup coconut milk
- ⅓ cup oats
- 4 tbsp crushed pistachios
- 6 cardamom pods, crushed
- 1 tsp rose water or 4 drops edible rose essential oil
- Optional sweetener: drizzle of honey or maple syrup
- Optional garnishes: rose petals, chopped nuts, dried fruit
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat the coconut milk, adding the oats and crushed cardamom pods. Simmer for 5–10 minutes depending on how cooked you want the oats to be.
2) Stir in the crushed pistachio nuts, as well as the rose water.
3) Serve in a bowl, adding any optional toppings:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s beta-glucan, which is fund abundantly in oats
- Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← coconut can!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing coconut to avocado, we picked the avocado.
Why?
In terms of macros, avocado is lower in carbs and also in net carbs—coconut’s a little higher in fiber, but not enough to make up for the difference in carbs nor, when it comes to glycemic index and insulin index, the impact of coconut’s much higher fat content on insulin responses too. On which note, while coconut’s fats are broadly considered healthy (its impressive saturated fat content is formed of medium-chain triglycerides which, in moderation, are heart-healthy), avocado’s fats are even healthier, being mostly monounsaturated fat with some polyunsaturated (and about 15x less saturated fat). All in all, a fair win for avocado on the macros front, but coconut isn’t bad in moderation.
When it comes to vitamins, avocados are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline. Most of those differences are by very large margins. Coconuts are not higher in any vitamins. A huge, easy, “perfect score” win for avocados.
In the category of minerals, however, it’s coconut’s turn to sweep with more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium—though the margins are mostly not nearly as impressive as avocado’s vitamin margins. Speaking of avocados, they do have more potassium than coconuts do, but the margin isn’t very large. A compelling win for coconut’s mineral content.
Adding up the sections, we get to a very credible win for avocados, but coconuts are also very respectable. So, as ever, enjoy both (although we do recommend exercising moderation in the case of coconuts, mainly because of the saturated fat content), and if you’re choosing between them for some purpose, then avocado will generally be the best option.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← defying Betteridge’s Law here!
- Avocado, Coconut & Lime Crumble Pots ← if you do want to enjoy both, here’s a fabulous way to do so in style
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
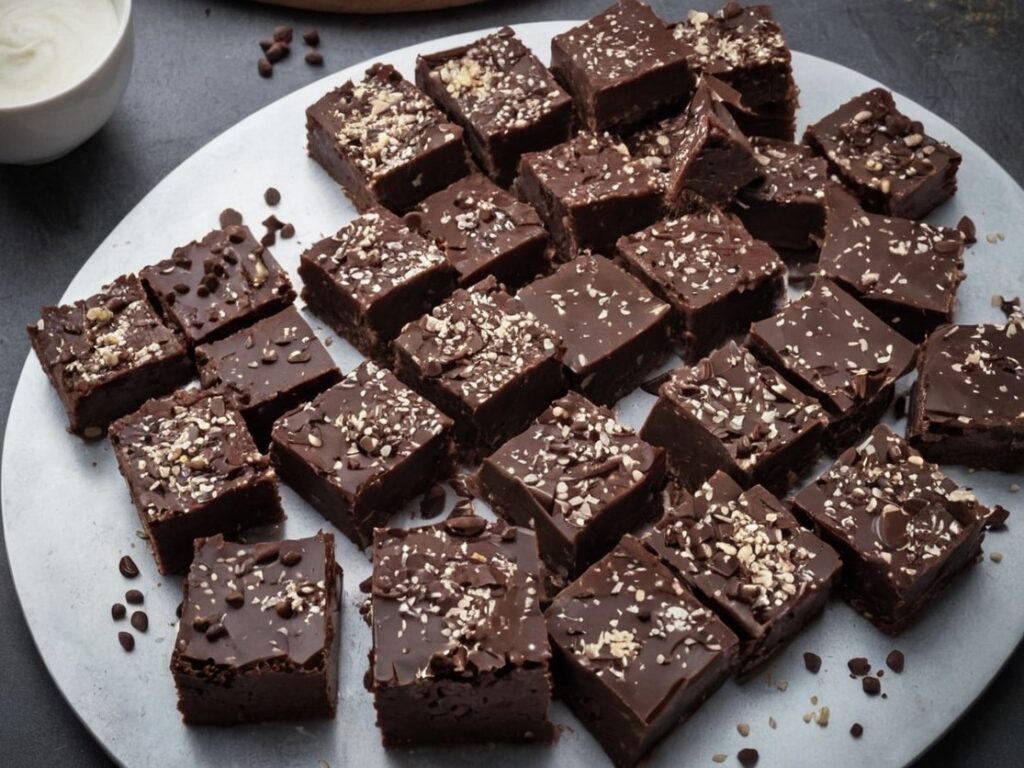
Sesame Chocolate Fudge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’d like a sweet treat without skyrocketing your blood sugars with, well, rocket fuel… Today’s recipe can help you enjoy a taste of decadence that’s not bad for your blood sugars, and good for your heart and brain.
You will need
- ½ cup sesame seeds
- ¼ cup cocoa powder
- 3 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tbsp coconut oil (plus a little extra for the pan)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Lightly toast the sesame seeds in a pan until golden brown. Remove from the heat and allow to cool.
2) Put them in a food processor, and blend on full speed until they start to form a dough-like mixture. This may take a few minutes, so be patient. We recommend doing it in 30-second sessions with a 30-second rest between them, to avoiding overheating the motor.
3) Add the rest of the ingredients and blend to combine thoroughly—this should go easily now and only take 10 seconds or so, but judge it by eye.
4) Grease an 8″ square baking tin with a little coconut oil, and add the mixture, patting it down to fill the tin, making sure it is well-compressed.
5) Allow to chill in the fridge for 6 hours, until firm.
6) Turn the fudge out onto a chopping board, and cut into the size squares you want. Serve, or store in the fridge until ready to serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tasty Polyphenols For Your Heart & Brain
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: