Becoming a Supple Leopard – by Dr. Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Starrett’s other book, “Built To Move“, and now today we’ll review his more famous book!
Why is this one so famous? It’s popularly considered “the Bible of Cross-Fit”, even though it’s not at all marketed as such, and nor does it talk about Cross Fit directly. But: people who are interested in being fit, fast, strong, mobile, stable, and so forth, tend to invest in this book at some point if they are serious.
The book is big, heavy, and textbook-like. This isn’t a quick light read. This is a “study over the course of a year or more while doing your physiotherapy degree” book. And yet, it’s written for the widest audience, and as such, everything is explained from the ground up, so no prior knowledge is expected.
It does have pictures, which are clear and helpful, though the print version is better for this than the Kindle edition.
The subtitle of the book is no lie; it does indeed cover all those things, deeply and at length, for everything musculoskeletal.
Bottom line: this book will seriously improve your knowledge and understanding of all things body mechanics and related body maintenance. If you care to get/remain fit/strong/mobile/etc, this book is a fine cornerstone for such endeavors.
Click here to check out Becoming A Supple Leopard, and become a supple leopard!*
*Metaphorically. Furry metamorphosis is not a side-effect. Suppleness, however, is on offer. Yes, even for you, dear reader!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Cook’s Anti-Inflammatory Diet & Cookbook – by Dr. Albert Orbinati
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of very many illnesses, and exacerbates almost all the ones it doesn’t cause. So, reducing inflammation is a very good way to stay well in general, reducing one’s risk factors for very many other diseases.
Dr. Orbinati starts by giving advice for adjusting to an anti-inflammatory diet, including advice on trying an elimination diet, if you suspect an undiagnosed allergy/intolerance.
Thereafter, he gives guidance on pantry-stocking—not just what anti-inflammatory foods to include and what inflammatory foods to skip, but also, what food and nutrient pairings are particularly beneficial, like how black pepper and turmeric are both anti-inflammatory by themselves, but the former greatly increases the bioavailability of the latter if consumed together.
The rest of the book—aside from assorted appendices, such as 8 pages of scientific references—is given over to the recipes.
The recipes themselves are, obviously, anti-inflammatory in focus. As one might expect, therefore, most are vegetarian and many are vegan, but we do find many recipes with chicken and fish as well; there’s also some use of eggs and fermented dairy in some of the recipes too.
The book certainly does deliver on its promise of flavorful healthy food; that’s what happens when one includes a lot of herbs and spices in one’s cooking, as well as the fact that many other polyphenol-rich foods are, by nature, tasty in and of themselves.
Bottom line: if you’d like to expand your anti-inflammatory culinary repertoire, this book is a top-tier choice for that.
Click here to check out Healthy Cook’s Anti-Inflammatory Diet & Cookbook, and spice up your kitchen!
Share This Post
-
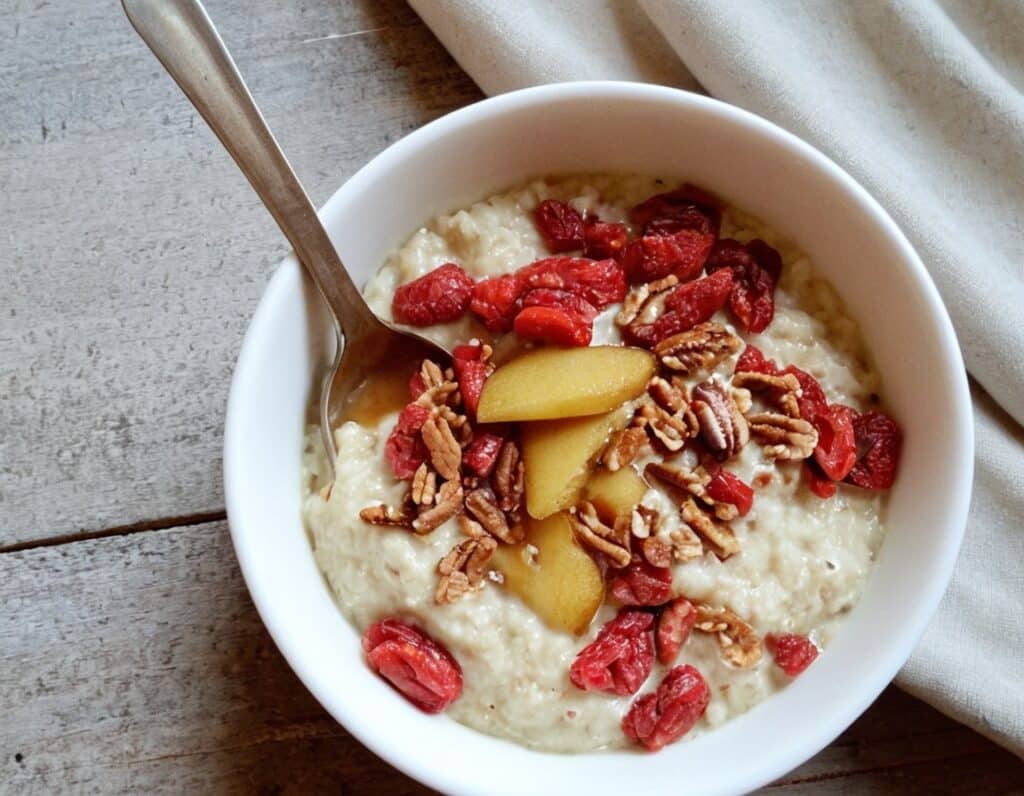
Spiced Pear & Pecan Polyphenol Porridge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Porridge doesn’t have to be boring; in fact, it can be a real treat. And while oats are healthy by default, this version has extra layers of benefits:
You will need
Per person:
- 1 cup milk (your choice what kind; we recommend almond for this)
- ½ cup oats
- 1 pear, peeled, cored, and sliced
- ¼ cup toasted pecans, chopped
- 2 tbsp goji berries
- 1 tsp sweet cinnamon
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the goji berries in a small amount of hot water. If you have an espresso cup or something of a similar size, that’s a great “bowl” for this task. A ramekin will suffice, otherwise, but use only as much water as is absolutely necessary to cover the goji berries (excess water will just leech polyphenols from the berries, reducing their nutritional value).
2) Combine the pear and cinnamon in a saucepan with a couple of tablespoons of water, and simmer for 5 minutes.
3) Combine the oats and milk in a separate saucepan (we imagine you know how to make porridge, but we’d be remiss to not include the step), and simmer for 5 minutes, stirring as necessary.
4) Drain the goji berries and the pear, if there is water remaining outside of the fruits.
5) Assemble: we recommend the order: goji berries, porridge, pear, pecans.
Alternative method: simply layer everything in a slow cooker, in the following order: goji berries (no need to pre-soak), oats, milk (stir it a little to ensure oats are all wet), pear-dusted-with-cinnamon (no need to pre-cook), pecans. Put it on the lowest heat with the lid on, and leave for a couple of hours.
Alternative alternative method: layer everything as we just said, but this time in portions of 1 jar per person, and leave it overnight, per overnight oats. Then, in the morning, gently warm it (if you like) by putting it in the microwave (lid removed!) for 2 minutes on medium power.
These latter methods are increasingly better nutritionally, as they won’t wash away some of the polyphenols from the goji berries and the lower temperatures keep the glycemic index of the oats lower, but we appreciate you won’t always have the time to do it this way.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s β-glucan, as found in oats!
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier? ← this is a very important distinction
- Make Overnight Oats Shorter Or Longer For Different Benefits!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them!
Hormones are vital for far more than they tend to get credit for. Even the hormones that people think of first—testosterone and estrogen—do a lot more than just build/maintain sexual characteristics and sexual function. Without them, we’d lack energy, we’d be depressed, and we’d soon miss the general smooth-running of our bodies that we take for granted.
And that’s without getting to the many less-talked-about hormones that play a secondary sexual role or are in the same general system…
How are your prolactin levels, for example?
Unless you’re ill, taking certain medications, recently gave birth, or picked a really interesting time to read this newsletter, they’re probably normal, by the way.
But, prolactin can explain “la petite mort”, the downturn in energy and the somewhat depressed mood that many men experience after orgasm.
Otherwise, if you have too much prolactin in general, you will be sleepy and depressed.
Prolactin’s primary role? In women, it stimulates milk production when needed. In men, it plays a role in regulating mood and metabolism.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Only walking for exercise? Here’s how to get the most out of it
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re living longer than in previous generations, with one in eight elderly Australians now aged over 85. But the current gap between life expectancy (“lifespan”) and health-adjusted life expectancy (“healthspan”) is about ten years. This means many of us live with significant health problems in our later years.
To increase our healthspan, we need planned, structured and regular physical activity (or exercise). The World Health Organization recommends 150–300 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise – such as brisk walking, cycling and swimming – per week and muscle strengthening twice a week.
Yet few of us meet these recommendations. Only 10% meet the strength-training recommendations. Lack of time is one of the most common reasons.
Walking is cost-effective, doesn’t require any special equipment or training, and can be done with small pockets of time. Our preliminary research, published this week, shows there are ways to incorporate strength-training components into walking to improve your muscle strength and balance.
Why walking isn’t usually enough
Regular walking does not appear to work as muscle-strengthening exercise.
In contrast, exercises consisting of “eccentric” or muscle-lengthening contractions improve muscle strength, prevent muscle wasting and improve other functions such as balance and flexibility.
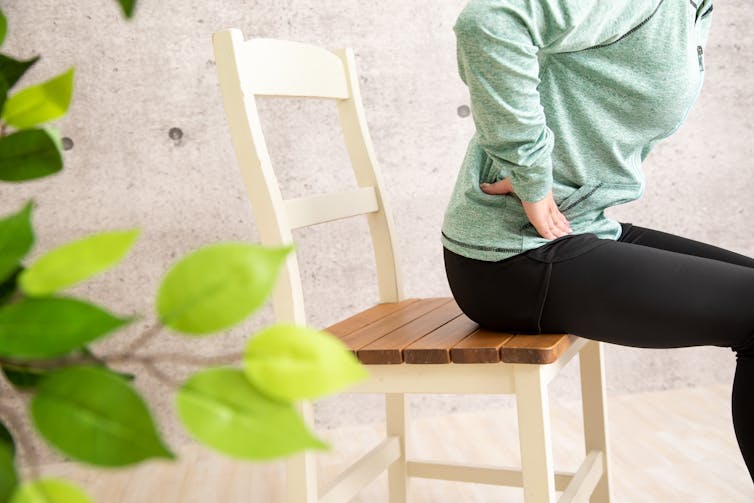
Typical eccentric contractions are seen, for example, when we sit on a chair slowly. The front thigh muscles lengthen with force generation.
When you sit down slowly on a chair, the front thigh muscles lengthen.
buritora/ShutterstockOur research
Our previous research found body-weight-based eccentric exercise training, such as sitting down on a chair slowly, improved lower limb muscle strength and balance in healthy older adults.
We also showed walking down stairs, with the front thigh muscles undergoing eccentric contractions, increased leg muscle strength and balance in older women more than walking up stairs. When climbing stairs, the front thigh muscles undergo “concentric” contractions, with the muscles shortening.
It can be difficult to find stairs or slopes suitable for eccentric exercises. But if they could be incorporated into daily walking, lower limb muscle strength and balance function could be improved.
This is where the idea of “eccentric walking” comes into play. This means inserting lunges in conventional walking, in addition to downstairs and downhill walking.
In our new research, published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology, we investigated the effects of eccentric walking on lower limb muscle strength and balance in 11 regular walkers aged 54 to 88 years.
The intervention period was 12 weeks. It consisted of four weeks of normal walking followed by eight weeks of eccentric walking.
The number of eccentric steps in the eccentric walking period gradually increased over eight weeks from 100 to 1,000 steps (including lunges, downhill and downstairs steps). Participants took a total of 3,900 eccentric steps over the eight-week eccentric walking period while the total number of steps was the same as the previous four weeks.
We measured the thickness of the participants’ front thigh muscles, muscle strength in their knee, their balance and endurance, including how many times they could go from a sitting position to standing in 30 seconds without using their arms. We took these measurements before the study started, at four weeks, after the conventional walking period, and at four and eight weeks into the eccentric walking period.
We also tested their cognitive function using a digit symbol-substitution test at the same time points of other tests. And we asked participants to complete a questionnaire relating to their activities of daily living, such as dressing and moving around at home.
Finally, we tested participants’ blood sugar, cholesterol levels and complement component 1q (C1q) concentrations, a potential marker of sarcopenia (muscle wasting with ageing).
Regular walking won’t contract your muscles in the same way as eccentric walking.
alexei_tm/ShutterstockWhat did we find?
We found no significant changes in any of the outcomes in the first four weeks when participants walked conventionally.
From week four to 12, we found significant improvements in muscle strength (19%), chair-stand ability (24%), balance (45%) and a cognitive function test (21%).
Serum C1q concentration decreased by 10% after the eccentric walking intervention, indicating participants’ muscles were effectively stimulated.
The sample size of the study was small, so we need larger and more comprehensive studies to verify our findings and investigate whether eccentric walking is effective for sedentary people, older people, how the different types of eccentric exercise compare and the potential cognitive and mental health benefits.
But, in the meantime, “eccentric walking” appears to be a beneficial exercise that will extend your healthspan. It may look a bit eccentric if we insert lunges while walking on the street, but the more people do it and benefit from it, the less eccentric it will become.
Ken Nosaka, Professor of Exercise and Sports Science, Edith Cowan University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Red-dy For Anything Polyphenol Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So, you’ve enjoyed your Supergreen Superfood Salad Slaw, and now you’re ready for another slice of the rainbow. Pigments in food aren’t just for decoration—they each contain unique benefits! Today’s focus is on some red foods that, combined, make a deliciously refreshing salad that’s great for the gut, heart, and brain.
You will need
- 1 cup crème fraîche or sour cream (if vegan, use our Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese recipe, and add the juice of 1 lime)
- ½ small red cabbage, thinly sliced
- 1 red apple, cored and finely chopped
- 1 red onion, thinly sliced
- 10 oz red seedless grapes, halved
- 10 oz red pomegranate seeds
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine all the red ingredients in a big bowl.
2) Add the crème fraîche and mix gently but thoroughly.
3) If you have time, let it sit in the fridge for 48 hours before enjoying, as its colors will intensify and its polyphenols will become more bioavailable. But if you want/need, you can serve immediately; that’s fine too.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Resveratrol & Healthy Aging
- Tasty Polyphenols For Your Heart And Brain
- Pomegranate vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Exercise Rewires Your Brain for Better Mental Wellbeing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Tracey Marks, psychiatrist, explains what happens immediately, and what happens over the long term:
For now and for later
First of all, a single workout can already alter brain chemistry and protect against stress. In the longer term, exercise promotes neurogenesis, primarily in the hippocampus, improving memory and reversing brain aging. It also strengthens the prefrontal cortex, which is critical for decision-making, focus, and emotional regulation.
In more general terms, exercise boosts brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels, which in turn boost neuron growth and connectivity.
Exercise also promotes angiogenesis (blood vessel construction), improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to the brain.
Timeline of benefits:
- Immediate: increased blood flow and temporary BDNF spike.
- Weeks: new neurons, connections, and blood vessel growth.
- Months: visible brain volume changes and better brain connectivity.
Dr. Marks’ Timing Tips
- Morning: boosts energy and helps regulate the circadian rhythm.
- Midday: resets stress levels (specifically: to low)
- Evening: helps process emotions (but it’s still recommended to avoid high-intensity exercise close to bedtime)
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Wondering what kind of exercise is best?
You might also like to read:
The Neuroscientist In The Gym: Dr. Wendy Suzuki Explains The Exercise That Protects Your Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: