Are Squats the Ultimate Game-Changer?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Jess Grochowsky, PT, DPT, MTC, CLT, CMPTP, says the answer is yes, and here’s why:
The most complete exercise
Squats are a powerful full-body exercise that targets legs, core, and (when weights are used) upper body. All in all, they enhance strength, mobility, metabolism, and joint health, making them essential for longevity and maintaining quality of movement throughout life.
In particular, they allow a much greater range of movement through more dimensions than most exercises do, meaning that (unlike a lot of more linear exercises) they build functional strength that sees us well in everyday life—mobility, joint control, and muscle stability.
Proper Squat Technique:
- The squat involves lowering the center of mass (which is slightly behind your navel and slightly down; exact position depends on your body composition and proportions) toward the floor.
- Use the “head to hips” principle to maintain a straight spine: as the head moves forward, the hips go back.
- Different foot positions (sumo, narrow, etc) target various muscles.
4 key variables to adjust squats:
- Base of support: the surface you stand on (firm vs unstable like a Bosu ball) affects stability and muscle engagement.
- Foot position: wide stances increase stability and target inner thighs and glutes; narrow stances focus more on quads.
- Weights: can use free weights, kettlebells, or bars. Adding weights increases intensity and can incorporate upper body exercises (e.g. bicep curls, overhead presses, etc).
- Squat depth: ranges from partial to deep squats, depending on functional goals.
Types of squats and variations given in the video:
- Firm surface squats: provide stability and allow even weight distribution.
- Unstable surface squats: engage smaller stabilizing muscles.
- Yoga ball squats: shift the center of mass backward, increasing quad and glute activation.
- Weighted squats: add resistance to increase muscle load and core stability (e.g. one-sided weights for oblique engagement).
- Dynamic weighted squats: incorporate quick movements, like kettlebell swings, for power and coordination.
- Single-leg squats: enhance balance and increase workload on one side of the body.
For more on all of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Top 5 Anti-Aging Exercises
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are some exercises that get called such things as “The King of Exercises!”, but how well-earned is that title and could it be that actually a mix of the top few is best?
The Exercises
While you don’t have to do all 5, your body will thank you if you are able to:
- Plank: strengthens most of the body, and can reduce back pain while improving posture.
- Squats: another core-strengthening exercise, this time with an emphasis on the lower body, which makes for strong foundations (including strong ankles, knees, and hips). Improves circulation also, and what’s good for circulation is good for the organs, including the brain!
- Push-ups: promotes very functional strength and fitness; great for alternating with planks, as despite their similar appearance, they work the abs and back more, respectively.
- Lunges: these are great for lower body strength and stability, and doing these greatly reduces the risk of falling.
- Glute Bridges: this nicely rounds off one’s core strength, increasing stability and improving posture, as well as reducing lower back pain too.
If the benefits of these seem to overlap a little, it’s because they do! But each does some things that the others don’t, so put together, they make for a very well-balanced workout.
For advice on how to do each of them, plus more about the muscles being used and the benefits, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
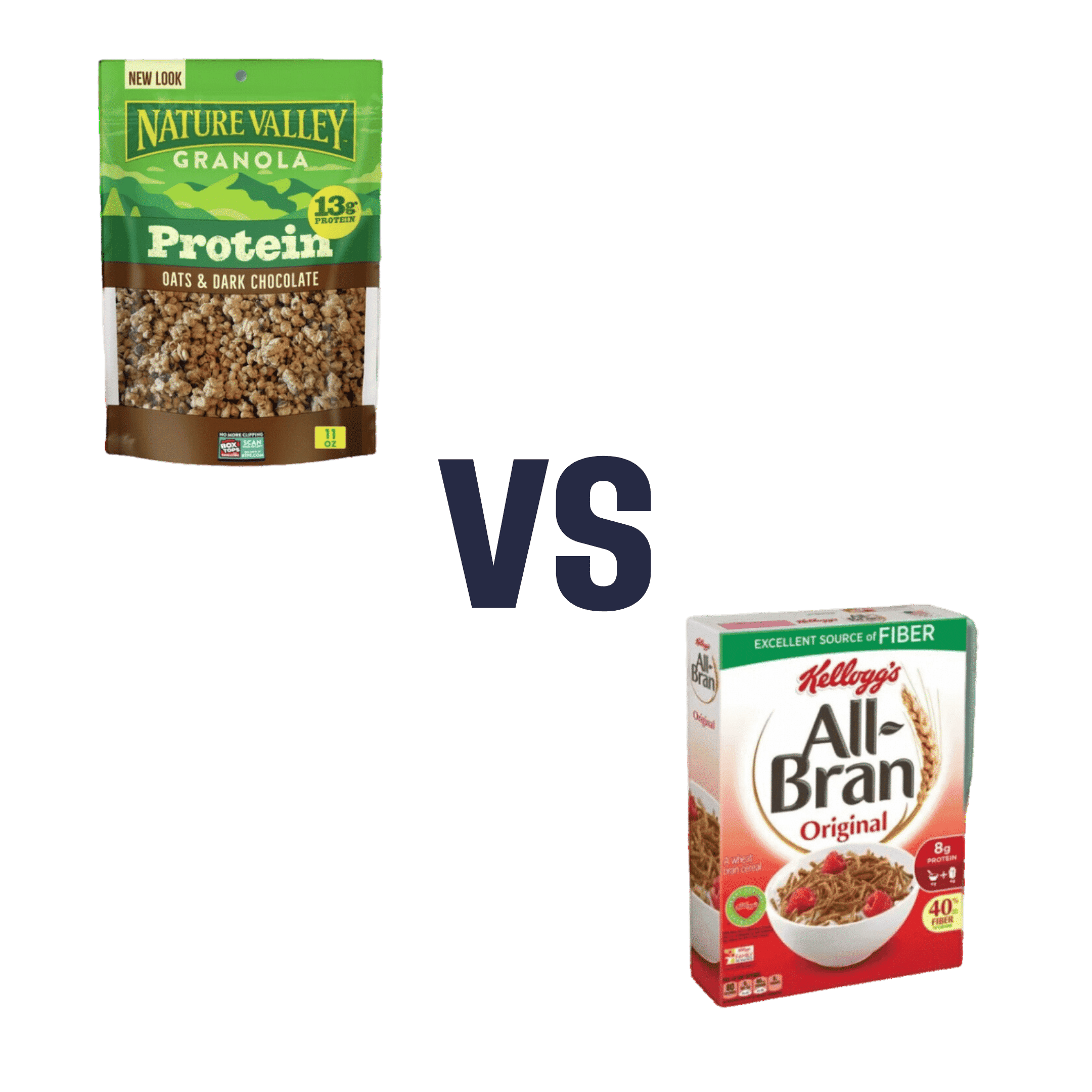
Nature Valley Protein Granola vs Kellog’s All-Bran – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Nature Valley Protein Granola to Kellog’s All-Bran, we picked the All-Bran.
Why?
While the Protein Granola indeed contains more protein (13g/cup, compared to 5g/cup), it also contains three times as much sugar (18g/cup, compared to 9g/cup) and only ⅓ as much fiber (4g/cup, compared to 12g/cup)
Given that fiber is what helps our bodies to absorb sugar more gently (resulting in fewer spikes), this is extremely important, especially since 18g of sugar in one cup of Protein Granola is already most of the recommended daily allowance, all at once!
For reference: the AHA recommends no more than 25g added sugar for women, or 32g for men
Hence, we went for the option with 3x as much fiber and ⅓ of the sugar, the All-Bran.
For more about keeping blood sugars stable, see:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Brain Health Book – by Dr. John Randolph
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a clinical neuropsychologist and brain health consultant, brings his professional knowledge and understanding to bear on the questions of what works, what doesn’t, and why?
In practical terms, the focus is mostly on maintaining/improving attention, memory, and executive functions. To that end, he covers what kinds of exercises to do (physical and mental!), and examines what strategies make the most difference—including the usual lifestyle considerations of course, but also more specifically than that, what to prioritize over what when it comes to daily choices.
The style is easy pop-science, with an emphasis on being directly useful to the reader, rather than giving an overabundance of citations for everything as we go along. He does, however, explain the necessary science as we go, making the book educational without being academic.
Bottom line: if you’d like to maintain/improve your brain, this book can certainly help with that, and as a bonus (unless you are already an expert) you’ll learn plenty about the brain as you go.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Walnuts vs Brazil Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing walnuts to Brazil nuts, we picked the walnuts.
Why?
Talking macros first, they are about equal in protein, carbs, fats, and fiber; their composition is almost identical in this regard. However, looking a little more closely at the fats, Brazil nuts have more than 2x the saturated fat, while walnuts have nearly 2x the polyunsaturated fat. So, we’ll declare the macros category a moderate win for walnuts.
The category of vitamins is not balanced; walnuts have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and choline, while Brazil nuts have more of vitamins B1 and E. A clear and easy win for walnuts.
The category of minerals is interesting, because of one mineral in particular. First let’s mention: walnuts have more iron and manganese, while Brazil nuts have more calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. Taken at face value, this is a clear win for Brazil nuts. However…
About that selenium… Specifically, it’s more than 391x higher, and a cup of Brazil nuts would give nearly 10,000x the recommended daily amount of selenium. Now, selenium is an essential mineral (needed for thyroid hormone production, for example), and at the RDA it’s good for good health. Your hair will be luscious and shiny. However, go much above that, and selenium toxicity becomes a thing, you may get sick, and it can cause your (luscious and shiny) hair to fall out. For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
There is one last consideration, and this is oxalates; walnuts are moderately high in oxalates (>50mg/100g) while Brazil nuts are very high in oxalates (>500mg/100g). This won’t affect most people at all, but if you have pre-existing kidney problems (including a history of kidney stones), you might want to go easy on oxalate-containing foods.
For most people, however, walnuts are a very healthy choice, and outshine Brazil nuts in most ways.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Oral retinoids can harm unborn babies. But many women taking them for acne may not be using contraception
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Oral retinoids are a type of medicine used to treat severe acne. They’re sold under the brand name Roaccutane, among others.
While oral retinoids are very effective, they can have harmful effects if taken during pregnancy. These medicines can cause miscarriages and major congenital abnormalities (harm to unborn babies) including in the brain, heart and face. At least 30% of children exposed to oral retinoids in pregnancy have severe congenital abnormalities.
Neurodevelopmental problems (in learning, reading, social skills, memory and attention) are also common.
Because of these risks, the Australasian College of Dermatologists advises oral retinoids should not be prescribed a month before or during pregnancy under any circumstances. Dermatologists are instructed to make sure a woman isn’t pregnant before starting this treatment, and discuss the risks with women of childbearing age.
But despite this, and warnings on the medicines’ packaging, pregnancies exposed to oral retinoids continue to be reported in Australia and around the world.
In a study published this month, we wanted to find out what proportion of Australian women of reproductive age were taking oral retinoids, and how many of these women were using contraception.
Our results suggest a high proportion of women are not using effective contraception while on these drugs, indicating Australia needs a strategy to reduce the risk oral retinoids pose to unborn babies.
Contraception options
Using birth control to avoid pregnancy during oral retinoid treatment is essential for women who are sexually active. Some contraception methods, however, are more reliable than others.
Long-acting-reversible contraceptives include intrauterine devices (IUDs) inserted into the womb (such as Mirena, Kyleena, or copper devices) and implants under the skin (such as Implanon). These “set and forget” methods are more than 99% effective.
Oral retinoids taken during pregnancy can cause complications in babies. Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock The effectiveness of oral contraceptive pills among “perfect” users (following the directions, with no missed or late pills) is similarly more than 99%. But in typical users, this can fall as low as 91%.
Condoms, when used as the sole method of contraception, have higher failure rates. Their effectiveness can be as low as 82% in typical users.
Oral retinoid use over time
For our study, we analysed medicine dispensing data among women aged 15–44 from Australia’s Pharmaceutical Benefit Scheme (PBS) between 2013 and 2021.
We found the dispensing rate for oral retinoids doubled from one in every 71 women in 2013, to one in every 36 in 2021. The increase occurred across all ages but was most notable in young women.
Most women were not dispensed contraception at the same time they were using the oral retinoids. To be sure we weren’t missing any contraception that was supplied before the oral retinoids, we looked back in the data. For example, for an IUD that lasts five years, we looked back five years before the oral retinoid prescription.
Our analysis showed only one in four women provided oral retinoids were dispensed contraception simultaneously. This was even lower for 15- to 19-year-olds, where only about one in eight women who filled a prescription for oral retinoids were dispensed contraception.
A recent study found 43% of Australian year 10 and 69% of year 12 students are sexually active, so we can’t assume this younger age group largely had no need for contraception.
One limitation of our study is that it may underestimate contraception coverage, because not all contraceptive options are listed on the PBS. Those options not listed include male and female sterilisation, contraceptive rings, condoms, copper IUDs, and certain oral contraceptive pills.
But even if we presume some of the women in our study were using forms of contraception not listed on the PBS, we’re still left with a significant portion without evidence of contraception.
What are the solutions?
Other countries such as the United States and countries in Europe have pregnancy prevention programs for women taking oral retinoids. These programs include contraception requirements, risk acknowledgement forms and regular pregnancy tests. Despite these programs, unintended pregnancies among women using oral retinoids still occur in these countries.
But Australia has no official strategy for preventing pregnancies exposed to oral retinoids. Currently oral retinoids are prescribed by dermatologists, and most contraception is prescribed by GPs. Women therefore need to see two different doctors, which adds costs and burden.
Preventing pregnancy during oral retinoid treatment is essential. Krakenimages.com/Shutterstock Rather than a single fix, there are likely to be multiple solutions to this problem. Some dermatologists may not feel confident discussing sex or contraception with patients, so educating dermatologists about contraception is important. Education for women is equally important.
A clinical pathway is needed for reproductive-aged women to obtain both oral retinoids and effective contraception. Options may include GPs prescribing both medications, or dermatologists only prescribing oral retinoids when there’s a contraception plan already in place.
Some women may initially not be sexually active, but change their sexual behaviour while taking oral retinoids, so constant reminders and education are likely to be required.
Further, contraception access needs to be improved in Australia. Teenagers and young women in particular face barriers to accessing contraception, including costs, stigma and lack of knowledge.
Many doctors and women are doing the right thing. But every woman should have an effective contraception plan in place well before starting oral retinoids. Only if this happens can we reduce unintended pregnancies among women taking these medicines, and thereby reduce the risk of harm to unborn babies.
Dr Laura Gerhardy from NSW Health contributed to this article.
Antonia Shand, Research Fellow, Obstetrician, University of Sydney and Natasha Nassar, Professor of Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology and Chair in Translational Childhood Medicine, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Squat Bible – by Dr. Aaron Horschig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably know the following three things about squats:
- Squatting is great for the health in many ways
- There are many different ways to squat
- Not all of them are correct, and some may even do harm
Dr. Aaron Horschig makes the case for squats being a movement first, and an exercise second. To this end, he takes us on a joint-by-joint tour of the anatomy of squatting, so that we get it right from top to toe.
Or rather: from toe to top, since he starts with the best foundation.
What this means is that if you’ve struggled to squat because you find some discomfort in your ankles, or a weakness in the knees, or you can’t get your back quite right, Dr. Horschig will have a fix for you. He also takes a realistic look about how people’s anatomy varies from person to person, and what differences this makes to how we each should best squat.
The explanations are clear and so are the pictures—we recommend getting the color print edition (linked), as the image quality is better than the black and white and/or Kindle edition.
Bottom-line: squats are one of the single best exercises we can do for our health—but we can miss out on benefits (or even do ourselves harm) if we don’t do them well. This book is a comprehensive reference resource for making sure we get the most out of our squatting ability.
Click here to check out The Squat Bible, and master this all-important movement!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: