Is Ant Oil Just “Snake Oil”?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Tested Out “Ant Egg Oil”
Did you know?! There’s a special protein found only in the eggs of a particular species of ant found in Turkey, that can painlessly and permanently stop (not just slow!) hair regrowth in places you’d rather not have hair.
Neither did we, and when we heard about it, we did our usual research, and discovered a startling secret.
…there probably isn’t.
We decided to dig deeper, and the plot (unlike the hair in question) thickens:
We could not find any science for or against (or even generally about) the use of ant egg oil to prevent hair regrowth. Not a peep. What we did find though was a cosmetic chemist who did an analysis of the oil as sold, and found its main ingredient appears to be furan-2-carbaldehyde, or Furfural, to its friends.
Surprise! There’s also no science that we could find about the effect of Furfural (we love the name, though! Fur for all!) on hair, except that it’s bad for rodents (and their hair) if they eat a lot of it. So please don’t eat it. Especially if you’re a mouse.
And yet, many ostensibly real reviews out in the wild claim it works wonders. So, we took the investigative reporting approach and tried it ourselves.
That’s right, a plucky member of our team tried it, and she reports:
❝ At first glance, it seems like olive oil. There’s something else though, adding a darker colour and a slight bitterness to the smell.
After waxing, I applied a little every few days. When the hair eventually regrew (and it did), it grew back thinner, and removing the new hairs was a strangely easy experience, like pulling hairs out of soft soap instead of out of skin. It didn’t hurt at all, either.
I had more of the oil, so I kept going with the treatment, and twelve weeks later there are very few hairs regrowing at all; probably there will be none left soon. Whatever’s in this, be it from ant eggs or wheat bran or something else entirely, it worked for me!❞
So in short: it remains a mystery for now! If you try it, let us know how it went for you.
Here’s the “interesting” website that sells it, though you may find it for less on eBay or similar. (Note, we aren’t earning any commissions from these links. We just wanted to make it easier for you to dive deeper).
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Air Purifiers & Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I’ve read that air pollution has a negative effect on sleep quality and duration. Since I live next to a busy road, I was wondering whether I should invest in an air purifier. What are 10Almonds’s views?❞
Going straight to the science, there are two questions here:
- Does air pollution negatively affect sleep quality and duration?
- Does the use of an air purify actually improve the air quality in the way(s) necessary to make a difference?
We thought we’d have to tackle these questions separately, but we did find one study that addressed your question directly. It was a small study (n=30 if you believe the abstract; n=29 if you read the paper itself—one person dropped out); the results were modest but clear:
❝The purifier filter was associated with increased total sleep time for an average of 12 min per night, and increased total time in bed for an average of 19 min per night relative to the placebo.
There were several sleep and mood outcomes for which no changes were observed, and time awake after sleep onset was higher for the purifier filter. Air quality was better during the high-efficiency particulate air filter condition.
These findings offer positive indications that environmental interventions that improve air quality can have benefits for sleep outcomes in healthy populations who are not exhibiting clinical sleep disturbances.❞
In the above-linked paper’s introduction, it does establish the deleterious effect of air pollution on a wide variety of health metrics, including sleep, this latter evidenced per Caddick et al. (2018): A review of the environmental parameters necessary for an optimal sleep environment
Now, you may be wondering: is an extra 12 minutes per night worth it?
That’s your choice to make, but we would argue that it is. We can make many choices in our lives that affect our health slightly for the better or the worse. If we make a stack of choices in a particular direction, the effects will also stack, if not outright compound.
So in the case of sleep, it might be (arbitrary numbers for the sake of illustration):
- Get good exercise earlier in the day (+3%)
- Get good food earlier in the day (+2.5%)
- Practice mindfulness/meditation before bed (+2.5%)
- Have a nice dark room (+5%)
- Have fresh bedding (+2.5%)
- Have an air purifier running (+3%)
Now, those numbers are, as we said, arbitrary*, but remember that percentages don’t add up; they compound. So that “+3%” starts being a lot more meaningful than if it were just by itself.
*Confession: the figure of 3% for the air purifier wasn’t entirely arbitrary; it was based on 100(12/405) = 80/27 ≈ 3, wherein the 405 figure was an approximation of the average total time (in minutes) spent sleeping with placebo, based on a peep at their results graph. There are several ways the average could be reasonably calculated, but 6h45 (i.e., 405 minutes) was an approximate average of those reasonable approximate averages.
So, 12 minutes is a 3% improvement on that.
Don’t have an air purifier and want one?
We don’t sell them, but here’s an example on Amazon, for your convenience
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Eat To Beat Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Controlling What We Can, To Avoid Cancer
Every time a cell in our body is replaced, there’s a chance it will be cancerous. Exactly what that chance is depends on very many factors. Some of them we can’t control; others, we can.
Diet is a critical, modifiable factor
We can’t choose, for example, our genes. We can, for the most part, choose our diet. Why “for the most part”?
- Some people live in a food desert (the Arctic Circle is a good example where food choices are limited by supply)
- Some people have dietary restrictions (whether by health condition e.g. allergy, intolerance, etc or by personal-but-unwavering choice, e.g. vegetarian, vegan, kosher, halal, etc)
But for most of us, most of the time, we have a good control over our diet, and so that’s an area we can and should focus on.
Choose your animal protein wisely
If you are vegan, you can skip this section. If you are not, then the short version is:
- Fish: almost certainly fine
- Poultry: the jury is out; data is leaning towards fine, though
- Red meat: significantly increased cancer risk
- Processed meat: significantly increased cancer risk
For more details (and a run-down on the science behind the above super-summarized version):
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy? ← A mythbuster article that outlines many health properties (good and bad) of animal products
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet ← A life-hack article about acting on that information
Skip The Ultra-Processed Foods
Ok, so this one’s probably not a shocker in its simplest form:
❝Studies are showing us is that not only do the ultraprocessed foods increase the risk of cancer, but that after a cancer diagnosis such foods increase the risk of dying❞
Source: Is there a connection between ultraprocessed food and cancer?
There’s an unfortunate implication here! If you took the previous advice to heart and cut out [at least some] meat, and/but then replaced that with ultra-processed synthetic meat, then this was not a great improvement in cancer risk terms.
Ultra-processed meat is worse than unprocessed, regardless of whether it was from an animal or was synthetic.
In other words: if you buy textured soy pieces (a common synthetic meat), it pays to look at the ingredients, because there’s a difference between:
- INGREDIENTS: SOY
- INGREDIENTS: Rehydrated Textured SOY Protein (52%), Water, Rapeseed Oil, SOY Protein Concentrate, Seasoning (SULPHITES) (Dextrose, Flavourings, Salt, Onion Powder, Food Starch Modified, Yeast Extract, Colour: Red Iron Oxide), SOY Leghemoglobin, Fortified WHEAT Flour (WHEAT Flour, Calcium Carbonate, Iron, Niacin, Thiamin), Bamboo Fibre, Methylcellulose, Tomato Purée, Salt, Raising Agent: Ammonium Carbonates
Now, most of those original base ingredients are/were harmless per se (as are/were the grapes in wine—before processing into alcohol), but it has clearly been processed to Hell and back to do all that.
Choose the one that just says “soy”. Or eat soybeans. Or other beans. Or lentils. Really there are a lot of options.
About soy, by the way…
There is (mostly in the US, mostly funded by the animal agriculture industry) a lot of fearmongering about soy. Which is ironic, given the amount of soy that is fed to livestock to be fed to humans, but it does bear addressing:
❝Soy foods are safe for all cancer patients and are an excellent source of plant protein. Studies show soy may improve survival after breast cancer❞
Source: Food risks and cancer: What to avoid
(obviously, if you have a soy allergy then you should not consume soy—for most people, the above advice stands, though)
Advanced Glycation End-Products
These (which are Very Bad™ for very many things, including cancer) occur specifically as a result of processing animal proteins and fats.
Note: not even necessarily ultra-processing, just processing can do it. But ultra-processing is worse. What’s the difference, you wonder?
The difference between “ultra-processed” and just “processed”:
- Your average hotdog has been ultra-processed. It’s not only usually been changed with many artificial additives, it’s also been through a series of processes (physical and chemical) and ends up bearing little relation to the creature it came from.
- Your bacon (that you bought fresh from your local butcher, not a supermarket brand of unknown provenance, and definitely not the kind that might come on the top of frozen supermarket pizza) has been processed. It’s undergone a couple of simple processes on its journey “from farm to table”. Remember also that when you cook it, that too is one more process (and one that results in a lot of AGEs).
Read more: What’s so bad about AGEs?
Note if you really don’t want to cut out certain foods, changing the way you cook them (i.e., the last process your food undergoes before you eat it) can also reduce AGES:
Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Get More Fiber
❝The American Institute for Cancer Research shows that for every 10-gram increase in fiber in the diet, you improve survival after cancer diagnosis by 13%❞
Source: Plant-based diet is encouraged for patients with cancer
Yes, that’s post-diagnosis, but as a general rule of thumb, what is good/bad for cancer when you have it is good/bad for cancer beforehand, too.
If you’re thinking that increasing your fiber intake means having to add bran to everything, happily there are better ways:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Stolen Focus – by Johann Hari
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Having trouble concentrating for long periods? It’s not just a matter of getting older…
Johann Hari outlines twelve key ways in which our attention has not merely “wandered”, so much as it has been outright stolen.
By whom? For what purpose? Obvious culprits include social media and outrage-stoking news outlets, but the problem, as Hari illustrates, goes much deeper than that.
He talks about how we cannot truly multi-task, and can only switch beween tasks, at a cost. And yet, the modern world is not at all friendly to single-tasking!
Writer’s note: as I write this, I have active two screens, containing four windows, one of which has three tabs open. I am not multitasking; all those things pertain to the work I am doing right now. If I closed them between use, it’d only cost me more time and attention opening and closing them all the time. And yet, my working conditions are considered practically “hyperfocused” in this century!
- We learn about how the working world has changed, and the rise of physical and mental exhaustion that has come with it.
- We learn about the collapse of sustained reading, that started well before the modern Internet.
- We learn about factors such as dietary shifts that sap our energy too.
…and more. Twelve key things, remember.
But, it’s not all doom and gloom. There are things we can do to fight back. Some are personal changes; others are societal changes to push for.
The last part of the book is given over to, essentially, a manifesto (and how-to guide) for reclaiming our attention and thinking deeply again.
Bottom line: if you struggle with maintaining attention; this is a book for you. You might want to put your phone in a drawer while you read it, though
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Medicinal Chef – by Dale Pinnock
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The philosophy here is very much like our own—to borrow from Hippocrates: “let food be thy medicine”. Obviously please do also let medicine be thy medicine if you need it, but the point is that food is a very good starting place for combatting a lot of disease.
To this end, instead of labelling the recipes with such things as “V”, “Ve”, “GF” and suchlike, it assumes we can tell those things from the ingredients lists, and instead labels things per what they are especially good for:
- S: skin
- J: joints & bones
- R: respiratory system
- I: immune system
- M: metabolic health
- N: nervous system and mental health
- H: heart and circulation
- D: digestive system
- U: reproductive & urinary systems
As for the recipes themselves… They’re a lot like the recipes we share here at 10almonds in their healthiness, skill level, and balance of easy-to-find ingredients with the occasional “order it online” items that punch above their weight. In fact, we’ll probably modify some of the recipes for sharing here.
Bottom line: if you’re looking for genuinely healthy recipes that are neither too basic nor too arcane, this book has about 80 of them.
Click here to check out The Medicinal Chef: Healthy Every Day, and be healthy every day!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between wholemeal and wholegrain bread? Not a whole lot
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you head to the shops to buy bread, you’ll face a variety of different options.
But it can be hard to work out the difference between all the types on sale.
For instance, you might have a vague idea that wholemeal or wholegrain bread is healthy. But what’s the difference?
Here’s what we know and what this means for shoppers in Australia and New Zealand.
Phish Photography/Shutterstock Let’s start with wholemeal bread
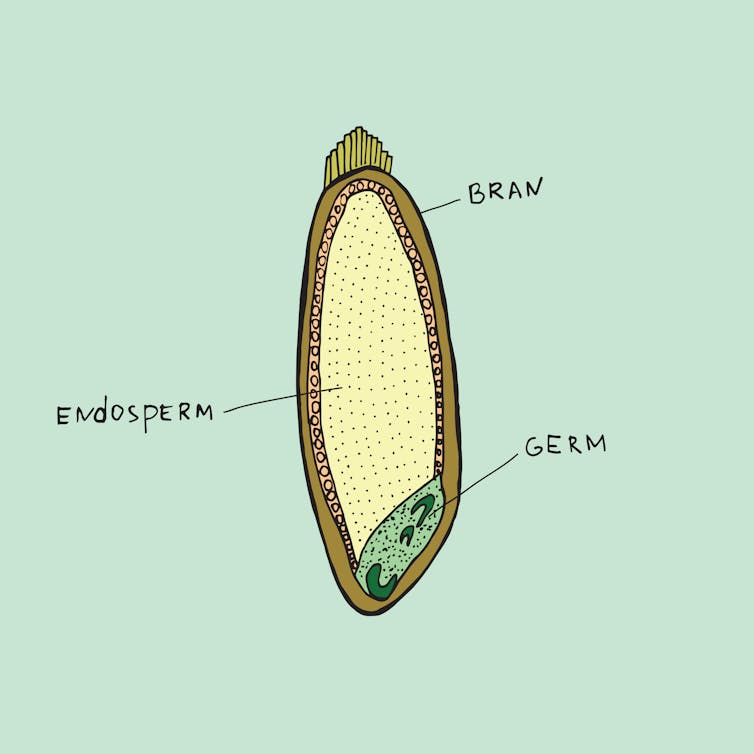
According to Australian and New Zealand food standards, wholemeal bread is made from flour containing all parts of the original grain (endosperm, germ and bran) in their original proportions.
Because it contains all parts of the grain, wholemeal bread is typically darker in colour and slightly more brown than white bread, which is made using only the endosperm.
Wholemeal flour is made from all parts of the grain. Rerikh/Shutterstock How about wholegrain bread?
Australian and New Zealand food standards define wholegrain bread as something that contains either the intact grain (for instance, visible grains) or is made from processed grains (flour) where all the parts of the grain are present in their original proportions.
That last part may sound familiar. That’s because wholegrain is an umbrella term that encompasses both bread made with intact grains and bread made with wholemeal flour. In other words, wholemeal bread is a type of wholegrain bread, just like an apple is a type of fruit.
Don’t be confused by labels such as “with added grains”, “grainy” or “multigrain”. Australian and New Zealand food standards don’t define these so manufacturers can legally add a small amount of intact grains to white bread to make the product appear healthier. This doesn’t necessarily make these products wholegrain breads.
So unless a product is specifically called wholegrain bread, wholemeal bread or indicates it “contains whole grain”, it is likely to be made from more refined ingredients.
Which one’s healthier?
So when thinking about which bread to choose, both wholemeal and wholegrain breads are rich in beneficial compounds including nutrients and fibre, more so than breads made from further-refined flour, such as white bread.
The presence of these compounds is what makes eating wholegrains (including wholemeal bread) beneficial for our overall health. Research has also shown eating wholegrains helps reduce the risk of common chronic diseases, such as heart disease.
The table below gives us a closer look at the nutritional composition of these breads, and shows some slight differences.
Wholegrain bread is slightly higher in fibre, protein, niacin (vitamin B3), iron, zinc, phosphorus and magnesium than wholemeal bread. But wholegrain bread is lower in carbohydrates, thiamin (vitamin B1) and folate (vitamin B9).
However the differences are relatively small when considering how these contribute to your overall dietary intake.
Which one should I buy?
Next time you’re shopping, look for a wholegrain bread (one made from wholemeal flour that has intact grains and seeds throughout) as your number one choice for fibre and protein, and to support overall health.
If you can’t find wholegrain bread, wholemeal bread comes in a very close second.
Wholegrain and wholemeal bread tend to cost the same, but both tend to be more expensive than white bread.
Margaret Murray, Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Podiatrists Debunk 11 Feet Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Podiatrists Dr. Sarah Haller and Dr. Brad Schaeffer put us on a better path:
Don’t get wrong-footed
We’ll not keep the 11 myths a mystery; they are…
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”
False! Warts are caused by a virus, not dirt. Viruses can be picked up from surfaces like yoga mats, pools, gyms, and showers. - “Bunions are caused by wearing heels.”
False! Bunions are genetic deformities where the bone behind the big toe shifts. Heels might worsen them but don’t cause them. - “Cutting the sides of my toenail will prevent an ingrown toenail.”
False! Toenails should be cut straight across. Cutting the sides can make ingrown toenails worse. - “Pedicures gave me toenail fungus.”
Partially true! You can get fungus from many places, but safe, sterile pedicures are generally fine. - “Only athletes get athlete’s foot.”
False! Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection caused by warm, moist environments. Anyone can get it, not just athletes. - “My feet are fine because I trained them to walk in stilettos.”
False! You can get used to stilettos, but they aren’t healthy long-term. They shorten the Achilles tendon and put pressure on the foot. - “You can’t do anything for a broken toe.”
False! Broken toes can be treated and should be checked by a doctor. They may need to be set for proper healing. - “It’s normal for your feet to hurt from standing all day.”
False! Foot pain isn’t normal and can be prevented with proper footwear, support, and compression socks. - “All inserts are the same.”
False! Everyone’s feet are different. Some may benefit from over-the-counter insoles, but others need custom orthotics. - “Sprained ankles are no big deal.”
False! Sprains can damage ligaments and lead to instability or arthritis if untreated. Proper stabilization is essential. - “If I can walk after an injury, I don’t need to see a doctor.”
False! You can still have serious injuries like fractures even if you can walk. Always get checked after an injury.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”