Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Which Addiction-Quitting Methods Work Best?
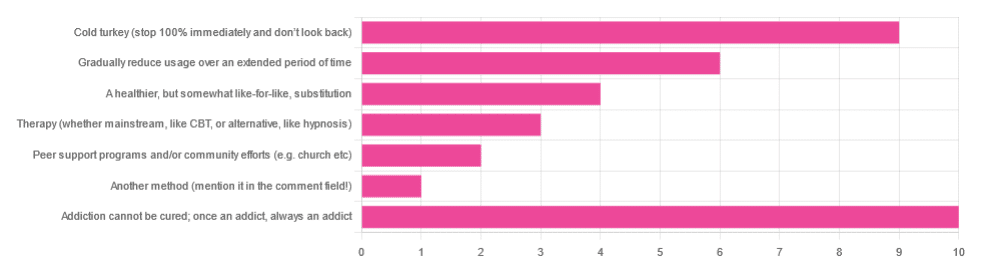
In Tuesday’s newsletter we asked you what, in your opinion, is the best way to cure an addiction. We got the above-depicted, below-described, interesting distribution of responses:
- About 29% said: “Addiction cannot be cured; once an addict, always an addict”
- About 26% said “Cold turkey (stop 100% and don’t look back)”
- About 17% said “Gradually reduce usage over an extended period of time”
- About 11% said “A healthier, but somewhat like-for-like, substitution”
- About 9% said “Therapy (whether mainstream, like CBT, or alternative, like hypnosis)”
- About 6% said “Peer support programs and/or community efforts (e.g. church etc)”
- About 3% said “Another method (mention it in the comment field)” and then did not mention it in the comment field
So what does the science say?
Addiction cannot be cured; once an addict, always an addict: True or False?
False, which some of the people who voted for it seemed to know, as some went on to add in the comment field what they thought was the best way to overcome the addiction.
The widespread belief that “once an addict, always an addict” is a “popular truism” in the same sense as “once a cheater, always a cheater”. It’s an observation of behavioral probability phrased as a strong generalization, but it’s not actually any kind of special unbreakable law of the universe.
And, certainly the notion that one cannot be cured keeps membership in many 12-step programs and similar going—because if you’re never cured, then you need to stick around.
However…
❝What is the definition of addiction?
Addiction is a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual’s life experiences. People with addiction use substances or engage in behaviors that become compulsive and often continue despite harmful consequences.
Prevention efforts and treatment approaches for addiction are generally as successful as those for other chronic diseases.❞
~ American Society of Addiction Medicine
Or if we want peer-reviewed source science, rather than appeal to mere authority as above, then:
❝What is drug addiction?
Addiction is defined as a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite adverse consequences. It is considered a brain disorder, because it involves functional changes to brain circuits involved in reward, stress, and self-control. Those changes may last a long time after a person has stopped taking drugs.
Addiction is a lot like other diseases, such as heart disease. Both disrupt the normal, healthy functioning of an organ in the body, both have serious harmful effects, and both are, in many cases, preventable and treatable.❞
~ Nora D. Volkow (Director, National Institute of Drug Abuse)
Read more: Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction
In short: part of the definition of addiction is the continued use; if the effects of the substance are no longer active in your physiology, and you are no longer using, then you are not addicted.
Just because you would probably become addicted again if you used again does not make you addicted when neither the substance nor its after-effects are remaining in your body. Otherwise, we could define all people as addicted to all things based on “well if they use in the future they will probably become addicted”.
This means: the effects of addiction can and often will last for long after cessation of use, but ultimately, addiction can be treated and cured.
(yes, you should still abstain from the thing to which you were formerly addicted though, or you indeed most probably will become addicted again)
Cold turkey is best: True or False?
True if and only if certain conditions are met, and then only for certain addictions. For all other situations… False.
To decide whether cold turkey is a safe approach (before even considering “effective”), the first thing to check is how dangerous the withdrawal symptoms are. In some cases (e.g. alcohol, cocaine, heroin, and others), the withdrawal symptoms can kill.
That doesn’t mean they will kill, so knowing (or being!) someone who quit this way does not refute this science by counterexample. The mortality rates that we saw while researching varied from 8% to 37%, so most people did not die, but do you really want (yourself or a loved one) to play those odds unnecessarily?
See also: Detoxification and Substance Abuse Treatment
Even in those cases where it is considered completely safe for most people to quit cold turkey, such as smoking, it is only effective when the quitter has appropriate reliable medical support, e.g.
- Without support: 3–5% success rate
- With support: 22% success rate
And yes, that 22% was for the “abrupt cessation” group; the “gradual cessation” group had a success rate of 15.5%. On which note…
Gradual reduction is the best approach: True or False?
False based on the above data, in the case of addictions where abrupt cessation is safe. True in other cases where abrupt cessation is not safe.
Because if you quit abruptly and then die from the withdrawal symptoms, then well, technically you did stay off the substance for the rest of your life, but we can’t really claim that as a success!
A healthier, but somewhat like-for-like substitution is best: True or False?
True where such is possible!
This is why, for example, medical institutions recommend the use of buprenorphine (e.g. Naloxone) in the case of opioid addiction. It’s a partial opioid receptor agonist, meaning it does some of the job of opioids, while being less dangerous:
It’s also why vaping—despite itself being a health hazard—is recommended as a method of quitting smoking:
Similarly, “zero alcohol drinks that seem like alcohol” are a popular way to stop drinking alcohol, alongside other methods:
This is also why it’s recommended that if you have multiple addictions, to quit one thing at a time, unless for example multiple doctors are telling you otherwise for some specific-to-your-situation reason.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Practical Optimism – by Dr. Sue Varma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about how to get your brain onto a more positive track (without toxic positivity), but there’s a lot more to be said than we can fit into an article, so here’s a whole book packed full with usable advice.
The subtitle claims “the art, science, and practice of…”, but mostly it’s the science of. If there’s art to be found here, then this reviewer missed it, and as for the practice of, well, that’s down to the reader, of course.
However, it is easy to use the contents of this book to translate science into practice without difficulty.
If you’re a fan of acronyms, initialisms, and other mnemonics (such as the rhyming “Name, Claim, Tame, and Reframe”), then you’ll love this book as they come thick and fast throughout, and they contribute to the overall ease of application of the ideas within.
The writing style is conversational but with enough clinical content that one never forgets who is speaking—not in the egotistical way that some authors do, but rather, just, she has a lot of professional experience to share and it shows.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be more optimistic without delving into the delusional, this book can really help a lot with that (in measurable ways, no less!).
Click here to check out Practical Optimism, and brighten up your life!
Share This Post
-
What immunocompromised people want you to know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While many people in the U.S. have abandoned COVID-19 mitigations like vaccines and masking, the virus remains dangerous for everyone, and some groups face higher risks than others. Immunocompromised people—whose immune systems don’t work as well as they should due to health conditions or medications—are more vulnerable to infection and severe symptoms from the virus.
Public Good News spoke with three immunocompromised people about the steps they take to protect themselves and what they want others to know about caring for each other.
[Editor’s note: The contents of these interviews have been condensed for length.]
PGN: What measures have you been taking to protect yourself since the COVID-19 pandemic began?
Tatum Spears, Virginia
From less than a year old, I had serious, chronic infections and have missed huge chunks of my life. In 2020, I quit my public job, and I have not worked publicly since.
I have a degree in vocal performance and have been singing my whole life, but I haven’t performed publicly since 2019. I feel like a bird without wings. I had to stop traveling. Since no one wears a mask anymore, I can’t go to the movies or social outings or any party.
All my friends live in my phone now. It’s a community of people—a lot of them are immunocompromised or disabled in some way.
There are a good portion of them who just take COVID-19 seriously and want to protect their health, who feel the existential abandonment and the burden of all of this. It’s really isolating having to step back from any sort of social life. I have to assess my risk every single time I leave the house.
Gwendolyn Alyse Bishop, Washington
I was hit by a car when I was very young. I woke up from surgery, and doctors told me I had lost almost all of my spleen. So, I was always the sickest kid in my school.
When COVID-19 hit, I started working from home. At first, I wore cloth masks. I didn’t really learn about KN95 masks until right around the time that COVID-19 disabled me. [Editor’s note: N95 and KN95 masks have been shown to be significantly more effective at preventing the transmission of viral particles than cloth masks.]
I actually don’t get out much anymore because I am disabled by long COVID now, but when I do leave, I wear a respirator in all shared air spaces. My roommate and I have HEPA filters going in every room.And then we test. I have a Pluslife testing dock, and so we keep a weekly testing schedule with that and then test if there are any symptoms. I got reinfected [with COVID-19] last winter, and a Pluslife test helped me catch it early and get Paxlovid. [Editor’s note: Pluslife is a brand of an at-home COVID-19 nucleic acid amplification test, which has been shown to be significantly more effective at detecting COVID-19 than at-home antigen rapid tests.]
Abby Mahler, California
I have lupus, and in 2016, I started taking the drug hydroxychloroquine, which is an immunomodulator. I’m not as immunocompromised as some people, but I certainly don’t have a normal immune system, which has resulted in long-term infections like C. diff.I started masking early. My roommates and I prioritize going outside. We don’t remove our masks inside in public places.
We are in a pod with one other household, and the pod has agreements on the way that we interact with public space. So, we will only unmask with people who have tested ahead of time. We use Metrix, an at-home nucleic acid amplification test.
While it’s not easy and it’s not the life that we had prior to COVID-19’s existence, it is a life that has provided us quite a lot of freedom, in the sense that we are not sick all the time. We are conscientiously making decisions that allow us to have a nice time without a monkey on our backs, which is freeing.
PGN: What do you want people who are not immunocompromised to know?
T.S.: Don’t be afraid to be the only person in a room wearing a mask. Your own health is worth it. And you have to realize how callous [people who don’t wear a mask are] by existing in spaces and breathing [their] air [on immunocompromised people].
People think that vaccines are magic, but vaccines alone are not enough. I would encourage people to look at the Swiss cheese model of risk assessment.
Each slice of Swiss cheese has holes in it in different places, and each layer represents a layer of virus mitigation. One layer is vaccines. Another layer is masks. Then there’s staying home when you’re sick and testing.
G.A.B.: I wish people were masking. I wish people understood how likely it is that they are also now immunocompromised and vulnerable because of the widespread immune dysregulation that COVID-19 is causing. [Editor’s note: Research shows that COVID-19 infections may cause long-term harm to the immune system in some people.]
I want people to be invested in being good community members, and part of that is understanding that COVID-19 hits the poorest the hardest—gig workers, underpaid employees, frontline service workers, people who were already disabled or immunocompromised.
If people want to be good community members, they not only need to protect immunocompromised and disabled people by wearing a mask when they leave their homes, but they also need to actually start taking care of their community members and participating in mutual aid. [Editor’s note: Mutual aid is the exchange of resources and services within a community, such as people sharing extra N95 masks.]
I spend pretty much all of my time working on LongCOVIDAidBot, which promotes mutual aid for people who have been harmed by COVID-19.
A.M.: An important thing to think about when you’re not disabled is that it becomes a state of being for all people, if they’re lucky. You will become disabled, or you will die.
It is a privilege, in my opinion, to become disabled because I can learn different ways of living my life. And being able to see yourself as a body that changes over time, I hope, opens up a way of looking at your body as the porous reality that it is.
Some people think of themselves as being willing to make concessions or change their behavior when immunocompromised people are around, but you don’t always know when someone is immunocompromised.
So, if you’re not willing to change the way that you think about yourself as a person who is susceptible [to illness], then you should change the way that you consider other people around you. Wearing a mask—at the very least in public indoor spaces—means considering the unknown realities of all the people who are interacting with that space.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
52 Weeks to Better Mental Health – by Dr. Tina Tessina
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about the health benefits of journaling, but how to get started, and how to make it a habit, and what even to write about?
Dr. Tessina presents a year’s worth of journaling prompts with explanations and exercises, and no, they’re not your standard CBT flowchart things, either. Rather, they not only prompt genuine introspection, but also are crafted to be consistently uplifting—yes, even if you are usually the most disinclined to such positivity, and approach such exercises with cynicism.
There’s an element of guidance beyond that, too, and as such, this book is as much a therapist-in-a-book as you might find. Of course, no book can ever replace a competent and compatible therapist, but then, competent and compatible therapists are often harder to find and can’t usually be ordered for a few dollars with next-day shipping.
Bottom line: if undertaken with seriousness, this book will be an excellent investment in your mental health and general wellbeing.
Click here to check out 52 Weeks to Better Mental Health, and get on the best path for you!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Maximize Your Misery! (7 Great Methods)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s imagine that instead of being healthily fulfilled in life, you wanted to spend your days as miserable as possible. What should you do?
Here are a few pointers:
Stay still
Avoid physical activity and/or outdoor exposure, to avoid any mood-lifting neurochemicals. In fact, remain indoors as much as possible, preferably in the same room.
If you want to absolutely maximize your misery, make your bedroom the sole space for all activities that it’s possible to do there.
Disrupt your sleep
Keep an irregular sleep schedule by varying your bedtime and wake-up times frequently. Sleep in as much as possible, and make up for it by staying up late to ensure ongoing exhaustion.
Maximize screentime
Use digital entertainment as much as possible to distract you from meaningful activities and rest—as a bonus, this will also help you to avoid self-reflection.
Begin and end your day with a device in hand.
Fuel negative emotions
If you’re going to focus on something, focus on problems you cannot control, to stoke the fires of anger and angst.
A good way of doing this is by staying informed about distressing events, while avoiding meaningful actions to address them. Contribute only in token gestures, and then lament the lack of change.
Follow your impulses
Act on short-term desires without considering long-term consequences, while avoiding behaviors that you know might improve your mood or wellbeing.
Trust that doing the same things that have not previously resulted in happiness, will continue to reliably deliver unhappiness.
Set goals to miss
It’s important that your goals should be vague, and overly ambitious in their scope and/or deliverability. Ideally you should also disregard any preparatory work that a person would normally do before embarking on such a project.
Bonus tip: you can further sabotage any chances of progress, by waiting for motivation to strike before you take any action.
Pursue happiness
Focus on chasing happiness itself, instead of improving your situation or skills. Treat happiness as an end goal, instead of a by-product of worthwhile activities.
Want to learn more?
If you’d like to know many more ways to be miserable, we featured these 7 from this book of 40, which we haven’t reviewed yet, but probably will one of these days:
How to Be Miserable: 40 Strategies You Already Use – by Dr. Randy Paterson
Alternatively…
If for some strange reason you’d rather not do those things, you might consider a previous article of ours:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Treat Your Own Knee – by Robin McKenzie
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, a note about the author: he’s a physiotherapist and not a doctor, but with 40 years of practice to his name and 33 letters after his name (CNZM OBE FCSP (Hon) FNZSP (Hon) Dip MDT Dip MT), he seems to know his stuff.
The book covers recognizing the difference between arthritis, degeneration, or normal wear and tear, before narrowing down what your actual problem is and what can be done about it.
While there are many possible causes of knee pain (and by causes, we mean the first-level cause, such as “bad posture” or “old sports injury” or “inflammatory diet” or “repetitive strain” etc, not second-level causes that are also symptoms, like inflammation), McKenzie’s approach involves customizing his system to your body’s specific problems and needs. That’s what most of the book is about.
The style is direct and to-the-point; there’s no sensationalization here nor a feel of being sold anything. There’s lots of science scattered throughout, but all with the intent of enabling the reader to understand what’s going on with the problems, processes, and solutions, and why/how the things that work, work. Where there are exercises offered they are clearly-described and well-illustrated.
Bottom line: this is not a fancy book but it is an effective one. If you have knee pain, this is a very worthwhile one to read.
Click here to check out Treat Your Own Knee, and treat your own knee!
PS: if you have musculoskeletal problems elsewhere in your body, you might want to check out the rest of his body parts series (back, hip, neck, wrist, ankle, etc) for the one that’s tailored to your specific problem.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How they did it: STAT reporters expose how ailing seniors suffer when Medicare Advantage plans use algorithms to deny care
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In a call with a long-time source, what stood out most to STAT reporters Bob Herman and Casey Ross was just how viscerally frustrated and angry the source was about an algorithm used by insurance companies to decide how long patients should stay in a nursing home or rehab facility before being sent home.
The STAT stories had a far-reaching impact:
- The U.S. Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Government Affairs took a rare step of launching a formal investigation into the use of algorithms by the country’s three largest Medicare Advantage insurers.
- Thirty-two House members urged the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to increase the oversight of algorithms that health insurers use to make coverage decisions.
- In a rare step, CMS launched its own investigation into UnitedHealth. It also stiffened its regulations on the use of proprietary algorithms and introduced plans to audit denials across Medicare Advantage plans in 2024.
- Based on STAT’s reporting, Medicare Advantage beneficiaries filed two class-action lawsuits against UnitedHealth and its NaviHealth subsidiary, the maker of the algorithm, and against Humana, another major health insurance company that was also using the algorithm.
- Amid scrutiny, UnitedHealth renamed NaviHealth.
The companies never allowed an on-the-record interview with their executives, but they acknowledged that STAT’s reporting was true, according to the news organization.
Ross and Herman spoke with The Journalist’s Resource about their project and shared the following eight tips.
1. Search public comments on proposed federal rules to find sources.
Herman and Ross knew that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services had put out a request for public comments, asking stakeholders within the Medicare Advantage industry how the system could improve.
There are two main ways to get Medicare coverage: original Medicare, which is a fee-for-service health plan, and Medicare Advantage, which is a type of Medicare health plan offered by private insurance companies that contract with Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans have increasingly become popular in recent years.
Under the Social Security Act, the public has the opportunity to submit comments on Medicare’s proposed national coverage determinations. CMS uses public comments to inform its proposed and final decisions. It responds in detail to all public comments when issuing a final decision.
The reporters began combing through hundreds of public comments attached to a proposed Medicare Advantage rule that was undergoing federal review. NaviHealth, the UnitedHealth subsidiary and the maker of the algorithm, came up in many of the comments, which include the submitters’ information.
“These are screaming all-caps comments to federal regulators about YOU NEED TO SOMETHING ABOUT THIS BECAUSE IT’S DISGUSTING,” Ross says.
“The federal government is proposing rules and regulations all the time,” adds Herman, STAT’s business of health care reporter. “If someone’s going to take the time and effort to comment on them, they must have at least some knowledge of what’s going on. It’s just a great tool for any journalist to use to figure out more and who to contact.”
The reporters also found several attorneys who had complained in the comments. They began reaching out to them, eventually gaining access to confidential documents and intermediaries who put them in touch with patients to show the human impact of the algorithm.
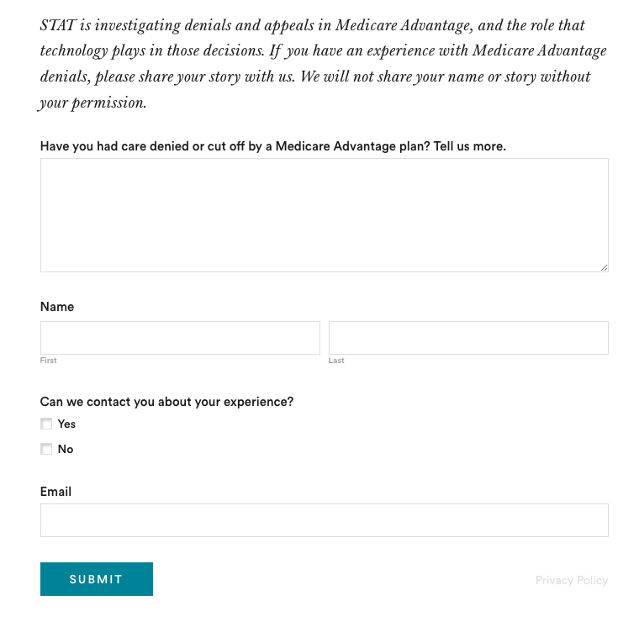
2. Harness the power of the reader submission box.
At the suggestion of an editor, the reporters added a reader submission box at the bottom of their first story, asking them to share their own experiences with Medicare Advantage denials.
The floodgates opened. Hundreds of submissions arrived.
By the end of their first story, Herman and Ross had confidential records and some patients, but they had no internal sources in the companies they were investigating, including Navihealth. The submission box led them to their first internal source.
(Screenshot of STAT’s submission box.) The journalists also combed through LinkedIn and reached out to former and current employees, but the response rate was much lower than what they received via the submission box.
The submission box “is just right there,” Herman says. “People who would want to reach out to us can do it right then and there after they read the story and it’s fresh in their minds.”
3. Mine podcasts relevant to your story.
The reporters weren’t sure if they could get interviews with some of the key figures in the story, including Tom Scully, the former head of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services who drew up the initial plans for NaviHealth years before UnitedHealth acquired it.
But Herman and another colleague had written previously about Scully’s private equity firm and they had found a podcast where he talked about his work. So Herman went back to the podcast — where he discovered Scully had also discussed NaviHealth.
The reporters also used the podcast to get Scully on the phone for an interview.
“So we knew we had a good jumping off point there to be like, ‘OK, you’ve talked about NaviHealth on a podcast, let’s talk about this,’” Herman says. “I think that helped make him more willing to speak with us.”
4. When covering AI initiatives, proceed with caution.
“A source of mine once said to me, ‘AI is not magic,’” Ross says. “People need to just ask questions about it because AI has this aura about it that it’s objective, that it’s accurate, that it’s unquestionable, that it never fails. And that is not true.”
AI is not a neutral, objective machine, Ross says. “It’s based on data that’s fed into it and people need to ask questions about that data.”
He suggests several questions to ask about the data behind AI tools:
- Where does the data come from?
- Who does it represent?
- How is this tool being applied?
- Do the people to whom the tool is being applied match the data on which it was trained? “If racial groups or genders or age of economic situations are not adequately represented in the training set, then there can be an awful lot of bias in the output of the tool and how it’s applied,” Ross says.
- How is the tool applied within the institution? Are people being forced to forsake their judgment and their own ability to do their jobs to follow the algorithm?
5. Localize the story.
More than half of all Medicare beneficiaries have Medicare Advantage and there’s a high likelihood that there are multiple Medicare Advantage plans in every county across the nation.
“So it’s worth looking to see how Medicare Advantage plans are growing in your area,” Herman says.
Finding out about AI use will most likely rely on shoe-leather reporting of speaking with providers, nursing homes and rehab facilities, attorneys and patients in your community, he says. Another source is home health agencies, which may be caring for patients who were kicked out of nursing homes and rehab facilities too soon because of a decision by an algorithm.
The anecdote that opens their first story involves a small regional health insurer in Wisconsin, which was using NaviHealth and a contractor to manage post-acute care services, Ross says.
“It’s happening to people in small communities who have no idea that this insurer they’ve signed up with is using this tool made by this other company that operates nationally,” Ross says.
There are also plenty of other companies like NaviHealth that are being used by Medicare Advantage plans, Herman says. “So it’s understanding which Medicare Advantage plans are being sold in your area and then which post-acute management companies they’re using,” he adds.
Some regional insurers have online documents that show which contractors they use to evaluate post-acute care services.
6. Get familiar with Medicare’s appeals databases
Medicare beneficiaries can contest Medicare Advantage denials through a five-stage process, which can last months to years. The appeals can be filed via the Office of Medicare Hearings and Appeals.
“Between 2020 and 2022, the number of appeals filed to contest Medicare Advantage denials shot up 58%, with nearly 150,000 requests to review a denial filed in 2022, according to a federal database,” Ross and Herman write in their first story. “Federal records show most denials for skilled nursing care are eventually overturned, either by the plan itself or an independent body that adjudicates Medicare appeals.”
There are several sources to find appeals data. Be mindful that the cases themselves are not public to protect patient privacy, but you can find the number of appeals filed and the rationale for decisions.
CMS has two quality improvement organizations, or QIOs, Livanta and Kepro, which are required to file free, publicly-available annual reports, about the cases they handle, Ross says.
Another company, Maximus, a Quality Improvement Contractor, also files reports on prior authorization cases it adjudicates for Medicare. The free annual reports include data on raw numbers of cases and basic information about the percentage denials either overturned or upheld on appeal, Ross explains.
CMS also maintains its own database on appeals for Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage plans) and Part D, which covers prescription drugs, although the data is not complete, Ross explains.
7. Give your editor regular updates.
“Sprinkle the breadcrumbs in front of your editors,” Ross says.
“If you wrap your editors in the process, you’re more likely to be able to get to the end of [the story] before they say, ‘That’s it! Give me your copy,’” Ross says.
8. Get that first story out.
“You don’t have to know everything before you write that first story,” Ross says. “Because with that first story, if it has credibility and it resonates with people, sources will come forward and sources will continue to come forward.”
Read the stories
Denied by AI: How Medicare Advantage plans use algorithms to cut off care for seniors in need
UnitedHealth pushed employees to follow an algorithm to cut off Medicare patients’ rehab care
UnitedHealth used secret rules to restrict rehab care for seriously ill Medicare Advantage patients
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: