What Most People Don’t Know About HIV
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What To Know About HIV This World AIDS Day
Yesterday, we asked 10almonds readers to engage in a hypothetical thought experiment with us, and putting aside for a moment any reason you might feel the scenario wouldn’t apply for you, asked:
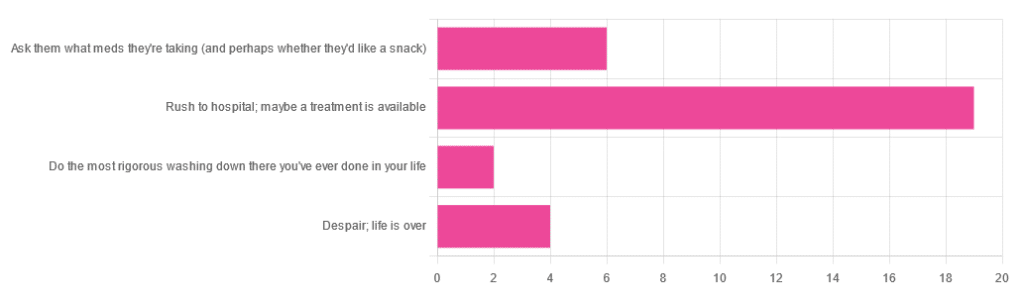
❝You have unprotected sex with someone who, afterwards, conversationally mentions their HIV+ status. Do you…❞
…and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses. Of those who responded…
- Just over 60% said “rush to hospital; maybe a treatment is available”
- Just under 20% said “ask them what meds they’re taking (and perhaps whether they’d like a snack)”
- Just over 10% said “despair; life is over”
- Two people said “do the most rigorous washing down there you’ve ever done in your life”
So, what does science say about it?
First, a quick note on terms
- HIV is the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It does what it says on the tin; it gives humans immunodeficiency. Like many viruses that have become epidemic in humans, it started off in animals (called SIV, because there was no “H” involved yet), which were then eaten by humans, passing the virus to us when it one day mutated to allow that.
- It’s technically two viruses, but that’s beyond the scope of today’s article; for our purposes they are the same. HIV-1 is more virulent and infectious than HIV-2, and is the kind more commonly found in most of the world.
- AIDS is Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, and again, is what it sounds like. When a person is infected with HIV, then without treatment, they will often develop AIDS.
- Technically AIDS itself doesn’t kill people; it just renders people near-defenseless to opportunistic infections (and immune-related diseases such as cancer), since one no longer has a properly working immune system. Common causes of death in AIDS patients include cancer, influenza, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
People who contract HIV will usually develop AIDS if untreated. Untreated life expectancy is about 11 years.
HIV/AIDS are only a problem for gay people: True or False?
False, unequivocally. Anyone can get HIV and develop AIDS.
The reason it’s more associated with gay men, aside from homophobia, is that since penetrative sex is more likely to pass it on, then if we go with the statistically most likely arrangements here:
- If a man penetrates a woman and passes on HIV, that woman will probably not go on to penetrate someone else
- If a man penetrates a man and passes on HIV, that man could go on to penetrate someone else—and so on
- This means that without any difference in safety practices or promiscuity, it’s going to spread more between men on average, by simple mathematics.
- This is why “men who have sex with men” is the generally-designated higher-risk category.
There is medication to cure HIV/AIDS: True or False?
False so far (though there have been individual case studies of gene treatments that may have cured people—time will tell).
But! There are medications that can prevent HIV from being a life-threatening problem:
- PrEP (Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis) is a medication that one can take in advance of potential exposure to HIV, to guard against it.
- This is a common choice for people aren’t sure about their partners’ statuses, or people working in risky environments.
- PEP (Post-Exposure Prophylaxis) is a medication that one can take after potential exposure to HIV, to “nip it in the bud”.
- Those of you who were rushing to hospital in our poll, this is what you’re rushing there for.
- ARVs (Anti-RetroVirals) are a class of medications (there are different options; we don’t have room to distinguish them) that reduce an HIV+ person’s viral load to undetectable levels.
- Those of you who were asking what meds your partner was taking, these will be those meds. Also, most of them are to be taken in the morning with food, so that’s what the snack was for.
If someone is HIV+, the risk of transmission in unprotected sex is high: True or False?
True or False, with false being the far more likely. It depends on their medications, and this is why you were asking. If someone is on ARVs and their viral load is undetectable (as is usual once someone has been on ARVs for 6 months), they cannot transmit HIV to you.
U=U is not a fancy new emoticon, it means “undetectable = untransmittable”, which is a mathematically true statement in the case of HIV viral loads.
See: NIH | HIV Undetectable=Untransmittable (U=U)
If you’re thinking “still sounds risky to me”, then consider this:
You are safer having unprotected sex with someone who is HIV+ and on ARVs with an undetectable viral load, than you are with someone you are merely assuming is HIV- (perhaps you assume it because “surely this polite blushing young virgin of a straight man won’t give me cooties” etc)
Note that even your monogamous partner of many decades could accidentally contract HIV due to blood contamination in a hospital or an accident at work etc, so it’s good practice to also get tested after things that involve getting stabbed with needles, cut in a risky environment, etc.
If you’re concerned about potential stigma associated with HIV testing, you can get kits online:
CDC | How do I find an HIV self-test?
(these are usually fingerprick blood tests, and you can either see the results yourself at home immediately, or send it in for analysis, depending on the kit)
If I get HIV, I will get AIDS and die: True or False?
False, assuming you get treatment promptly and keep taking it. So those of you who were at “despair; life is over” can breathe a sigh of relief now.
However, if you get HIV, it does currently mean you will have to take those meds every day for the rest of your (no reason it shouldn’t be long and happy) life.
So, HIV is definitely still something to avoid, because it’s not great to have to take a life-saving medication every day. For a little insight as to what that might be like:
HIV.gov | Taking HIV Medication Every Day: Tips & Challenges
(as you’ll see there, there are also longer-lasting injections available instead of daily pulls, but those are much less widely available)
Summary
Some quick take-away notes-in-a-nutshell:
- Getting HIV may have been a death sentence in the 1980s, but nowadays it’s been relegated to the level of “serious inconvenience”.
- Happily, it is very preventable, with PrEP, PEP, and viral loads so low that they can’t transmit HIV, thanks to ARVs.
- Washing will not help, by the way. Safe sex will, though!
- As will celibacy and/or sexual exclusivity in seroconcordant relationships, e.g. you have the same (known! That means actually tested recently! Not just assumed!) HIV status as each other.
- If you do get it, it is very manageable with ARVs, but prevention is better than treatment
- There is no certain cure—yet. Some people (small number of case studies) may have been cured already with gene therapy, but we can’t know for sure yet.
Want to know more? Check out:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s Your Vascular Dementia Risk?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We often say that “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain”, and this is because the former feeds the latter, with oxygen and nutrients, and also clears away detritus like beta-amyloid (associated with Alzheimer’s) and alpha-synuclein (associated with Parkinson’s).
For more on those, see: How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer)
For this reason, there are many risk factors that apply equally cardiovascular disease (CVD), and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and other vascular dementias, as well as stroke risk.
The link between the two has also been studied; recently a team of scienists led by Dr. Anisa Dhana asked the question:
❝What is the association between cardiovascular health (CVH) and biomarkers of neurodegeneration, including neurofilament light chain and total tau?❞
To answer this, they looked at data from more than 10,000 Americans aged 65+; of these, they were able to get serum samples from 5,470 of them, and tested those samples for the biomarkers of neurodegeneration mentioned above.
They then tabulated the results with cardiovascular health scores based on the American Heart Association (AHA)’s “Life’s Simple 7” tool, and found, amongst other things:
- 34.6% of participants carried the APOE e4 allele, a genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s.
- Higher CVH scores were associated with lower NfL levels, but not with t-tau concentrations.
- APOE e4 carriers with high CVH had significantly lower NfL levels.
- Race did not influence the CVH-NfL relationship.
- Higher CVH was linked to a slower annual increase in NfL levels but did not affect t-tau changes.
- Over 10 years, participants with the lowest CVH scores saw a 7.1% annual increase in NfL levels, while those with the highest CVH scores had a 5.2% annual increase.
- Better CVH is linked to lower serum NfL levels, regardless of age, sex, or race.
- CVH is particularly crucial for APOE e4 carriers
In other words: higher cardiovascular health meant lower markers of neurodegeneration, and this not only still held true for APOE e4 carriers, but also, the benefits actually even more pronounced in those participants.
You may be wondering: “but it said it helped with NfL levels, not t-tau concentrations?” And, indeed, it is so. But this means that the overall neurodegeneration risk is still inversely proportional to cardiovascular health; it just means it’s not a magical panacea and we must still do other things too.
See also: How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
And as for the study, you can read the paper itself in full here:
Cardiovascular Health and Biomarkers of Neurodegenerative Disease in Older Adults
Life’s Simple 7
We mentioned that they used the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” tool to assess cardiovascular health; it is indeed simple, but important. Here it is:
Metric Poor Intermediate Ideal Current smoking Yes Former ≤12 mo Never or quit >12 mo BMI, kg/m2 ≥30 25–29.9 <25 Physical activity None 1–149 min/wk of moderate activity or 1–74 min/wk of vigorous activity or 1–149 min/wk of moderate and vigorous activity ≥150 min/wk of moderate activity or ≥75 min/wk of vigorous activity or ≥150 min/wk of moderate and vigorous activity Diet pattern score* 0–1 2–3 4–5 Total cholesterol, mg/dL ≥240 200–239 or treated to goal <200 Blood pressure, mm Hg SBP ≥140 or DBP ≥90 SBP 120–139 or DBP 80–89 or treated to goal <120/<80 Fasting plasma glucose, mg/dL ≥126 100–125 or treated to goal <100 *Each of the following 5 diet elements is given a score of 1: (1) ≥4.5 cups/day of fruits and vegetables; (2) ≥2 servings/week of fish; (3) ≥3 servings/day of whole grains; (4) no more than 36 oz/wk of sugar‐sweetened beverages; and (5) no more than 1500 mg/d of sodium.
As the AHA notes,
❝Unfortunately, 99% of the U.S. adult population has at least one of seven cardiovascular health risks: tobacco use,
poor diet, physical inactivity, unhealthy weight, high blood pressure, high cholesterol or high blood glucose.❞It then goes on to talk about the financial burden of this on employers, but this was taken from a workplace health resource, and we recognize the rest of it won’t be of pressing concern for most of our readers. In case you are interested though, here it is:
American Heart Association | Life’s Simple 7® Journey to Health™
For a more practical (if you’re just a private individual and employee healthcare is not your main concern) overview, see:
Want to know more?
Here are some very good starting points for improving each of those 7 metrics, as necessary:
- Which Addiction-Quitting Methods Work Best?
- How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
- The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, & Move More
- Which Diet? Top Diets Ranked By Experts
- Lower Cholesterol Naturally, Without Statins
- 10 Ways To Lower Blood Pressure Naturally
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cashew nuts to coconut, we picked the cashews.
Why?
It can be argued this isn’t a fair comparison, as coconuts aren’t true nuts, but it’s at the very least a useful comparison, because they have very similar (often the same) culinary uses, so deciding between one or the other is something people will often do.
In terms of macros, cashews have 6x the protein and more than 2x the fiber, as well as slightly more fat (but the fats are healthy, as are those of coconut, by the way) and 2x the carbs. Depending on what you’re looking for, this head-to-head could come out differently, but we say it’s a win for cashews.
You may be wondering: if cashews have more of all those things, what are coconuts made of? And the answer is that coconuts have 8x the water (and yes, this is counting the coconut meat only, not including the milk inside). Of course, if you get dessicated coconut, then it won’t have that, but we’re comparing fresh to fresh.
In the category of vitamins, cashews have a lot more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, E, and K. Meanwhile, coconut has more vitamin C, but it’s not a lot. An easy win for cashews here.
When it comes to minerals, cashews have rather more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, coconut has more sodium. Another easy win for cashews.
Cashews also have the lower glycemic index.
All in all, cashews win the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Shoe Wear Patterns: What They Mean, Why It Matters, & How To Fix It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you look under your shoes, do you notice how the tread is worn more in some places than others? Specific patterns of shoe wear correspond to how our body applies force, weight, and rotational movement. This reveals how we move, and uneven wear can indicate problematic movement dynamics.
The clues in your shoes
Common shoe wear patterns include:
- Diagonal wear on the outside of the heel: caused by foot angle, leg position, and instability, leading to joint stress.
- Rotational wear at specific points: due to internal or external rotation, often originating from the hip, pelvis, or torso.
- Wear above the big toe: caused by excessive toe lifting, often associated with a “lighter” or kicking leg.
Fixing movement issues to prevent wear involves correcting posture, improving balance, and adjusting how the legs land during walking/running.
Key fixes include:
- Aligning the center of gravity properly to prevent leg overcompensation.
- Ensuring feet land under the hips and not far in front.
- Stabilizing the torso to avoid unnecessary rotation.
- Engaging the glutes effectively to reduce hip flexor dominance and improve leg mechanics.
- Maintaining even weight distribution on both legs to prevent excessive lifting or twisting.
Posture and walking mechanics are vital to reducing uneven wear, but meaningful, lasting change takes time and focused effort, to build new habits.
For more on all this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
53 Studies Later: The Best Way to Improve VO2 Max
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
VO2 max measures maximum oxygen usage during intense exercise and reflects overall health and performance. To have a high VO2 max, efficient functioning of lungs, heart, red blood cells, muscles, and mitochondria is crucial. So, how to get those?
Let’s HIIT it!
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) outperforms moderate-intensity exercise, by a long way. Further, based on the data from the 53 studies mentioned in the title, we can know which of the protocols tested work best, and they are:
- 15×15 Interval Training: 15 seconds sprint (90–95% max heart rate) + 15 seconds active rest (70% max heart rate), repeated 47 times.
- 4×4 Interval Training: 4 minutes sprint (90–95% max heart rate) + 3 minutes active rest (70% max heart rate), repeated 4 times.
Whichever you choose, it is best to then do that 3x per week.
Note that “sprint” can mean any maximum-effort cardio exercise; it doesn’t have to be running specifically. Cycling or swimming, for example, are fine options too, as is jumping rope.
For more on each of these, plus how the science got there, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Your Metabolism Says About How Aggressive Breast Cancer Is Likely To Be For You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ll get straight to it:
More than 120 million Americans have diabetes or pre-diabetes, and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)* is the most aggressive breast cancer form.
These may seem like unrelated statements, until we consider that patients with obesity-driven** diabetes have much worse TNBC outcomes.
*The “triple-negative” refers to:
- the cancer cells don’t have estrogen receptors
- the cancer cells don’t have progesterone receptors
- the cancer cells don’t make the protein HER2, or at least not in clinically relevant amounts.
**with regard to “obesity-driven”, that is what it is called, and the presence of excess fat does play an important role as we will see, but the fundamental culprit is insulin resistance, as we will also see.
The connection
Superficially, the connection between obesity-driven diabetes and worse TNBC outcomes could be put down to “a person who is already unhealthy will generally fare worse in most health things than an otherwise healthy person”. And, in and of itself, that’s a fair point. Comorbidities certainly do tend to flock together and make each other worse.
On the flipside, this does also mean that the more points of good health we have in our favor, the greater our chances of faring better if something (such as a cancer) does strike us regardless. So, there’s a fair motivation to always keep on top of all aspects of health, so far as reasonably possible.
However, there’s more to it than that.
Dr. Naomi Ko et al., a team of researchers at Boston University, found that diabetes alters breast cancer biology, making TNBC more aggressive and increasing the risk of brain metastasis (i.e., the cancer spreading to the brain).
Specifically, exosomes from fat cells carry microRNAs that worsen TNBC behavior, enhancing the cancer’s:
- cell growth
- movement
- survival under stress
- brain colonization
This also means that certain microRNA patterns predict breast cancer progression and/or survival.
You can find the paper itself here:
Insulin Resistance Increases TNBC Aggressiveness and Brain Metastasis via Adipocyte-derived Exosomes
Why this matters
The researchers argue that their findings suggest the need for special monitoring and treatment for TNBC patients with metabolic disorders like diabetes, and that treating underlying conditions (such as diabetes) alongside cancer is likely to improve outcomes.
On an individual level rather than systemic (assuming you, dear reader, to be a private individual who is not, for example, in charge of health policy for a region, or something like that), what this means is:
We must avoid carrying too much excess fat yes, and/but we must also particularly focus on avoiding/reversing insulin resistance, which can be a silent killer even without excess adiposity, because the noticeable signs and symptoms (including blood sugar irregularities) occur only well into insulin resistance, when the poor overworked pancreas can no longer crank out enough insulin to keep things ticking over.
With that in mind, do check out in particular the two following articles:
How To Lose Weight (Healthily!) ← if applicable. If on the other hand you’re already in the “healthy” body fat percentage range of 20–25% for women or 15–20% for men, then losing what fat you have will not be beneficial, and may even be harmful, depending on other factors.
How To Avoid & Reverse Insulin Resistance ← this one’s super-important!
And of course:
How To Triple Your Breast Cancer Survival Chances
And if you want to get really well-informed, then we highly recommend checking out:
The Smart Woman’s Guide to Breast Cancer – by Dr. Jenn Simmons
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
We’re aware that very many of our readers are women, who do not have a prostate.
However, dear reader: if you do have one, and/or love someone who has one, this is a good thing to know about.
The prostate gland is a (hopefully) walnut-sized gland (it actually looks a bit like a walnut too), that usually sits just under the bladder.
See also: How to Locate Your Prostate*
*The scale is not great in these diagrams, but they’ll get the job done. Besides, everyone is different on the inside, anyway. Not in a “special unique snowflake” way, but in a “you’d be surprised how much people’s insides move around” way.
Fun fact: did you ever feel like your intestines are squirming? That’s because they are.
You can’t feel it most of the time due to the paucity of that kind of nervous sensation down there, but the peristaltic motion that they use to move food along them on the inside, also causes them push against the rest of your guts, on the outside of them. This is the exact same way that many snakes move about.
If someone has to perform an operation in that region, sometimes it will be necessary to hang the intestines on a special rack, to keep them in one place for the surgery.
What can go wrong?
There are two very common things that can go wrong with the prostate:
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH), otherwise known as an enlarged prostate
- Prostate cancer
For most men, the prostate gland continues to grow with age, which is how the former comes about so frequently.
For everyone, due to the nature of the mathematics involved in cellular mutation and replication, we will eventually get cancer if something else doesn’t kill us first.
- Prostate cancer affects 12% of men overall, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing each year thereafter.
- Prostate cancer can look like BPH in the early stages (and/or, an enlarged prostate can turn cancerous) so it’s important to not shrug off the symptoms of BPH.
How can BPH be avoided/managed?
There are prescription medications that can help reduce the size of the prostate, including testosterone blockers (such as spironolactone and bicalutamide) and 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride. Each have their pros and cons:
- Testosterone-blockers are the heavy-hitters, and work very well… but have more potential adverse side effects (your body is used to running on testosterone, after all)
- 5α-reductase inhibitors aren’t as powerful, but they block the conversion of free testosterone to dihydrogen testosterone (DHT), and it’s primarily DHT that causes the problems. By blocking the conversion of T to DHT, you may actually end up with higher serum testosterone levels, but fewer ill-effects. Exact results will vary depending on your personal physiology, and what else you are taking, though.
There are also supplements that can help, including saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil. Here’s a good paper that covers both:
We have recommended saw palmetto before for a variety of uses, including against BPH:
Too much or too little testosterone? This one supplement may fix that
You might want to avoid certain medications that can worsen BPH symptoms (but not actually the size of the prostate itself). They include:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (most modern antidepressants aren’t this kind; ask your pharmacist/doctor if unsure)
You also might want to reduce/skip:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
In all the above cases, it’s because of how they affect the bladder, not the prostate, but given their neighborliness, each thing affects the other.
What if it’s cancer? How do I know and what do I do?
The creator of the Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test has since decried it as “a profit-driven health disaster” that is “no better than a coin toss”, but it remains the first go-to of many medical services.
However, there’s a newer, much more accurate test, called the Prostate Screening Episwitch (PSE) test, which is 94% accurate, so you might consider asking your healthcare provider whether that’s an option:
The new prostate cancer blood test with 94 per cent accuracy
As for where to go from there, we’re out of space for today, but we previously reviewed a very good book about this, Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer, and we highly recommend it—it could easily be a literal lifesaver.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: