Inhaled Eucalyptus’s Immunomodulatory and Antimicrobial Effects
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
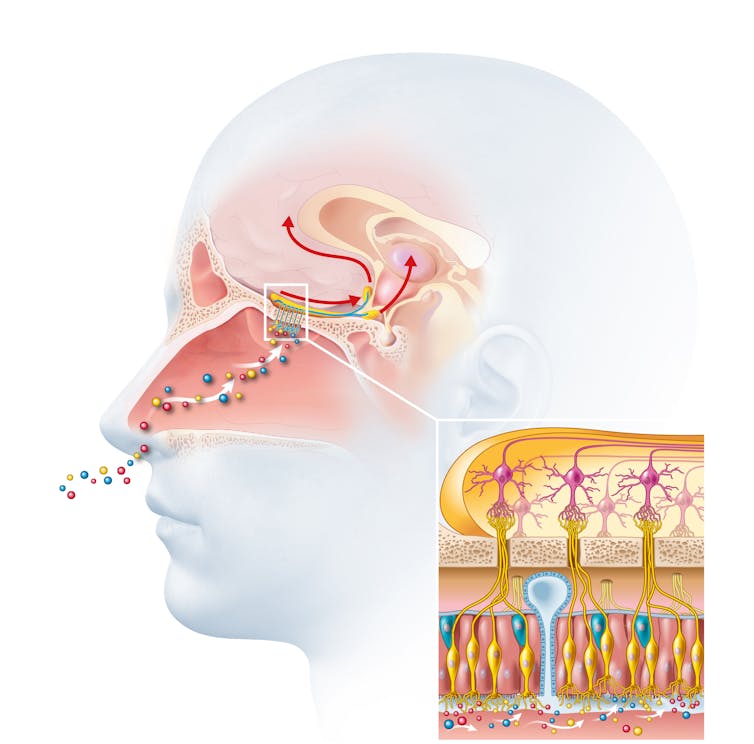
❝At the first hint of a cough or a cold, I resort to steam inhalation. Some people add herbs or aromatic oils to the boiling water. What do you recommend?❞
First of all, please do be careful:
Western science’s view is predominantly “this is popular and/but evidence for its usefulness is lacking”:
But! Traditional Chinese Medicine indicates shuanghuanglian, yuxingcao and qingkailing, which the China Food and Drug Administration has also approved:
Chinese Medicine in Inhalation Therapy: A Review of Clinical Application and Formulation Development
Indian scientists are also looking at modern scientific applications of certain Ayurvedic herbs:
Promising phytochemicals of traditional Indian herbal steam inhalation therapy to combat COVID-19
In terms of what is likely more available to you, there are several reasons to choose eucalyptus over popular alternatives:
Immune-modifying and antimicrobial effects of Eucalyptus oil and simple inhalation devices
For the sake of being methodical, here’s an example product on Amazon, though we’re sure you’d have no trouble finding this in your local pharmacy if you prefer.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Peanuts vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peanuts to walnuts, we picked the peanuts.
Why?
What heresy is this?!
“But walnuts are more expensive!”, we hear you cry. “They have omega-3s! They look like little brains!”
And, we must confess, all of these things are true. However…
In terms of macros, peanuts have much more protein, and a little more fiber, while walnuts have more fat. And yes, those fats are healthy, and yes, the omega-3 content of walnuts is worth noting. However, while walnuts are higher in total and polyunsaturated fats, peanuts are higher in monounsaturated fats, which are also beneficial. All in all, we’re calling it either a tie on macros, or a win for peanuts, as it really is a lot more protein, and we always consider fiber of top importance.
In the category of vitamins, peanuts have (a lot) more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B9, E, and choline, while walnuts have a (very) little more of vitamins B2 and B6. So, a clear win for peanuts here, and that’s without considering that in terms of margins of difference, peanuts have 11x the vitamin E, for example.
Looking at minerals, peanuts have more iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while walnuts have more calcium, copper, and manganese. Another clear win for peanuts.
When it comes to polyphenols, peanuts have more diverse polyphenols, while walnuts have a greater total mass of polyphenols. A tie here, or possibly a subjective win for walnuts.
In short, both are great and both have their merits, but by the numbers, and adding up the sections, peanuts take the win today. Still (assuming no allergy), by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
How to Boost Your Metabolism When Over 50
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Dawn Andalon, a physiotherapist, explains the role of certain kinds of exercise in metabolism; here’s what to keep in mind:
Work with your body
Many people make the mistake of thinking that it is a somehow a battle of wills, and they must simply will their body to pick up the pace. That’s not how it works though, and while that can occasionally get short-term results, at best it’ll quickly result in exhaustion. So, instead:
- Strength training: engage in weight training 2–3 times per week; build muscle and combat bone loss too. Proper guidance from trainers familiar with older adults is recommended. Pilates (Dr. Andalon is a Pilates instructor) can also complement strength training by enhancing core stability and preventing injuries. The “building muscle” thing is important for metabolism, because muscle increases the body’s metabolic base rate.
- Protein intake: Dr. Andalon advises to consume 25–30 grams of lean protein per meal to support muscle growth and repair (again, important for the same reason as mentioned above re exercise). Dr. Andalon’s recommendation is more protein per meal than is usually advised, as it is generally held that the body cannot use more than about 20g at once.
- Sleep quality: prioritize good quality sleep, by practising good sleep hygiene, and also addressing any potential hormonal imbalances affecting sleep. If you do not get good quality sleep, your metabolism will get sluggish in an effort to encourage you to sleep more.
- Exercise to manage stress: regular walking (such as the popular 10,000 steps daily) helps manage stress and improve metabolism. Zone two cardio (low-intensity movement) also supports joint health, blood flow, and recovery—but the main issue about stress here is that if your body experiences unmanaged stress, it will try to save you from whatever is stressing you by reducing your metabolic base rate so that you can out-survive the bad thing. Which is helpful if the stressful thing is that the fruit trees got stripped by giraffes and hunting did not yield a kill, but not so helpful if the stressful thing is the holiday season.
- Hydration: your body cannot function properly without adequate hydration; water is needed (directly or indirectly) for all bodily processes, and your metabolism will also “dry up” without it.
- Antidiabetic & anti-inflammatory diet: minimize sugar intake and reduce processed foods, especially those with inflammatory refined oils (esp. canola & sunflower) and the like. This has very directly to do with your body’s energy metabolism, and as they say in computing, “garbage in; garbage out”.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Mung Beans vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mung beans to black beans, we picked the black beans.
Why?
Both are great! But…
In terms of macros, black beans have more protein, carbs, and fiber, as well as the lower glycemic index (although both are already low). So, a clear win for black beans here.
In the category of vitamins, mung beans have more of vitamins A, B5, B9, and C, while black beans have more of vitamins B1, B6, E, K, and choline. Thus, a slight win for black beans this time.
When it comes to minerals, mung beans have more selenium and zinc, while black beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. An easy win for black beans.
Of course, enjoy either or both—but if you’re going to pick one, we say black beans win the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head-to-Head
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Capsaicin’s Hot Benefits
Capsaicin, the compound in hot peppers that makes them spicy, is a chemical irritant and a neurotoxin. However, humans being humans, we decided to eat them for fun.
In contrast to many other ways in which humans recreationally enjoy things that are objectively poisonous, consuming capsaicin (in moderation) is considered to have health benefits, such as aiding weight loss (by boosting metabolism) and reducing inflammation.
Let’s see what the science says…
First: is it safe?
Capsaicin is classified as “Generally Recognized As Safe”. That said, the same mechanism that causes them to boost metabolism, does increase blood pressure:
Mechanisms underlying the hypertensive response induced by capsaicin
If you are in good cardiovascular health, this increase should be slight and not pose any threat, unless for example you enter a chili-eating contest when not acclimated to such:
Capsaicin and arterial hypertensive crisis
As ever, if unsure, do check with your doctor first, especially if you are taking any blood pressure medications, or otherwise have known blood pressure issues.
Does it really boost metabolism?
It certainly does; it works by increasing oxygen consumption and raising body temperature, both of which mean more calories will be burned for the same amount of work:
Dietary capsaicin and its anti-obesity potency: from mechanism to clinical implications
This means, of course, that chili peppers enjoy the status of being functionally a “negative calorie” food, and a top-tier one at that:
Chili pepper as a body weight-loss food
Here’s a good quality study that showed a statistically significant* fat loss improvement over placebo:
*To put it in numbers, the benefit was:
- 5.91 percentage points lower body fat percentage than placebo
- 6.68 percentage points greater change in body fat mass than placebo
See also: Difference between percentages and percentage points
For those who prefer big reviews than single studies, we’ve got you covered:
Does it really reduce inflammation?
Counterintuitive as it may seem, yes. By means of reducing oxidative stress. Given that things that reduce oxidative stress tend to reduce inflammation, and in turn tend to reduce assorted disease risks (from diabetes to cancer to Alzheimer’s), this probably has more knock-on benefits too, but we don’t have room to explore all of those today.
Fresh peppers are best for this, but dried peppers (such as when purchased as a ground spice in the supermarket, or when purchased as a capsule-based supplement) still have a very respectable anti-inflammatory effect:
- Capsaicinoids, Polyphenols and Antioxidant Activities of Capsicum annuum: Comparative Study of the Effect of Ripening Stage and Cooking Methods
- A Review on the Effect of Drying on Antioxidant Potential of Fruits and Vegetables
How much should we take?
It’s recommended to start at a low dose and gradually increase it, but 2–6mg of capsaicin per day is the standard range used in studies.
If you’re getting this from peppers, then for example cayenne pepper (a good source of capsaicin) contains around 2.5mg of capsaicin per 1 gram of cayenne.
In the case of capsules, if for example you don’t like eating hot pepper, this will usually mean taking 2–6 capsules per day, depending on dosage.
Make sure to take it with plenty of water!
Where can we get it?
Fresh peppers or ground spice from your local grocery store is fine. Your local health food store probably sells the supplements, too.
If you’d like to buy it online, here is an example product on Amazon.
Note: options on Amazon were more limited than usual, so this product is not vegan, and probably not halal or kosher, as the capsule contains an unspecified gelatin.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
You can train your nose – and 4 other surprising facts about your sense of smell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Would you give up your sense of smell to keep your hair? What about your phone?
A 2022 US study compared smell to other senses (sight and hearing) and personally prized commodities (including money, a pet or hair) to see what people valued more.
The researchers found smell was viewed as much less important than sight and hearing, and valued less than many commodities. For example, half the women surveyed said they’d choose to keep their hair over sense of smell.
Smell often goes under the radar as one of the least valued senses. But it is one of the first sensory systems vertebrates developed and is linked to your mental health, memory and more.
Here are five fascinating facts about your olfactory system.
DimaBerlin/Shutterstock 1. Smell is linked to memory and emotion
Why can the waft of fresh baking trigger joyful childhood memories? And why might a certain perfume jolt you back to a painful breakup?
Smell is directly linked to both your memory and emotions. This connection was first established by American psychologist Donald Laird in 1935 (although French novelist Marcel Proust had already made it famous in his reverie about the scent of madeleines baking.)
Odours are first captured by special olfactory nerve cells inside your nose. These cells extend upwards from the roof of your nose towards the smell-processing centre of your brain, called the olfactory bulb.
Smells are first detected by nerve cells in the nose. Axel_Kock/Shutterstock From the olfactory bulb they form direct connection with the brain’s limbic system. This includes the amygdala, where emotions are generated, and the hippocampus, where memories are created.
Other senses – such as sight and hearing – aren’t directly connected to the lymbic system.
One 2004 study used functional magnetic resonance imaging to demonstrate odours trigger a much stronger emotional and memory response in the brain than a visual cue.
2. Your sense of smell constantly regenerates
You can lose your ability to smell due to injury or infection – for example during and after a COVID infection. This is known as olfactory dysfunction. In most cases it’s temporary, returning to normal within a few weeks.
This is because every few months your olfactory nerve cells die and are replaced by new cells.
We’re not entirely sure how this occurs, but it likely involves your nose’s stem cells, the olfactory bulb and other cells in the olfactory nerves.
Other areas of your nervous system – including your brain and spinal cord – cannot regenerate and repair after an injury.
Constant regeneration may be a protective mechanism, as the olfactory nerves are vulnerable to damage caused by the external environment, including toxins (such as cigarette smoke), chemicals and pathogens (such as the flu virus).
But following a COVID infection some people might continue to experience a loss of smell. Studies suggest the virus and a long-term immune response damages the cells that allow the olfactory system to regenerate.
3. Smell is linked to mental health
Around 5% of the global population suffer from anosmia – total loss of smell. An estimated 15-20% suffer partial loss, known as hyposmia.
Given smell loss is often a primary and long-term symptom of COVID, these numbers are likely to be higher since the pandemic.
Yet in Australia, the prevalence of olfactory dysfunction remains surprisingly understudied.
Losing your sense of smell is shown to impact your personal and social relationships. For example, it can mean you miss out on shared eating experiences, or cause changes in sexual desire and behaviour.
In older people, declining ability to smell is associated with a higher risk of depression and even death, although we still don’t know why.
Losing your sense of smell can have a major impact on mental health. Halfpoint/Shutterstock 4. Loss of smell can help identify neurodegenerative diseases
Partial or full loss of smell is often an early indicator for a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Patients frequently report losing their sense of smell years before any symptoms show in body or brain function. However many people are not aware they are losing their sense of smell.
There are ways you can determine if you have smell loss and to what extent. You may be able to visit a formal smell testing centre or do a self-test at home, which assesses your ability to identify household items like coffee, wine or soap.
5. You can train your nose back into smelling
“Smell training” is emerging as a promising experimental treatment option for olfactory dysfunction. For people experiencing smell loss after COVID, it’s been show to improve the ability to detect and differentiate odours.
Smell training (or “olfactory training”) was first tested in 2009 in a German psychology study. It involves sniffing robust odours — such as floral, citrus, aromatic or fruity scents — at least twice a day for 10—20 seconds at a time, usually over a 3—6 month period.
Participants are asked to focus on the memory of the smell while sniffing and recall information about the odour and its intensity. This is believed to help reorganise the nerve connections in the brain, although the exact mechanism behind it is unclear.
Some studies recommend using a single set of scents, while others recommend switching to a new set of odours after a certain amount of time. However both methods show significant improvement in smelling.
This training has also been shown to alleviate depressive symptoms and improve cognitive decline both in older adults and those suffering from dementia.
Just like physiotherapy after a physical injury, olfactory training is thought to act like rehabilitation for your sense of smell. It retrains the nerves in your nose and the connections it forms within the brain, allowing you to correctly detect, process and interpret odours.
Lynn Nazareth, Research Scientist in Olfactory Biology, CSIRO
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Green Coffee Bean Extract: Coffee Benefits Without The Coffee?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coffee is, on balance, very good for the health in moderation. We wrote about it here:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Some quick facts before moving on:
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
Those are some compelling statistics!
But what about the caffeine content?
Assuming one doesn’t have a caffeine sensitivity, caffeine is also healthy in moderation—but it is easy to accidentally become dependent on it, so it can be good to take a “tolerance break” once in a while, and then reintroduce it with more modest moderation:
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
We also, for that matter, have discussed its impact on the gut:
Coffee & Your Gut ← surprise, it’s a positive impact
What if I don’t like coffee?
We suspect that, having seen the title of this article, you know what the answer’s going to be here:
Green coffee bean extract is the extract from green (i.e. unroasted) coffee beans. It has one or two advantages over drinking coffee:
- For those who do not like drinking coffee, this supplement sidesteps that neatly
- Roasting coffee beans destroys a lot (sometimes almost all; it depends on the temperature and duration) of their chlorogenic acid, a highly beneficial polyphenol; using unroasted (i.e. green) coffee beans avoids that
See: Role of roasting conditions in the level of chlorogenic acid content in coffee beans
All about GCE and CGA
That’s “green coffee extract” and “chlorogenic acid”, respectively, bearing in mind that the latter is found generously in the former.
As to what it does:
❝CGA is an important and biologically active dietary polyphenol, playing several important and therapeutic roles such as antioxidant activity, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, neuroprotective, anti-obesity, antiviral, anti-microbial, anti-hypertension, free radicals scavenger and a central nervous system (CNS) stimulator. Furthermore, CGA causes hepatoprotective effects.❞
👆 Those are the things we know for sure that it does. And it may do even more things:
❝In addition, it has been found that CGA could modulate lipid metabolism and glucose in both genetically and healthy metabolic related disorders. It is speculated that CGA can perform crucial roles in lipid and glucose metabolism regulation and thus help to treat many disorders such as hepatic steatosis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity as well.❞
Read in full: Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research
About lipid metabolism…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum total cholesterol levels.
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels.
- Increases in HDL (“good” cholesterol) after green coffee bean extract consumption are significant in green coffee bean extract dosages ≥400mg/day.
About blood glucose and insulin…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly improved fasting blood sugar levels
- Green coffee extract supplementation at ≥400 mg/day significantly lowered postprandial insulin levels (that’s good)
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: