Gluten: What’s The Truth?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gluten: What’s The Truth?
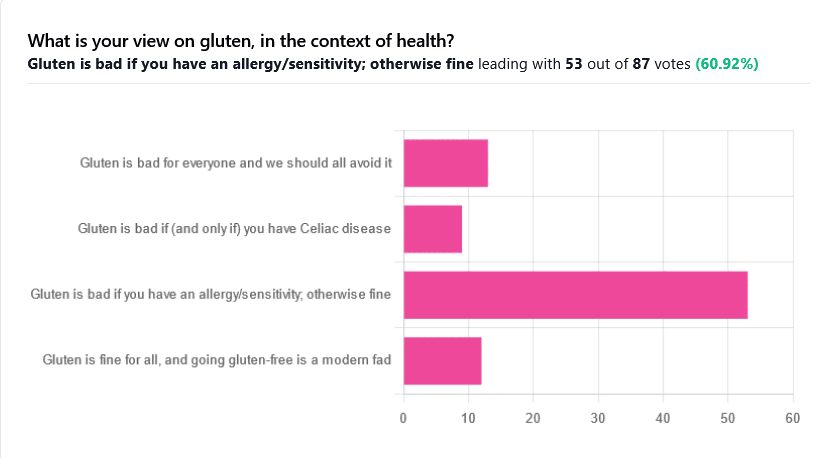
We asked you for your health-related view of gluten, and got the above spread of results. To put it simply:
Around 60% of voters voted for “Gluten is bad if you have an allergy/sensitivity; otherwise fine”
The rest of the votes were split fairly evenly between the other three options:
- Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it
- Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease
- Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad
First, let’s define some terms so that we’re all on the same page:
What is gluten?
Gluten is a category of protein found in wheat, barley, rye, and triticale. As such, it’s not one single compound, but a little umbrella of similar compounds. However, for the sake of not making this article many times longer, we’re going to refer to “gluten” without further specification.
What is Celiac disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease. Like many autoimmune diseases, we don’t know for sure how/why it occurs, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors have been strongly implicated, with the latter putatively including overexposure to gluten.
It affects about 1% of the world’s population, and people with Celiac disease will tend to respond adversely to gluten, notably by inflammation of the small intestine and destruction of enterocytes (the cells that line the wall of the small intestine). This in turn causes all sorts of other problems, beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but suffice it to say, it’s not pleasant.
What is an allergy/intolerance/sensitivity?
This may seem basic, but a lot of people conflate allergy/intolerance/sensitivity, so:
- An allergy is when the body mistakes a harmless substance for something harmful, and responds inappropriately. This can be mild (e.g. allergic rhinitis, hayfever) or severe (e.g. peanut allergy), and as such, responses can vary from “sniffly nose” to “anaphylactic shock and death”.
- In the case of a wheat allergy (for example), this is usually somewhere between the two, and can for example cause breathing problems after ingesting wheat or inhaling wheat flour.
- An intolerance is when the body fails to correctly process something it should be able to process, and just ejects it half-processed instead.
- A common and easily demonstrable example is lactose intolerance. There isn’t a well-defined analog for gluten, but gluten intolerance is nonetheless a well-reported thing.
- A sensitivity is when none of the above apply, but the body nevertheless experiences unpleasant symptoms after exposure to a substance that should normally be safe.
- In the case of gluten, this is referred to as non-Celiac gluten sensitivity
A word on scientific objectivity: at 10almonds we try to report science as objectively as possible. Sometimes people have strong feelings on a topic, especially if it is polarizing.
Sometimes people with a certain condition feel constantly disbelieved and mocked; sometimes people without a certain condition think others are imagining problems for themselves where there are none.
We can’t diagnose anyone or validate either side of that, but what we can do is report the facts as objectively as science can lay them out.
Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad: True or False?
Definitely False, Celiac disease is a real autoimmune disease that cannot be faked, and allergies are also a real thing that people can have, and again can be validated in studies. Even intolerances have scientifically measurable symptoms and can be tested against nocebo.
See for example:
- Epidemiology and clinical presentations of Celiac disease
- Severe forms of food allergy that can precipitate allergic emergencies
- Properties of gluten intolerance: gluten structure, evolution, and pathogenicity
However! It may not be a modern fad, so much as a modern genuine increase in incidence.
Widespread varieties of wheat today contain a lot more gluten than wheat of ages past, and many other molecular changes mean there are other compounds in modern grains that never even existed before.
However, the health-related impact of these (novel proteins and carbohydrates) is currently still speculative, and we are not in the business of speculating, so we’ll leave that as a “this hasn’t been studied enough to comment yet but we recognize it could potentially be a thing” factor.
Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease: True or False?
Definitely False; allergies for example are well-evidenced as real; same facts as we discussed/linked just above.
Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it: True or False?
False, tentatively and contingently.
First, as established, there are people with clinically-evidenced Celiac disease, wheat allergy, or similar. Obviously, they should avoid triggering those diseases.
What about the rest of us, and what about those who have non-Celiac gluten sensitivity?
Clinical testing has found that of those reporting non-Celiac gluten sensitivity, nocebo-controlled studies validate that diagnosis in only a minority of cases.
In the following study, for example, only 16% of those reporting symptoms showed them in the trials, and 40% of those also showed a nocebo response (i.e., like placebo, but a bad rather than good effect):
This one, on the other hand, found that positive validations of diagnoses were found to be between 7% and 77%, depending on the trial, with an average of 30%:
Re-challenge Studies in Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
In other words: non-Celiac gluten sensitivity is a thing, and/but may be over-reported, and/but may be in some part exacerbated by psychosomatic effect.
Note: psychosomatic effect does not mean “imagining it” or “all in your head”. Indeed, the “soma” part of the word “psychosomatic” has to do with its measurable effect on the rest of the body.
For example, while pain can’t be easily objectively measured, other things, like inflammation, definitely can.
As for everyone else? If you’re enjoying your wheat (or similar) products, it’s well-established that they should be wholegrain for the best health impact (fiber, a positive for your health, rather than white flour’s super-fast metabolites padding the liver and causing metabolic problems).
Wheat itself may have other problems, for example FODMAPs, amylase trypsin inhibitors, and wheat germ agglutinins, but that’s “a wheat thing” rather than “a gluten thing”.
That’s beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but you might want to check out today’s featured book!
For a final scientific opinion on this last one, though, here’s what a respected academic journal of gastroenterology has to say:
From coeliac disease to noncoeliac gluten sensitivity; should everyone be gluten-free?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Debunking the vitamin D fad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Throughout the pandemic, many unproven miracle COVID-19 “cures” emerged, and vitamin D claims have been one of the most persistent. This is not new for the vitamin. It’s been touted in recent decades as a way to “boost” the immune system, improve overall health, prevent a host of diseases, and allegedly even substitute for vaccines.
But as with many internet-popular health “remedies,” the reality is far less flashy and far more nuanced.
What is vitamin D, and why is it important?
Vitamin D is a nutrient that helps the body absorb calcium, which is essential for bone health. In the sunlight, your skin naturally produces vitamin D that is then stored in fat cells until it is used.
The skin pigment melanin absorbs the UV rays necessary for vitamin D production, meaning that more highly pigmented or darker skin produces less vitamin D than lighter skin with the same amount of sun exposure. Thus, people with darker skin are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Most of our vitamin D comes from the sun. An additional 10 percent to 20 percent of our vitamin D comes from foods like fatty fish (such as salmon), eggs, and mushrooms. Vitamin D supplements are another source of the nutrient for people who are unable to get enough from sun exposure and diet.
Vitamin D deficiency is real, but there’s no epidemic
Some people who promote vitamin D supplements claim that vitamin D deficiency is an epidemic causing widespread health issues. There is little evidence to support this claim. A 2022 analysis of 2001-2018 data found that 2.6 percent of people in the U.S. had severe vitamin D deficiency.
Severe vitamin D deficiency can cause serious health issues, such as muscle weakness, bone loss in adults, and rickets (weak bones) in children. Some people are at higher risk for the deficiency, including individuals with certain disorders that prevent the body from absorbing or processing vitamin D or those with a family history of vitamin D deficiency.
Black Americans have the highest rates of severe vitamin D deficiency at nearly 12 percent. Severe vitamin D deficiency is also slightly higher in the U.S. during the winter when people get less sun exposure. Rates of moderate vitamin D deficiency are higher at 22 percent overall and are highest among Black Americans (49 percent) and Mexican Americans (35 percent).
Although severe vitamin D deficiency exists in the U.S., it is far from common. Most tellingly, conditions that are directly linked to vitamin D deficiency are not widespread. There is no epidemic of rickets, for example, or bone loss in adults.
There’s little evidence that vitamin D supplements improve overall health
Vitamin D supplements have clear, proven positive effects for people with vitamin D deficiency. Other health benefits of vitamin D supplements are less certain.
There is some evidence that the supplement may reduce the risk of fracture in adults with osteoporosis, a condition that causes weak, fragile bones. However, the benefit appears to be limited to people who have low vitamin D levels. In adults with normal vitamin D levels, supplements have no effect on fracture risk.
The largest randomized controlled trial of vitamin D, called VITAL, investigated the effects of vitamin D supplementation in people without an existing deficiency. The study found that vitamin D supplements had no effects on the risk of cancer, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke. The study concluded that more research is necessary to determine who may benefit from vitamin D supplements.
Independent analyses found that vitamin D supplementation may be associated with a long-term decrease in cancer mortality, but results are mixed and also require more investigation.
A 2021 analysis of past vitamin D trials found no overall health benefits from vitamin D supplements in people with normal vitamin D levels. Most large-scale studies have found no link between vitamin D supplements and lower all-cause mortality (deaths from any cause), except in older adults and those with vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D provides modest protection against respiratory infections
Vitamin D is important for immune function, but this is often misconstrued as vitamin D “boosting” the immune system.
Some people falsely believe that taking vitamin D supplements will keep them healthy and prevent infections like the flu or COVID-19. In reality, clinical trials and large-scale studies of vitamin D have found only minimal protective effects against respiratory infections.
A 2021 analysis of 46 trials found that 61.3 percent of participants who took daily vitamin D supplements got respiratory infections during the study periods—compared to 62.3 percent of people who did not take the supplements. A 2024 meta-analysis of 43 trials found no overall protective effect against respiratory infections, but it detected a slight decrease in risk among people who took specific doses daily.
In young children, there is some evidence that vitamin D supplementation may reduce the length of respiratory infections. However, it does not affect the number or severity of infections that children have.
Despite claims that taking vitamin D can protect against COVID-19, two clinical trials found that taking daily vitamin D supplements did not reduce the risk or severity of COVID-19 infections, even at high doses.
Context is key when considering vitamin D’s benefits
None of these studies contradict the well-established evidence that people with vitamin D deficiency benefit from vitamin D supplements. But it’s important to remember that many of the most popular health claims about vitamin D’s benefits are based on research in people with vitamin D deficiency.
Research in vitamin D-deficient populations is important, but it tells us little about how vitamin D will affect people with normal or close to normal vitamin D levels. A closer look at vitamin D research in people without low levels reveals little evidence to support the idea that the general population benefits from taking vitamin D supplements.
For more information, or to learn about your vitamin D levels, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Menopause: 50 Things You Need to Know – by Dr. Felice Gersh
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Can you list 50 important facts about the menopause? If not, you’ll surely find things to learn in here.
The book is divided into three main sections:
- What to expect in perimenopause
- What to expect in early menopause
- What to expect in late menopause
Each section comes with an alarming array of symptoms, ranging from perimenopause fatigue and acne to late menopause tooth loss and vaginal prolapse. This is not to say that everyone will experience everything (fortunately), but rather, that these are the things that can happen and should not arrive unexpected.
Helpfully, of course, Dr. Gersh also gives advice on how to improve your energy and skin health, as well as keep your teeth and vagina in place. And similar professional insights for the rest of the “50 things you need to know”.
The style is like one big (182 pages) patient information leaflet—thus, very clear, explaining everything, and offering reassurance where possible and also what things are reasonable cause for seeking personalized medical attention.
Bottom line: if menopause is in your future, present, or very near past, this is an excellent book for you.
Click here to check out Menopause: 50 Things You Need To Know, and know them!
Share This Post
-
Invigorating Sabzi Khordan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever looked at the nutritional values and phytochemical properties of herbs, and thought “well that’s all well and good, but we only use a tiny amount”? Sabzi khordan is a herb-centric traditional Levantine sharing platter served most commonly as an appetizer, and it is indeed appetizing! Never again will “start your meal with a green salad to ensure a gentle blood sugar curve” seem like a chore:
You will need
- Large bunch of parsley
- Small bunch of tarragon leaves
- Small bunch of basil leaves
- Small bunch of mint
- Small bunch of sorrel leaves
- 7 oz block of feta cheese (if vegan, a plant-based substitution is fine in culinary terms, but won’t have the same gut-healthy benefits, as plant-based cheeses are not fermented)
- 9 oz labneh-stuffed vine leaves in olive oil (if vegan, same deal as the above, except it’s harder to find plant-based substitutes for labneh (strained yogurt cheese), so you might want to use our Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese recipe instead and make your own)
- 2 tbsp za’atar (you can make your own by blending dried hyssop, dried sumac berries, sesame seeds, dried thyme, and salt—but if you haven’t had za’atar before, we recommend first buying some like the one that we linked, so that next time you know what you’re aiming for)
- 3 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 10 radishes
- 6 scallions
- 9 oz walnuts, soaked in water overnight and drained
- 1 cucumber, cut into batons
- Warm flatbreads (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Arrange the feta, labneh, za’atar, and olive oil in separate little serving dishes.
2) Arrange everything else around them on a platter.
3) Serve! You may be thinking: did we really need a recipe to tell us “put the things on a plate”? The answer here is that this one today was shared mostly as a matter of inspiration, because when was the last time you thought to serve herbs as the star of the dish? Plus, it’s an excuse to try za’atar, not something so commonly seen outside of the Levant.
An alternative presentation
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Herbs for Evidence-Based Health & Healing
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cancer is increasingly survivable – but it shouldn’t depend on your ability to ‘wrangle’ the health system
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One in three of us will develop cancer at some point in our lives. But survival rates have improved to the point that two-thirds of those diagnosed live more than five years.
This extraordinary shift over the past few decades introduces new challenges. A large and growing proportion of people diagnosed with cancer are living with it, rather than dying of it.
In our recently published research we examined the cancer experiences of 81 New Zealanders (23 Māori and 58 non-Māori).
We found survivorship not only entailed managing the disease, but also “wrangling” a complex health system.
Surviving disease or surviving the system
Our research focused on those who had lived longer than expected (four to 32 years since first diagnosis) with a life-limiting or terminal diagnosis of cancer.
Common to many survivors’ stories was the effort it took to wrangle the system or find others to advocate on their behalf, even to get a formal diagnosis and treatment.
By wrangling we refer to the practices required to traverse complex and sometimes unwelcoming systems. This is an often unnoticed but very real struggle that comes on top of managing the disease itself.
The common focus of the healthcare system is on symptoms, side effects of treatment and other biological aspects of cancer. But formal and informal care often falls by the wayside, despite being key to people’s everyday experiences.
Survival is often linked to someone’s social connections and capacity to access funds. Getty Images The inequities of cancer survivorship are well known. Analyses show postcodes and socioeconomic status play a strong role in the prevalence of cancer and survival.
Less well known, but illustrated in our research, is that survival is also linked to people’s capacity to manage the entire healthcare system. That includes accessing a diagnosis or treatment, or identifying and accessing alternative treatments.
Survivorship is strongly related to material resources, social connections, and understandings of how the health system works and what is available. For instance, one participant who was contemplating travelling overseas to get surgery not available in New Zealand said:
We don’t trust the public system. So thankfully we had private health insurance […] But if we went overseas, health insurance only paid out to $30,000 and I think the surgery was going to be a couple of hundred thousand. I remember Dad saying and crying and just being like, I’ll sell my business […] we’ll all put in money. It was really amazing.
Assets of survivorship
In New Zealand, the government agency Pharmac determines which medications are subsidised. Yet many participants were advised by oncologists or others to “find ways” of taking costly, unsubsidised medicines.
This often meant finding tens of thousands of dollars with no guarantees. Some had the means, but for others it meant drawing on family savings, retirement funds or extending mortgages. This disproportionately favours those with access to assets and influences who survives.
But access to economic capital is only one advantage. People also have cultural resources – often described as cultural capital.
In one case, a participant realised a drug company was likely to apply to have a medicine approved. They asked their private oncologist to lobby on their behalf to obtain the drug through a compassionate access scheme, without having to pay for it.
Others gained community support through fundraising from clubs they belonged to. But some worried about where they would find the money, or did not want to burden their community.
I had my doctor friend and some others that wanted to do some public fundraising. But at the time I said, “Look, most of the people that will be contributing are people from my community who are poor already, so I’m not going to do that option”.
Accessing alternative therapies, almost exclusively self-funded, was another layer of inequity. Some felt forced to negotiate the black market to access substances such as marijuana to treat their cancer or alleviate the side effects of orthodox cancer treatment.
Cultural capital is not a replacement for access to assets, however. Māori survivorship was greatly assisted by accessing cultural resources, but often limited by lack of material assets.
Persistence pays
The last thing we need when faced with the possibility of cancer is to have to push for formal diagnosis and care. Yet this was a common experience.
One participant was told nothing could be found to explain their abdominal pain – only to find later they had pancreatic cancer. Another was told their concerns about breathing problems were a result of anxiety related to a prior mental health history, only to learn later their earlier breast cancer had spread to their lungs.
Persistence is another layer of wrangling and it often causes distress.
Once a diagnosis was given, for many people the public health system kicked in and delivered appropriate treatment. However, experiences were patchy and variable across New Zealand.
Issues included proximity to hospitals, varying degrees of specialisation available, and the requirement of extensive periods away from home and whānau. This reflects an ongoing unevenness and lack of fairness in the current system.
When facing a terminal or life-limiting diagnosis, the capacity to wrangle the system makes a difference. We shouldn’t have to wrangle, but facing this reality is an important first step.
We must ensure it doesn’t become a continuing form of inequity, whereby people with access to material resources and social and cultural connections can survive longer.
Kevin Dew, Professor of Sociology, Te Herenga Waka — Victoria University of Wellington; Alex Broom, Professor of Sociology & Director, Sydney Centre for Healthy Societies, University of Sydney; Chris Cunningham, Professor of Maori & Public Health, Massey University; Elizabeth Dennett, Associate Professor in Surgery, University of Otago; Kerry Chamberlain, Professor of Social and Health Psychology, Massey University, and Richard Egan, Associate Professor in Health Promotion, University of Otago
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How they did it: STAT reporters expose how ailing seniors suffer when Medicare Advantage plans use algorithms to deny care
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In a call with a long-time source, what stood out most to STAT reporters Bob Herman and Casey Ross was just how viscerally frustrated and angry the source was about an algorithm used by insurance companies to decide how long patients should stay in a nursing home or rehab facility before being sent home.
The STAT stories had a far-reaching impact:
- The U.S. Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Government Affairs took a rare step of launching a formal investigation into the use of algorithms by the country’s three largest Medicare Advantage insurers.
- Thirty-two House members urged the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to increase the oversight of algorithms that health insurers use to make coverage decisions.
- In a rare step, CMS launched its own investigation into UnitedHealth. It also stiffened its regulations on the use of proprietary algorithms and introduced plans to audit denials across Medicare Advantage plans in 2024.
- Based on STAT’s reporting, Medicare Advantage beneficiaries filed two class-action lawsuits against UnitedHealth and its NaviHealth subsidiary, the maker of the algorithm, and against Humana, another major health insurance company that was also using the algorithm.
- Amid scrutiny, UnitedHealth renamed NaviHealth.
The companies never allowed an on-the-record interview with their executives, but they acknowledged that STAT’s reporting was true, according to the news organization.
Ross and Herman spoke with The Journalist’s Resource about their project and shared the following eight tips.
1. Search public comments on proposed federal rules to find sources.
Herman and Ross knew that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services had put out a request for public comments, asking stakeholders within the Medicare Advantage industry how the system could improve.
There are two main ways to get Medicare coverage: original Medicare, which is a fee-for-service health plan, and Medicare Advantage, which is a type of Medicare health plan offered by private insurance companies that contract with Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans have increasingly become popular in recent years.
Under the Social Security Act, the public has the opportunity to submit comments on Medicare’s proposed national coverage determinations. CMS uses public comments to inform its proposed and final decisions. It responds in detail to all public comments when issuing a final decision.
The reporters began combing through hundreds of public comments attached to a proposed Medicare Advantage rule that was undergoing federal review. NaviHealth, the UnitedHealth subsidiary and the maker of the algorithm, came up in many of the comments, which include the submitters’ information.
“These are screaming all-caps comments to federal regulators about YOU NEED TO SOMETHING ABOUT THIS BECAUSE IT’S DISGUSTING,” Ross says.
“The federal government is proposing rules and regulations all the time,” adds Herman, STAT’s business of health care reporter. “If someone’s going to take the time and effort to comment on them, they must have at least some knowledge of what’s going on. It’s just a great tool for any journalist to use to figure out more and who to contact.”
The reporters also found several attorneys who had complained in the comments. They began reaching out to them, eventually gaining access to confidential documents and intermediaries who put them in touch with patients to show the human impact of the algorithm.
2. Harness the power of the reader submission box.
At the suggestion of an editor, the reporters added a reader submission box at the bottom of their first story, asking them to share their own experiences with Medicare Advantage denials.
The floodgates opened. Hundreds of submissions arrived.
By the end of their first story, Herman and Ross had confidential records and some patients, but they had no internal sources in the companies they were investigating, including Navihealth. The submission box led them to their first internal source.
(Screenshot of STAT’s submission box.) The journalists also combed through LinkedIn and reached out to former and current employees, but the response rate was much lower than what they received via the submission box.
The submission box “is just right there,” Herman says. “People who would want to reach out to us can do it right then and there after they read the story and it’s fresh in their minds.”
3. Mine podcasts relevant to your story.
The reporters weren’t sure if they could get interviews with some of the key figures in the story, including Tom Scully, the former head of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services who drew up the initial plans for NaviHealth years before UnitedHealth acquired it.
But Herman and another colleague had written previously about Scully’s private equity firm and they had found a podcast where he talked about his work. So Herman went back to the podcast — where he discovered Scully had also discussed NaviHealth.
The reporters also used the podcast to get Scully on the phone for an interview.
“So we knew we had a good jumping off point there to be like, ‘OK, you’ve talked about NaviHealth on a podcast, let’s talk about this,’” Herman says. “I think that helped make him more willing to speak with us.”
4. When covering AI initiatives, proceed with caution.
“A source of mine once said to me, ‘AI is not magic,’” Ross says. “People need to just ask questions about it because AI has this aura about it that it’s objective, that it’s accurate, that it’s unquestionable, that it never fails. And that is not true.”
AI is not a neutral, objective machine, Ross says. “It’s based on data that’s fed into it and people need to ask questions about that data.”
He suggests several questions to ask about the data behind AI tools:
- Where does the data come from?
- Who does it represent?
- How is this tool being applied?
- Do the people to whom the tool is being applied match the data on which it was trained? “If racial groups or genders or age of economic situations are not adequately represented in the training set, then there can be an awful lot of bias in the output of the tool and how it’s applied,” Ross says.
- How is the tool applied within the institution? Are people being forced to forsake their judgment and their own ability to do their jobs to follow the algorithm?
5. Localize the story.
More than half of all Medicare beneficiaries have Medicare Advantage and there’s a high likelihood that there are multiple Medicare Advantage plans in every county across the nation.
“So it’s worth looking to see how Medicare Advantage plans are growing in your area,” Herman says.
Finding out about AI use will most likely rely on shoe-leather reporting of speaking with providers, nursing homes and rehab facilities, attorneys and patients in your community, he says. Another source is home health agencies, which may be caring for patients who were kicked out of nursing homes and rehab facilities too soon because of a decision by an algorithm.
The anecdote that opens their first story involves a small regional health insurer in Wisconsin, which was using NaviHealth and a contractor to manage post-acute care services, Ross says.
“It’s happening to people in small communities who have no idea that this insurer they’ve signed up with is using this tool made by this other company that operates nationally,” Ross says.
There are also plenty of other companies like NaviHealth that are being used by Medicare Advantage plans, Herman says. “So it’s understanding which Medicare Advantage plans are being sold in your area and then which post-acute management companies they’re using,” he adds.
Some regional insurers have online documents that show which contractors they use to evaluate post-acute care services.
6. Get familiar with Medicare’s appeals databases
Medicare beneficiaries can contest Medicare Advantage denials through a five-stage process, which can last months to years. The appeals can be filed via the Office of Medicare Hearings and Appeals.
“Between 2020 and 2022, the number of appeals filed to contest Medicare Advantage denials shot up 58%, with nearly 150,000 requests to review a denial filed in 2022, according to a federal database,” Ross and Herman write in their first story. “Federal records show most denials for skilled nursing care are eventually overturned, either by the plan itself or an independent body that adjudicates Medicare appeals.”
There are several sources to find appeals data. Be mindful that the cases themselves are not public to protect patient privacy, but you can find the number of appeals filed and the rationale for decisions.
CMS has two quality improvement organizations, or QIOs, Livanta and Kepro, which are required to file free, publicly-available annual reports, about the cases they handle, Ross says.
Another company, Maximus, a Quality Improvement Contractor, also files reports on prior authorization cases it adjudicates for Medicare. The free annual reports include data on raw numbers of cases and basic information about the percentage denials either overturned or upheld on appeal, Ross explains.
CMS also maintains its own database on appeals for Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage plans) and Part D, which covers prescription drugs, although the data is not complete, Ross explains.
7. Give your editor regular updates.
“Sprinkle the breadcrumbs in front of your editors,” Ross says.
“If you wrap your editors in the process, you’re more likely to be able to get to the end of [the story] before they say, ‘That’s it! Give me your copy,’” Ross says.
8. Get that first story out.
“You don’t have to know everything before you write that first story,” Ross says. “Because with that first story, if it has credibility and it resonates with people, sources will come forward and sources will continue to come forward.”
Read the stories
Denied by AI: How Medicare Advantage plans use algorithms to cut off care for seniors in need
UnitedHealth pushed employees to follow an algorithm to cut off Medicare patients’ rehab care
UnitedHealth used secret rules to restrict rehab care for seriously ill Medicare Advantage patients
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I Will Make You Passionate About Exercise – by Bevan Eyles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What this isn’t: a “just do it!” motivational pep-talk.
What this is:a compassionate and thoughtful approach to help non-exercisers become regular exercisers, by looking at the real life factors of what holds people back (learning from his own early failures as a coach, by paying attention now to things he inadvertently neglected back then), both in the material/practical and in the psychological/emotional.
Further, he gives a 10-step method, for those who would like to be walked through it by the hand, making the transition to exercising regularly (and as a leisure habit, rather than as a chore) as frictionless as possible.
The style is friendly and energetic, and very easy-reading throughout.
Bottom line: if you are someone who finds exercising to be a chore, this book can definitely help you “get from here to there” in terms of finding joy in it, and finding exercise even easier than not exercising. Yes, really.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: