Strategic Wellness
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Strategic Wellness: planning ahead for a better life!
This is Dr. Michael Roizen. With hundreds of peer-reviewed publications and 14 US patents, his work has been focused on the importance of lifestyle factors in healthy living. He’s the Chief Wellness Officer at the world-famous Cleveland Clinic, and is known for his “RealAge” test and related personalized healthcare services.
If you’re curious about that, you can take the RealAge test here.
(they will require you inputting your email address if you do, though)
What’s his thing?
Dr. Roizen is all about optimizing health through lifestyle factors—most notably, diet and exercise. Of those, he is particularly keen on optimizing nutritional habits.
Is this just the Mediterranean Diet again?
Nope! Although: he does also advocate for that. But there’s more, he makes the case for what he calls “circadian eating”, optimally timing what we eat and when.
Is that just Intermittent Fasting again?
Nope! Although: he does also advocate for that. But there’s more:
Dr. Roizen takes a more scientific approach. Which isn’t to say that intermittent fasting is unscientific—on the contrary, there’s mountains of evidence for it being a healthful practice for most people. But while people tend to organize their intermittent fasting purely according to convenience, he notes some additional factors to take into account, including:
- We are evolved to eat when the sun is up
- We are evolved to be active before eating (think: hunting and gathering)
- Our insulin resistance increases as the day goes on
Now, if you’ve a quick mind about you, you’ll have noticed that this means:
- We should keep our eating to a particular time window (classic intermittent fasting), and/but that time window should be while the sun is up
- We should not roll out of bed and immediately breakfast; we need to be active for a bit first (moderate exercise is fine—this writer does her daily grocery-shopping trip on foot before breakfast, for instance… getting out there and hunting and gathering those groceries!)
- We should not, however, eat too much later in the day (so, dinner should be the smallest meal of the day)
The latter item is the one that’s perhaps biggest change for most people. His tips for making this as easy as possible include:
- Over-cater for dinner, but eat only one portion of it, and save the rest for an early-afternoon lunch
- First, however, enjoy a nutrient-dense protein-centric breakfast with at least some fibrous vegetation, for example:
- Salmon and asparagus
- Scrambled tofu and kale
- Yogurt and blueberries
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Real Immune-Boosters
What comes to your mind when we say “immune support”? Vitamin C and maybe zinc? Those have their place, but there are things we can do that are a lot more important!
It’s just, these things are not talked about as much, because stores can’t sell them to you
Sleep
One of the biggest difference-makers. Get good sleep! Getting at least 7 hours decent sleep (not lying in bed, not counting interruptions to sleep as part of the sleep duration) can improve your immune system by three or four times.
Put another way, people are 3–4 times more likely to get sick if they get less sleep than that on average.
Check it out: Behaviorally Assessed Sleep and Susceptibility to the Common Cold
Eat an anti-inflammatory diet
In short, for most of us this means lots of whole plant foods (lots of fiber), and limited sugar, flour, alcohol.
For more details, you can see our main feature on this: Keep Inflammation At Bay!
You may wonder why eating to reduce inflammation (inflammation is a form of immune response) will help improve immune response. Put it this way:
If your town’s fire service is called out eleventy-two times per day to deal with things that are not, in fact, fires, then when there is a fire, they will be already exhausted, and will not do their job so well.
Look after your gut microbiota
Additionally, healthy gut microbiota (fostered by the same diet we just described) help keep your body pathogen-free, by avoiding “leaky gut syndrome” that occurs when, for example, C. albicans (you do not want this in your gut, and it thrives on the things we just told you to avoid) puts its roots through your intestinal walls, making holes in them. And through those holes? You definitely do not want bacteria from your intestines going into the rest of your body.
See also: Gut Health 101
Actually get that moderate exercise
There’s definitely a sweet-spot here, because too much exercise will also exhaust you and deplete your body’s resources. However, the famous “150 minutes per week” (so, a little over 20 minutes per day, or 25 minutes per day with one day off) will make a big difference.
See: Exercise and the Regulation of Immune Functions
Manage your stress levels (good and bad!)
This one swings both ways:
- Acute stress (like a cold shower) is good for immune response. Think of it like a fire drill for your body.
- Chronic stress (“the general everything” persistently stressful in life) is bad for immune response. This is the fire drill that never ends. Your body’s going to know what to do really well, but it’s going to be exhausted already by the time an actual threat hits.
Read more: Effects of Stress on Immune Function: the Good, the Bad, and the Beautiful
Supplement, yes.
These are far less critical than the above things, but are also helpful. Good things to take include:
Enjoy, and stay well!
Share This Post
-
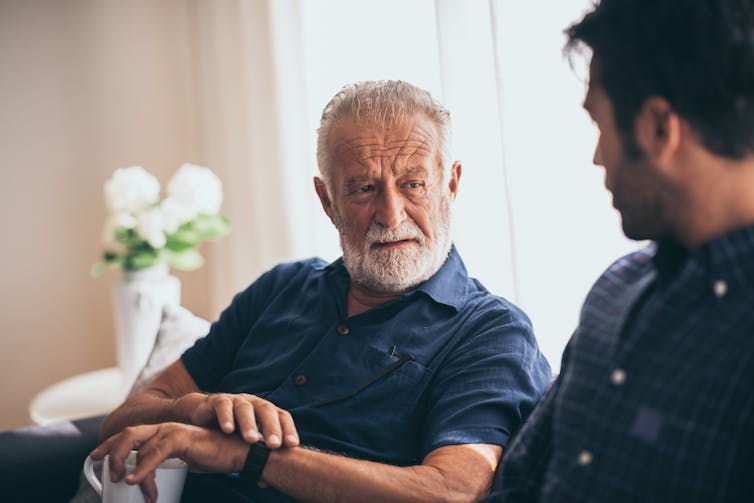
Your friend has been diagnosed with cancer. Here are 6 things you can do to support them
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Across the world, one in five people are diagnosed with cancer during their lifetime. By age 85, almost one in two Australians will be diagnosed with cancer.
When it happens to someone you care about, it can be hard to know what to say or how to help them. But providing the right support to a friend can make all the difference as they face the emotional and physical challenges of a new diagnosis and treatment.
Here are six ways to offer meaningful support to a friend who has been diagnosed with cancer.
1. Recognise and respond to emotions
When facing a cancer diagnosis and treatment, it’s normal to experience a range of emotions including fear, anger, grief and sadness. Your friend’s moods may fluctuate. It is also common for feelings to change over time, for example your friend’s anxiety may decrease, but they may feel more depressed.
Spending time together can mean a lot to someone who is feeling isolated during cancer treatment. Chokniti-Studio/Shutterstock Some friends may want to share details while others will prefer privacy. Always ask permission to raise sensitive topics (such as changes in physical appearance or their thoughts regarding fears and anxiety) and don’t make assumptions. It’s OK to tell them you feel awkward, as this acknowledges the challenging situation they are facing.
When they feel comfortable to talk, follow their lead. Your support and willingness to listen without judgement can provide great comfort. You don’t have to have the answers. Simply acknowledging what has been said, providing your full attention and being present for them will be a great help.
2. Understand their diagnosis and treatment
Understanding your friend’s diagnosis and what they’ll go through when being treated may be helpful.
Being informed can reduce your own worry. It may also help you to listen better and reduce the amount of explaining your friend has to do, especially when they’re tired or overwhelmed.
Explore reputable sources such as the Cancer Council website for accurate information, so you can have meaningful conversations. But keep in mind your friend has a trusted medical team to offer personalised and accurate advice.
3. Check in regularly
Cancer treatment can be isolating, so regular check-ins, texts, calls or visits can help your friend feel less alone.
Having a normal conversation and sharing a joke can be very welcome. But everyone copes with cancer differently. Be patient and flexible in your support – some days will be harder for them than others.
Remembering key dates – such as the next round of chemotherapy – can help your friend feel supported. Celebrating milestones, including the end of treatment or anniversary dates, may boost morale and remind your friend of positive moments in their cancer journey.
Always ask if it’s a good time to visit, as your friend’s immune system may be compromised by their cancer or treatments such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy. If you’re feeling unwell, it’s best to postpone visits – but they may still appreciate a call or text.
4. Offer practical support
Sometimes the best way to show your care is through practical support. There may be different ways to offer help, and what your friend needs might change at the beginning, during and after treatment.
For example, you could offer to pick up prescriptions, drive them to appointments so they have transport and company to debrief, or wait with them at appointments.
Meals will always be welcome. However it’s important to remember cancer and its treatments may affect taste, smell and appetite, as well as your friend’s ability to eat enough or absorb nutrients. You may want to check first if there are particular foods they like. Good nutrition can help boost their strength while dealing with the side effects of treatment.
There may also be family responsibilities you can help with, for example, babysitting kids, grocery shopping or taking care of pets.
There may be practical ways you can help, such as dropping off meals. David Trinks/Unsplash 5. Explore supports together
Studies have shown mindfulness practices can be an effective way for people to manage anxiety associated with a cancer diagnosis and its treatment.
If this is something your friend is interested in, it may be enjoyable to explore classes (either online or in-person) together.
You may also be able to help your friend connect with organisations that provide emotional and practical help, such as the Cancer Council’s support line, which offers free, confidential information and support for anyone affected by cancer, including family, friends and carers.
Peer support groups can also reduce your friend’s feelings of isolation and foster shared understanding and empathy with people who’ve gone through a similar experience. GPs can help with referrals to support programs.
6. Stick with them
Be committed. Many people feel isolated after their treatment. This may be because regular appointments have reduced or stopped – which can feel like losing a safety net – or because their relationships with others have changed.
Your friend may also experience emotions such as worry, lack of confidence and uncertainty as they adjust to a new way of living after their treatment has ended. This will be an important time to support your friend.
But don’t forget: looking after yourself is important too. Making sure you eat well, sleep, exercise and have emotional support will help steady you through what may be a challenging time for you, as well as the friend you love.
Our research team is developing new programs and resources to support carers of people who live with cancer. While it can be a challenging experience, it can also be immensely rewarding, and your small acts of kindness can make a big difference.
Stephanie Cowdery, Research Fellow, Carer Hub: A Centre of Excellence in Cancer Carer Research, Translation and Impact, Deakin University; Anna Ugalde, Associate Professor & Victorian Cancer Agency Fellow, Deakin University; Trish Livingston, Distinguished Professor & Director of Special Projects, Faculty of Health, Deakin University, and Victoria White, Professor of Pyscho-Oncology, School of Psychology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Science-Backed Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Beginners – by Dr. Yasmine Elamir & Dr. William Grist
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We have written about how to eat to beat inflammation, but what we didn’t do is include 75 recipes and a plan for building up one’s culinary repertoire around those core dishes!
That’s what this book does. It covers briefly the science of inflammation and anti-inflammatory diet, discusses experimental elimination diets (e.g. you eliminate likely culprits of triggering your inflammation, then reintroduce them one by one to see which it was), and ingredients likely to increase or decrease inflammation.
The 75 recipes are good, and/but a caveat is “yes, one of the recipes is ketchup and another is sour cream” so it’s not exactly 75 mains.
However! Where this book excels is in producing anti-inflammatory versions of commonly inflammatory dishes. That ketchup? Not sugary. The sour cream? Vegan. And so forth. We also see crispy roast potatoes, an array of desserts, and sections for popular holiday dishes too, so you will not need to be suddenly inflamed into the next dimension when it comes to festive eating.
The recipes are what the title claims them to be, “science-backed anti-inflammatory”, and that is clearly the main criterion for their inclusion. They are not by default vegan, vegetarian, dairy-free, nut-free, gluten-free, etc. For this reason, all recipes are marked with such tags as “V, VG, DF, GF, EF, NF” etc as applicable.
Bottom line: we’d consider this book more of a jumping-off point than a complete repertoire, but it’s a very good jumping-off point, and will definitely get you “up and running” (there’s a 21-day meal plan, for example).
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Drug & Supplement Combo That Reverses Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So far, its effects have been dramatic (in a good way) in mice; human trials are now underway.
How does it work?
It builds from previous work, in which a Japanese research team created an “anti-aging vaccine”, that responded to a problem more specific than aging as a whole, namely atherosclerosis.
They found that a certain* protein was upregulated (i.e., it was made at a greater rate resulting in greater quantities) in patients (mouse and human alike) with atherosclerosis. So, they immunized the mice against that protein, and long story short, everything improved for them, from their atherosclerosis to general markers of aging—including growing back fur that had been lost due to age-related balding (just like in humans). They also lived longer, as is to be expected of a mouse who is now biologically younger.
*To avoid being mysterious: it was glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma protein B, known to its friends as GPNMB.
You may be wondering: how can one be immunized against a protein? If so, do bear in mind, a virus is also a protein. In this case, they developed an RNA vaccine, that works in a similar way to the COVID vaccines we all know and love (albeit with a different target).
You can read about this in abundant detail here: Senolytic vaccination improves normal and pathological age-related phenotypes and increases lifespan in progeroid mice
Hot on the heels of that, new approaches were found, including…
The combination
We’ll not keep you waiting; the combination is dasatinib plus quercetin, or else fisetin alone.
It’s about killing senescent (aging) “zombie cells” while sparing healthy cells, which that drug (dasatinib) and those supplements (quercetin and fisetin) do.
The researchers noted:
❝Senescent cells are resistant to apoptosis, which is governed through the upregulation of senescent cell anti-apoptotic pathways (SCAPs). Compounds were subsequently identified that disrupted the SCAPs, inducing death of senescent cells while leaving healthy cells unaffected. Forty-six potential senolytic agents were discovered through this process. To advance translational efforts, the majority of research has focused on agents with known safety profiles and limited off-target effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
The best characterized senolytic agents are dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for use in humans for cancer treatment, and quercetin, a naturally occurring plant flavonoid. The agents have a synergistic effect, making their combination more potent for senescent cell clearance (Zhu et al., 2015). As senescent cells do not divide and accumulate over a period of weeks, they can be administered using an intermittent approach, which further serves to reduce the risk of side effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
In preclinical trials, the combination of dasatinib and quercetin (D + Q) have been found to alleviate numerous chronic medical conditions including vascular stiffness, osteoporosis, frailty, and hepatic stenosis❞
Source: A geroscience motivated approach to treat Alzheimer’s disease: Senolytics move to clinical trials
As to how they expanded on this research:
❝In our study, oral D + Q were intermittently administered to tau transgenic mice with late-stage pathology (approximated to a 70-year-old human with advanced AD) (Musi et al., 2018). The treatment effectively reduced cellular senescence and associated senescence-associated secretory phenotype incidence. The 35 % reduction in neurofibrillary tangles was accompanied by enhanced neuron density, decreased ventricular enlargement, diminished tau accumulation, and restoration of aberrant cerebral blood flow. A subsequent preclinical study validated the findings, reporting that intermittently administered D + Q cleared senescent cells in the central nervous system, reduced amyloid-β plaques, attenuated neuroinflammation, and enhanced cognition❞
Source: Ibid.
And now taking it to humans:
❝The first clinical trial of D + Q for early-stage Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) has completed enrollment (Gonzales et al., 2021). The primary aim of the open-label pilot study was to examine the central nervous system penetrance of D and Q in a small sample of older adults with early-stage AD (NCT04063124). In addition, two placebo-controlled trials of D + Q for neurodegenerative disease are underway (NCT04685590 and NCT04785300).
One of the trials in development is a multi-site, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of senolytic therapy in older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or early-stage dementia (Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) Global 0.5–1) due to AD (elevated CSF total tau/Aβ42 ratio).
The treatment regimen will consist of 12-weeks of intermittently administered oral D + Q.❞
Source: Ibid.
The study is actually completed now, but its results are not yet published (again, at time of writing). Which means: they have the data, and now they’re writing the paper.
We look forward to providing an update about that, when the paper is published!
In the meantime…
Dasatinib is a drug usually prescribed to people with certain kinds of leukemia, and suffice it to say, it’s prescription-only. And unlike drugs that are often prescribed off-label (such as metformin for weight loss), getting your doctor to prescribe you an anticancer drug is unlikely unless you have the cancer in question.
You may be wondering: how is an anticancer drug helpful against aging? And the answer is that cancer and aging are very interrelated, and both have to do with “these old cells just won’t die, and are using the resources needed for young healthy cells”. So in both cases, killing those “zombie cells” while sparing healthy ones, is what’s needed. However, your doctor will probably not buy that as a reason to prescribe you a drug that is technically chemotherapy.
Quercetin, on the other hand, is a readily-available supplement, as is fisetin, and both have glowing (in a good way) safety profiles.
Want to know more?
You can read more about each of quercetin and fisetin (including how to get them), here:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Foam Rolling – by Karina Inkster
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’ve ever bought a foam roller only to place it under your lower back once and then put it somewhere for safekeeping and never use it again, this book will help fix that.
Karina Inkster (what a cool name) is a personal trainer, and the book also features tips and advice from physiotherapists and sports medicine specialist doctors too, so all bases are well and truly covered.
This is not, in case you’re wondering, a book that could have been a pamphlet, with photos of the exercises and one-liner explanation and that’s it. Rather, Inkster takes us through the anatomy and physiology of what’s going on, so that we can actually use this thing correctly and get actual noticeable improvements to our health from it—as promised in the subtitle’s mention of “for massage, injury prevention, and core strength”. To be clear, a lot of it is also about soft tissue mobilization, and keeping our fascia healthy (an oft-underestimated aspect of general mobility).
We would mention that since the photos are pleasantly colorful (like those on the cover) and this adds to the clarity, we’d recommend springing for the (quite inexpensive) physical copy, rather than a Kindle edition (if your e-reader is a monochrome e-ink device like this reviewer’s, anyway).
Bottom line: this book will enable your foam roller to make a difference to your life.
Click here to check out Foam Rolling, and get rolling (correctly)!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Best Exercise to Stop Your Legs From Giving Out
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Doug Weiss, seniors-specialist physio, has an exercise that stops your knees from being tricked into collapsing (which is very common) by a misfiring (also common) reflex.
Step up…
Setup to step up thus:
- Use a sturdy support like a countertop or chair.
- Have an aerobic step or similar firm surface to step onto.
When you’re ready:
- Stand facing away from the step.
- Place one hand on the support for stability.
- Step backwards up onto the step with your right leg, then your left leg, so both feet are on the step.
- Step forward to come back down.
Once you’re confident of the series of movements, do it without the support, and do it for a few minutes each day. Don’t worry about how easy it becomes; this is not, first and foremost, a strength-training exercise; you don’t have to start adding weights or anything (although of course you can if you want).
How it works: there’s a part of you called the Golgi tendon organ, and it can trigger a Golgi tendon reflex, which is one of the body’s equivalents of a steam valve. However, instead of letting off steam to avoid a boiler explosion, it collapses a joint to save it from overload. However, if not exercised regularly, it can get overly sensitive, causing it to mistake your mere bodyweight for an overload. So, it collapses, thinking it is saving you from snapping a tendon, but it’s not. By exercising in the way described, the Golgi tendon reflex will go back to only being triggered by an actual overload, not the mere act of stepping.
Writer’s note: this one’s interesting to me as I have a) a strong lower body b) hypermobile joints that thus occasionally just fold like laundry regardless. Could it be that this will fix that? I guess I’ll find out 🙂
Meanwhile, for more on all of the above plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
What Nobody Teaches You About Strengthening Your Knees
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: