Fix Tight Hamstrings In Just 3 Steps
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a better way to increase your flexibility than just stretching and stretching and hoping for the best. Here’s a 3-step method that will transform your flexibility:
As easy as 1-2-3
Only one part actually involves stretching:
Step 1: reciprocal inhibition
- Concept: when one muscle contracts, the opposing muscle relaxes—which is what we need.
- Goal: engage hip flexors to encourage hamstring relaxation.
- Method:
- Kneeling hamstring stretch position with one leg forward.
- Support with yoga blocks or a chair; use a cushion for comfort.
- Maintain a slight arch in the lower back and hinge forward slightly.
- Attempt to lift the foot off the floor, even if it doesn’t move.
- Hold for around 10 seconds.
Step 2: engaging more muscle fibers
- Concept: our muscles contain a lot of fibers, and often not all of them come along for the ride when we do something (exercising, stretching, etc), and those fibers that weren’t engaged will hold back the whole process.
- Goal: activate more fibers in the hamstring for a deeper stretch.
- Method:
- Same kneeling position, slight back arch, and forward hinge.
- Drive the heel into the floor as if trying to dent it.
- Apply significant effort but hold for only 10 seconds.
- A small bend in the knee is acceptable.
Step 3: manipulating the nervous system
- Concept: the nervous system often limits flexibility due to safety signals (causing sensations of discomfort to tell us to stop a lot sooner than we really need to).
- Goal: passive stretching to reduce nervous system resistance.
- Method:
- Avoid muscle engagement or movement—stay completely relaxed.
- Focus on calmness, with slow, steady breaths.
- Avoid signs of tension (e.g. clenched fists, short/sharp breathing). While your nervous system is trying to communicate to you that you are in danger, you need to communicate to your nervous system that this is fine actually, so in order to reassure your nervous system you need to avoid signs that will tip it off that you’re worried too.
- Don’t overstretch; prioritize a relaxed, safe feeling.
For more on all of this, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Tight Hamstrings? Here’s A Test To Know If It’s Actually Your Sciatic Nerve
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck – by Mark Manson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may wonder from the title: is this book arguing that we should all be callous heartless monsters? And no, it is not.
Instead, author Mark Manson advocates for cynicism, but less in the manner of Scrooge, and more in the manner of Diogenes:
- That life will involve struggle, so we might as well at least choose our struggles.
- That we will make mistakes, so we might as well accept them as learning experiences.
- That we will love and we will lose, so we might as well do it right while we can.
In short, the book is less about not caring… And more about caring about the right things only.
So, what are “the right things”? Manson bids us decide for ourselves, but certainly has ideas and pointers, with regard to what may or may not be healthy values to pursue.
The style throughout is casual and almost conversational, without being overly padded. It makes for very easy reading.
If the book has a weak point, it’s that when it briefly makes a suprisingly prescriptive turn into recommending we take up Buddhism, it may feel a bit like our friend who wants us to join in the latest MLM scheme. But, he’s soon back on track.
Bottom line: if you ever find yourself stressed with living up to unwanted expectations—your own, other people’s, and society’s—this book can really help streamline things.
Share This Post
-
“Unfuck Your Body” In Under 10 Minutes A Day!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot that can go wrong with mobility, but fortunately, a few compound exercises will take care of most parts of it:
Full Body Mobility Routine
Eleven exercises, 10 minutes, follow-along video if you want it!
Kneeling side bend stretch:
- Targets obliques, lats, hip flexors, and spinal mobility.
- 10 reps total, focusing on stability and core engagement.
Seated ankle stretch:
- This one’s for ankle mobility and deep squat comfort.
- 10 reps, adjust intensity by leaning forward or pressing on knees.
Deep squat with prayer stretch:
- Improves hip, ankle, and lower back flexibility.
- 10 reps, maintain an upright chest and push knees outward.
Deep squat with high reach:
- Boosts thoracic mobility, hip, and ankle flexibility.
- 5 reps per side, focus on spinal rotation and open chest.
Deep shoulder stretch:
- Improves overhead mobility and shoulder tension relief.
- 10 reps in a child’s pose position with a forward reach.
Frog rocks:
- Opens hip abductors, groin, and inner thighs.
- 10 reps, keep spine neutral and adjust knee position if needed.
“World’s greatest stretch” (with variations):
- This is great for hip, spine, and shoulder mobility.
- 5 reps per side, integrates a deep lunge and rotational movements.
Hamstring stretch (from lunge position):
- Focus on hamstring and calf flexibility.
- 5 reps, maintain hands on the ground and shift hips back.
Pigeon stretch with forward crawl:
- Opens hips, glutes, and lower back.
- 5 reps per side, adjust foot placement if knee discomfort occurs.
Cat-cow stretch:
- Mobilizes spine, improves posture, and relieves back tension.
- 10 reps, synchronize movement with breath.
Couch stretch:
- Targets hip flexors and quadriceps mobility.
- 5 reps per side, add a forward lunge for a deeper stretch.
For more on each of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
5 Exercises That Fix 95% Of Your Problems
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Carrot vs Kale – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing carrot to kale, we picked the kale.
Why?
These are both known as carotene-containing heavyweights, but kale emerges victorious:
In terms of macros, carrot has more carbs while kale has more protein and fiber. An easy win there for kale.
When it comes to vitamins, both are great! But, carrots contain more of vitamins A, B5, and choline, whereas kale contains more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, and K. And while carrot’s strongest point is vitamin A, a cup of carrots contains around 10x the recommended daily dose of vitamin A, whereas a cup of kale contains “only” 6x the recommended daily dose of vitamin A. So, did we really need the extra in carrots? Probably not. In any case, kale already won on overall vitamin coverage, by a long way.
In the category of minerals, kale again sweeps. On the one hand, carrots contain more sodium. On the other hand, kale contains a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. Not a tricky choice!
But don’t be fooled: carrots really are a nutritional powerhouse and a great food. Kale is just better—nutritionally speaking, in any case. If you’re making a carrot cake, please don’t try substituting kale; it will not work 😉
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Green Roasting Tin – by Rukmini Iyer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: “do I really need a book to tell me to put some vegetables in a roasting tin and roast them?” and maybe not, but the book offers a lot more than that.
Indeed, the author notes “this book was slightly in danger of becoming the gratin and tart book, because I love both”, but don’t worry, most of the recipes are—as you might expect—very healthy.
As for formatting: the 75 recipes are divided first into vegan or vegetarian, and then into quick/medium/slow, in terms of how long they take.
However, even the “slow” recipes don’t actually take more effort, just, more time in the oven.
One of the greatest strengths of this book is that not only does it offer a wide selection of wholesome mains, but also, if you’re putting on a big spread, these can easily double up as high-class low-effort sides.
Bottom line: if you’d like to eat more vegetables in 2024 but want to make it delicious and with little effort, put this book on your Christmas list!
Click here to check out The Green Roasting Tin, and level-up yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Water Water Everywhere, But Which Is Best To Drink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Well Well Well…
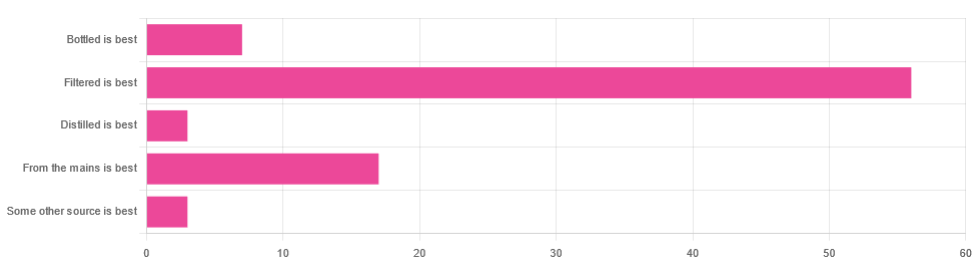
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on drinking water—with the understanding that this may vary from place to place. We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 65% said “Filtered is best”
- About 20% said “From the mains is best”
- About 8% said “Bottled is best”
- About 3% said “Distilled is best”
- About 3% said “Some other source is best”
Of those who said “some other source is best”, one clarified that their preferred source was well water.
So what does the science say?
Fluoridated water is bad for you: True or False?
False, assuming a normal level of consumption. Rather than take up more space today though, we’ll link to what we previously wrote on this topic:
You may be wondering: but what if my level of consumption is higher than normal?
Let’s quickly look at some stats:
- The maximum permitted safety level varies from place to place, but is (for example) 2mg/l in the US, 1.5mg/l in Canada & the UK.
- The minimum recommended amount also varies from place to place, but is (for example) 0.7mg/l in Canada and the US, and 1mg/l in the UK.
It doesn’t take grabbing a calculator to realize that if you drink twice as much water as someone else, then depending on where you are, water fluoridated to the minimum may give you more than the recommended maximum.
However… Those safety margins are set so much lower than the actual toxicity levels of fluoride, that it doesn’t make a difference.
For example: your writer here takes a medication that has the side effect of causing dryness of the mouth, and consequently she drinks at least 3l of water per day in a climate that could not be described as hot (except perhaps for about 2 weeks of the year). She weighs 72kg (that’s about 158 pounds), and the toxicity of fluoride (for ill symptoms, not death) is 0.2mg/kg. So, she’d need 14.4mg of fluoride, which even if the water fluoridation here were 2mg/l (it’s not; it’s lower here, but let’s go with the highest figure to make a point), would require drinking more than 7l of water faster than the body can process it.
For more about the numbers, check out:
Acute Fluoride Poisoning from a Public Water System
Bottled water is the best: True or False?
False, if we consider “best” to be “healthiest”, which in turn we consider to be “most nutrients, with highest safety”.
Bottled water generally does have higher levels of minerals than most local mains supply water does. That’s good!
But you know what else is generally has? Microplastics and nanoplastics. That’s bad!
We don’t like to be alarmist in tone; it’s not what we’re about here, but the stats on bottled water are simply not good; see:
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
You may be wondering: “but what about bottled water that comes in glass bottles?”
Indeed, water that comes in glass bottles can be expected to have lower levels of plastic than water that comes in plastic bottles, for obvious reasons.
However, we invite you to consider how likely you believe it to be that the water wasn’t stored in plastic while being processed, shipped and stored, before being portioned into its final store-ready glass bottles for end-consumer use.
Distilled water is the best: True or False?
False, generally, with caveats:
Distilled water is surely the safest water anywhere, because you know that you’ve removed any nasties.
However, it’s also devoid of nutrients, because you also removed any minerals it contained. Indeed, if you use a still, you’ll be accustomed to the build-up of these minerals (generally simplified and referenced as “limescale”, but it’s a whole collection of minerals).
Furthermore, that loss of nutrients can be more than just a “something good is missing”, because having removed certain ions, that water could now potentially strip minerals from your teeth. In practice, however, you’d probably have to swill it excessively to cause this damage.
Nevertheless, if you have the misfortune of living somewhere like Flint, Michigan, then a water still may be a fair necessity of life. In other places, it can simply be useful to have in case of emergency, of course.
Here’s an example product on Amazon if you’d like to invest in a water still for such cases.
PS: distilled water is also tasteless, and is generally considered bad, tastewise, for making tea and coffee. So we really don’t recommend distilling your water unless you have a good reason to do so.
Filtered water is the best: True or False?
True for most people in most places.
Let’s put it this way: it can’t logically be worse than whatever source of water you put into it…
Provided you change the filter regularly, of course.
Otherwise, after overusing a filter, at best it won’t be working, and at worst it’ll be adding in bacteria that have multiplied in the filter over however long you left it there.
You may be wondering: can water filters remove microplastics, and can they remove minerals?
The answer in both cases is: sometimes.
- For microplastics it depends on the filter size and the microplastic size (see our previous article for details on that).
- For minerals, it depends on the filter type. Check out:
The H2O Chronicles | 5 Water Filters That Remove Minerals
One other thing to think about: while most water filtration jugs are made of PFAS-free BPA-free plastics for obvious reasons, for greater peace of mind, you might consider investing in a glass filtration jug, like this one ← this is just one example product on Amazon; by all means shop around and find one you like
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why do I need to take some medicines with food?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have you ever been instructed to take your medicine with food and wondered why? Perhaps you’ve wondered if you really need to?
There are varied reasons, and sometimes complex science and chemistry, behind why you may be advised to take a medicine with food.
To complicate matters, some similar medicines need to be taken differently. The antibiotic amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (sold as Amoxil Duo Forte), for example, is recommended to be taken with food, while amoxicillin alone (sold as Amoxil), can be taken with or without food.
Different brands of the same medicine may also have different recommendations when it comes to taking it with food.
Ron Lach/Pexels Food impacts drug absorption
Food can affect how fast and how much a drug is absorbed into the body in up to 40% of medicines taken orally.
When you have food in your stomach, the makeup of the digestive juices change. This includes things like the fluid volume, thickness, pH (which becomes less acidic with food), surface tension, movement and how much salt is in your bile. These changes can impair or enhance drug absorption.
Eating a meal also delays how fast the contents of the stomach move into the small intestine – this is known as gastric emptying. The small intestine has a large surface area and rich blood supply – and this is the primary site of drug absorption.
Eating a meal with medicine will delay its onset. Farhad/Pexels Eating a larger meal, or one with lots of fibre, delays gastric emptying more than a smaller meal. Sometimes, health professionals will advise you to take a medicine with food, to help your body absorb the drug more slowly.
But if a drug can be taken with or without food – such as paracetamol – and you want it to work faster, take it on an empty stomach.
Food can make medicines more tolerable
Have you ever taken a medicine on an empty stomach and felt nauseated soon after? Some medicines can cause stomach upsets.
Metformin, for example, is a drug that reduces blood glucose and treats type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome. It commonly causes gastrointestinal symptoms, with one in four users affected. To combat these side effects, it is generally recommended to be taken with food.
The same advice is given for corticosteroids (such as prednisolone/prednisone) and certain antibiotics (such as doxycycline).
Taking some medicines with food makes them more tolerable and improves the chance you’ll take it for the duration it’s prescribed.
Can food make medicines safer?
Ibuprofen is one of the most widely used over-the-counter medicines, with around one in five Australians reporting use within a two-week period.
While effective for pain and inflammation, ibuprofen can impact the stomach by inhibiting protective prostaglandins, increasing the risk of bleeding, ulceration and perforation with long-term use.
But there isn’t enough research to show taking ibuprofen with food reduces this risk.
Prolonged use may also affect kidney function, particularly in those with pre-existing conditions or dehydration.
The Australian Medicines Handbook, which guides prescribers about medicine usage and dosage, advises taking ibuprofen (sold as Nurofen and Advil) with a glass of water – or with a meal if it upsets your stomach.
If it doesn’t upset your stomach, ibuprofen can be taken with water. Tbel Abuseridze/Unsplash A systematic review published in 2015 found food delays the transit of ibuprofen to the small intestine and absorption, which delays therapeutic effect and the time before pain relief. It also found taking short courses of ibuprofen without food reduced the need for additional doses.
To reduce the risk of ibuprofen causing damage to your stomach or kidneys, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration, stay hydrated and avoid taking other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines at the same time.
For people who use ibuprofen for prolonged periods and are at higher risk of gastrointestinal side effects (such as people with a history of ulcers or older adults), your prescriber may start you on a proton pump inhibitor, a medicine that reduces stomach acid and protects the stomach lining.
How much food do you need?
When you need to take a medicine with food, how much is enough?
Sometimes a full glass of milk or a couple of crackers may be enough, for medicines such as prednisone/prednisolone.
However, most head-to-head studies that compare the effects of a medicine “with food” and without, usually use a heavy meal to define “with food”. So, a cracker may not be enough, particularly for those with a sensitive stomach. A more substantial meal that includes a mix of fat, protein and carbohydrates is generally advised.
Your health professional can advise you on which of your medicines need to be taken with food and how they interact with your digestive system.
Mary Bushell, Clinical Associate Professor in Pharmacy, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: