Exhausted To Energized – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are very many possible causes of low energy; some are obvious; some are not.
Dr. Weaver goes through a comprehensive list that goes beyond the common, to encompass also the “not rare” options—how to test for them where appropriate, and how to improve/fix them where appropriate.
Thus, she talks us through the marvels of mitochondria (including how to keep them happy and healthy and how to promote the generation of new ones), antioxidant defense mechanisms, coenzyme Q10 and friends, B vitamins of various kinds, macronutrients, the autonomic nervous system, sleep and its many factors, blood oxygenation, digestive issues, what’s going on in the spleen, the gallbladder, the liver, the kidneys, the adrenal glands, our thyroid goings-on in all its multifarious wonders, minerals like iodine, iron, magnesium, zinc, our epigenetic factors, and even psychological considerations ranging from stress to grief. In short—and we have shortened the list to pick out particularly salient points—quite a comprehensive rundown of the human body to make your human body less run-down.
The style is on the very readable pop-science, and/but she does bring her professional knowledge to bear on topic (her doctorate is a PhD in biochemistry, and it shows; a lot of explanations come from that angle).
Bottom line: if you are often exhausted and would rather be energized, this this book almost certainly address at least a couple of things you probably haven’t considered—and even just one would make it worthwhile.
Click here to check out Exhausted To Energized, go from exhausted to energized!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Aging with Grace – by Dr. David Snowdon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book is not: a book about Christianity. Don’t worry, we didn’t suddenly change the theme of 10almonds.
Rather, what this book is: a book about a famous large (n=678) study into the biology of aging, that took a population sample of women who had many factors already controlled-for, e.g. they ate the same food, had the same schedule, did the same activities, etc—for many years on end. In other words, a convent of nuns.
This allowed for a lot more to be learned about other factors that influence aging, such as:
- Heredity / genetics in general
- Speaking more than one language
- Supplementing with vitamins or not
- Key adverse events (e.g. stroke)
- Key chronic conditions (e.g. depression)
The book does also cover (as one might expect) the role that community and faith can play in healthy longevity, but since the subjects were 678 communally-dwelling people of faith (thus: no control group of faithless loners), this aspect is discussed only in anecdote, or in reference to other studies.
The author of this book, by the way, was the lead researcher of the study, and he is a well-recognised expert in the field of Alzheimer’s in particular (and Alzheimer’s does feature quite a bit throughout).
The writing style is largely narrative, and/but with a lot of clinical detail and specific data; this is by no means a wishy-washy book.
Bottom line: if you’d like to know what nuns were doing in the 1980s to disproportionally live into three-figure ages, then this book will answer those questions.
Click here to check out Aging with Grace, and indeed age with grace!
Share This Post
-
An Addiction Expert’s Insights On Festive Drinking
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
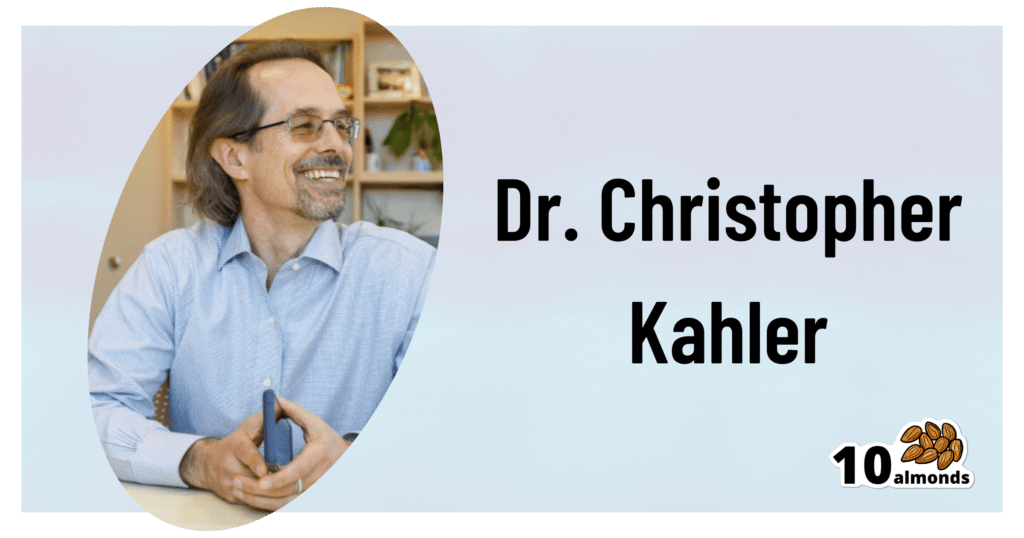
This is Dr. Christopher Kahler. He’s Professor of Behavioral and Social Sciences, Director of Alcohol and Addiction Studies, Professor of Psychiatry and Human Behavior, all at Brown University.
What does he want us to know?
It’s the trickiest time of the year
Per stats, alcohol sales peak in December, with the heaviest drinking being from mid-December (getting an early start on the Christmas cheer) to New Year’s Eve. As for why, there’s a collection of reasons, as he notes:
❝The main challenge is there’s an extra layer of stress, with a lot of obligations and expectations from friends and family. We’re around people who maybe we’re not usually around, and in larger groups. It’s also a time of heightened emotion and, for some people, loneliness.
On top of that, alcohol use is built into a lot of our winter holiday traditions. It’s often marketed as part of the “good life.” We’re expected to have alcohol when we celebrate.❞
As for how much alcohol is safe to drink… According to the World Health Organization, the only safe amount of alcohol is zero:
Dr. Kahler acknowledges, however, that many people will wish to imbibe anyway, and indeed, he himself does drink a little, but endeavours to do so mindfully, and as such, he recommends that we…
HALT!
Dr. Kahler counsels us against making decisions (including the decision to drink alcohol), on occasions when we are one or more of the following:
- Hungry
- Angry
- Lonely
- Tired
He also notes that around this time of year, often our normal schedules and habits are disrupted, which introduces more microdecisions to our daily lives, which in turn means more “decision fatigue”, and the greater chance of making bad decisions.
We share some practical tips on how to reduce the chances of thusly erring, here:
Set your intentions now
He bids us figure out what our goal is, and really think it through, including not just “how many drinks to have” if we’re drinking, but also such things as “what feelings are likely to come up”. Because, if we’ve historically used alcohol as a maladaptive coping mechanism, we’re going to need a different, better, healthier coping mechanism (we talked more about that in our above-linked article about reducing or quitting alcohol, too, with some examples).
He also suggests that we memorize our social responses—exactly what we’re going to say if offered a drink, for example:
❝It’s important to know what you’re going to say about your alcohol use. If someone asks if they can get you a drink, good responses could be: “A glass of water would be great” or “Do you have any non-alcoholic cider?” You don’t have to explain yourself. Just ask for what you want, because saying no to someone can be difficult.❞
See also:
December’s Traps To Plan Around
Mix it up and slow it down
No, that doesn’t mean mix yourself a sloe gin cocktail. But rather, it’s about alternating alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks, to give your body half a chance to process the alcohol, and also to rehydrate a little along the way.
We talk about this and other damage-limitation methods, here:
How To Reduce The Harm Of Festive Drinking (Without Abstaining)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Book of Lymph – by Lisa Levitt Gainsely
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book starts with an overview of what lymph is and why it matters, before getting into the main meat of the book, which is lymphatic massage techniques to improve lymphatic flow/drainage throughout different parts of the body, and in the context of an assortment of common maladies that may merit particular attention.
There’s an element of aesthetic medicine here, and improving beauty, but there’s also a whole section devoted to such things as breast care and the like (bearing in mind, the lymphatic system is one of our main defenses against cancer). There’s also a lot about managing lymph in the context of chronic health conditions.
The style is light pop-science; the science is explained clearly throughout, but without academic citations every few lines as some books might have. The author is, after all, a practitioner (CLT) and/but not an academic.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your lymphatic health, whether for beauty or health maintenance or recovery, this book will walk you through it.
Click here to check out The Book of Lymph, and give yours some love!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Circadian Diabetes Code – by Dr. Satchin Panda
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We have previously reviewed Dr. Panda’s “The Circadian Code” which pertains to the circadian rhythms (yes, plural) in general; this one uses much of the same research, but with a strong focus on the implications for blood sugar management.
It’s first a primer in diabetes (and prediabetes, and, in contrast, what things should look like if healthy). You’ll understand about glucose metabolism and glycogen and insulin and more; you’ll understand what blood sugar readings mean, and you’ll know what an Hb1AC count actually is and what it should look like too, things like that.
After that, it’s indeed about what the subtitle promises: the right times to eat (and what to eat), when to exercise (and how, at which time), and how to optimize your sleep in the context of circadian rhythm and blood sugar management.
You may be wondering: why does circadian rhythm matter for blood sugars? And the answer is explained at some length in the first part of the book, but to oversimplify greatly: your body needs energy all the time, no matter when it was that you last ate. Thus, it has to organize its energy reserves to that at all times you can 1) function, on a cellular level 2) maintain a steady balance of sugar in your blood despite using it at slightly higher or lower levels at different times of day. Because the basal metabolic rate accounts for most of our energy use, the body has to plan for a base rate of so much energy per day, and to do that, it needs to know what a day is. Dr. Panda explains this in detail (the marvels of PER proteins and all that), but basically, that’s the relevance of circadian rhythm.
However, it’s not all theory and biochemistry; there is also a 12-week program to reverse prediabetes and type 2 diabetes (it will not, of course, reverse Type 1 Diabetes, sorry—but the program will still be beneficial even in that case, since more even blood sugars means fewer woes).
They style is friendly and clear, explaining the science simply, yet without patronizing the reader. References are given, with claims sourced in an extensive bibliography.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one have diabetes or prediabetes, or just have a strong desire to avoid getting such and generally keep your metabolic health in good order, this book will definitely help.
Click here to check out The Diabetes Code, and enjoy better blood sugar health than ever!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
He Thinks His Wife Died in an Understaffed Hospital. Now He’s Trying to Change the Industry.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For the past year, police Detective Tim Lillard has spent most of his waking hours unofficially investigating his wife’s death.
The question has never been exactly how Ann Picha-Lillard died on Nov. 19, 2022: She succumbed to respiratory failure after an infection put too much strain on her weakened lungs. She was 65.
For Tim Lillard, the question has been why.
Lillard had been in the hospital with his wife every day for a month. Nurses in the intensive care unit had told him they were short-staffed, and were constantly rushing from one patient to the next.
Lillard tried to pitch in where he could: brushing Ann’s shoulder-length blonde hair or flagging down help when her tracheostomy tube gurgled — a sign of possible respiratory distress.
So the day he walked into the ICU and saw staff members huddled in Ann’s room, he knew it was serious. He called the couple’s adult children: “It’s Mom,” he told them. “Come now.”
All he could do then was sit on Ann’s bed and hold her hand, watching as staff members performed chest compressions, desperately trying to save her life.
A minute ticked by. Then another. Lillard’s not sure how long the CPR continued — long enough for the couple’s son to arrive and take a seat on the other side of Ann’s bed, holding her other hand.
Finally, the intensive care doctor called it and the team stopped CPR. Time of death: 12:37 p.m.
Lillard didn’t know what to do in a world without Ann. They had been married almost 25 years. “We were best friends,” he said.
Just days before her death, nurses had told Lillard that Ann could be discharged to a rehabilitation center as soon as the end of the week. Then, suddenly, she was gone. Lillard didn’t understand what had happened.
Lillard said he now believes that overwhelmed, understaffed nurses hadn’t been able to respond in time as Ann’s condition deteriorated. And he has made it his mission to fight for change, joining some nursing unions in a push for mandatory ratios that would limit the number of patients in a nurse’s care. “I without a doubt believe 100% Ann would still be here today if they had staffing levels, mandatory staffing levels, especially in ICU,” Lillard said.
Last year, Oregon became the second state after California to pass hospital-wide nurse ratios that limit the number of patients in a nurse’s care. Michigan, Maine, and Pennsylvania are now weighing similar legislation.
But supporters of mandatory ratios are going up against a powerful hospital industry spending millions of dollars to kill those efforts. And hospitals and health systems say any staffing ratio regulations, however well-intentioned, would only put patients in greater danger.
Putting Patients at Risk
By next year, the United States could have as many as 450,000 fewer nurses than it needs, according to one estimate. The hospital industry blames covid-19 burnout, an aging workforce, a large patient population, and an insufficient pipeline of new nurses entering the field.
But nursing unions say that’s not the full story. There are now 4.7 million registered nurses in the country, more than ever before.
The problem, the unions say, is a hospital industry that’s been intentionally understaffing their units for years in order to cut costs and bolster profits. The unions say there isn’t a shortage of nurses but a shortage of nurses willing to work in those conditions.
The nurse staffing crisis is now affecting patient care. The number of Michigan nurses who say they know of a patient who has died because of understaffing has nearly doubled in recent years, according to a Michigan Nurses Association survey last year.
Just months before Ann Picha-Lillard’s death, nurses and doctors at the health system where she died had asked the Michigan attorney general to investigate staffing cuts they believed were leading to dangerous conditions, including patient deaths, according to The Detroit News.
But Lillard didn’t know any of that when he drove his wife to the hospital in October 2022. She had been feeling short of breath for a few weeks after she and Lillard had mild covid infections. They were both vaccinated, but Ann was immunocompromised. She suffered from rheumatoid arthritis, a condition that had also caused scarring in her lungs.
To be safe, doctors at DMC Huron Valley-Sinai Hospital wanted to keep Ann for observation. After a few days in the facility, she developed pneumonia. Doctors told the couple that Ann needed to be intubated. Ann was terrified but Lillard begged her to listen to the doctors. Tearfully, she agreed.
With Ann on a ventilator in the ICU, it seemed clear to Lillard that nurses were understaffed and overwhelmed. One nurse told him they had been especially short-staffed lately, Lillard said.
“The alarms would go off for the medications, they’d come into the room, shut off the alarm when they get low, run to the medication room, come back, set them down, go to the next room, shut off alarms,” Lillard recalled. “And that was going on all the time.”
Lillard felt bad for the nurses, he said. “But obviously, also for my wife. That’s why I tried doing as much as I could when I was there. I would comb her hair, clean her, just keep an eye on things. But I had no idea what was really going on.”
Finally, Ann’s health seemed to be stabilizing. A nurse told Lillard they’d be able to discharge Ann, possibly by the end of that week.
By Nov. 17, Ann was no longer sedated and she cried when she saw Lillard and her daughter. Still unable to speak, she tried to mouth words to her husband “but we couldn’t understand what she was saying,” Lillard said.
The next day, Lillard went home feeling hopeful, counting down the days until Ann could leave the hospital.
Less than 24 hours later, Ann died.
Lillard couldn’t wrap his head around how things went downhill so fast. Ann’s underlying lung condition, the infection, and her weakened state could have proved fatal in the best of circumstances. But Lillard wanted to understand how Ann had gone from nearly discharged to dying, seemingly overnight.
He turned his dining room table into a makeshift office and started with what he knew. The day Ann died, he remembered her medical team telling him that her heart rate had spiked and she had developed another infection the night before. Lillard said he interviewed two DMC Huron Valley-Sinai nurse administrators, and had his own doctor look through Ann’s charts and test results from the hospital. “Everybody kept telling me: sepsis, sepsis, sepsis,” he said.
Sepsis is when an infection triggers an extreme reaction in the body that can cause rapid organ failure. It’s one of the leading causes of death in U.S. hospitals. Some experts say up to 80% of sepsis deaths are preventable, while others say the percentage is far lower.
Lives can be saved when sepsis is caught and treated fast, which requires careful attention to small changes in vital signs. One study found that for every additional patient a nurse had to care for, the mortality rate from sepsis increased by 12%.
Lillard became convinced that had there been more nurses working in the ICU, someone could have caught what was happening to Ann.
“They just didn’t have the time,” he said.
DMC Huron Valley-Sinai’s director of communications and media relations, Brian Taylor, declined a request for comment about the 2022 staffing complaint to the Michigan attorney general.
Following the Money
When Lillard asked the hospital for copies of Ann’s medical records, DMC Huron Valley-Sinai told him he’d have to request them from its parent company in Texas.
Like so many hospitals in recent years, the Lillards’ local health system had been absorbed by a series of other corporations. In 2011, the Detroit Medical Center health system was bought for $1.5 billion by Vanguard Health Systems, which was backed by the private equity company Blackstone Group.
Two years after that, in 2013, Vanguard itself was acquired by Tenet Healthcare, a for-profit company based in Dallas that, according to its website, operates 480 ambulatory surgery centers and surgical hospitals, 52 hospitals, and approximately 160 additional outpatient centers.
As health care executives face increasing pressure from investors, nursing unions say hospitals have been intentionally understaffing nurses to reduce labor costs and increase revenue. Also, insurance reimbursements incentivize keeping nurse staffing levels low. “Hospitals are not directly reimbursed for nursing services in the same way that a physician bills for their services,” said Karen Lasater, an associate professor of nursing in the Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research at the University of Pennsylvania. “And because hospitals don’t perceive nursing as a service line, but rather a cost center, they think about nursing as: How can we reduce this to the lowest denominator possible?” she said.
Lasater is a proponent of mandatory nurse ratios. “The nursing shortage is not a pipeline problem, but a leaky bucket problem,” she said. “And the solutions to this crisis need to address the root cause of the issue, which is why nurses are saying they’re leaving employment. And it’s rooted in unsafe staffing. It’s not safe for the patients, but it’s also not safe for nurses.”
A Battle Between Hospitals and Unions
In November, almost one year after Ann’s death, Lillard told a room of lawmakers at the Michigan State Capitol that he believes the Safe Patient Care Act could save lives. The health policy committee in the Michigan House was holding a hearing on the proposed act, which would limit the amount of mandatory overtime a nurse can be forced to work, and require hospitals to make their staffing levels available to the public.
Most significantly, the bills would require hospitals to have mandatory, minimum nurse-to-patient ratios. For example: one nurse for every patient in the ICU; one for every three patients in the emergency room; a nurse for triage; and one nurse for every four postpartum birthing patients and well-baby care.
Efforts to pass mandatory ratio laws failed in Washington and Minnesota last year after facing opposition from the hospital industry. In Minnesota, the Minnesota Nurses Association accused the Mayo Clinic of using “blackmail tactics”: Mayo had told lawmakers it would pull billions of dollars in investment from the state if mandatory ratio legislation passed. Soon afterward, lawmakers removed nurse ratios from the legislation.
While Lillard waited for his turn to speak to Michigan lawmakers about the Safe Patient Care Act in November, members of the Michigan Nurses Association, which says it represents some 13,000 nurses, told lawmakers that its units were dangerously understaffed. They said critical care nurses were sometimes caring for up to 11 patients at a time.
“Last year I coded someone in an ICU for 10 minutes, all alone, because there was no one to help me,” said the nurses association president and registered nurse Jamie Brown, reading from another nurse’s letter.
“I have been left as the only specially trained nurse to take care of eight babies on the unit: eight fragile newborns,” said Carolyn Clemens, a registered nurse from the Grand Blanc area of Michigan.
Nikia Parker said she has left full-time emergency room nursing, a job she believes is her calling. After her friend died in the hospital where she worked, she was left wondering whether understaffing may have contributed to his death.
“If the Safe Patient Care Act passed, and we have ratios, I’m one of those nurses who would return to the bedside full time,” Parker told lawmakers. “And so many of my co-workers who have left would join me.”
But not all nurses agree that mandatory ratios are a good idea.
While the American Nurses Association supports enforceable ratios as an “essential approach,” that organization’s Michigan chapter does not, saying there may not be enough nurses in the state to satisfy the requirements of the Safe Patient Care Act.
For some lawmakers, the risk of collateral damage seems too high. State Rep. Graham Filler said he worries that mandating ratios could backfire.
“We’re going to severely hamper health care in the state of Michigan. I’m talking closed wards because you can’t meet the ratio in a bill. The inability for a hospital to treat an emergent patient. So it feels kind of to me like a gamble we’re taking,” said Filler, a Republican.
Michigan hospitals are already struggling to fill some 8,400 open positions, according to the Michigan Health & Hospital Association. That association says that complying with the Safe Patient Care Act would require hiring 13,000 nurses.
Every major health system in the state signed a letter opposing mandatory ratios, saying it would force them to close as many as 5,100 beds.
Lillard watched the debate play out in the hearing. “That’s a scare tactic, in my opinion, where the hospitals say we’re going to have to start closing stuff down,” he said.
He doesn’t think legislation on mandatory ratios — which are still awaiting a vote in the Michigan House’s health policy committee — are a “magic bullet” for such a complex, national problem. But he believes they could help.
“The only way these hospitals and the administrations are gonna make any changes, and even start moving towards making it better, is if they’re forced to,” Lillard said.
Seated in the center of the hearing room in Lansing, next to a framed photo of Ann, Lillard’s hands shook as he recounted those final minutes in the ICU.
“Please take action so that no other person or other family endures this loss,” he said. “You can make a difference in saving lives.”
Grief is one thing, Lillard said, but it’s another thing to be haunted by doubts, to worry that your loved one’s care was compromised before they ever walked through the hospital doors. What he wants most, he said, is to prevent any other family from having to wonder, “What if?”
This article is from a partnership that includes Michigan Public, NPR, and KFF Health News.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Their First Baby Came With Medical Debt. These Illinois Parents Won’t Have Another.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
JACKSONVILLE, Ill. — Heather Crivilare was a month from her due date when she was rushed to an operating room for an emergency cesarean section.
The first-time mother, a high school teacher in rural Illinois, had developed high blood pressure, a sometimes life-threatening condition in pregnancy that prompted doctors to hospitalize her. Then Crivilare’s blood pressure spiked, and the baby’s heart rate dropped. “It was terrifying,” Crivilare said.
She gave birth to a healthy daughter. What followed, though, was another ordeal: thousands of dollars in medical debt that sent Crivilare and her husband scrambling for nearly a year to keep collectors at bay.
The Crivilares would eventually get on nine payment plans as they juggled close to $5,000 in bills.
“It really felt like a full-time job some days,” Crivilare recalled. “Getting the baby down to sleep and then getting on the phone. I’d set up one payment plan, and then a new bill would come that afternoon. And I’d have to set up another one.”
Crivilare’s pregnancy may have been more dramatic than most. But for millions of new parents, medical debt is now as much a hallmark of having children as long nights and dirty diapers.
About 12% of the 100 million U.S. adults with health care debt attribute at least some of it to pregnancy or childbirth, according to a KFF poll.
These people are more likely to report they’ve had to take on extra work, change their living situation, or make other sacrifices.
Overall, women between 18 and 35 who have had a baby in the past year and a half are twice as likely to have medical debt as women of the same age who haven’t given birth recently, other KFF research conducted for this project found.
“You feel bad for the patient because you know that they want the best for their pregnancy,” said Eilean Attwood, a Rhode Island OB-GYN who said she routinely sees pregnant women anxious about going into debt.
“So often, they may be coming to the office or the hospital with preexisting debt from school, from other financial pressures of starting adult life,” Attwood said. “They are having to make real choices, and what those real choices may entail can include the choice to not get certain services or medications or what may be needed for the care of themselves or their fetus.”
Best-Laid Plans
Crivilare and her husband, Andrew, also a teacher, anticipated some of the costs.
The young couple settled in Jacksonville, in part because the farming community less than two hours north of St. Louis was the kind of place two public school teachers could afford a house. They saved aggressively. They bought life insurance.
And before Crivilare got pregnant in 2021, they enrolled in the most robust health insurance plan they could, paying higher premiums to minimize their deductible and out-of-pocket costs.
Then, two months before their baby was due, Crivilare learned she had developed preeclampsia. Her pregnancy would no longer be routine. Crivilare was put on blood pressure medication, and doctors at the local hospital recommended bed rest at a larger medical center in Springfield, about 35 miles away.
“I remember thinking when they insisted that I ride an ambulance from Jacksonville to Springfield … ‘I’m never going to financially recover from this,’” she said. “‘But I want my baby to be OK.’”
For weeks, Crivilare remained in the hospital alone as covid protocols limited visitors. Meanwhile, doctors steadily upped her medications while monitoring the fetus. It was, she said, “the scariest month of my life.”
Fear turned to relief after her daughter, Rita, was born. The baby was small and had to spend nearly two weeks in the neonatal intensive care unit. But there were no complications. “We were incredibly lucky,” Crivilare said.
When she and Rita finally came home, a stack of medical bills awaited. One was already past due.
Crivilare rushed to set up payment plans with the hospitals in Jacksonville and Springfield, as well as the anesthesiologist, the surgeon, and the labs. Some providers demanded hundreds of dollars a month. Some settled for monthly payments of $20 or $25. Some pushed Crivilare to apply for new credit cards to pay the bills.
“It was a blur of just being on the phone constantly with all the different people collecting money,” she recalled. “That was a nightmare.”
Big Bills, Big Consequences
The Crivilares’ bills weren’t unusual. Parents with private health coverage now face on average more than $3,000 in medical bills related to a pregnancy and childbirth that aren’t covered by insurance, researchers at the University of Michigan found.
Out-of-pocket costs are even higher for families with a newborn who needs to stay in a neonatal ICU, averaging $5,000. And for 1 in 11 of these families, medical bills related to pregnancy and childbirth exceed $10,000, the researchers found.
“This forces very difficult trade-offs for families,” said Michelle Moniz, a University of Michigan OB-GYN who worked on the study. “Even though they have insurance, they still have these very high bills.”
Nationwide polls suggest millions of these families end up in debt, with sometimes devastating consequences.
About three-quarters of U.S. adults with debt related to pregnancy or childbirth have cut spending on food, clothing, or other essentials, KFF polling found.
About half have put off buying a home or delayed their own or their children’s education.
These burdens have spurred calls to limit what families must pay out-of-pocket for medical care related to pregnancy and childbirth.
In Massachusetts, state Sen. Cindy Friedman has proposed legislation to exempt all these bills from copays, deductibles, and other cost sharing. This would parallel federal rules that require health plans to cover recommended preventive services like annual physicals without cost sharing for patients. “We want … healthy children, and that starts with healthy mothers,” Friedman said. Massachusetts health insurers have warned the proposal will raise costs, but an independent state analysis estimated the bill would add only $1.24 to monthly insurance premiums.
Tough Lessons
For her part, Crivilare said she wishes new parents could catch their breath before paying down medical debt.
“No one is in the right frame of mind to deal with that when they have a new baby,” she said, noting that college graduates get such a break. “When I graduated with my college degree, it was like: ‘Hey, new adult, it’s going to take you six months to kind of figure out your life, so we’ll give you this six-month grace period before your student loans kick in and you can get a job.’”
Rita is now 2. The family scraped by on their payment plans, retiring the medical debt within a year, with help from Crivilare’s side job selling resources for teachers online.
But they are now back in debt, after Rita’s recurrent ear infections required surgery last year, leaving the family with thousands of dollars in new medical bills.
Crivilare said the stress has made her think twice about seeing a doctor, even for Rita. And, she added, she and her husband have decided their family is complete.
“It’s not for us to have another child,” she said. “I just hope that we can put some of these big bills behind us and give [Rita] the life that we want to give her.”
About This Project
“Diagnosis: Debt” is a reporting partnership between KFF Health News and NPR exploring the scale, impact, and causes of medical debt in America.
The series draws on original polling by KFF, court records, federal data on hospital finances, contracts obtained through public records requests, data on international health systems, and a yearlong investigation into the financial assistance and collection policies of more than 500 hospitals across the country.
Additional research was conducted by the Urban Institute, which analyzed credit bureau and other demographic data on poverty, race, and health status for KFF Health News to explore where medical debt is concentrated in the U.S. and what factors are associated with high debt levels.
The JPMorgan Chase Institute analyzed records from a sampling of Chase credit card holders to look at how customers’ balances may be affected by major medical expenses. And the CED Project, a Denver nonprofit, worked with KFF Health News on a survey of its clients to explore links between medical debt and housing instability.
KFF Health News journalists worked with KFF public opinion researchers to design and analyze the “KFF Health Care Debt Survey.” The survey was conducted Feb. 25 through March 20, 2022, online and via telephone, in English and Spanish, among a nationally representative sample of 2,375 U.S. adults, including 1,292 adults with current health care debt and 382 adults who had health care debt in the past five years. The margin of sampling error is plus or minus 3 percentage points for the full sample and 3 percentage points for those with current debt. For results based on subgroups, the margin of sampling error may be higher.
Reporters from KFF Health News and NPR also conducted hundreds of interviews with patients across the country; spoke with physicians, health industry leaders, consumer advocates, debt lawyers, and researchers; and reviewed scores of studies and surveys about medical debt.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: