Why Some Friendships Last And Others Don’t
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Friendships matter a lot, playing a significant role in our wellbeing, physical as well as mental. They bring additional meaning to our lives, help us cope with setbacks, and hopefully will be at our side through the highs and lows of life. And yet, for something that’s in principle good for everyone involved, there can be problems:
Friend to the end?
Firstly, some people find it harder to make (and then further deepen) friendships with others, which can be for a whole host of reasons.
Approaching new people can feel intimidating, but it’s a common struggle. Research shows that people often underestimate how much others enjoy their company, a phenomenon known as the “liking gap.” By reminding ourselves that others are likely to appreciate our presence and expecting to be well-received (the “acceptance prophecy”), we can approach social interactions with greater confidence.
As relationships grow, they often deepen through companionship and closeness:
- Companionship arises from shared hobbies, interests, or values, and it builds rapport.
- Closeness involves sharing thoughts, feelings, and experiences, which can build intimacy together.
An important key to these is consistency, which—whether through regular chats, honoring plans, or showing support—helps strengthen bonds, even in long-distance friendships (something often considered a barrier to closeness).
Even the strongest friendships can face challenges, of course. Conflicts may arise from a lack of support during difficult moments, or worse, betrayal. Or it could all be a misunderstanding. These situations are best addressed through honest, non-judgmental conversations. Avoiding defensiveness or accusations, and instead focusing on sharing feelings and understanding the other person’s perspective, can turn these tough discussions into opportunities for growth and stronger connections.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Accidental falls in the older adult population: What academic research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Accidental falls are among the leading causes of injury and death among adults 65 years and older worldwide. As the aging population grows, researchers expect to see an increase in the number of fall injuries and related health spending.
Falls aren’t unique to older adults. Nealy 684,000 people die from falls each year globally. Another 37.3 million people each year require medical attention after a fall, according to the World Health Organization. But adults 65 and older account for the greatest number of falls.
In the United States, more than 1 in 4 older adults fall each year, according to the National Institute on Aging. One in 10 report a fall injury. And the risk of falling increases with age.
In 2022, health care spending for nonfatal falls among older adults was $80 billion, according to a 2024 study published in the journal Injury Prevention.
Meanwhile, the fall death rate in this population increased by 41% between 2012 and 2021, according to the latest CDC data.
“Unfortunately, fall-related deaths are increasing and we’re not sure why that is,” says Dr. Jennifer L. Vincenzo, an associate professor at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in the department of physical therapy and the Center for Implementation Research. “So, we’re trying to work more on prevention.”
Vincenzo advises journalists to write about how accidental falls can be prevented. Remind your audiences that accidental falls are not an inevitable consequence of aging, and that while we do decline in many areas with age, there are things we can do to minimize the risk of falls, she says. And expand your coverage beyond the national Falls Prevention Awareness Week, which is always during the first week of fall — Sept. 23 to 27 this year.
Below, we explore falls among older people from different angles, including injury costs, prevention strategies and various disparities. We have paired each angle with data and research studies to inform your reporting.
Falls in older adults
In 2020, 14 million older adults in the U.S. reported falling during the previous year. In 2021, more than 38,700 older adults died due to unintentional falls, according to the CDC.
A fall could be immediately fatal for an older adult, but many times it’s the complications from a fall that lead to death.
The majority of hip fractures in older adults are caused by falls, Vincenzo says, and “it could be that people aren’t able to recover [from the injury], losing function, maybe getting pneumonia because they’re not moving around, or getting pressure injuries,” she says.
In addition, “sometimes people restrict their movement and activities after a fall, which they think is protective, but leads to further functional declines and increases in fall risk,” she adds.
Factors that can cause a fall include:
- Poor eyesight, reflexes and hearing. “If you cannot hear as well, anytime you’re doing something in your environment and there’s a noise, it will be really hard for you to focus on hearing what that noise is and what it means and also moving at the same time,” Vincenzo says.
- Loss of strength, balance, and mobility with age, which can lessen one’s ability to prevent a fall when slipping or tripping.
- Fear of falling, which usually indicates decreased balance.
- Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or problems with nerves or feet that can affect balance.
- Conditions like incontinence that cause rushed movement to the bathroom.
- Cognitive impairment or certain types of dementia.
- Unsafe footwear such as backless shoes or high heels.
- Medications or medication interactions that can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Safety hazards in the home or outdoors, such as poor lighting, steps and slippery surfaces.
Related Research
Nonfatal and Fatal Falls Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2020–2021
Ramakrishna Kakara, Gwen Bergen, Elizabeth Burns and Mark Stevens. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, September 2023.Summary: Researchers analyzed data from the 2020 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System — a landline and mobile phone survey conducted each year in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia — and data from the 2021 National Vital Statistics System to identify patterns of injury and death due to falls in the U.S. by sex and state for adults 65 years and older. Among the findings:
- The percentage of women who reported falling was 28.9%, compared with 26.1% of men.
- Death rates from falls were higher among white and American Indian or Alaska Native older adults than among older adults from other racial and ethnic groups.
- In 2020, the percentage of older adults who reported falling during the past year ranged from 19.9% in Illinois to 38.0% in Alaska. The national estimate for 18 states was 27.6%.
- In 2021, the unintentional fall-related death rate among older adults ranged from 30.7 per 100,000 older adults in Alabama to 176.5 in Wisconsin. The national estimate for 26 states was 78.
“Although common, falls among older adults are preventable,” the authors write. “Health care providers can talk with patients about their fall risk and how falls can be prevented.”
Trends in Nonfatal Falls and Fall-Related Injuries Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2012-2018
Briana Moreland, Ramakrishna Kakara and Ankita Henry. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, July 2020.Summary: Researchers compared data from the 2018 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Among the findings:
- The percentage of older adults reporting a fall increased from 2012 to 2016, then slightly decreased from 2016 to 2018.
- Even with this decrease in 2018, older adults reported 35.6 million falls. Among those falls, 8.4 million resulted in an injury that limited regular activities for at least one day or resulted in a medical visit.
“Despite no significant changes in the rate of fall-related injuries from 2012 to 2018, the number of fall-related injuries and health care costs can be expected to increase as the proportion of older adults in the United States grows,” the authors write.
Understanding Modifiable and Unmodifiable Older Adult Fall Risk Factors to Create Effective Prevention Strategies
Gwen Bergen, et al. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, October 2019.Summary: Researchers used data from the 2016 U.S. Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System to better understand the association between falls and fall injuries in older adults and factors such as health, state and demographic characteristics. Among the findings:
- Depression had the strongest association with falls and fall injuries. About 40% of older adults who reported depression also reported at least one fall; 15% reported at least one fall injury.
- Falls and depression have several factors in common, including cognitive impairment, slow walking speed, poor balance, slow reaction time, weakness, low energy and low levels of activity.
- Other factors associated with an increased risk of falling include diabetes, vision problems and arthritis.
“The multiple characteristics associated with falls suggest that a comprehensive approach to reducing fall risk, which includes screening and assessing older adult patients to determine their unique, modifiable risk factors and then prescribing tailored care plans that include evidence-based interventions, is needed,” the authors write.
Health care use and cost
In addition to being the leading cause of injury, falls are the leading cause of hospitalization in older adults. Each year, about 3 million older adults visit the emergency department due to falls. More than 1 million get hospitalized.
In 2021, falls led to more than 38,000 deaths in adults 65 and older, according to the CDC.
The annual financial medical toll of falls among adults 65 years and older is expected to be more than $101 billion by 2030, according to the National Council on Aging, an organization advocating for older Americans.
Related research
Healthcare Spending for Non-Fatal Falls Among Older Adults, USA
Yara K. Haddad, et al. Injury Prevention, July 2024.Summary: In 2015, health care spending related to falls among older adults was roughly $50 billion. This study aims to update the estimate, using the 2017, 2019 and 2021 Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey, the most comprehensive and complete survey available on the Medicare population. Among the findings:
- In 2020, health care spending for non-fatal falls among older adults was $80 billion.
- Medicare paid $53.3 billion of the $80 billion, followed by $23.2 billion paid by private insurance or patients and $3.5 billion by Medicaid.
“The burden of falls on healthcare systems and healthcare spending will continue to rise if the risk of falls among the aging population is not properly addressed,” the authors write. “Many older adult falls can be prevented by addressing modifiable fall risk factors, including health and functional characteristics.”
Cost of Emergency Department and Inpatient Visits for Fall Injuries in Older Adults Lisa Reider, et al. Injury, February 2024.
Summary: The researchers analyzed data from the 2016-2018 National Inpatient Sample and National Emergency Department Sample, which are large, publicly available patient databases in the U.S. that include all insurance payers such as Medicare and private insurance. Among the findings:
- During 2016-2018, more than 920,000 older adults were admitted to the hospital and 2.3 million visited the emergency department due to falls. The combined annual cost was $19.2 billion.
- More than half of hospital admissions were due to bone fractures. About 14% of these admissions were due to multiple fractures and cost $2.5 billion.
“The $20 billion in annual acute treatment costs attributed to fall injury indicate an urgent need to implement evidence-based fall prevention interventions and underscores the importance of newly launched [emergency department]-based fall prevention efforts and investments in geriatric emergency departments,” the authors write.
Hip Fracture-Related Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations and Deaths by Mechanism of Injury Among Adults Aged 65 and Older, United States 2019
Briana L. Moreland, Jaswinder K. Legha, Karen E. Thomas and Elizabeth R. Burns. Journal of Aging and Health, June 2024.Summary: The researchers calculated hip fracture-related U.S. emergency department visits, hospitalizations and deaths among older adults, using data from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project and the National Vital Statistics System. Among the findings:
- In 2019, there were 318,797 emergency department visits, 290,130 hospitalizations and 7,731 deaths related to hip fractures among older adults.
- Nearly 88% of emergency department visits and hospitalizations and 83% of deaths related to hip fractures were caused by falls.
- These rates were highest among those living in rural areas and among adults 85 and older. More specifically, among adults 85 and older, the rate of hip fracture-related emergency department visits was nine times higher than among adults between 65 and 74 years old.
“Falls are common among older adults, but many are preventable,” the authors write. “Primary care providers can prevent falls among their older patients by screening for fall risk annually or after a fall, assessing modifiable risk factors such as strength and balance issues, and offering evidence-based interventions to reduce older adults’ risk of falls.”
Fall prevention
Several factors, including exercising, managing medication, checking vision and making homes safer can help prevent falls among older adults.
“Exercise is one of the best interventions we know of to prevent falls,” Vincenzo says. But “walking in and of itself will not help people to prevent falls and may even increase their risk of falling if they are at high risk of falls.”
The National Council on Aging also has a list of evidence-based fall prevention programs, including activities and exercises that are shown to be effective.
The National Institute on Aging has a room-by-room guide on preventing falls at home. Some examples include installing grab bars near toilets and on the inside and outside of the tub and shower, sitting down while preparing food to prevent fatigue, and keeping electrical cords near walls and away from walking paths.
There are also national and international initiatives to help prevent falls.
Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries, or STEADI, is an initiative by the CDC’s Injury Center to help health care providers who treat older adults. It helps providers screen patients for fall risk, assess their fall risk factors and reduce their risk by using strategies that research has shown to be effective. STEADI’s guidelines are in line with the American and British Geriatric Societies’ Clinical Practice Guidelines for fall prevention.
“We’re making some iterations right now to STEADI that will come out in the next couple of years based on the World Falls Guidelines, as well as based on clinical providers’ feedback on how to make [STEADI] more feasible,” Vincenzo says.
The World Falls Guidelines is an international initiative to prevent falls in older adults. The guidelines are the result of the work of 14 international experts who came together in 2019 to consider whether new guidelines on fall prevention were needed. The task force then brought together 96 experts from 39 countries across five continents to create the guidelines.
The CDC’s STEADI initiative has a screening questionnaire for consumers to check their risk of falls, as does the National Council on Aging.
On the policy side, U.S. Rep. Carol Miller, R-W.V., and Melanie Stansbury, D-N.M., introduced the Stopping Addiction and Falls for the Elderly (SAFE) Act in March 2024. The bill would allow occupational and physical therapists to assess fall risks in older adults as part of the Medicare Annual Wellness Benefit. The bill was sent to the House Subcommittee on Health in the same month.
Meanwhile, older adults’ attitudes toward falls and fall prevention are also pivotal. For many, coming to terms with being at risk of falls and making changes such as using a cane, installing railings at home or changing medications isn’t easy for all older adults, studies show.
“Fall is a four-letter F-word in a way to older adults,” says Vincenzo, who started her career as a physical therapist. “It makes them feel ‘old.’ So, it’s a challenge on multiple fronts: U.S. health care infrastructure, clinical and community resources and facilitating health behavior change.”
Related research
Environmental Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older People Living in the Community
Lindy Clemson, et al. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, March 2023.Summary: This review includes 22 studies from 10 countries involving a total of 8,463 older adults who live in the community, which includes their own home, a retirement facility or an assisted living facility, but not a hospital or nursing home. Among the findings:
- Removing fall hazards at home reduced the number of falls by 38% among older adults at a high risk of having a fall, including those who have had a fall in the past year, have been hospitalized or need support with daily activities. Examples of fall hazards at home include a stairway without railings, a slippery pathway or poor lighting.
- It’s unclear whether checking prescriptions for eyeglasses, wearing special footwear or installing bed alarm systems reduces the rate of falls.
- It’s also not clear whether educating older adults about fall risks reduces their fall risk.
The Influence of Older Adults’ Beliefs and Attitudes on Adopting Fall Prevention Behaviors
Judy A. Stevens, David A. Sleet and Laurence Z. Rubenstein. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. January 2017.Summary: Persuading older adults to adopt interventions that reduce their fall risk is challenging. Their attitudes and beliefs about falls play a large role in how well they accept and adopt fall prevention strategies, the authors write. Among the common attitudes and beliefs:
- Many older adults believe that falls “just happen,” are a normal result of aging or are simply due to bad luck.
- Many don’t acknowledge or recognize their fall risk.
- For many, falls are considered to be relevant only for frail or very old people.
- Many believe that their home environment or daily activities can be a risk for fall, but do not consider biological factors such as dizziness or muscle weakness.
- For many, fall prevention simply consists of “being careful” or holding on to things when moving about the house.
“To reduce falls, health care practitioners have to help patients understand and acknowledge their fall risk while emphasizing the positive benefits of fall prevention,” the authors write. “They should offer patients individualized fall prevention interventions as well as provide ongoing support to help patients adopt and maintain fall prevention strategies and behaviors to reduce their fall risk. Implementing prevention programs such as CDC’s STEADI can help providers discuss the importance of falls and fall prevention with their older patients.”
Reframing Fall Prevention and Risk Management as a Chronic Condition Through the Lens of the Expanded Chronic Care Model: Will Integrating Clinical Care and Public Health Improve Outcomes?
Jennifer L. Vincenzo, Gwen Bergen, Colleen M. Casey and Elizabeth Eckstrom. The Gerontologist, June 2024.Summary: The authors recommend approaching fall prevention from the lens of chronic disease management programs because falls and fall risk are chronic issues for many older adults.
“Policymakers, health systems, and community partners can consider aligning fall risk management with the [Expanded Chronic Care Model], as has been done for diabetes,” the authors write. “This can help translate high-quality research on the effectiveness of fall prevention interventions into daily practice for older adults to alter the trajectory of older adult falls and fall-related injuries.”
Disparities
Older adults face several barriers to reducing their fall risk. Accessing health care services and paying for services such as physical therapy is not feasible for everyone. Some may lack transportation resources to go to and from medical appointments. Social isolation can increase the risk of death from falls. In addition, physicians may not have the time to fit in a fall risk screening while treating older patients for other health concerns.
Moreover, implementing fall risk screening, assessment and intervention in the current U.S. health care structure remains a challenge, Vincenzo says.
Related research
Mortality Due to Falls by County, Age Group, Race, and Ethnicity in the USA, 2000-19: A Systematic Analysis of Health Disparities
Parkes Kendrick, et al. The Lancet Public Health, August 2024.Summary: Researchers analyzed death registration data from the U.S. National Vital Statistics System and population data from the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics to estimate annual fall-related mortality. The data spanned from 2000 to 2019 and includes all age groups. Among the findings:
- The disparities between racial and ethnic populations varied widely by age group. Deaths from falls among younger adults were highest for the American Indian/Alaska Native population, while among older adults it was highest for the white population.
- For older adults, deaths from falls were particularly high in the white population within clusters of counties across states including Florida, Minnesota and Wisconsin.
- One factor that could contribute to higher death rates among white older adults is social isolation, the authors write. “Studies suggest that older Black and Latino adults are more likely to have close social support compared with older white adults, while AIAN and Asian individuals might be more likely to live in multigenerational households,” they write.
“Among older adults, current prevention techniques might need to be restructured to reduce frailty by implementing early prevention and emphasizing particularly successful interventions. Improving social isolation and evaluating the effectiveness of prevention programs among minoritized populations are also key,” the authors write.
Demographic Comparisons of Self-Reported Fall Risk Factors Among Older Adults Attending Outpatient Rehabilitation
Mariana Wingood, et al. Clinical Interventions in Aging, February 2024.Summary: Researchers analyzed the electronic health record data of 108,751 older adults attending outpatient rehabilitation within a large U.S. health care system across seven states, between 2018 and 2022. Among the findings:
- More than 44% of the older adults were at risk of falls; nearly 35% had a history of falls.
- The most common risk factors for falls were diminished strength, gait and balance.
- Compared to white older adults, Native American/Alaska Natives had the highest prevalence of fall history (43.8%) and Hispanics had the highest prevalence of falls with injury (56.1%).
“Findings indicate that rehabilitation providers should perform screenings for these impairments, including incontinence and medication among females, loss of feeling in the feet among males, and all Stay Independent Questionnaire-related fall risk factors among Native American/Alaska Natives, Hispanics, and Blacks,” the authors write.
Resources and articles
- National Institute on Aging
- National Council on Aging
- Gerontological Society of America
- Home Health Agencies Failed To Report Over Half of Falls With Major Injury and Hospitalization Among Their Medicare Patients, a 2023 report from the U.S Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General.
- 6 tips for improving new coverage of older people, a tip sheet from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Crosswalk and pedestrian safety: What you need to know from recent research, from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Aging-in-place technology challenges and trends, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
- Successful aging at home: what reporters should know, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Let’s Get Letting Go (Of These Three Things)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let It Go…
This is Dr. Mitika Kanabar. She’s triple board-certified in addiction medicine, lifestyle medicine, and family medicine.
What does she want us to know?
Let go of what’s not good for you
Take a moment to release any tension you were holding, perhaps in your shoulders or jaw.
Now release the breath you might have been holding while doing that.
Dr. Kanabar is a keen yoga practitioner, and recommends it for alleviating stress, as well as its more general somatic benefits. And yes, stress is in large part somatic too!
One method she recommends for de-stressing quickly is to imagine holding a pin-wheel (the kind that whirls around when blown), and imagine slowly blowing it. The slowness of the exhalation here not only means we exhale more (shallow breathing starts with the out-breath!), but also gives us time to focus on the present moment.
Having done that, she recommends to ask yourself:
- What can you change right now?
- What about next time?
- How can you do better?
And then the much more relaxing questions:
- What can you not change?
- What can you let go?
- Whom can you ask for help?
Why did we ask the first questions first? It’s a lot like a psychological version of the physical process of progressive relaxation, involving first a deliberate tensing up, and then a greater relaxation:
How To Deal With The Body’s “Wrong” Stress Response
The diet that’s not good for you
Dr. Kanabar also recommends letting go of the diet that’s not good for you, too. In particular, she recommends dropping alcohol, sugar, and animal products.
Note: from a purely health perspective, general scientific consensus is that fermented dairy products are healthy in small amounts, as are well-sourced fish and poultry in moderation, assuming they’re not ultraprocessed or fried. However, we’re reporting Dr. Kanabar’s advice as it is.
Dr. Kanabar recommends either doing a 21-day challenge of abstention (and likely finding after 21 days that, in fact, you’re fine without), or taking a slow-and-gentle approach.
Some things will be easier one way or the other, and in particular if you drink heavily or use some other substance that gives withdrawal symptoms if withdrawn, the slow-and-gentle approach will be best:
Which Addiction-Quitting Methods Work Best?
If it’s sugar you’re quitting, you might like to check out:
Food Addictions: When It’s More Than “Just” Cravings
If it’s meat, though (in particular, quitting red meat is a big win for your health), the following can help:
The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet
Want more from Dr. Kanabar?
There’s one more thing she advises to let go of, and that’s excessive use of technology (the kind with screens) in the evening, and not just because of the blue light thing.
With full appreciation of the irony of a one-hour video about too much screentime:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Gymnema Sylvestre: The “Sugar Destroyer”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Leaf That Stops Sugar From “Working”
Gymnema sylvestre, whose botanical name in Greek and Latin means “naked thread of the woods”, and is in various Indian languages referred to be names that translate as “sugar destroyer”, has the most prosaic name in Australia: the Australian cowplant.
In English it’s mostly called by the Greek “gymnema” though, so that’s what we’ll call it here.
You may be wondering: “the sugar destroyer?”
And no, it doesn’t actually destroy sugar. But it does do quite a bit of sugar-related stuff. Here’s the science for it…
Blocks sugar receptors in your tongue
This is what it is most well-known for, and it is a topical effect, so you won’t get this from a pill, but you will get this from the leaves, or from drinking it as a tea made from the leaves.
The effect last several hours, during which time your ability to taste sweetness will be reduced, which not only makes sweet foods less appealing because they’re no longer tasting sweet, but also, once you get used to it, when you actually do taste sweet foods, they will now taste too sweet.
So, it doesn’t just temporarily curb cravings; it offers a long-term escape from such, too.
You may be wondering: “what about artificially sweetened foods and drinks?”
And the answer is: yes, it blocks perception of the sweetness of those too:
Effects of sweetness perception and caloric value of a preload on short term intake ← this study used gymnema as the sweetness-blocker, testing sugary drinks, aspartame-sweetened drinks, and unsweetened drinks
Blocks sugar receptors in the gut, too
Long story short: this slows down the absorption of sugars from the gut, thus resulting in a gentler blood sugar curve, minimizing spikes, and (because of the body’s use of blood sugars as it goes) overall lower blood sugar levels.
Want the long version? Here it is:
Benefits beyond sugar-blocking
It also prevents the accumulation of triglycerides in muscles and the liver, as well as decreasing fatty acid accumulation in the blood. In simpler terms: it lowers LDL (“bad” cholesterol”, including VLDL). As a bonus, it increases HDL (“good” cholesterol) while it’s at it.
The vast majority of the studies for this are on rats and mice though, of which you can see very many listed in the “similar articles” under this systematic review of studies:
A systematic review of Gymnema sylvestre in obesity and diabetes management
We did find one good quality human RCT, testing gymnema along with several other treatments (they found that each worked, and/but using a combination yielded the best results):
(the title says “on weight loss”, but rest assured the study also gives information about its effects on total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, overall triglycerides, and serum leptin levels, as well as excretion of urinary fat metabolites—suffice it to say, they were thorough)
Is it safe?
It has a good safety profile in general, but if you are diabetic, proceed with caution and discuss it with your endocrinologist, since it will be affecting your blood sugar levels and insulin levels. While it’s probably not enough to replace metformin or similar, it is enough that taking it carelessly could result in an unexpected hypo.
Similarly, if you have any heart condition and especially if you are being treated for that with medication, do speak with your cardiologist since its antilipemic action could potentially lower your cholesterol more than expected, and doctors don’t like surprises.
As ever, no list of contraindications will be exhaustive, and we can’t speak for your specific situation, so checking with your pharmacist/doctor is always a good idea.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon ← we’ve linked to a tea version of it so you can enjoy the full effects; if you prefer capsule form, you can click through from there to shop around 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong?
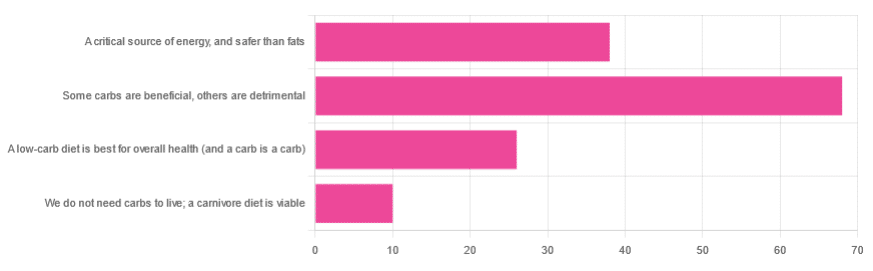
We asked you for your health-related view of carbs, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses
- About 48% said “Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental”
- About 27% said “Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats”
- About 18% said “A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb)”
- About 7% said “We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable”
But what does the science say?
Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats: True or False?
True and False, respectively! That is: they are a critical source of energy, and carbs and fats both have an important place in our diet.
❝Diets that focus too heavily on a single macronutrient, whether extreme protein, carbohydrate, or fat intake, may adversely impact health.❞
Source: Low carb or high carb? Everything in moderation … until further notice
(the aforementioned lead author Dr. de Souza, by the way, served as an external advisor to the World Health Organization’s Nutrition Guidelines Advisory Committee)
Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental: True or False?
True! Glycemic index is important here. There’s a big difference between eating a raw carrot and drinking high-fructose corn syrup:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
While some say grains and/or starchy vegetables are bad, best current science recommends:
- Eat some whole grains regularly, but they should not be the main bulk of your meal (non-wheat grains are generally better)
- Starchy vegetables are not a critical food group, but in moderation they are fine.
To this end, the Mediterranean Diet is the current gold standard of healthful eating, per general scientific consensus:
A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb): True or False?
True-ish and False, respectively. We covered the “a carb is a carb” falsehood earlier, so we’ll look at “a low-carb diet is best”.
Simply put: it can be. One of the biggest problems facing the low-carb diet though is that adherence tends to be poor—that is to say, people crave their carby comfort foods and eat more carbs again. As for the efficacy of a low-carb diet in the context of goals such as weight loss and glycemic control, the evidence is mixed:
❝There is probably little to no difference in weight reduction and changes in cardiovascular risk factors up to two years’ follow-up, when overweight and obese participants without and with T2DM are randomised to either low-carbohydrate or balanced-carbohydrate weight-reducing diets❞
Source: Low-carbohydrate versus balanced-carbohydrate diets for reducing weight and cardiovascular risk
❝On the basis of moderate to low certainty evidence, patients adhering to an LCD for six months may experience remission of diabetes without adverse consequences.
Limitations include continued debate around what constitutes remission of diabetes, as well as the efficacy, safety, and dietary satisfaction of longer term LCDs❞
~ Dr. Joshua Goldenberg et al.
Source: Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission
❝There should be no “one-size-fits-all” eating pattern for different patient´s profiles with diabetes.
It is clinically complex to suggest an ideal percentage of calories from carbohydrates, protein and lipids recommended for all patients with diabetes.❞
Source: Current Evidence Regarding Low-carb Diets for The Metabolic Control of Type-2 Diabetes
We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable: True or False?
False. For a simple explanation:
The Carnivore Diet: Can You Have Too Much Meat?
There isn’t a lot of science studying the effects of consuming no plant products, largely because such a study, if anything other than observational population studies, would be unethical. Observational population studies, meanwhile, are not practical because there are so few people who try this, and those who do, do not persist after their first few hospitalizations.
Putting aside the “Carnivore Diet” as a dangerous unscientific fad, if you are inclined to meat-eating, there is some merit to the Paleo Diet, at least for short-term weight loss even if not necessarily long-term health:
What’s The Real Deal With The Paleo Diet?
For longer-term health, we refer you back up to the aforementioned Mediterranean Diet.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Continuous Glucose Monitors Without Diabetes: Pros & Cons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The “Glucose Goddess”, biochemist Jessie Inchauspé, gives us the low-down:
Knowledge is power (but watch out)
A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device that continually monitors glucose levels, without the need to stab one’s finger every few hours to test blood.
It was designed for diabetics, especially for those with Type 1 Diabetes, where around-the-clock monitoring is necessary for appropriate insulin dosing.
For non-diabetics, they can be a good way of learning what our body’s response to various foods and activities is like, the better to be able to tweak our habits to avoid undue glucose spikes (which are harmful for our pancreas, liver, heart, brain, kidneys, and more).
How it works: there’s a sensor that sits on the arm (or elsewhere, but the arm is a popular placement) with a little probe that goes under the skin. It’s applied using a device that inserts it automatically using a needle (you only need to press a button, you don’t need to guide the needle yourself); the needle then retracts, leaving the soft, flexible probe in place. Having been attached, that sensor can now stay in place for 2 weeks (usually; depends on brand, but for example FreeStyle Libre, the most popular brand, the sensors last 2 weeks), and yes, it’s fine to bathe/shower/etc with it. When you want an update from your CGM, you scan it with your phone (or you can buy a dedicated reader, but that is more expensive and unnecessary), and it uploads the data since your last scan.
Pros: it’s convenient and gives a lot of data, so even if you only use it for a short period of time (for example, a month) you can get a very good idea of what affects your blood sugar levels and how. Also, because of the constant nature of the monitoring, it helps avoid accidental sample bias of the kind that can occur with manual testing, by testing a little too soon or too late, and missing a spike/dip.
Cons: it can be expensive, depending on where you live and what options are available for you locally, so you might not want to do it long-term (since that would require buying two sensors per month). It’s also, for all its wealth of data, slightly less accurate than fingerprick testing—that’s because it takes an interstitial reading instead of directly from the blood. For this reason, if you test both ways, you may find a discrepancy of about 3mg/dL. Given that the healthy range is about 70–140mg/dL, a discrepancy of 3mg/dL is probably not going to be important, but it is a thing to mention can (and probably will) happen.
Patterns to bear in mind (with any kind of blood sugar monitoring):
- Dawn phenomenon: a natural glucose rise upon waking.
- Exercise-induced spikes (normal due to energy demands).
- Fat in meals slowing glucose absorption.
- Different foods can sometimes cause a double-wave after dinner (because glucose from different foods is absorbed differently, and/or different foods affect insulin response independent of glucose)
- Steep, rapid spikes that are more harmful than gradual, sustained increases.
- Vitamin C spikes: temporary chemical interference with the sensor, not actual glucose rises.
- Nighttime glucose dips (often false readings caused by sleeping position).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Maca Root’s Benefits For The Mood And The Ability
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Maca Root: What It Does And Doesn’t Do
Maca root, or Lepidium meyenii, gets thought of as a root vegetable, though it’s in fact a cruciferous vegetable and more closely related to cabbage—notwithstanding that it also gets called “Peruvian ginseng”.
- Nutritionally, it’s full of all manner of nutrients (vitamins, minerals, fiber, and a wide array of phytochemicals)
- Medicinally, it’s long enjoyed traditional use against a wide variety of illnesses, including respiratory infections and inflammatory diseases.
It’s also traditionally an aphrodisiac.
Is it really anti-inflammatory?
Probably not… Unless fermented. This hasn’t been studied deeply, but a 2023 study found that non-fermented and fermented maca root extracts had opposite effects in this regard:
However, this was an in vitro study, so we can’t say for sure that the results will carry over to humans.
Is it really an aphrodisiac?
Actually yes, it seems so. Here’s a study in which 45 women with antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction found it significantly improved both libido and sexual function:
❝In summary, maca root may alleviate antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction as women age, particularly in the domain of orgasm❞
~ Dr. Christina Dording et al.
Read in full: A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial of Maca Root as Treatment for Antidepressant-Induced Sexual Dysfunction in Women
As for men, well these mice (not technically men) found it beneficial too:
Effects of combined extracts of Lepidium meyenii and Allium tuberosum Rottl. on [e-word] dysfunction
(pardon the censorship; we’re trying to avoid people’s spam filters)
It did also improve fertility (and, actually in real men this time):
Does Lepidium meyenii (Maca) improve seminal quality?
Oh, to be in the mood
Here’s an interesting study in which 3g/day yielded significant mood improvement in these 175 (human) subjects:
And yes, it was found to be “well-tolerated” which is scientist-speak for “this appears to be completely safe, but we don’t want to commit ourselves to an absolutist statement and we can’t prove a negative”.
Oh, to have the energy
As it turns out, maca root does also offer benefits in this regard too:
(that’s not an added ingredient; it’s just a relevant chemical that the root naturally contains)
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: