Brain Health Action Plan – by Dr. Teryn Clarke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is a physician and neurologist, and she brings a lot of science with her when she sets out to Alzheimer’s-proof our brains:
- She talks about brain nourishment, and what things in contrast sabotage our brains, and how.
- She talks intermittent fasting, and optimal scheduling when it comes to food, sleep, exercise, and more.
- She talks about how the rest of our health affects our brain health, and vice versa.
The “action plan” promised by the title includes all of those elements, plus such matters as ongoing education, cognitive stimulation, stress management, dealing with depression, and other mostly-brain-based factors.
As such, it’s not just a “for your information” book, and Dr. Clarke does outline suggested goals, tasks, and habits, advises the use of a streak tracker, provides suggested recipes, and in all ways does what she can to make it easy for the reader to implement the information within.
Bottom line: if you’d like to dodge dementia, this book is quite a comprehensive guide.
Click here to check out Brain Health Action Plan, and enact yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
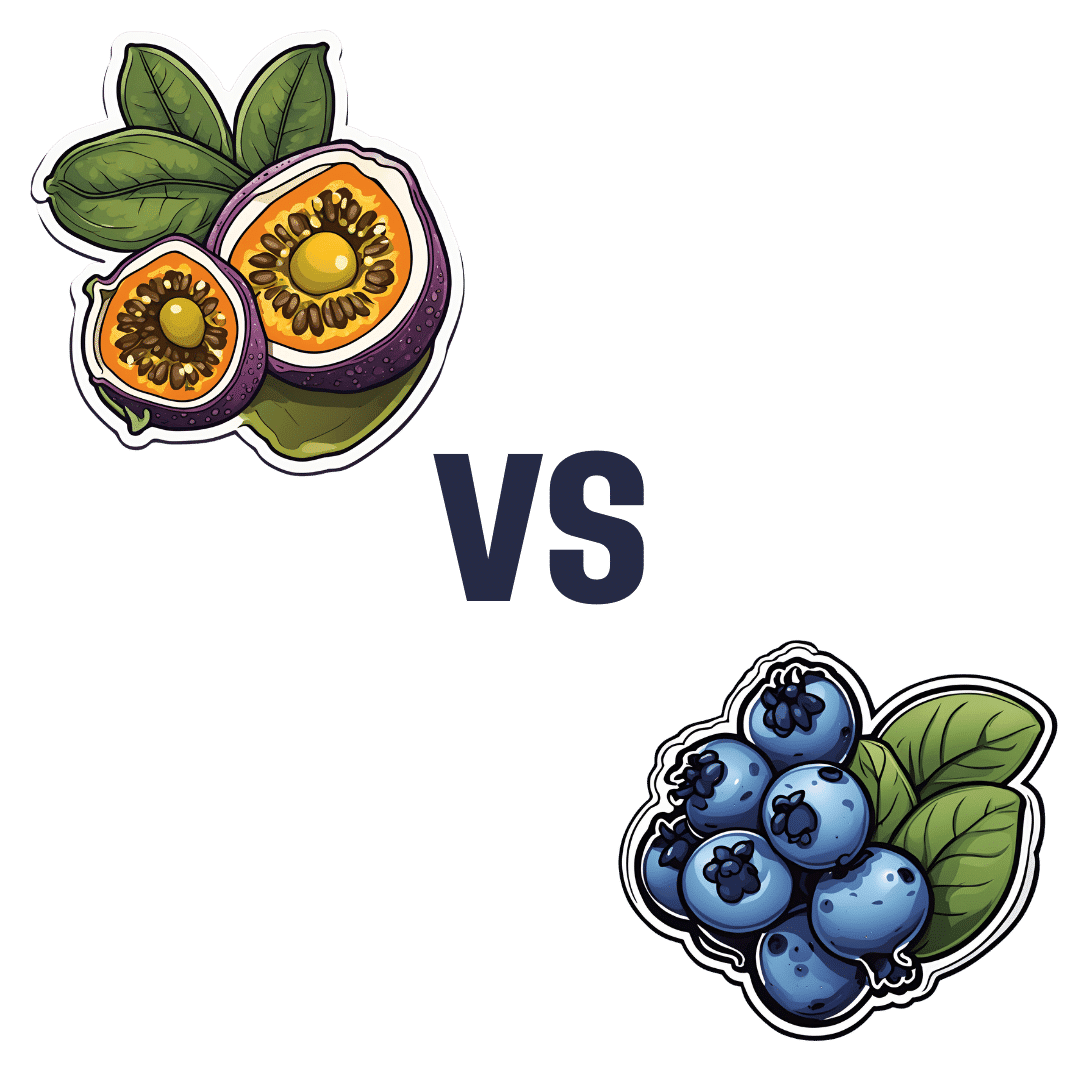
Passion Fruit vs Blueberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing passion fruit to blueberries, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
It wasn’t close!
In terms of macros, the passion fruit has 3x the protein, 1.5x the carbs, and more than 4x the fiber. An easy win for passion fruit!
In the category of vitamins, passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline, while blueberries have more of vitamins B1, E, and K. So, blueberries are not without their merits, but all in all, another win for passion fruit here.
When it comes to minerals, passion fruit has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while blueberries have slightly more zinc.
Looking at polyphenols, this is one category where blueberry wins, and by a fair margin. We think that’s a great reason to enjoy blueberries, but not enough to reverse the win for passion fruit based on all the other categories!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Undoing Creatine’s Puffiness Side Effect
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Creatine is known to increase “puffiness”, especially in my face. Are there any supplements that do the opposite?!❞
So first, let’s examine why this happens: creatine is most often taken to boost muscle size and performance. Your muscles are, of course, mostly water by mass, and so building your muscles requires extra water, which triggers systemic water retention.
In other words: you take creatine, exercise, and as the muscles start growing, the body goes “oh heck, we are running out of water, better save as much as possible in order to keep hydrating the muscles without running out” and starts putting it anywhere it can that’s not your bladder, so this will largely be the soft tissues of your body.
So, this results in classic water retentions symptoms including bloating and, yes, facial puffiness.
How much this happens, and how long the effects last, depend on three main things:
- What daily dose of creatine you are taking
- What kind of exercise you are doing
- What your hydration is like
The dose is relevant as it’s most common to get this puffiness during the “loading” phase, i.e. if you’re taking an increased dose to start with.
The exercise is relevant as it affects how much your body is actually using the water to build muscles.
The hydration is relevant because the less water you are taking, the more the body will try to retain whatever you do have.
This means, of course, that the supplement you are looking for to undo the facial puffiness is, in fact, water (even, nay, especially, if you feel bloated too):
Water For Everything? Water’s Counterintuitive Properties
Additionally, you could scale back the dose of creatine you’re taking, if you’re not currently doing heavy muscle-building exercise.
That said, the recommended dose for cognitive benefits is 5g/day, which is a very standard main-phase (i.e., post-loading) bodybuilding dose, so do with that information what you will.
See also: Creatine’s Brain Benefits Increase With Age
On which note: whether or not you want to take creatine for brain benefits, however, may depend on your age:
Creatine: Very Different For Young & Old People
Most research on creatine’s effects on humans has usually been either collegiate athletes or seniors, which leaves quite a research gap in the middle—so it’s unclear at what age the muscle-building effects begin to taper off, and at what age the cognitive benefits begin to take off.
Want a quicker fix?
If you want to reduce your facial puffiness acutely (e.g., you have a date in an hour and would like to not have a puffy face), then there are two things you can do that will help immediately, and/but only have short-term effects, meaning you’d have to do them daily to enjoy the results every day:
The first is an ice bath; simply fill a large bowl with water and ice cubes, give it a couple of minutes to get down to temperature, hold your breath and plunge your face in for as long as you can comfortably hold your breath. Repeat a few times, and towel off.
This helps by waking up the vasculature in your face, helping it to reduce puffiness naturally.
The second is facial yoga or guā shā, which is the practice of physically manipulating the soft tissues of your face to put them where you want them, rather than where you don’t want them. This will work against water retention puffiness, as well as cortisol puffiness, lymphatic puffiness, and more:
7-Minute Face Fitness For Lymphatic Drainage & Youthful Jawline
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Can You Shrink A Waist In Seven Days?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We don’t usually do this sort of video, but it seems timely before the new year. The exercises shown here are very good, and the small dietary tweak is what makes it work:
The method
Firstly, the small dietary tweak is: abstaining from foods that cause bloating, such as flour and dairy. She does say “брожение” (fermentation), but we don’t really use the word that way in English. On which note: she is Ukrainian and speaking Russian (context: many Ukrainians grew up speaking both languages), so you will need the subtitles on if you don’t understand Russian, but a) it’s worth it b) the subtitles have been put in manually so they’re a respectable translation.
Secondly, spoiler, she loses about 2 inches.
The exercises are:
- Pelvic swing-thrusts: sit, supporting yourself on your hands with your butt off the floor; raise your pelvis up to a table position, do 30 repetitions.
- Leg raises in high plank: perform 20 lifts per leg, each to its side.
- Leg raises (lying on back): do 20 repetitions.
- V-crunches: perform 30 repetitions.
- V-twists: lean on hands and do 25 repetitions.
These exercises (all five done daily for the 7 days) are great for core strength, and core muscletone is what keeps your innards in place, rather than letting them drop down (and out).
Thus, there’s only a small amount of actual fat loss going on here (if any), but it slims the waistline by improving muscletone and simultaneously decreasing bloating, which are both good changes.
For more on all of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Brain Power – by Michael Gelb & Kelly Howell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s most important when it comes to brain health? Is it the right diet? Supplements? Brain-training? Attitude? Sleep? Physical exercise? Social connections? Something else?
This book covers a lot of bases, including all of the above and more. The authors are not scientists by training and this is not a book of science, so much as a book of aggregated science-based advice from other sources. The authors did consult with many scientists, and their input is shown throughout.
In the category of criticism, nothing here goes very deeply into the science, and there’s also nothing you wouldn’t find we’ve previously written about in a 10almonds article somewhere. But all the same, it’s good to have a wide variety of brain-healthy advices all in one place.
Bottom line: if you’re looking for a one-stop-shop “look after your brain as you age” guide, then this is a good one.
Click here to check out Brain Power, and improve your mind as you age!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Walk Like You’re 20 Years Younger Again
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How fit, healthy, strong, and mobile were you 20 years ago? For most people, the answer is “better than now”. Physiotherapist Dr. Doug Weiss has advice on turning back the clock:
The exercises
If you already have no problems walking, this one is probably not for you. However, if you’re not so able to comfortably walk as you used to be, then Dr. Weiss recommends:
- Pillow squat: putting pillow on a chair, crossing hands on chest, standing up and sitting down. Similar to the very important “getting up off the floor without using your hands” exercise, but easier.
- Wall leaning: standing against a wall with heels 4″ away from it, crossing arms over chest again, and pulling the body off the wall using the muscles in the front of the shin. Note, this means not cheating by using other muscles, leveraging the upper body, pushing off with the buttocks, or anything else like that.
- Stepping forward: well, this certainly is making good on the promise of walking like we did 20 years ago; there sure was a lot of stepping forward involved. More seriously, this is actually about stepping over some object, first with support, and then without.
- Heel raise: is what it sounds like, raising up on toes and back down again; first with support, then without.
- Side stepping: step sideways 2–3 steps in each direction. First with support, then without. Bonus: if your support is your partner, then congratulations, you are now dancing bachata.
For more details (and visual demonstration) of these exercises and more, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
4 Tips To Stand Without Using Hands
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
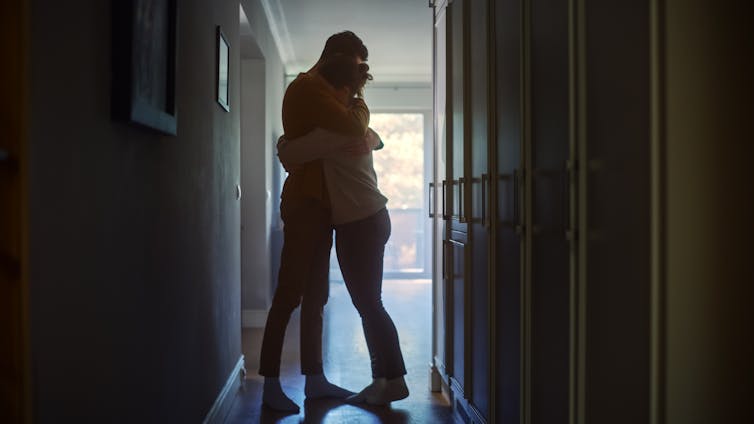
Families including someone with mental illness can experience deep despair. They need support
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In the aftermath of the tragic Bondi knife attack, Joel Cauchi’s parents have spoken about their son’s long history of mental illness, having been diagnosed with schizophrenia at age 17. They said they were “devastated and horrified” by their son’s actions. “To you he’s a monster,” said his father. “But to me he was a very sick boy.”
Globally, one out of every eight people report a mental illness. In Australia, one in five people experience a mental illness in their lifetime.
Mental illness and distress affects not only the person living with the condition, but family members and communities. As the prevalence of mental health problems grows, the flow-on effect to family members, including caregivers, and the impact on families as a unit, is also rising.
While every family is different, the words of the Cauchis draw attention to how families can experience distress, stress, fear, powerlessness, and still love, despite the challenges and trauma. How can they help a loved one? And who can they turn to for support?
The role of caregivers
Informal caregivers help others within the context of an existing relationship, such as a family member. The care they provide goes beyond the usual expectations or demands of such relationships.
Around 2.7 million Australians provide informal care. For almost a third of these the person’s primary medical diagnosis is psychological or psychiatric.
It has long been acknowledged that those supporting a family member with ongoing mental illness need support themselves.
In the 1980s, interest grew in caregiving dynamics within families of people grappling with mental health issues. Subsequent research recognised chronic health conditions not only affect the quality of life and wellbeing of the people experiencing them, but also impose burdens that reverberate within relationships, caregiving roles, and family dynamics over time.
Past studies have shown families of those diagnosed with chronic mental illness are increasingly forced to manage their own depression, experience elevated levels of emotional stress, negative states of mind and decreased overall mental health.
Conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia can severely impact daily functioning, relationships, and overall quality of life. Living with mental illness is often accompanied by a myriad of challenges. From stigma and discrimination to difficulty accessing adequate health care and support services. Patients and their families navigate a complex and often isolating journey.
The family is a system
The concept of family health acknowledges the physical and psychological wellbeing of a person is significantly affected by the family.
Amid these challenges, family support emerges as a beacon of hope. Research consistently demonstrates strong familial relationships and support systems play a pivotal role in mitigating the adverse effects of mental illness. Families provide emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging that are vital for people struggling with mental illness.
My recent research highlights the profound impact of mental illness on family dynamics, emphasising the resilience and endurance shown by participants. Families struggling with mental illness often experience heightened emotional fluctuations, with extreme highs and lows. The enduring nature of family caregiving entails both stress and adaptation over an extended period. Stress associated with caregiving and the demands on personal resources and coping mechanisms builds and builds.
Yet families I’ve interviewed find ways to live “a good life”. They prepare for the peaks and troughs, and show endurance and persistence. They make space for mental illness in their daily lives, describing how it spurs adaptation, acceptance and inner strength within the family unit.
When treating a person with mental illness, health practitioners need to consider the entire family’s needs and engage with family members. By fostering open and early dialogue and providing comprehensive support, health-care professionals can empower families to navigate the complexities of mental illness while fostering resilience and hope for the future. Family members express stories of an inner struggle, isolation and exhaustion.
Family bonds can be a cornerstone of wellbeing. Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock Shifting the focus
There is a pressing need for a shift in research priorities, from illness-centered perspectives to a strengths-based focus when considering families “managing” mental illness.
There is transformative potential in harnessing strengths to respond to challenges posed by mental illnesses, while also supporting family members.
For people facing mental health challenges, having loved ones who listen without judgement and offer empathy can alleviate feelings of despair. Beyond emotional support, families often serve as crucial caregivers, assisting with daily tasks, medication management and navigating the health-care system.
As the Cauchi family so painfully articulated, providing support for a family member with mental illness is intensely challenging. Research shows caregiver burnout, financial strain and strained relationships are common.
Health-care professionals should prioritise support for family members at an early stage. In Australia, there are various support options available for families living with mental illness. Carer Gateway provides information, support and access to services. Headspace offers mental health services and supports to young people and their families.
Beyond these national services, GPs, nurses, nurse practitioners and local community health centres are key to early conversations. Mental health clinics and hospitals often target family involvement in treatment plans.
While Australia has made strides in recognising the importance of family support, challenges persist. Access to services can vary based on geographic location and demand, leaving some families under-served or facing long wait times. And the level of funding and resources allocated to family-oriented mental health support often does not align with the demand or complexity of need.
In the realm of mental illness, family support serves as a lifeline for people navigating the complexities of their conditions.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Amanda Cole, Lead, Mental Health, Edith Cowan University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: